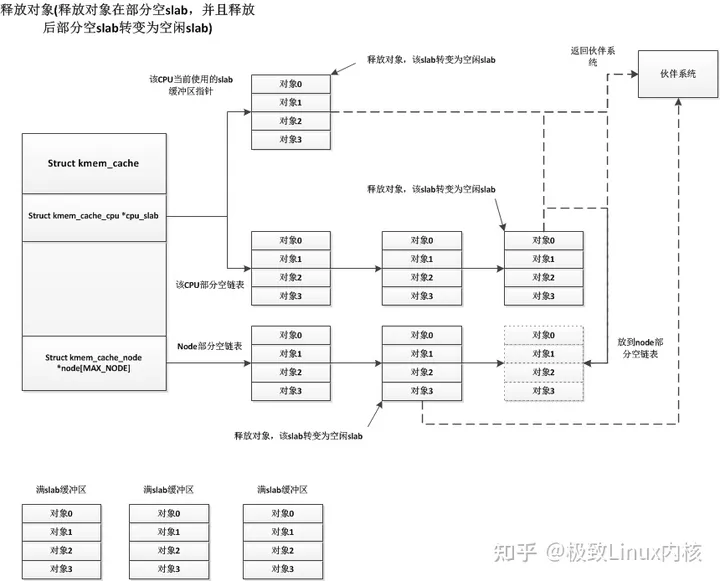
初始化
内核的大部分管理数据结构都是通过kmalloc分配内存的,那么slab本身结构的内存管理就出现了一个鸡与蛋的问题,slab数据结构所需内存远小于一整页的内存块,这些最适合kmalloc分配,而kmalloc只有在slab初始化完之后才能使用。
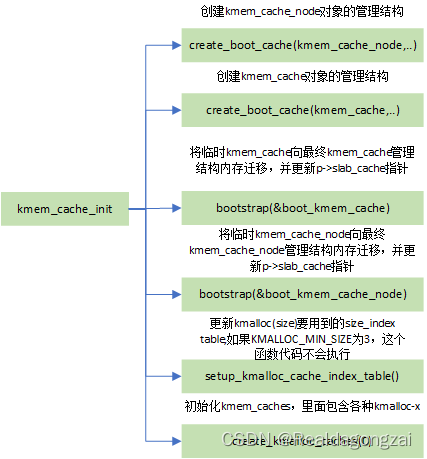
start_kernel->mm_init->kmem_cache_init
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{static __initdata struct kmem_cache boot_kmem_cache,boot_kmem_cache_node;if (debug_guardpage_minorder())slub_max_order = 0;kmem_cache_node = &boot_kmem_cache_node;kmem_cache = &boot_kmem_cache;create_boot_cache(kmem_cache_node, "kmem_cache_node",sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node), SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN, 0, 0);register_hotmemory_notifier(&slab_memory_callback_nb);/* Able to allocate the per node structures */slab_state = PARTIAL;create_boot_cache(kmem_cache, "kmem_cache",offsetof(struct kmem_cache, node) +nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node *),SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN, 0, 0);kmem_cache = bootstrap(&boot_kmem_cache);kmem_cache_node = bootstrap(&boot_kmem_cache_node);/* Now we can use the kmem_cache to allocate kmalloc slabs */setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table();create_kmalloc_caches(0);/* Setup random freelists for each cache */init_freelist_randomization();cpuhp_setup_state_nocalls(CPUHP_SLUB_DEAD, "slub:dead", NULL,slub_cpu_dead);pr_info("SLUB: HWalign=%d, Order=%u-%u, MinObjects=%u, CPUs=%u, Nodes=%u\n",cache_line_size(),slub_min_order, slub_max_order, slub_min_objects,nr_cpu_ids, nr_node_ids);
}
create_kmalloc_caches中循环通过new_kmalloc_cache创建kmem_cache。
struct kmem_cache *kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH + 1] __ro_after_init;
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_caches);#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
struct kmem_cache *kmalloc_dma_caches[KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH + 1] __ro_after_init;
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_dma_caches);
#endifvoid __init create_kmalloc_caches(slab_flags_t flags)
{int i, type;for (type = KMALLOC_NORMAL; type <= KMALLOC_RECLAIM; type++) {for (i = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {if (!kmalloc_caches[type][i])new_kmalloc_cache(i, type, flags); //创建kmem_cache数组。/** Caches that are not of the two-to-the-power-of size.* These have to be created immediately after the* earlier power of two caches*/if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32 && i == 6 &&!kmalloc_caches[type][1])new_kmalloc_cache(1, type, flags);if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64 && i == 7 &&!kmalloc_caches[type][2])new_kmalloc_cache(2, type, flags);}}/* Kmalloc array is now usable */slab_state = UP;#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMAfor (i = 0; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {struct kmem_cache *s = kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_NORMAL][i];if (s) {unsigned int size = kmalloc_size(i);const char *n = kmalloc_cache_name("dma-kmalloc", size);BUG_ON(!n);kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_DMA][i] = create_kmalloc_cache(n, size, SLAB_CACHE_DMA | flags, 0, 0);}}
#endif
}new_kmalloc_cache创建内核预先准备的固定大小的内存块。
static void __init new_kmalloc_cache(int idx, slab_flags_t flags)
{kmalloc_caches[idx] = create_kmalloc_cache(kmalloc_info[idx].name,kmalloc_info[idx].size, flags, 0,kmalloc_info[idx].size);
}/** kmalloc_info[] is to make slub_debug=,kmalloc-xx option work at boot time.* kmalloc_index() supports up to 2^26=64MB, so the final entry of the table is* kmalloc-67108864.*/
const struct kmalloc_info_struct kmalloc_info[] __initconst = {{NULL, 0}, {"kmalloc-96", 96},{"kmalloc-192", 192}, {"kmalloc-8", 8},{"kmalloc-16", 16}, {"kmalloc-32", 32},{"kmalloc-64", 64}, {"kmalloc-128", 128},{"kmalloc-256", 256}, {"kmalloc-512", 512},{"kmalloc-1024", 1024}, {"kmalloc-2048", 2048},{"kmalloc-4096", 4096}, {"kmalloc-8192", 8192},{"kmalloc-16384", 16384}, {"kmalloc-32768", 32768},{"kmalloc-65536", 65536}, {"kmalloc-131072", 131072},{"kmalloc-262144", 262144}, {"kmalloc-524288", 524288},{"kmalloc-1048576", 1048576}, {"kmalloc-2097152", 2097152},{"kmalloc-4194304", 4194304}, {"kmalloc-8388608", 8388608},{"kmalloc-16777216", 16777216}, {"kmalloc-33554432", 33554432},{"kmalloc-67108864", 67108864}
};kmem_cache_create
内核通过kmem_cache_create()接口来创建一个slab缓存。
一共有5个参数。
name: 要创建的slab对象的名称
size: slab对象的大小
align: slab对象的对齐大小
flags: slab内存分配器的掩码和标志位, 比如常用的SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN标志位,创建的kmem_cache管理的object按照硬件cache 对齐
ctor: 对象的构造函数
struct kmem_cache *
kmem_cache_create(const char *name, unsigned int size, unsigned int align,slab_flags_t flags, void (*ctor)(void *))
{return kmem_cache_create_usercopy(name, size, align, flags, 0, 0,ctor);
}/*内容通过精简*/
struct kmem_cache *
kmem_cache_create_usercopy(const char *name,unsigned int size, unsigned int align,slab_flags_t flags,unsigned int useroffset, unsigned int usersize,void (*ctor)(void *))
{struct kmem_cache *s = NULL;const char *cache_name;int err;if (!usersize)s = __kmem_cache_alias(name, size, align, flags, ctor);if (s)goto out_unlock;cache_name = kstrdup_const(name, GFP_KERNEL);if (!cache_name) {err = -ENOMEM;goto out_unlock;}
/*通过create_cache函数 创建*/s = create_cache(cache_name, size,calculate_alignment(flags, align, size),flags, useroffset, usersize, ctor, NULL, NULL);if (IS_ERR(s)) {err = PTR_ERR(s);kfree_const(cache_name);}out_unlock:return s;
}
create_cache函数
static struct kmem_cache *create_cache(const char *name,unsigned int object_size, unsigned int align,slab_flags_t flags, unsigned int useroffset,unsigned int usersize, void (*ctor)(void *),struct mem_cgroup *memcg, struct kmem_cache *root_cache)
{struct kmem_cache *s;int err;if (WARN_ON(useroffset + usersize > object_size))useroffset = usersize = 0;err = -ENOMEM;s = kmem_cache_zalloc(kmem_cache, GFP_KERNEL); //kmem_cache是 kmem 初始化创建的 kmem_cache对象if (!s)goto out;s->name = name;s->size = s->object_size = object_size;s->align = align;s->ctor = ctor;s->useroffset = useroffset;s->usersize = usersize;err = init_memcg_params(s, memcg, root_cache);if (err)goto out_free_cache;err = __kmem_cache_create(s, flags); //进一步初始化if (err)goto out_free_cache;s->refcount = 1;list_add(&s->list, &slab_caches); //加入到slab_caches链表中memcg_link_cache(s);
out:if (err)return ERR_PTR(err);return s;out_free_cache:destroy_memcg_params(s);kmem_cache_free(kmem_cache, s);goto out;
}__kmem_cache_create函数
int __kmem_cache_create(struct kmem_cache *s, slab_flags_t flags)
{int err;err = kmem_cache_open(s, flags);if (err)return err;/* Mutex is not taken during early boot */if (slab_state <= UP)return 0;memcg_propagate_slab_attrs(s);err = sysfs_slab_add(s);if (err)__kmem_cache_release(s);return err;
}//内容精简
static int kmem_cache_open(struct kmem_cache *s, slab_flags_t flags)
{
....................s->flags = kmem_cache_flags(s->size, flags, s->name, s->ctor);
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_HARDENEDs->random = get_random_long();
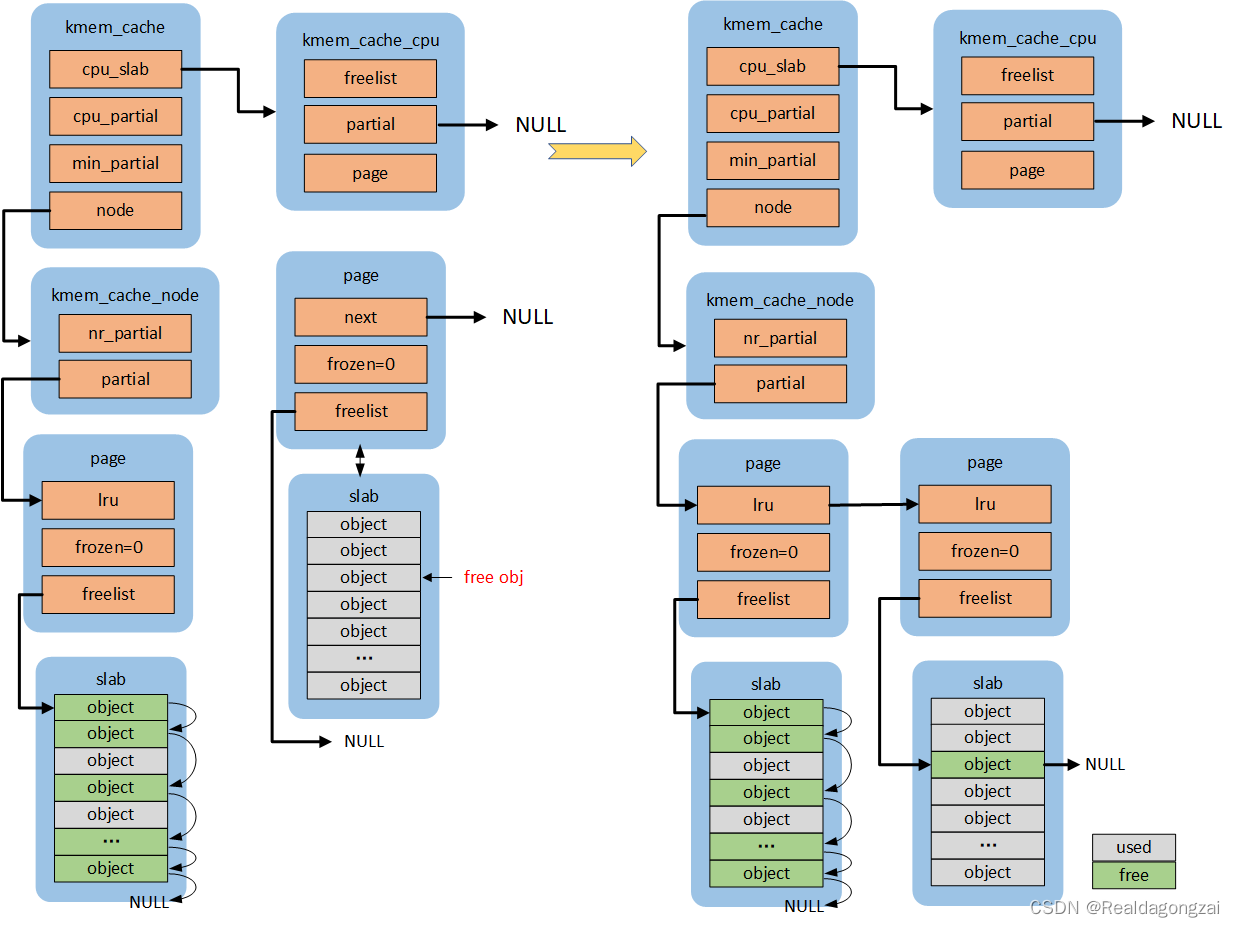
#endifif (!calculate_sizes(s, -1))goto error;if (!init_kmem_cache_nodes(s)) //创建kmem_cache 的struct kmem_cache_node *node[MAX_NUMNODES];goto error;if (alloc_kmem_cache_cpus(s)) //创建kmem_cache的struct kmem_cache_cpu __percpu *cpu_slab;...........
}
kmalloc函数
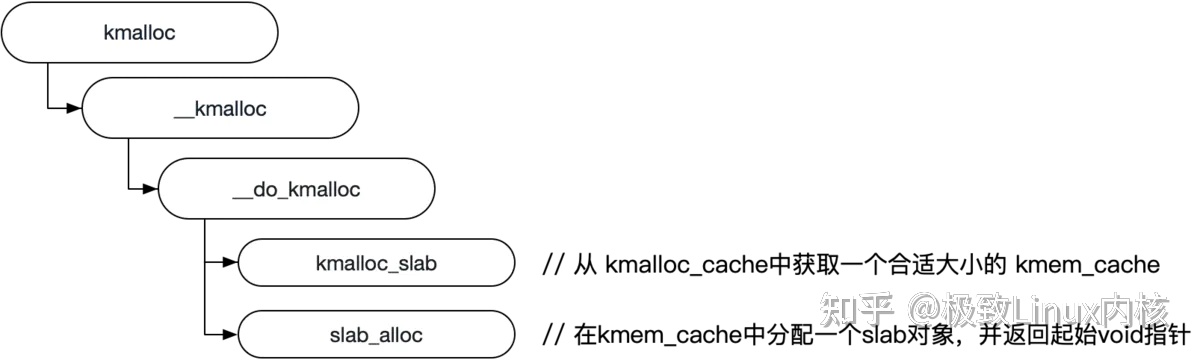
从kmalloc函数看,内核如何分配小块内存:
KMALLOC(SLUB):
static __always_inline void *kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{if (__builtin_constant_p(size)) {
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOBunsigned int index;
#endifif (size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE)return kmalloc_large(size, flags);
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOBindex = kmalloc_index(size);if (!index)return ZERO_SIZE_PTR;return kmem_cache_alloc_trace(kmalloc_caches[kmalloc_type(flags)][index],flags, size);
#endif}return __kmalloc(size, flags);
}void *__kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{struct kmem_cache *s;void *ret;if (unlikely(size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE))return kmalloc_large(size, flags);s = kmalloc_slab(size, flags); // 1 获取kmem_cacheif (unlikely(ZERO_OR_NULL_PTR(s)))return s;ret = slab_alloc(s, flags, _RET_IP_); //2 ,分配内存trace_kmalloc(_RET_IP_, ret, size, s->size, flags);ret = kasan_kmalloc(s, ret, size, flags);return ret;
}static __always_inline void *slab_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s,gfp_t gfpflags, unsigned long addr)
{return slab_alloc_node(s, gfpflags, NUMA_NO_NODE, addr);
}
1:kmalloc_slab获取kmem_cahce
struct kmem_cache *kmalloc_slab(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{unsigned int index;if (unlikely(size > KMALLOC_MAX_SIZE)) {WARN_ON_ONCE(!(flags & __GFP_NOWARN));return NULL;}if (size <= 192) {if (!size)return ZERO_SIZE_PTR;index = size_index[size_index_elem(size)];} elseindex = fls(size - 1);#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMAif (unlikely((flags & GFP_DMA)))return kmalloc_dma_caches[index];#endifreturn kmalloc_caches[index]; //从已经存在的kmalloc_caches中获取 。
}
2 slab_alloc函数
static __always_inline void *slab_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s,gfp_t gfpflags, unsigned long addr)
{return slab_alloc_node(s, gfpflags, NUMA_NO_NODE, addr);
}
kmem_cache_alloc
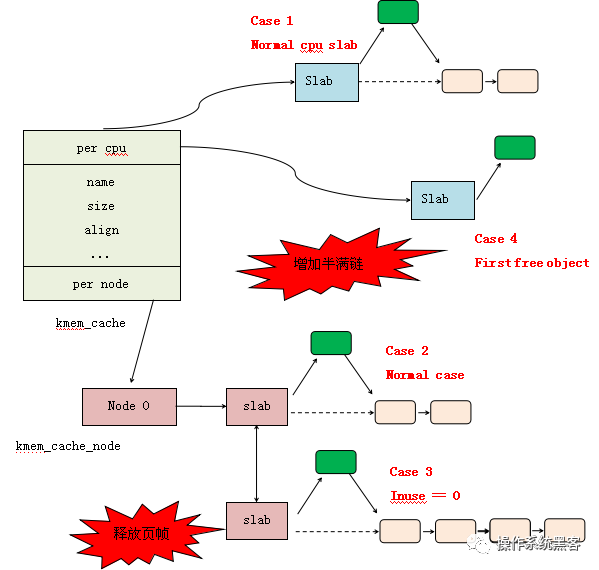
相比于kmalloc。kmem_cache_alloc创建内存是需要携带kmem_cache * 指针,其创建的内存块大小是固定的。因为kmalloc所利用的内存块的大小是事先定义好的,所以很多情况下会产生内部碎片,浪费空间,而kmem_cache_alloc由于内存大小也是量身定做的缘故则不会。
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s, gfp_t gfpflags)
{void *ret = slab_alloc(s, gfpflags, _RET_IP_); // 依然是slab_alloc函数分配内存trace_kmem_cache_alloc(_RET_IP_, ret, s->object_size,s->size, gfpflags);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_alloc);
static __always_inline void *slab_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s,gfp_t gfpflags, unsigned long addr)
{return slab_alloc_node(s, gfpflags, NUMA_NO_NODE, addr);
}static __always_inline void *slab_alloc_node(struct kmem_cache *s,gfp_t gfpflags, int node, unsigned long addr)
{void *object;struct kmem_cache_cpu *c;struct page *page;unsigned long tid;s = slab_pre_alloc_hook(s, gfpflags);if (!s)return NULL;
redo:/** Must read kmem_cache cpu data via this cpu ptr. Preemption is* enabled. We may switch back and forth between cpus while* reading from one cpu area. That does not matter as long* as we end up on the original cpu again when doing the cmpxchg.** We should guarantee that tid and kmem_cache are retrieved on* the same cpu. It could be different if CONFIG_PREEMPT so we need* to check if it is matched or not.*/do {tid = this_cpu_read(s->cpu_slab->tid);c = raw_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab);} while (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PREEMPT) &&unlikely(tid != READ_ONCE(c->tid)));/** Irqless object alloc/free algorithm used here depends on sequence* of fetching cpu_slab's data. tid should be fetched before anything* on c to guarantee that object and page associated with previous tid* won't be used with current tid. If we fetch tid first, object and* page could be one associated with next tid and our alloc/free* request will be failed. In this case, we will retry. So, no problem.*/barrier();/** The transaction ids are globally unique per cpu and per operation on* a per cpu queue. Thus they can be guarantee that the cmpxchg_double* occurs on the right processor and that there was no operation on the* linked list in between.*/object = c->freelist;page = c->page;if (unlikely(!object || !node_match(page, node))) { //当前per-cpu 没有空闲或者node节点不匹配 从新创建一个缓冲区object = __slab_alloc(s, gfpflags, node, addr, c);stat(s, ALLOC_SLOWPATH);} else {void *next_object = get_freepointer_safe(s, object);/** The cmpxchg will only match if there was no additional* operation and if we are on the right processor.** The cmpxchg does the following atomically (without lock* semantics!)* 1. Relocate first pointer to the current per cpu area.* 2. Verify that tid and freelist have not been changed* 3. If they were not changed replace tid and freelist** Since this is without lock semantics the protection is only* against code executing on this cpu *not* from access by* other cpus.*/
/* 下面交换cpu_slab->freelist 与next_object的值,使得freelist指向下次申请的object地址*/if (unlikely(!this_cpu_cmpxchg_double(s->cpu_slab->freelist, s->cpu_slab->tid,object, tid,next_object, next_tid(tid)))) {note_cmpxchg_failure("slab_alloc", s, tid);goto redo;}prefetch_freepointer(s, next_object);stat(s, ALLOC_FASTPATH);}if (unlikely(gfpflags & __GFP_ZERO) && object)memset(object, 0, s->object_size);slab_post_alloc_hook(s, gfpflags, 1, &object);return object;
}slab_alloc_node函数
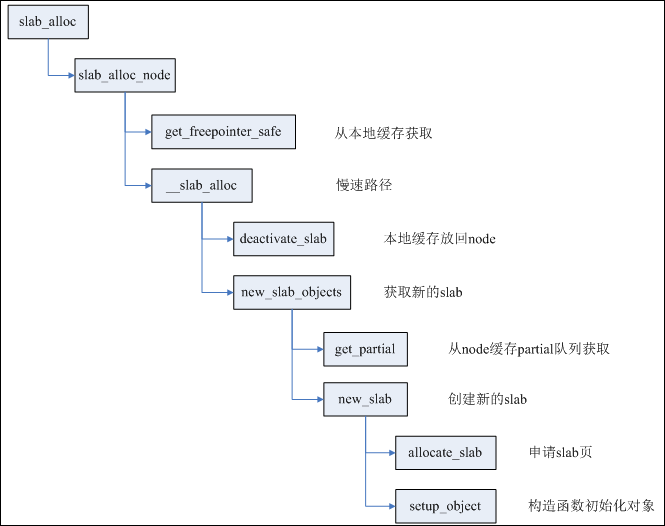
slab_alloc_node
__slab_alloc
___slab_alloc
new_slab_objects
new_slab
allocate_slab
alloc_slab_page
shuffle_freelist //会循环填充page中的object中的地址内容。
c=raw_cpu_ptr
c->page = pagec->freelist = get_freepoint
get_freepointer_safe //获取下一个object的地址
___slab_alloc 精简
static void *___slab_alloc(struct kmem_cache *s, gfp_t gfpflags, int node,unsigned long addr, struct kmem_cache_cpu *c)
{void *freelist;struct page *page;page = c->page;if (!page)goto new_slab;
redo:.....load_freelist:/** freelist is pointing to the list of objects to be used.* page is pointing to the page from which the objects are obtained.* That page must be frozen for per cpu allocations to work.*/VM_BUG_ON(!c->page->frozen);c->freelist = get_freepointer(s, freelist);c->tid = next_tid(c->tid);return freelist;new_slab:freelist = new_slab_objects(s, gfpflags, node, &c);page = c->page;if (likely(!kmem_cache_debug(s) && pfmemalloc_match(page, gfpflags)))goto load_freelist; //跳转,设置c->freelist........}
shuffle_freelist函数
static bool shuffle_freelist(struct kmem_cache *s, struct page *page)
{void *start;void *cur;void *next;unsigned long idx, pos, page_limit, freelist_count;if (page->objects < 2 || !s->random_seq)return false;freelist_count = oo_objects(s->oo);pos = get_random_int() % freelist_count;page_limit = page->objects * s->size;start = fixup_red_left(s, page_address(page));/* First entry is used as the base of the freelist */cur = next_freelist_entry(s, page, &pos, start, page_limit,freelist_count);page->freelist = cur;for (idx = 1; idx < page->objects; idx++) {setup_object(s, page, cur);next = next_freelist_entry(s, page, &pos, start, page_limit,freelist_count);set_freepointer(s, cur, next); //设置每个object的地址,根据偏移量。cur = next;}setup_object(s, page, cur);set_freepointer(s, cur, NULL);return true;
}//往当前object 偏移 offset 的位置中,填充下一个object的地址fp 。
static inline void set_freepointer(struct kmem_cache *s, void *object, void *fp)
{unsigned long freeptr_addr = (unsigned long)object + s->offset;#ifdef CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_HARDENEDBUG_ON(object == fp); /* naive detection of double free or corruption */
#endif*(void **)freeptr_addr = freelist_ptr(s, fp, freeptr_addr);
}
slab缓存区的object布局:
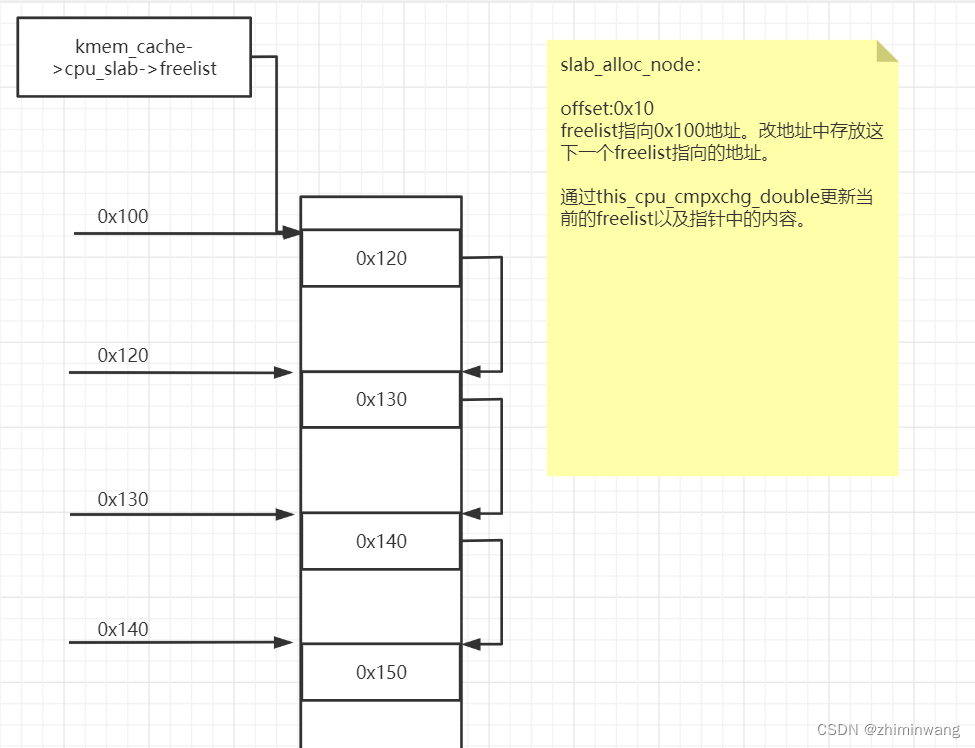
static inline void *get_freepointer_safe(struct kmem_cache *s, void *object)
{unsigned long freepointer_addr;void *p;if (!debug_pagealloc_enabled())return get_freepointer(s, object);freepointer_addr = (unsigned long)object + s->offset;probe_kernel_read(&p, (void **)freepointer_addr, sizeof(p)); //从地址freepointer_addr读取8字节的内容,到p。 实际上该位置存储这下一个object的地址。return freelist_ptr(s, p, freepointer_addr);
}static inline void *freelist_ptr(const struct kmem_cache *s, void *ptr,unsigned long ptr_addr)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_HARDENEDreturn (void *)((unsigned long)ptr ^ s->random ^ ptr_addr);
#elsereturn ptr;
#endif
}