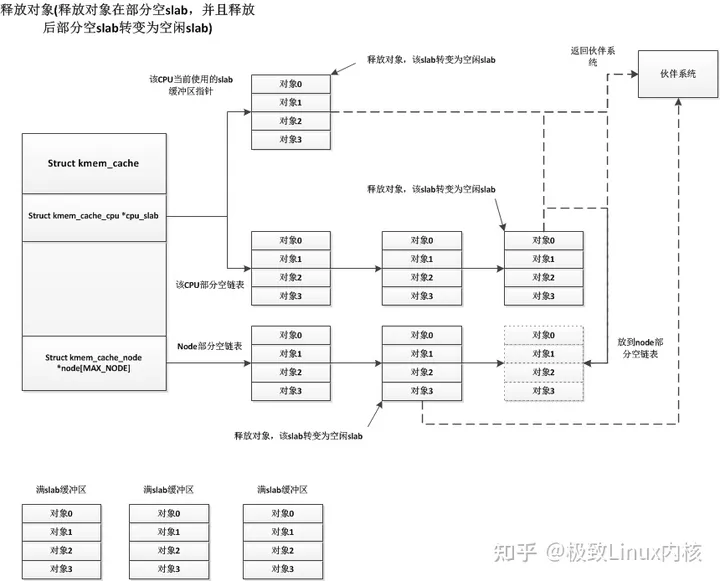
slub内存管理的4个主要接口函数如下(参考kernel-4.19):
//slab缓存的创建
struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache_create(const char *name, size_t size, size_t align, unsigned long flags, void (*ctor)(void *));
//slab object的分配
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, int flags);
//slab object的释放
void kmem_cache_free(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp);
//slab缓存的释放
void kmem_cache_destroy(struct kmem_cache *);本篇主要介绍slab 缓存释放的函数kmem_cache_destroy,相比前面三个函数,destory比较简单
一、函数调用关系图
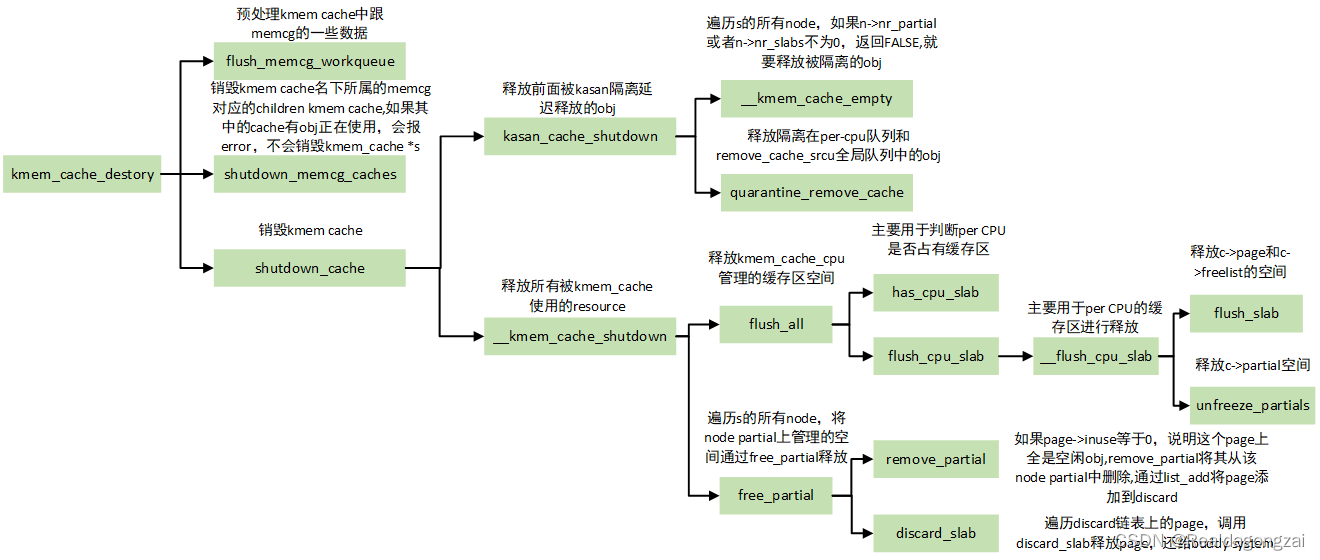
二、kmem_cache_destroy函数
void kmem_cache_destroy(struct kmem_cache *s)
{int err;
//如果s为NULL,直接退出if (unlikely(!s))return;
//如果使能了CONFIG_MEMCG,先预处理memcg中跟这个kmem_cache相关的一些数据flush_memcg_workqueue(s);//get_online_cpus是对cpu_online_map的加锁,其与末尾的put_online_cpus()是配对使用的;get_online_mems类似,不过是对mem操作get_online_cpus();get_online_mems();//获取slab_mutex互斥锁,用于全局资源保护mutex_lock(&slab_mutex);//kmem_cache的引用计数减1,如果不为0,说明其他kmem_cache别名挂靠,有依赖,不能释放,走out_unlock;否则删除该kmem_caches->refcount--;if (s->refcount)goto out_unlock;//如果引用计数为0,先销毁s名下所属的memcg对应的children kmem cache,如果成功的话err等于零,最后通过shutdown_cache销毁s本身err = shutdown_memcg_caches(s);if (!err)
//调用shutdown_cache销毁s,成功返回0err = shutdown_cache(s);//否则,打印error信息,dump_stack,退出if (err) {pr_err("kmem_cache_destroy %s: Slab cache still has objects\n",s->name);dump_stack();}//销毁kmem_cache *s成功,释放销毁前所加的锁
out_unlock:mutex_unlock(&slab_mutex);put_online_mems();put_online_cpus();
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_destroy);2.1 shutdown_memcg_caches函数
该函数要销毁s名下所属的memcg对应的children kmem cache,实际上也是调用shutdown_cache来实现的,分别销毁online memory cgroups和offline memory cgroups上面的kmem cache,当然对于还有obj在使用的kmem cache最后会放回到s->memcg_params.children里面,同时返回-EBUSY。此时,kmem_cache_destroy走pr_err和dump_stack流程,不会这个kmem_cache *s给释放。
static int shutdown_memcg_caches(struct kmem_cache *s)
{struct memcg_cache_array *arr;struct kmem_cache *c, *c2;LIST_HEAD(busy);int i;
//通过s->memcg_params.root_cache得出判断BUG_ON(!is_root_cache(s));/** First, shutdown active caches, i.e. caches that belong to online* memory cgroups.*/
//第一步,销毁active cache,如,属于online memory cgroups的caches
//函数rcu_dereference_protected,根据kmemcg ID 子缓存索引表(memcg_caches)得到指向受RCU protected的指针arr,该指针指向将要被释放的kemem_cache,arr = rcu_dereference_protected(s->memcg_params.memcg_caches,lockdep_is_held(&slab_mutex));
//循环遍历这个数组arrfor_each_memcg_cache_index(i) {c = arr->entries[i];if (!c)continue;
//如果shutdown_cache返回非0,表示这个cache上仍然有obj在被使用,将这个cache从原有的list上删除,并添加到临时list(busy)上面,避免下面second会重复遍历if (shutdown_cache(c))/** The cache still has objects. Move it to a temporary* list so as not to try to destroy it for a second* time while iterating over inactive caches below.*/list_move(&c->memcg_params.children_node, &busy);
//如果shutdown_cache返回0,表示这个cache上没有obj在被使用,那么可以直接被销毁
//同时清除memcg_caches 数组中指向它的指针,这样即使root cache还活着,它也永远不会被访问else/** The cache is empty and will be destroyed soon. Clear* the pointer to it in the memcg_caches array so that* it will never be accessed even if the root cache* stays alive.*/arr->entries[i] = NULL;}/** Second, shutdown all caches left from memory cgroups that are now* offline.*/
//第二步,循环遍历所有inactive cache(offline memory cgroups的caches),调用shutdown_cache销毁kmem_cachelist_for_each_entry_safe(c, c2, &s->memcg_params.children,memcg_params.children_node)shutdown_cache(c);
//根据第一步,有个临时list(busy)保存obj仍然在被使用的kmem cache,这里将其放回到s->memcg_params.children list中list_splice(&busy, &s->memcg_params.children);/** A cache being destroyed must be empty. In particular, this means* that all per memcg caches attached to it must be empty too.*/
//如果s名下的all per memcg caches有继续在使用的,那么s->memcg_params.children肯定不为NULL,返回-EBUSY,否则返回0if (!list_empty(&s->memcg_params.children))return -EBUSY;return 0;
}2.2 shutdown_cache函数
该函数首先释放被kasan隔离延迟释放的obj,kmem_cache_free->slab_free->slab_free_freelist_hook函数做了隔离,然后就是开始释放kmem cache使用的resource,包括kmem_cache_cpu和kmem_cache_node管理的空间。
static int shutdown_cache(struct kmem_cache *s)
{/* free asan quarantined objects */
//1、释放前面被kasan隔离延迟释放的obj,kmem_cache_free->slab_free->slab_free_freelist_hook函数做了隔离kasan_cache_shutdown(s);//2、释放所有被kmem_cache使用的resource,如果执行成功,返回0;返回1,说明有异常,销毁失败if (__kmem_cache_shutdown(s) != 0)return -EBUSY;memcg_unlink_cache(s);
//将这个kmem_cache从系统全局slab_caches链表中删除list_del(&s->list);//如果有rcu的话,通过slab_caches_to_rcu_destroy_work来释放if (s->flags & SLAB_TYPESAFE_BY_RCU) {
#ifdef SLAB_SUPPORTS_SYSFS
//如果使能了sysfs,从hierarchy中取消链接struct kobjectsysfs_slab_unlink(s);
#endif
//将这个kmem_cache添加到slab_caches_to_rcu_destroy尾部,然后调用slab_caches_to_rcu_destroy_work来释放list_add_tail(&s->list, &slab_caches_to_rcu_destroy);schedule_work(&slab_caches_to_rcu_destroy_work);} else {
#ifdef SLAB_SUPPORTS_SYSFSsysfs_slab_unlink(s);
//如果使能了sysfs,需要将kobject的引用计数减1sysfs_slab_release(s);
#else
//前面释放完后,将s->cpu_slab和s->node置为NULL,如果使能了CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_RANDOM,也会将s->random_seq置为NULL,实际上就是释放name占用的资源slab_kmem_cache_release(s);
#endif}return 0;
}2.2.1 kasan_cache_shutdown函数
//1、释放前面被kasan隔离延迟释放的obj
void kasan_cache_shutdown(struct kmem_cache *cache)
{if (!__kmem_cache_empty(cache))
//如果该kmem_cache的所有node,有一个不为空的,就会执行,确保该kmem_cache中被隔离的obj也要释放quarantine_remove_cache(cache);
}bool __kmem_cache_empty(struct kmem_cache *s)
{int node;struct kmem_cache_node *n;
//遍历s的所有node,如果n->nr_partial不为0或者n->nr_slabs不为0,则返回FALSE,意味着不为emptyfor_each_kmem_cache_node(s, node, n)if (n->nr_partial || slabs_node(s, node))return false;
//否则,返回truereturn true;
}/* Free all quarantined objects belonging to cache. */
void quarantine_remove_cache(struct kmem_cache *cache)
{unsigned long flags, i;struct qlist_head to_free = QLIST_INIT;/** Must be careful to not miss any objects that are being moved from* per-cpu list to the global quarantine in quarantine_put(),* nor objects being freed in quarantine_reduce(). on_each_cpu()* achieves the first goal, while synchronize_srcu() achieves the* second.*/
//隔离的obj放在per-cpu队列和remove_cache_srcu全局队列中,这里on_each_cpu先释放per-cpu队列上的obj(访问per-cpu是原子操作,可以不用上锁)on_each_cpu(per_cpu_remove_cache, cache, 1);//上锁quarantine_lock,因为要访问remove_cache_srcu了,通过qlist_move_cache和qlist_free_all完成这个全局队列的释放,
//然后,通过synchronize_srcu同步这个全局队列信息spin_lock_irqsave(&quarantine_lock, flags);for (i = 0; i < QUARANTINE_BATCHES; i++) {if (qlist_empty(&global_quarantine[i]))continue;qlist_move_cache(&global_quarantine[i], &to_free, cache);/* Scanning whole quarantine can take a while. */spin_unlock_irqrestore(&quarantine_lock, flags);cond_resched();spin_lock_irqsave(&quarantine_lock, flags);}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&quarantine_lock, flags);qlist_free_all(&to_free, cache);synchronize_srcu(&remove_cache_srcu);
}2.2.2 __kmem_cache_shutdown函数
//2、释放所有被kmem_cache使用的resource
/** Release all resources used by a slab cache.*/
int __kmem_cache_shutdown(struct kmem_cache *s)
{int node;struct kmem_cache_node *n;
//2.1 首先,释放本地CPU的缓存区,即kmem_cache_cpu管理的缓存区空间flush_all(s);//2.2 然后,循环遍历s的所有node,将node partial上管理的空间通过free_partial释放,
//如果n->nr_partial不为0或者n->nr_slabs不为0,则返回1/* Attempt to free all objects */for_each_kmem_cache_node(s, node, n) {free_partial(s, n);if (n->nr_partial || slabs_node(s, node))return 1;}//如果循环遍历s的所有node都为empty,继续对sysfs的slab做移除操作sysfs_slab_remove(s);return 0;
}//2.1 首先,释放本地CPU的缓存区,即kmem_cache_cpu管理的缓存区空间
static void flush_all(struct kmem_cache *s)
{
/*
看似封装了on_each_cpu_cond()函数,实际上该函数并不执行任何与资源释放的操作,
其主要是遍历各个CPU,然后执行作为入参传入的函数has_cpu_slab(),
以判断各个CPU上的资源是否存在,存在将会通过flush_cpu_slab()对该CPU上的资源进行释放处理
*/on_each_cpu_cond(has_cpu_slab, flush_cpu_slab, s, 1, GFP_ATOMIC);
}//主要是用于判断per CPU是否占有缓存区
static bool has_cpu_slab(int cpu, void *info)
{struct kmem_cache *s = info;struct kmem_cache_cpu *c = per_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab, cpu);
//slub_percpu_partial(c)得到c->partial,如果c->page或者c->partial不为空,则认为per CPU占有了缓存区,返回truereturn c->page || slub_percpu_partial(c);
}//主要用于将per CPU的缓存区进行释放
static void flush_cpu_slab(void *d)
{struct kmem_cache *s = d;
//smp_processor_id()得到current CPU ID__flush_cpu_slab(s, smp_processor_id());
}/** Flush cpu slab.** Called from IPI handler with interrupts disabled.*/
static inline void __flush_cpu_slab(struct kmem_cache *s, int cpu)
{
//先获取per CPU的kmem_cache_cpustruct kmem_cache_cpu *c = per_cpu_ptr(s->cpu_slab, cpu);if (likely(c)) {
//如果c->page不为空,调用flush_slab释放c->page和c->freelist指向的空间if (c->page)flush_slab(s, c);
//如果c->partial不为空,调用unfreeze_partials释放c->partial管理的空间,
//关于unfreeze_partials函数,在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(3)中有介绍unfreeze_partials(s, c);}
}//2.2 将node partial上管理的空间通过free_partial释放
/** Attempt to free all partial slabs on a node.* This is called from __kmem_cache_shutdown(). We must take list_lock* because sysfs file might still access partial list after the shutdowning.*/
static void free_partial(struct kmem_cache *s, struct kmem_cache_node *n)
{LIST_HEAD(discard);struct page *page, *h;BUG_ON(irqs_disabled());spin_lock_irq(&n->list_lock);
//遍历访问n->partial上的所有pagelist_for_each_entry_safe(page, h, &n->partial, lru) {
//如果page->inuse等于0,说明这个page上全是空闲obj,remove_partial将其从该node partial中删除
//关于remove_partial函数,在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(3)中有介绍
//list_add将这个page,添加到discard链表中if (!page->inuse) {remove_partial(n, page);list_add(&page->lru, &discard);
//否则,这个page上是部分空闲,有部分obj还在使用,会报error信息} else {list_slab_objects(s, page,"Objects remaining in %s on __kmem_cache_shutdown()");}}spin_unlock_irq(&n->list_lock);
//遍历这个discard链表上的page,调用discard_slab释放page,还给buddy system
//关于discard_slab函数,在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(3)中有介绍list_for_each_entry_safe(page, h, &discard, lru)discard_slab(s, page);
}
参考资料
【原创】(十一)Linux内存管理slub分配器
图解slub
mm-slab对象的回收
【Linux内存源码分析】SLUB分配算法(6)
ARM64内存管理十一:slub销毁
内存管理API之kmem_cache_destroy