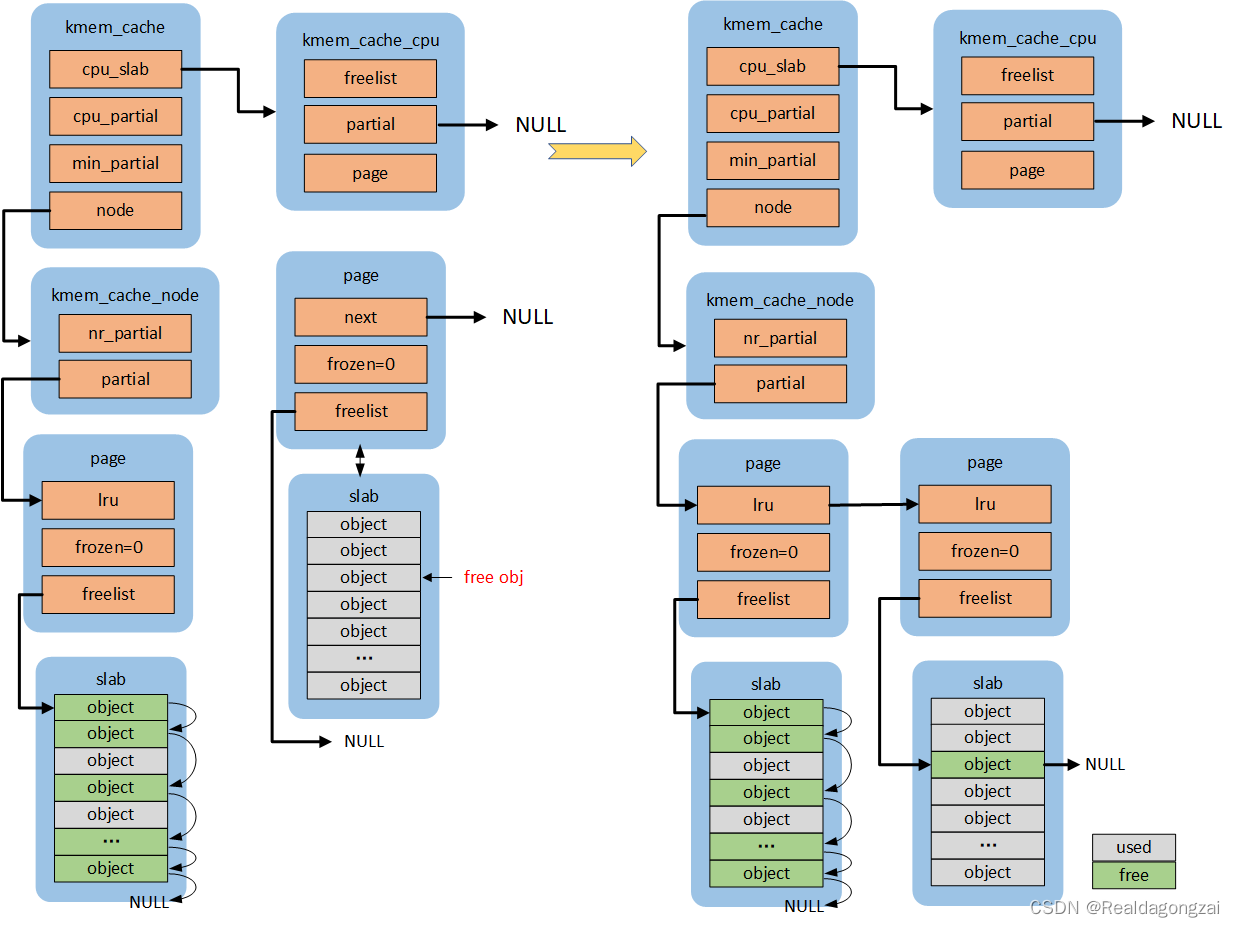
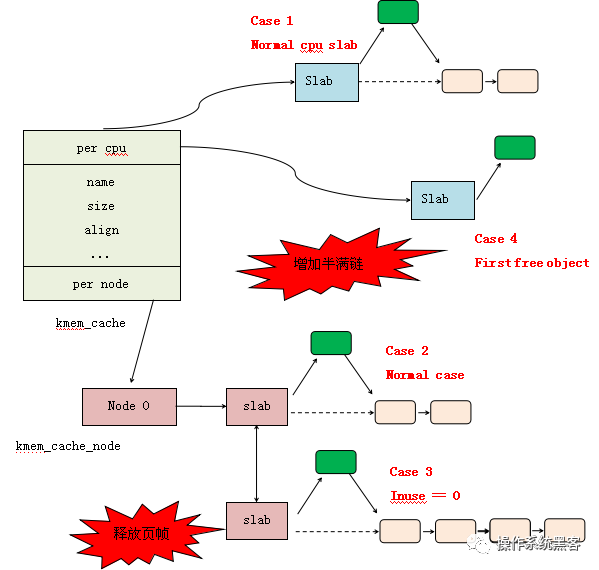
在讲slub内存管理涉及的四个函数之前,先从slub内存分配算法的初始化开始。系统启动时,会进行slub内存分配算法的初始化,函数流程是:start_kernel() -> mm_init()->kmem_cache_init()。在start_kernel()函数中的setup_arch()里面会利用bootmem分配器进行启动阶段早期的内存分配,然后调用paging_init() -> bootmem_init()进行分页机制和内存管理的初始化。有了前面的基础,在mm_init()里面,首先,调用mem_init()初始化buddy system内存管理算法,至此bootmem分配器完成了任务;后面kmem_cache_init()在buddy system的基础上,进行slub内存分配的初始化。完成 kmem_cache_node 、 kmem_cache 、 kmalloc_caches 三个slab cache管理结构的初始化,对于内核中其他的slab cache的创建通过kmem_cache_create()函数完成。
一、函数详细调用关系图
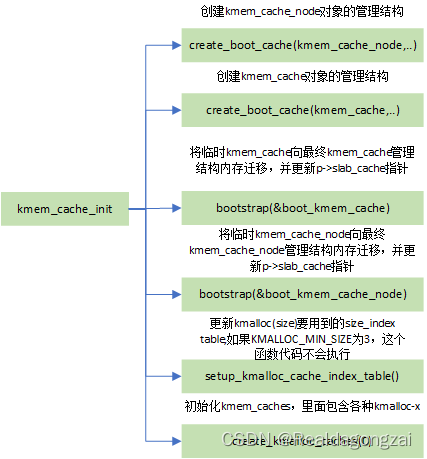
二、kmem_cache_init函数代码流程
主要完成三个工作:创建 kmem_cache_node 、 kmem_cache 和 kmalloc_caches 三个slab cache
static struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache_node; //linux-4.19.49/mm/slub.c
struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache; //linux-4.19.49/mm/slab_common.c /* Align objs on cache lines */
#define SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN ((slab_flags_t __force)0x00002000U)/*mm/slab.h* State of the slab allocator.** This is used to describe the states of the allocator during bootup.* Allocators use this to gradually bootstrap themselves. Most allocators* have the problem that the structures used for managing slab caches are* allocated from slab caches themselves.*/
enum slab_state {DOWN, /* No slab functionality yet */PARTIAL, /* SLUB: kmem_cache_node available */PARTIAL_NODE, /* SLAB: kmalloc size for node struct available */UP, /* Slab caches usable but not all extras yet */FULL /* Everything is working */
};//主要完成三个工作:创建 kmem_cache_node 、 kmem_cache 和 kmalloc_caches 三个slab cache
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{static __initdata struct kmem_cache boot_kmem_cache,boot_kmem_cache_node; //声明静态变量,存储临时kmem_cache结构;if (debug_guardpage_minorder())slub_max_order = 0;
//这两个全局变量定义的位置在上面kmem_cache_node = &boot_kmem_cache_node;kmem_cache = &boot_kmem_cache;//1、创建kmem_cache_node对象的管理结构create_boot_cache(kmem_cache_node, "kmem_cache_node",sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node), SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN, 0, 0);//注册热插拔内存内核通知链回调函数用于热插拔内存处理,注册到memory_chain上 register_hotmemory_notifier(&slab_memory_callback_nb);//因为前面创建了创建kmem_cache_node,意味着kmem_cache_node available,所以slab_state状态改为partial,
//slab_state开始默认是DOWN,表示slab完全不可用/* Able to allocate the per node structures */slab_state = PARTIAL;/*
2、创建kmem_cache对象的管理结构,这里相比前面,主要是kmem_cache的size会有变化,因为包含了kmem_cache_node
offsetof(struct kmem_cache, node) 得到node成员变量的在struct kmem_cache结构体偏移量,
然后最终得到整个struct kmem_cache结构的size,进行完整的kmem_cache的创建(前面kmem_cache_node
已经进行了部分创建)
*/create_boot_cache(kmem_cache, "kmem_cache",offsetof(struct kmem_cache, node) +nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node *),SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN, 0, 0);//3、申请保存管理结构的内存,将临时kmem_cache和boot_kmem_cache_node分别向最终kmem_cache和kmem_cache_node管理结构内存迁移,
//并修正上面node的page(slab)指针,使其指向最终的kmem_cache和kmem_cache_nodekmem_cache = bootstrap(&boot_kmem_cache);kmem_cache_node = bootstrap(&boot_kmem_cache_node);/* Now we can use the kmem_cache to allocate kmalloc slabs */
//4、根据KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE,更新kmalloc时要用到的size_index table,kmalloc会在slub allocator工作原理里详细描述setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table();
//5、初始化kmem_caches,里面包含各种kmalloc-xcreate_kmalloc_caches(0);/* Setup random freelists for each cache */
//遍历全局链表slab_caches上面的kmem_cache,将随机化的值放到结构体里面random_seq数组里面,
//后面freelist指针的随机化时会用到(出于安全考虑)init_freelist_randomization();//设置好CPU进行热插拔时slub的回调函数slub_cpu_dead,以便在CPU热插拔时做相应处理cpuhp_setup_state_nocalls(CPUHP_SLUB_DEAD, "slub:dead", NULL,slub_cpu_dead);
//打印slub管理结构初始化后,当前slub的硬件对齐大小,阶数,单个slab里面最小obj数目,逻辑cpu数目,节点数目pr_info("SLUB: HWalign=%d, Order=%u-%u, MinObjects=%u, CPUs=%u, Nodes=%d\n",cache_line_size(),//返回L1 cache line的大小slub_min_order, slub_max_order, slub_min_objects,nr_cpu_ids, nr_node_ids);
}2.1 create_boot_cache函数
在boot阶段时创建slab cache管理结构,包含: kmem_cache_node,kmem_cache,kmalloc_caches
/* Create a cache during boot when no slab services are available yet */
void __init create_boot_cache(struct kmem_cache *s, const char *name,unsigned int size, slab_flags_t flags,unsigned int useroffset, unsigned int usersize)
{int err;
//进行参数的初始化,calculate_alignment计算内存对齐值,具体在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(1)中有讲s->name = name;s->size = s->object_size = size;s->align = calculate_alignment(flags, ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN, size);s->useroffset = useroffset;s->usersize = usersize;slab_init_memcg_params(s);
//核心函数,这个在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(1)中也有讲,正常是返回0
/*
__kmem_cache_crete 主要通过 kmem_cache_open 实现,这个函数除了设置kmem cache的一些参数以外,
还会调用 init_kmem_cache_nodes 和 alloc_kmem_cache_cpus;
前者用于初始化kmem_cache中的 struct kmem_cache_node *node[MAX_NUMNODES] 成员,
后者用于分配 struct kmem_cache 中的per-cpu成员变量 struct kmem_cache_cpu __percpu *cpu_slab 。
*/err = __kmem_cache_create(s, flags);if (err)panic("Creation of kmalloc slab %s size=%u failed. Reason %d\n",name, size, err);
//初始化keme cache引用计数为-1s->refcount = -1; /* Exempt from merging for now */
}2.2 bootstrap函数
在系统启动阶段,前期的管理很多都是借用临时变量空间的,所以将会通过bootstrap()将kmem_cache_node和kmem_cache的管理结构迁入到slub管理框架的对象空间中,实现自管理
/*
* 将boot_kmem_cache和boot_kmem_cache_node中的内容拷贝到新申请的slub对象中,并更新每个node上每个page(slab)指向kmem_cache的指针
* 从而完成了struct kmem_cache和struct kmem_cache_node管理结构的bootstrap(自引导)
*/
/** Used for early kmem_cache structures that were allocated using* the page allocator. Allocate them properly then fix up the pointers* that may be pointing to the wrong kmem_cache structure.*/
static struct kmem_cache * __init bootstrap(struct kmem_cache *static_cache)
{int node;//为前面create_boot_cache()创建的kmem_cache申请slub空间,值得注意的是该函数申请调用kmem_cache_zalloc()->kmem_cache_alloc()->slab_alloc(),
//kmem_cache_alloc函数在SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(2)会详细介绍struct kmem_cache *s = kmem_cache_zalloc(kmem_cache, GFP_NOWAIT);struct kmem_cache_node *n;//将bootstrap()入参的kmem_cache结构数据memcpy()至申请的空间中memcpy(s, static_cache, kmem_cache->object_size);/** This runs very early, and only the boot processor is supposed to be* up. Even if it weren't true, IRQs are not up so we couldn't fire* IPIs around.*/
//刷新cpu的slab信息,主要更新c->page,c->freelist和c->partial__flush_cpu_slab(s, smp_processor_id());//循环遍历s->node数组中的所有node,然后遍历每个node上面的partial链表,
//修改上面的struct page的slab_cache指针,指向当前的kmem_cachefor_each_kmem_cache_node(s, node, n) {struct page *p;list_for_each_entry(p, &n->partial, lru)p->slab_cache = s;
//如果使能了slub debug,每个node上面会多一个full链表,指针也要进行更新
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUGlist_for_each_entry(p, &n->full, lru)p->slab_cache = s;
#endif}
//初始化s->memcg_params里面的部分参数slab_init_memcg_params(s);//将kmem_cache添加到全局slab_caches链表中list_add(&s->list, &slab_caches);//根据判断s是不是root_cache,继续初始化s->memcg_params里面的参数memcg_link_cache(s);return s;
}void slab_init_memcg_params(struct kmem_cache *s)
{s->memcg_params.root_cache = NULL;RCU_INIT_POINTER(s->memcg_params.memcg_caches, NULL);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&s->memcg_params.children);s->memcg_params.dying = false;
}
2.3 setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table函数
根据KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE(默认是3),更新创建kmalloc时要用到的size_index table,默认情况是不会执行,使用已经定义好的size_index table即可
/** Conversion table for small slabs sizes / 8 to the index in the* kmalloc array. This is necessary for slabs < 192 since we have non power* of two cache sizes there. The size of larger slabs can be determined using* fls.*/
static u8 size_index[24] __ro_after_init = {3, /* 8 */4, /* 16 */5, /* 24 */5, /* 32 */6, /* 40 */6, /* 48 */6, /* 56 */6, /* 64 */1, /* 72 */1, /* 80 */1, /* 88 */1, /* 96 */7, /* 104 */7, /* 112 */7, /* 120 */7, /* 128 */2, /* 136 */2, /* 144 */2, /* 152 */2, /* 160 */2, /* 168 */2, /* 176 */2, /* 184 */2 /* 192 */
};static inline unsigned int size_index_elem(unsigned int bytes)
{return (bytes - 1) / 8;
}//linux/slab.h
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB
/** SLUB directly allocates requests fitting in to an order-1 page* (PAGE_SIZE*2). Larger requests are passed to the page allocator.*/
#define KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH (PAGE_SHIFT + 1) //PAGE_SHIFT=12
#define KMALLOC_SHIFT_MAX (MAX_ORDER + PAGE_SHIFT - 1) //MAX_ORDER=11
#ifndef KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW
#define KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW 3
#endif
#endif
/* Maximum allocatable size */
#define KMALLOC_MAX_SIZE (1UL << KMALLOC_SHIFT_MAX)
/* Maximum size for which we actually use a slab cache */
#define KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE (1UL << KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH)
/* Maximum order allocatable via the slab allocagtor */
#define KMALLOC_MAX_ORDER (KMALLOC_SHIFT_MAX - PAGE_SHIFT)/** Kmalloc subsystem.*/
#ifndef KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE
//根据这个默认值为8,所以setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table函数里面的基本不会对size_index数组里面的值进行修改
#define KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE (1 << KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW)
#endif/** Patch up the size_index table if we have strange large alignment* requirements for the kmalloc array. This is only the case for* MIPS it seems. The standard arches will not generate any code here.** Largest permitted alignment is 256 bytes due to the way we* handle the index determination for the smaller caches.** Make sure that nothing crazy happens if someone starts tinkering* around with ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,the value is ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN * if define ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN && ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN > 8, and * ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN generally euqal to L1_cache_bytes;* otherwise ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN is __alignof__(unsigned long long)*///条件为真,则编译时会报错,因为char[1-2],是有问题的
#define BUILD_BUG_ON(condition) ((void)sizeof(char[1 - 2*!!(condition)]))void __init setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table(void)
{unsigned int i;
//如果KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE大于256,或者KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE大小不是2的幂次方,此时condition为真,那么就会在编译时报错BUILD_BUG_ON(KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE > 256 ||(KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE & (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE - 1)));
//对大小在8byte与KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE之间的对象,将其在size_index数组的索引设置为KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOWfor (i = 8; i < KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE; i += 8) {
//得到size_index数组中对应的索引unsigned int elem = size_index_elem(i);
//如果索引超过数组size_index的大小,直接breakif (elem >= ARRAY_SIZE(size_index))break;
//这个数组元素开始已经定义好的,但在系统启动阶段会可能更新一次size_index数组,后面不会再更新,只能读size_index[elem] = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW;//如前面宏定义,KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW为3}//下面两个if语句也是根据KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE值,判断在系统启动阶段是否需要更新size_index数组
//对64byte至96byte及128byte至192byte之间的对象,对其在size_index数组的index值进行设置if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE >= 64) {/** The 96 byte size cache is not used if the alignment* is 64 byte.*/for (i = 64 + 8; i <= 96; i += 8)size_index[size_index_elem(i)] = 7;}if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE >= 128) {/** The 192 byte sized cache is not used if the alignment* is 128 byte. Redirect kmalloc to use the 256 byte cache* instead.*/for (i = 128 + 8; i <= 192; i += 8)size_index[size_index_elem(i)] = 8;}
}2.4 create_kmalloc_caches函数
初始化kmem_caches,里面包含各种kmalloc-x,后面kmalloc会用到这个kmem_caches,在slub allocator工作原理这篇文章里面有介绍kmalloc函数
struct kmem_cache *
kmalloc_caches[NR_KMALLOC_TYPES][KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH + 1] __ro_after_init;
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmalloc_caches);/** Whenever changing this, take care of that kmalloc_type() and* create_kmalloc_caches() still work as intended.*/
enum kmalloc_cache_type {KMALLOC_NORMAL = 0,KMALLOC_RECLAIM,
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMAKMALLOC_DMA,
#endifNR_KMALLOC_TYPES
};/* A table of kmalloc cache names and sizes */
extern const struct kmalloc_info_struct {const char *name;unsigned int size;
} kmalloc_info[];
/** kmalloc_info[] is to make slub_debug=,kmalloc-xx option work at boot time.* kmalloc_index() supports up to 2^26=64MB, so the final entry of the table is* kmalloc-67108864.*/
const struct kmalloc_info_struct kmalloc_info[] __initconst = { //__initconst 用于初始化数据{NULL, 0}, {"kmalloc-96", 96},{"kmalloc-192", 192}, {"kmalloc-8", 8},{"kmalloc-16", 16}, {"kmalloc-32", 32},{"kmalloc-64", 64}, {"kmalloc-128", 128},{"kmalloc-256", 256}, {"kmalloc-512", 512},{"kmalloc-1k", 1024}, {"kmalloc-2k", 2048},{"kmalloc-4k", 4096}, {"kmalloc-8k", 8192},{"kmalloc-16k", 16384}, {"kmalloc-32k", 32768},{"kmalloc-64k", 65536}, {"kmalloc-128k", 131072},{"kmalloc-256k", 262144}, {"kmalloc-512k", 524288},{"kmalloc-1M", 1048576}, {"kmalloc-2M", 2097152},{"kmalloc-4M", 4194304}, {"kmalloc-8M", 8388608},{"kmalloc-16M", 16777216}, {"kmalloc-32M", 33554432},{"kmalloc-64M", 67108864}
};
/** Create the kmalloc array. Some of the regular kmalloc arrays* may already have been created because they were needed to* enable allocations for slab creation.*/
void __init create_kmalloc_caches(slab_flags_t flags)
{int i, type;for (type = KMALLOC_NORMAL; type <= KMALLOC_RECLAIM; type++) {
//KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH默认为13,看kmalloc_info可知默认通过kmalloc分配的最大内存是8K=2*pagefor (i = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {if (!kmalloc_caches[type][i])
//5.1循环调用new_kmalloc_cache来初始化kmalloc_caches数组new_kmalloc_cache(i, type, flags);/** Caches that are not of the two-to-the-power-of size.* These have to be created immediately after the* earlier power of two caches*/
/*
原则上系统会为每个2次幂大小的内存块申请一个缓存,
但是内存块过小时,会产生很多碎片浪费,所以系统为96B和192B也各自创建了一个缓存。
大小为64~96B和128B~192B,单独创建了两个kmem_cache保存在kmalloc_caches [1]和kmalloc_caches [2]
*/if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32 && i == 6 &&!kmalloc_caches[type][1])new_kmalloc_cache(1, type, flags);if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64 && i == 7 &&!kmalloc_caches[type][2])new_kmalloc_cache(2, type, flags);}}
//初始化完kmalloc_caches(在初始化kmalloc_caches时,相当于也是把对应size的kmem_cache也给初始化了),
//此时slab_state状态从partial变成UP,Slab 缓存可用,基本功能已经有了,但还不是所有功能都可以用了/* Kmalloc array is now usable */slab_state = UP;#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
//如果定义了CONFIG_ZONE_DMA,那么对应的kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_DMA][i]要进行初始化for (i = 0; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {
//首先获取kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_NORMAL][i],基本结构直接复用struct kmem_cache *s = kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_NORMAL][i];if (s) {
//得到此时i对应的size,实际上跟kmalloc_info里面的size对应unsigned int size = kmalloc_size(i);
//kmalloc cache name 为"dma-kmalloc-x"const char *n = kmalloc_cache_name("dma-kmalloc", size);BUG_ON(!n);
//最后调用create_kmalloc_cache完成DMA对应的kmem_cache和kmalloc_caches的初始化kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_DMA][i] = create_kmalloc_cache(n, size, SLAB_CACHE_DMA | flags, 0, 0);}}
#endif
}//5.1
static void __init
new_kmalloc_cache(int idx, int type, slab_flags_t flags)
{const char *name;
//5.1.1 type为KMALLOC_RECLAIM,走这里得到kmalloc cache name,形如"kmalloc-rcl-X"if (type == KMALLOC_RECLAIM) {flags |= SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT;name = kmalloc_cache_name("kmalloc-rcl",kmalloc_info[idx].size);BUG_ON(!name);} else {
//type为KMALLOC_NORMAL,直接从kmalloc_info根据idx,得到kmalloc cache name,形如"kmalloc-X"name = kmalloc_info[idx].name;}//5.1.2 这里开始初始化kmalloc_caches数组kmalloc_caches[type][idx] = create_kmalloc_cache(name,kmalloc_info[idx].size, flags, 0,kmalloc_info[idx].size);}//5.1.1
static const char *
kmalloc_cache_name(const char *prefix, unsigned int size)
{
//对于type为KMALLOC_RECLAIM,输出的name,前缀是kmalloc-rcl,
//同时根据size大小,进行k和M的转换,如size为8,则为"kmalloc-rcl-8";
//1024为"kmalloc-rcl-1k";因为idx默认最大为13,导致size最大为8k,不会出现Mstatic const char units[3] = "\0kM";int idx = 0;while (size >= 1024 && (size % 1024 == 0)) {size /= 1024;idx++;}return kasprintf(GFP_NOWAIT, "%s-%u%c", prefix, size, units[idx]);
}//5.1.2 开始真正初始化kmalloc_caches数组的核心函数
struct kmem_cache *__init create_kmalloc_cache(const char *name,unsigned int size, slab_flags_t flags,unsigned int useroffset, unsigned int usersize)
{
//通过kmem_cache_zalloc()->kmem_cache_alloc()路径申请一个obj大小为0的kmem_cachestruct kmem_cache *s = kmem_cache_zalloc(kmem_cache, GFP_NOWAIT);//如果内存不够,s为null,则panicif (!s)panic("Out of memory when creating slab %s\n", name);//最后调用前面描述的create_boot_cache,size和usersize都是obj size,完整真正意义上的slab初始化
//前面创建kmem_cache和kmem_cache_node管理结构时,size就是结构体的大小,usersize为0create_boot_cache(s, name, size, flags, useroffset, usersize);//同时还会将这个kmem_cache添加到全局链表slab_cacheslist_add(&s->list, &slab_caches);memcg_link_cache(s);//这个kmem_cache引用计数从-1改为1s->refcount = 1;
//返回,添加到对应的kmalloc_caches数组中,后面kmalloc就会用到这个kmalloc_caches数组return s;
}/** Shortcuts*/
static inline void *kmem_cache_zalloc(struct kmem_cache *k, gfp_t flags)
{return kmem_cache_alloc(k, flags | __GFP_ZERO);
}/** Determine size used for the nth kmalloc cache.* return size or 0 if a kmalloc cache for that* size does not exist*/
static __always_inline unsigned int kmalloc_size(unsigned int n)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_SLOB
//进行一个简单的判断,返回对应的sizeif (n > 2)return 1U << n;
//对应大小为64~96B和128B~192B,系统为96B和192B也各自创建了一个缓存if (n == 1 && KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32)return 96;if (n == 2 && KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64)return 192;
#endifreturn 0;
}参考资料
【Linux基础系列之】内存管理(1)-buddy和slub算法
【Linux内存源码分析】SLUB分配算法(2)
ARM64内存管理七:slub初始化
图解slub
mm-slab初始化
SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(1)
linux内核:一文读懂IPI核间中断(arm64架构)
SLUB内存管理的4个主要接口函数介绍(2)
slub分配器