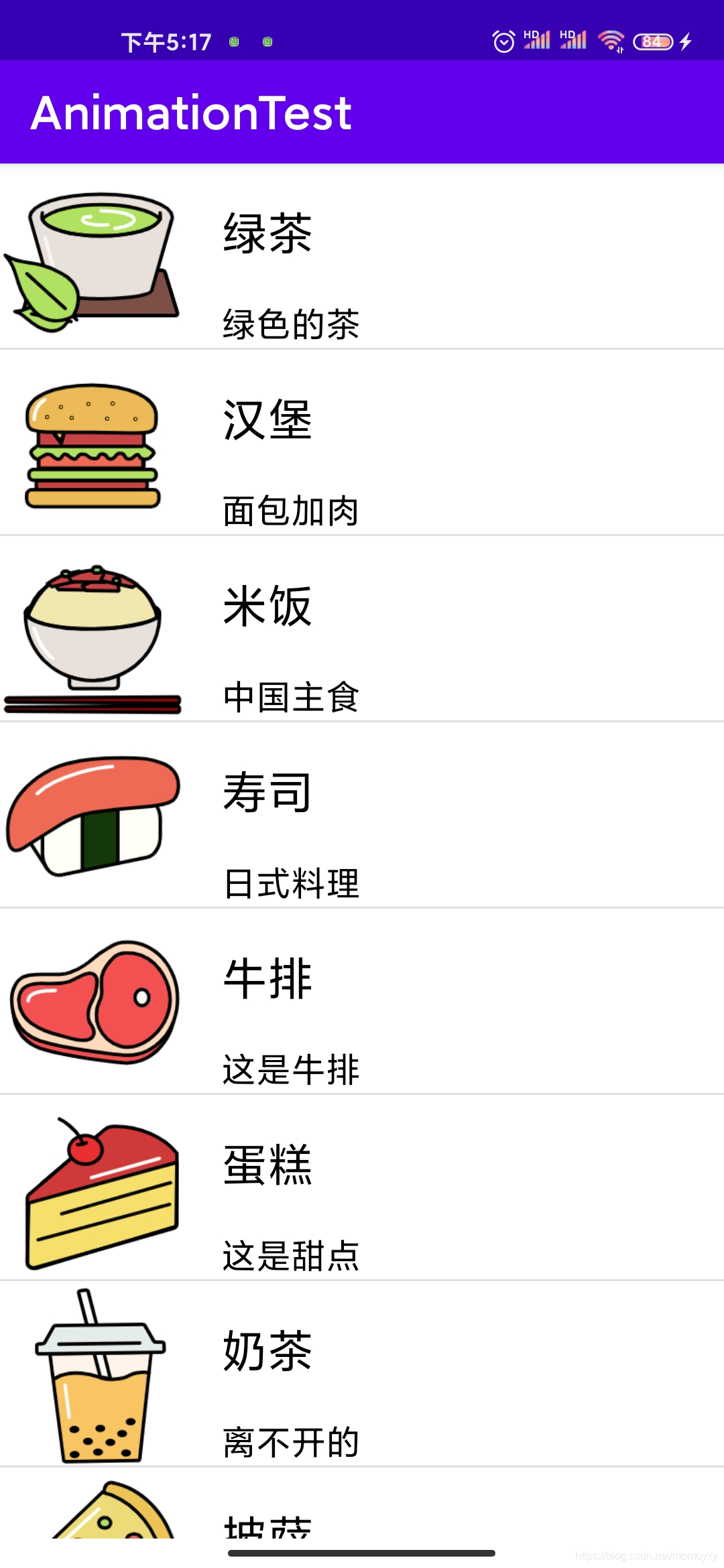
1、什么是ListView?它可以实现怎样的功能?
列表视图是android中最常用的一种视图组件,它以垂直列表的形式列出需要显示的列表项。手机屏幕空间有限,能显示的内容不多。可以借助ListView来显示更多、更丰富的内容。ListView允许用户通过上下滑动来将屏幕外的数据滚动到屏幕内,同时屏幕内原有的数据滚动出屏幕,从而显示更多的数据内容。列表视图如下图所示。

2、由于列表视图中的每一个列表项的格式都是一样的,所以我们只需要定义出一个列表项的格式(框架),再把数据逐个放入这样的框架中即可。
(1)那么如何定义出这种框架呢?
在Android中提供了两种适配器用于实现列表项格式的设置。
①ArrayAdapter
这是一种简单易用的Adapter,通常用于将数组或List集合作为列表项数据源
②SimpleAdapter
SimpleAdapter(Context context, List<? extends Map<String, ?>> data, int resource, String[] from, int[] to)
它共有5个参数:
Context context:-------------------------------------
List<? extends Map<String, ?>> data:--------- 数据源
int resource----------------------------------------------布局文件
String[] from----------------------------------------------数据源中键值对数据中的键
int[] to------------------------------------------------------布局文件中控件对象名
3、实例

(1)首先在布局文件activity_main.xml里面插入ListView组件
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"tools:context="com.example.listview.MainActivity" ><ListView android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/listview"></ListView>
</RelativeLayout>(2)建立列表项框架showfruit.xml布局文件
我们分析一下单个的列表项 可以把它看成是从左至右的水平线性布局,第一个为图片,
可以把它看成是从左至右的水平线性布局,第一个为图片,
考虑使用ImageView组件,第二个再次看成一个垂直的线性布局(分别是水果名称和水果产地)。这里用到了LinearLayout的嵌套。代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="horizontal" ><ImageViewandroid:id="@+id/fruitPic"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"/><LinearLayoutandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:orientation="vertical"><TextView android:id="@+id/fruitName"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"android:text="苹果"/><TextView android:id="@+id/fruitHome"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="新疆"/></LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
(3)最后我们编写MainActivity.java文件
package com.example.listviewproject;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;public class MainActivity extends Activity {ListView list;Map<String,Object> fruit1,fruit2,fruit3;List<Map<String,Object>> fruits;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);list=(ListView)findViewById(R.id.listview);fruits=new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();fruit1=new HashMap();fruit1.put("fruitpic", R.drawable.ic_launcher);fruit1.put("fruitname", "苹果");fruit1.put("fruithome", "新疆");fruits.add(fruit1);fruit2=new HashMap();fruit2.put("fruitpic", R.drawable.ic_launcher);fruit2.put("fruitname", "香蕉");fruit2.put("fruithome", "河南");fruits.add(fruit2);fruit3=new HashMap();fruit3.put("fruitpic", R.drawable.ic_launcher);fruit3.put("fruitname", "柠檬");fruit3.put("fruithome", "广西");fruits.add(fruit3);String []from={"fruitpic","fruitname","fruithome"};int []to={R.id.fruitPic,R.id.fruitName,R.id.fruitHome};SimpleAdapter adapter=new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this,fruits,R.layout.showfruit, from, to);list.setAdapter(adapter);}
}