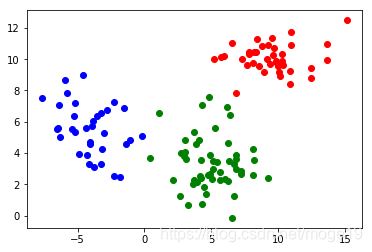
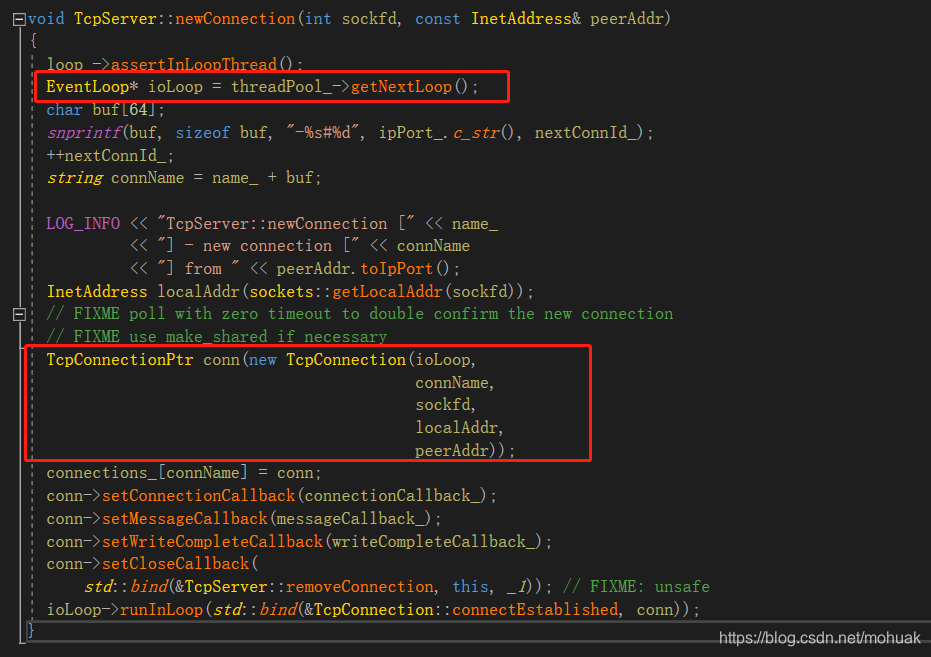
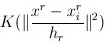Mean Shift算法,又称均值聚类算法,聚类中心是通过在给定区域中的样本均值确定的,通过不断更新聚类中心,直到聚类中心不再改变为止,在聚类、图像平滑、分割和视频跟踪等方面有广泛的运用。
Mean Shift向量
对于给定的n维空间 R n R^n Rn中的m个样本点 X ( i ) , i = 1 , . . . , m X^{(i)},i=1,...,m X(i),i=1,...,m对于其中的一个样本X,其Mean Shift向量为:
M h ( X ) = 1 k ∑ X ( i ) ϵ S k ( X ( i ) − X ) M_h(X) = \frac{1}{k}\sum_{X^{(i)}\epsilon S_{k}} (X^{(i)}-X) Mh(X)=k1X(i)ϵSk∑(X(i)−X)
其中 S h S_h Sh指的是一个半径为h的高维球区域,定义为:
S h ( x ) = ( y ∣ ( y − x ) ( y − x ) T ≤ h 2 S_h (x) = (y|(y-x)(y-x)^T \leq h^2 Sh(x)=(y∣(y−x)(y−x)T≤h2
Mean Shift算法原理
步骤1:在指定区域内计算出每个样本点漂移均值;
步骤2:移动该点到漂移均值处;
步骤3:重复上述过程;
步骤4:当满足条件时,退出
Mean Shift算法流程
(1) 计算 m h ( X ) m_h(X) mh(X);
(2)令 X = m h ( X ) X = m_h(X) X=mh(X);
(3) 如果 ∣ ∣ m h ( X ) − X ∣ ∣ < ε ||m_h(X) -X||<\varepsilon ∣∣mh(X)−X∣∣<ε,结束循环,否则重复上述步骤。
Mean Shift向量:
M h ( X ) = ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ∗ ( X ( i ) − X ) ] ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ] M_h(X)=\frac{\sum_{i=1} ^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)}-X}{h})*(X^{(i)}-X)]}{\sum_{i=1}^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)}-X}{h})]} Mh(X)=∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)]∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)∗(X(i)−X)]
= ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ∗ X ( i ) ] ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ] − X =\frac{\sum_{i=1} ^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)-X}}{h})*X^{(i)}]}{\sum_{i=1}^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)}-X}{h})]}- X =∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)]∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)∗X(i)]−X
记 m h ( x ) = ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ∗ X ( i ) ] ∑ i = 1 n [ K ( X ( i ) − X h ) ] m_h(x)=\frac{\sum_{i=1} ^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)-X}}{h})*X^{(i)}]}{\sum_{i=1}^n[K(\frac{X^{(i)}-X}{h})]} mh(x)=∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)]∑i=1n[K(hX(i)−X)∗X(i)]则上式变成:
M h ( X ) = m h ( X ) − X M_h(X) = m_h(X) - X Mh(X)=mh(X)−X
且
K ( X ( i ) − X h ) = 1 2 π h e ( x 1 − x 2 ) 2 2 h 2 K(\frac{X^{(i)-X}}{h}) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}h}e^{\frac{(x_1-x_2)^2}{2h^2}} K(hX(i)−X)=2πh1e2h2(x1−x2)2
为高斯核函数。
Python实现
(1)计算两个点的欧式距离:
def euclidean_dist(pointA, pointB):'''计算欧式距离input: pointA(mat):A点的坐标pointB(mat):B点的坐标output: math.sqrt(total):两点之间的欧式距离'''# 计算pointA和pointB之间的欧式距离total = (pointA - pointB) * (pointA - pointB).Treturn math.sqrt(total) # 欧式距离
(2)计算高斯核函数:
def gaussian_kernel(distance, bandwidth):'''高斯核函数input: distance(mat):欧式距离bandwidth(int):核函数的带宽output: gaussian_val(mat):高斯函数值'''m = np.shape(distance)[0] # 样本个数right = np.mat(np.zeros((m, 1))) # mX1的矩阵for i in range(m):right[i, 0] = (-0.5 * distance[i] * distance[i].T) / (bandwidth * bandwidth)right[i, 0] = np.exp(right[i, 0])left = 1 / (bandwidth * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))gaussian_val = left * rightreturn gaussian_val
(3)计算均值漂移点
def shift_point(point, points, kernel_bandwidth):'''计算均值漂移点input: point(mat)需要计算的点points(array)所有的样本点kernel_bandwidth(int)核函数的带宽output: point_shifted(mat)漂移后的点'''points = np.mat(points)m = np.shape(points)[0] # 样本的个数# 计算距离point_distances = np.mat(np.zeros((m, 1)))for i in range(m):point_distances[i, 0] = euclidean_dist(point, points[i])# 计算高斯核 point_weights = gaussian_kernel(point_distances, kernel_bandwidth) # mX1的矩阵# 计算分母all_sum = 0.0for i in range(m):all_sum += point_weights[i, 0]# 均值偏移point_shifted = point_weights.T * points / all_sumreturn point_shifted(4)迭代更新漂移均值(训练过程)
def train_mean_shift(points, kenel_bandwidth=2):'''训练Mean shift模型input: points(array):特征数据kenel_bandwidth(int):核函数的带宽output: points(mat):特征点mean_shift_points(mat):均值漂移点group(array):类别'''mean_shift_points = np.mat(points)max_min_dist = 1iteration = 0 # 训练的代数m = np.shape(mean_shift_points)[0] # 样本的个数need_shift = [True] * m # 标记是否需要漂移# 计算均值漂移向量while max_min_dist > MIN_DISTANCE:max_min_dist = 0iteration += 1print("\titeration : " + str(iteration))for i in range(0, m):# 判断每一个样本点是否需要计算偏移均值if not need_shift[i]:continuep_new = mean_shift_points[i]p_new_start = p_newp_new = shift_point(p_new, points, kenel_bandwidth) # 对样本点进行漂移dist = euclidean_dist(p_new, p_new_start) # 计算该点与漂移后的点之间的距离if dist > max_min_dist:max_min_dist = distif dist < MIN_DISTANCE: # 不需要移动need_shift[i] = Falsemean_shift_points[i] = p_new# 计算最终的groupgroup = group_points(mean_shift_points) # 计算所属的类别return np.mat(points), mean_shift_points, group
(5)数据源:
10.91079039 8.389412017
9.875001645 9.9092509
7.8481223 10.4317483
8.534122932 9.559085609
10.38316846 9.618790857
8.110615952 9.774717608
10.02119468 9.538779622
9.37705852 9.708539909
7.670170335 9.603152306
10.94308287 11.76207349
9.247308233 10.90210555
9.54739729 11.36170176
7.833343667 10.363034
10.87045922 9.213348128
8.228513384 10.46791102
12.48299028 9.421228147
6.557229658 11.05935349
7.264259221 9.984256737
4.801721592 7.557912927
6.861248648 7.837006973
13.62724419 10.94830031
13.6552565 9.924983717
9.606090699 10.29198795
12.43565716 8.813439258
10.0720656 9.160571589
8.306703028 10.4411646
8.772436599 10.84579091
9.841416158 9.848307202
15.11169184 12.48989787
10.2774241 9.85657011
10.1348076 8.892774944
8.426586093 11.30023345
9.191199877 9.989869949
5.933268578 10.21740004
9.666055456 10.68814946
5.762091216 10.12453436
5.224273746 9.98492559
10.26868537 10.31605475
10.92376708 10.93351512
8.935799678 9.181397458
2.978214427 3.835470435
4.91744201 2.674339991
3.024557256 4.807509213
3.019226157 4.041811881
4.131521545 2.520604653
0.411345842 3.655696597
5.266443567 5.594882041
4.62354099 1.375919061
5.67864342 2.757973123
3.905462712 2.141625079
8.085352646 2.58833713
6.852035583 3.610319053
4.230846663 3.563377115
6.042905325 2.358886853
4.20077289 2.382387946
4.284037893 7.051142553
3.820640884 4.607385052
5.417685111 3.436339164
8.21146303 3.570609885
6.543095544 -0.150071185
9.217248861 2.40193675
6.673038102 3.307612539
4.043040861 4.849836388
3.704103266 2.252629794
4.908162271 3.870390681
5.656217904 2.243552275
5.091797066 3.509500134
6.334045598 3.517609974
6.820587567 3.871837206
7.209440437 2.853110887
2.099723775 2.256027992
4.720205587 2.620700716
6.221986574 4.665191116
5.076992534 2.359039927
3.263027769 0.652069899
3.639219475 2.050486686
7.250113206 2.633190935
4.28693774 0.741841034
4.489176633 1.847389784
6.223476314 2.226009922
2.732684384 4.026711236
6.704126155 1.241378687
6.406730922 6.430816427
3.082162445 3.603531758
3.719431124 5.345215168
6.190401933 6.922594241
8.101883247 4.283883063
2.666738151 1.251248672
5.156253707 2.957825121
6.832208664 3.004741194
-1.523668483 6.870939176
-6.278045454 5.054520751
-4.130089867 3.308967776
-2.298773883 2.524337553
-0.186372986 5.059834391
-5.184077845 5.32761477
-5.260618656 6.373336994
-4.067910691 4.56450199
-4.856398444 3.94371169
-5.169024046 7.199650795
-2.818717016 6.775475264
-3.013197129 5.307372667
-1.840258223 2.473016216
-3.806016495 3.099383642
-1.353873198 4.60008787
-5.422829607 5.540632064
-3.571899549 6.390529804
-4.037978273 4.70568099
-1.110354346 4.809405537
-3.8378779 6.029098753
-6.55038578 5.511809253
-5.816344971 7.813937668
-4.626894927 8.979880178
-3.230779355 3.295580582
-4.333569224 5.593364339
-3.282896829 6.590185797
-7.646892109 7.527347421
-6.461822847 5.62944836
-6.368216425 7.083861849
-4.284758729 3.842576327
-2.29626659 7.288576999
1.101278199 6.548796127
-5.927942727 8.655087775
-3.954602311 5.733640188
-3.160876539 4.267409415
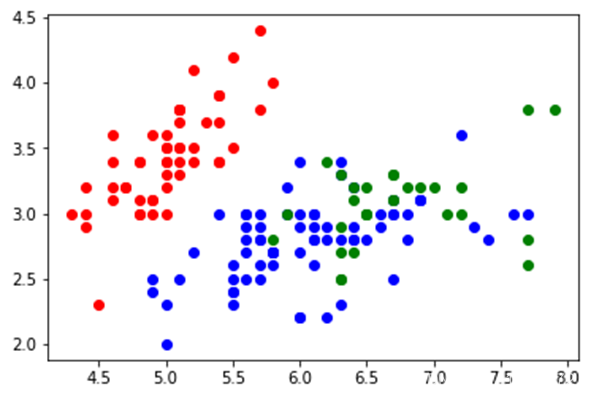
完整代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Oct 14 21:52:09 2018@author: ASUS
"""
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
MIN_DISTANCE = 0.000001 # mini errordef load_data(path, feature_num=2):'''导入数据input: path(string)文件的存储位置feature_num(int)特征的个数output: data(array)特征'''f = open(path) # 打开文件data = []for line in f.readlines():lines = line.strip().split("\t")data_tmp = []if len(lines) != feature_num: # 判断特征的个数是否正确continuefor i in range(feature_num):data_tmp.append(float(lines[i]))data.append(data_tmp)f.close() # 关闭文件return datadef gaussian_kernel(distance, bandwidth):'''高斯核函数input: distance(mat):欧式距离bandwidth(int):核函数的带宽output: gaussian_val(mat):高斯函数值'''m = np.shape(distance)[0] # 样本个数right = np.mat(np.zeros((m, 1))) # mX1的矩阵for i in range(m):right[i, 0] = (-0.5 * distance[i] * distance[i].T) / (bandwidth * bandwidth)right[i, 0] = np.exp(right[i, 0])left = 1 / (bandwidth * math.sqrt(2 * math.pi))gaussian_val = left * rightreturn gaussian_valdef shift_point(point, points, kernel_bandwidth):'''计算均值漂移点input: point(mat)需要计算的点points(array)所有的样本点kernel_bandwidth(int)核函数的带宽output: point_shifted(mat)漂移后的点'''points = np.mat(points)m = np.shape(points)[0] # 样本的个数# 计算距离point_distances = np.mat(np.zeros((m, 1)))for i in range(m):point_distances[i, 0] = euclidean_dist(point, points[i])# 计算高斯核 point_weights = gaussian_kernel(point_distances, kernel_bandwidth) # mX1的矩阵# 计算分母all_sum = 0.0for i in range(m):all_sum += point_weights[i, 0]# 均值偏移point_shifted = point_weights.T * points / all_sumreturn point_shifteddef euclidean_dist(pointA, pointB):'''计算欧式距离input: pointA(mat):A点的坐标pointB(mat):B点的坐标output: math.sqrt(total):两点之间的欧式距离'''# 计算pointA和pointB之间的欧式距离total = (pointA - pointB) * (pointA - pointB).Treturn math.sqrt(total) # 欧式距离def group_points(mean_shift_points):'''计算所属的类别input: mean_shift_points(mat):漂移向量output: group_assignment(array):所属类别'''group_assignment = []m, n = np.shape(mean_shift_points)index = 0index_dict = {}for i in range(m):item = []for j in range(n):item.append(str(("%5.2f" % mean_shift_points[i, j])))item_1 = "_".join(item)if item_1 not in index_dict:index_dict[item_1] = indexindex += 1for i in range(m):item = []for j in range(n):item.append(str(("%5.2f" % mean_shift_points[i, j])))item_1 = "_".join(item)group_assignment.append(index_dict[item_1])return group_assignmentdef train_mean_shift(points, kenel_bandwidth=2):'''训练Mean shift模型input: points(array):特征数据kenel_bandwidth(int):核函数的带宽output: points(mat):特征点mean_shift_points(mat):均值漂移点group(array):类别'''mean_shift_points = np.mat(points)max_min_dist = 1iteration = 0 # 训练的代数m = np.shape(mean_shift_points)[0] # 样本的个数need_shift = [True] * m # 标记是否需要漂移# 计算均值漂移向量while max_min_dist > MIN_DISTANCE:max_min_dist = 0iteration += 1print("\titeration : " + str(iteration))for i in range(0, m):# 判断每一个样本点是否需要计算偏移均值if not need_shift[i]:continuep_new = mean_shift_points[i]p_new_start = p_newp_new = shift_point(p_new, points, kenel_bandwidth) # 对样本点进行漂移dist = euclidean_dist(p_new, p_new_start) # 计算该点与漂移后的点之间的距离if dist > max_min_dist:max_min_dist = distif dist < MIN_DISTANCE: # 不需要移动need_shift[i] = Falsemean_shift_points[i] = p_new# 计算最终的groupgroup = group_points(mean_shift_points) # 计算所属的类别return np.mat(points), mean_shift_points, groupdef save_result(file_name, data):'''保存最终的计算结果input: file_name(string):存储的文件名data(mat):需要保存的文件'''f = open(file_name, "w")m, n = np.shape(data)for i in range(m):tmp = []for j in range(n):tmp.append(str(data[i, j]))f.write("\t".join(tmp) + "\n")f.close()if __name__ == "__main__":color=['.r','.g','.b','.y']#颜色种类# 导入数据集print ("----------1.load data ------------")data = load_data("data", 2)N = len(data)# 训练,h=2print ("----------2.training ------------")points, shift_points, cluster = train_mean_shift(data, 2)# 保存所属的类别文件# save_result("center_1", shift_points) data = np.array(data)for i in range(N):if cluster[i]==0:plt.plot(data[i, 0], data[i, 1],'ro')elif cluster[i]==1:plt.plot(data[i, 0], data[i, 1],'go')elif cluster[i]==2:plt.plot(data[i, 0], data[i, 1],'bo')plt.show() 运行结果