栈
1、栈的定义
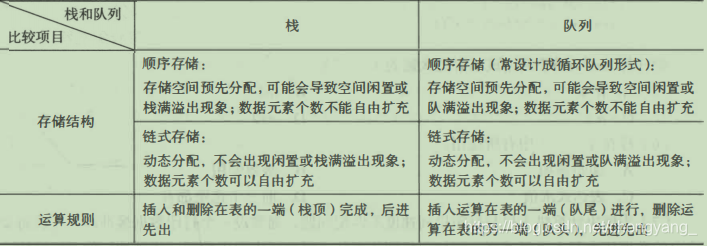
栈(Stack):是只允许在一端进行插入或删除的线性表。首先栈是一种线性表,但限定这种线性表只能在某一端进行插入和删除操作。

栈顶(Top):线性表允许进行插入删除的那一端。
栈底(Bottom):固定的,不允许进行插入和删除的另一端。
空栈:不含任何元素的空表。
栈又称为后进先出(Last In First Out)的线性表,简称LIFO结构
2、栈的常见基本操作
- InitStack(&S):初始化一个空栈S。
- StackEmpty(S):判断一个栈是否为空,若栈为空则返回true,否则返回false。
- Push(&S, x):进栈(栈的插入操作),若栈S未满,则将x加入使之成为新栈顶。
- Pop(&S, &x):出栈(栈的删除操作),若栈S非空,则弹出栈顶元素,并用x返回。
- GetTop(S, &x):读栈顶元素,若栈S非空,则用x返回栈顶元素。
- DestroyStack(&S):栈销毁,并释放S占用的存储空间(“&”表示引用调用)
3、栈的应用场景
1)子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以回到原来的程序中。
2)处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆栈中。
3)表达式的转换[中缀表达式转后缀表达式]与求值(实际解决)。
4)二叉树的遍历。
5)图形的深度优先(depth一first)搜索法。
2、栈的基础入门
2.1用数组模拟栈
/*** 使用数组模拟栈* 1.使用数组来模拟栈* 2.定义一个top来表示栈顶,初始化为-1* 3.入栈的操作,当有数据加入到栈时,top++,stack[top] = data;* 4.出栈的操作,int value = stack[top],top--,return value*/
public class Stack {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(10);stack.push(1);stack.push(2);stack.push(3);stack.push(4);stack.push(5);stack.list();System.out.println("---");//理论上来说应该是4没有了stack.pop();stack.list();}
}class ArrayStack {private int maxSize;//栈的大小private int[] stack;//数组,模拟栈,数据放在该数组private int top = -1;//标记栈的值//构造器public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {this.maxSize = maxSize;this.stack = new int[this.maxSize];}//判断栈满public boolean isFull() {return top == maxSize - 1;}//判断栈空public boolean isEmpty() {return top == -1;}//入栈-pushpublic void push(int i) {if (isFull()) {System.out.println("栈满");return;}top++;stack[top] = i;}//出栈-poppublic int pop() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("栈空");}return stack[top--];}//遍历栈[需要从栈顶开始显示数据]public void list() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("栈空没有数据");return;}//如果从栈顶开始显示数据for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]);}}
}
2.2用链表模拟栈
public class LinkStack {public static void main(String[] args) {Node a1 = new Node(1);Node a2 = new Node(2);Node a3 = new Node(3);LinkStackList ll = new LinkStackList(5);ll.push(a1);ll.push(a2);ll.push(a3);Node pop = ll.pop();System.out.println(pop);ll.list();}}class LinkStackList {private int maxSize;//栈的大小private Node head = new Node(0);//数组,模拟栈,数据放在该头节点private int top = -1;//标记栈的值private Node tmp;public LinkStackList(int maxSize) {this.maxSize = maxSize;}//判断栈空public boolean isEmpty() {return top == -1;}//判断栈满public boolean isFull() {return top == maxSize - 1;}//入栈-pushpublic void push(Node node) {if (isFull()) {System.out.println("栈满");return;}top++;tmp = head;while (true) {if (tmp.next == null) {break;}tmp = tmp.next;}tmp.next = node;tmp = tmp.next;}//出栈-poppublic Node pop() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("栈空");return null;}top--;Node node;node = tmp;tmp = head;while (true) {if (tmp.next.next == null) {tmp.next = null;break;}tmp = tmp.next;}return node;}// 展示public void list() {tmp = head.next;while (tmp != null) {System.out.println(tmp);tmp = tmp.next;}}
}class Node {public int id;public Node next;public Node(int id) {this.id = id;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Node{" +"id=" + id +'}';}
}
3、利用栈来实现一个计算器
简单的中缀表达式计算器

这是我们的思路分析
public class Calculator {public static void main(String[] args) {String expression = "103+2*6-1";
// int a = Integer.parseInt(expression);
// System.out.println(a);//创建两个栈//一个数栈一个符号栈ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);//定义相关的变量int index = 0;int num1 = 0;int num2 = 0;int oper = 0;int res = 0;char ch = ' ';String keepNum = "";//开始循环的扫描expressionwhile (true) {//依次得到expression 的每一个字符ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);//开始判断if (operStack.isOper(ch)) {//如果运算符//判断当前符号栈为空if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {//不为空处理//进行比较,如果当前的操作符优先级小于或等于栈中的操作符,就要从数栈中pop出两个数if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {//如果这个元素满足num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.pop();oper = operStack.pop();res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);//把运算的结果入数栈numStack.push(res);//然后把当前的操作符入符号栈operStack.push(ch);} else {//如果当前的操作符的优先级大于栈中操作符直接入栈operStack.push(ch);}} else {//如果为空直接入栈operStack.push(ch);}} else {//因为0在ascii中是48而不是0
// numStack.push(ch - 48);//当入数栈的时候不能发现是一个数就立刻入栈,因为他可能是多位数//这样做的话无论多少位也没有关系keepNum += ch;//如果ch已经是最后一位就直接入栈if (index == expression.length() - 1) {numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));//重要的!!!keepNum = "";} else {//判断下一个字符表示数组,如果是数字就继续扫描,如果是运算符,则入栈if (operStack.isOper(expression.substring(index + 1, index + 2).charAt(0))) {//如果下一位是运算符则入栈numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));//重要的!!!keepNum = "";}}}//让index++,如果字符串没有字符了跳出循环index++;if (index >= expression.length()) {break;}}//当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序从符号栈中去出相应的数和符号,并运行while (true) {//如果符号栈为空则计算到最后了if (operStack.isEmpty()) {break;}//执行最后的运算//如果这个元素满足num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.pop();oper = operStack.pop();res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);//把运算的结果入数栈numStack.push(res);}int sum = numStack.pop();System.out.println(sum);}
}//先创建一个栈,需要扩展一下功能
class ArrayStack2 {private int maxSize;//栈的大小private int[] stack;//数组,模拟栈,数据放在该数组private int top = -1;//标记栈的值//构造器public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {this.maxSize = maxSize;this.stack = new int[this.maxSize];}//判断栈满public boolean isFull() {return top == maxSize - 1;}//判断栈空public boolean isEmpty() {return top == -1;}//入栈-pushpublic void push(int i) {if (isFull()) {System.out.println("栈满");return;}top++;stack[top] = i;}//出栈-poppublic int pop() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("栈空");}return stack[top--];}//展示当前栈顶的元素public int peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("栈空");}return stack[top];}//遍历栈[需要从栈顶开始显示数据]public void list() {if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("栈空没有数据");return;}//如果从栈顶开始显示数据for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);}}//扩展功能:返回运算符的优先级,优先级越高数字越大public int priority(int oper) {if (oper == '*' || oper == '/') {return 1;} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {return 0;} else {return -1; //假设当前的表达式只有加减乘除}}//判断是不是一个运算符public boolean isOper(char val) {return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';}//计算方法public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {int tmp = 0;switch (oper) {case '+':tmp = num1 + num2;break;case '-':tmp = num2 - num1;break;case '*':tmp = num1 * num2;break;case '/':tmp = num2 / num1;break;}return tmp;}
}
后缀表达式计算器
代码
首先我们先需要一个把后缀表达式转换为List的方法
//将逆波兰表达式,依次将数据和运算符放入ArrayList中
public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) {//将suffixExpressionString[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (String ele : split) {list.add(ele);}return list;
}
然后就是我们真正的计算方法
//完成对逆波兰表达式的运算
//这次我们使用系统提供的栈
public static int calculate(List<String> ls) {//创建一个栈,只需要一个栈就okStack<String> stringStack = new Stack<String>();//遍历lsfor (String item : ls) {//这里使用正则表达式if (item.matches("\\d+")) {//匹配的是多位数//入栈stringStack.push(item);} else {//pop出两个数,并运算,再入栈int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stringStack.pop());int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stringStack.pop());int res = 0;if (item.equals("+")) {res = num1 + num2;} else if (item.equals("-")) {res = num1 - num2;} else if (item.equals("*")) {res = num1 * num2;} else if (item.equals("/")) {res = num1 / num2;} else {throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");}//把res入栈,把整数转换位字符串stringStack.push(res + "");}}//最后留着栈的元素是运算结果return Integer.parseInt(stringStack.pop());
}
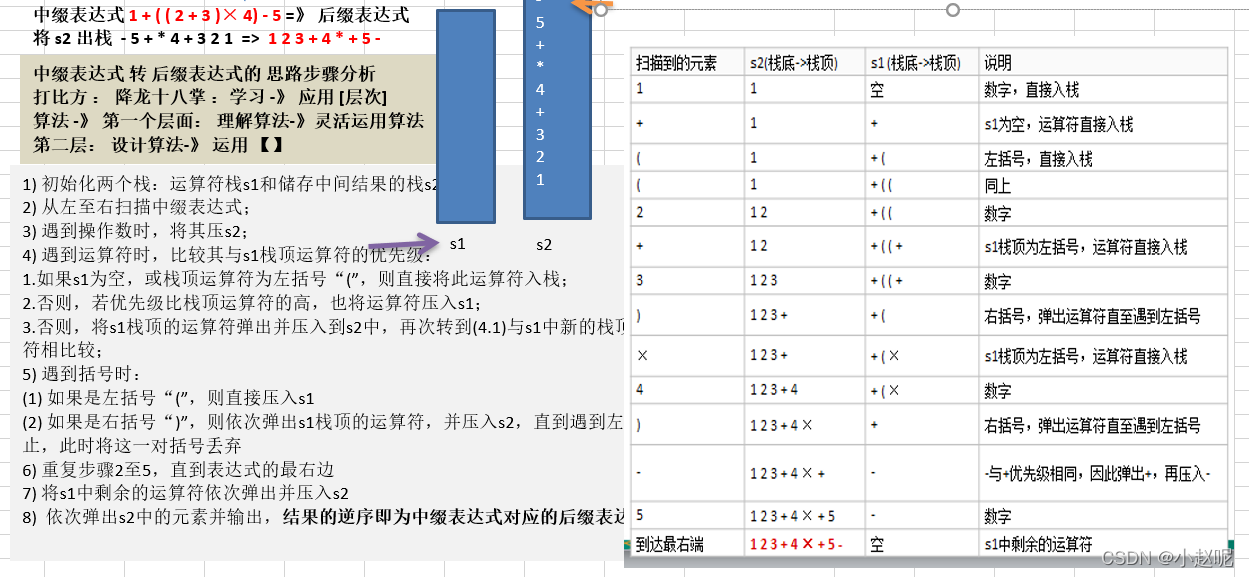
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";
现在我们的需求是把他转换为后缀表达式的list
思路分析
代码
首先要先将中缀表达式转换为对应的list
//将中缀转换为对应的list
public static List<String> getInfixListString(String s) {//定义一个List,存放对应的内容List<String> ls = new ArrayList<String>();int i = 0; //这是一个指针,用于遍历sString str;//做多位数拼接char c;//用于存放到cdo {//如果c是一个非数字,我们就需要加入到ls中去if ((c = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = s.charAt(i)) > 57) {ls.add("" + c);i++;//i需要后移} else {//如果是一个数,需要考虑多位数的问题str = "";//先至空while (i < s.length() && (c = s.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c = s.charAt(i)) <= 57) {str += c;//拼接字符串i++;}ls.add(str);}} while (i < s.length());return ls;
}
把中缀list转换为后缀
//将中缀表达式转换为对应的后缀表达式对应的List
public static List<String> parseSuffixExpressionList(List<String> ls){//定义1个栈Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<String>();//符号栈//定义一个链表List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<String>();//遍历lsfor(String str : ls){//如果是一个数加入s2if(str.matches("\\d+")){s2.add(str);}else if (str.equals("(")) {s1.push(str);}else if (str.equals(")")) {//如果是右括号,依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,压入s2,直到左括号为止,此时这对括号丢弃while (!s1.peek().equals("(")){s2.add(s1.pop());}s1.pop();//!!!将(弹出小括号} else {//这个就是判断的来的是运算符的情况//当str的优先级小于等于栈顶的优先级//问题我们缺失一个优先级方法//来一个循环不停的对比来的运算符和s1栈顶的运算符优先级while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.getPriority(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getPriority(str)){s2.add(s1.pop());}//还需要将str压入栈s1.push(str);}}//将s1剩余的运算符依次加入s2while (s1.size() != 0){s2.add(s1.pop());}return s2;//因为是存放到List因此顺序输出就是对应的逆波兰表达式
}
辅助类
帮助我们判断运算符的优先级
class Operation {private static int ADD = 1;private static int SUB = 1;private static int MUL = 1;private static int DIV = 1;//写一个方法,返回对应的优先级public static int getPriority(String operation){int res = 0;switch (operation) {case "+":res = ADD;break;case "-":res = SUB;break;case "*":res = MUL;break;case "/":res = DIV;break;default :break;}return res;}
}int SUB = 1;private static int MUL = 1;private static int DIV = 1;//写一个方法,返回对应的优先级public static int getPriority(String operation){int res = 0;switch (operation) {case "+":res = ADD;break;case "-":res = SUB;break;case "*":res = MUL;break;case "/":res = DIV;break;default :break;}return res;}
}