目录
- 说明
- 1. AXI 的时钟与复位
- 1.1 时钟
- 1.2 复位
- 2. 五个通道
- 2.1 Write Address Channel
- 2.2 Write Data Channel
- 2.3 Write Response (B) Channel
- 2.4 Read Address Channel
- 2.5 Read Data (and Response) Channel
- 3 突发传输机制
- 3.1 突发传输长度和宽度
- 3.2 突发传输类型
说明
文字说明来自"AMBA® AXI™ and ACE™ ProtocolSpecification",百度直接可以搜到。
代码源自Xilinx的AXI IP,获取方法如下:
选择create and package new IP.
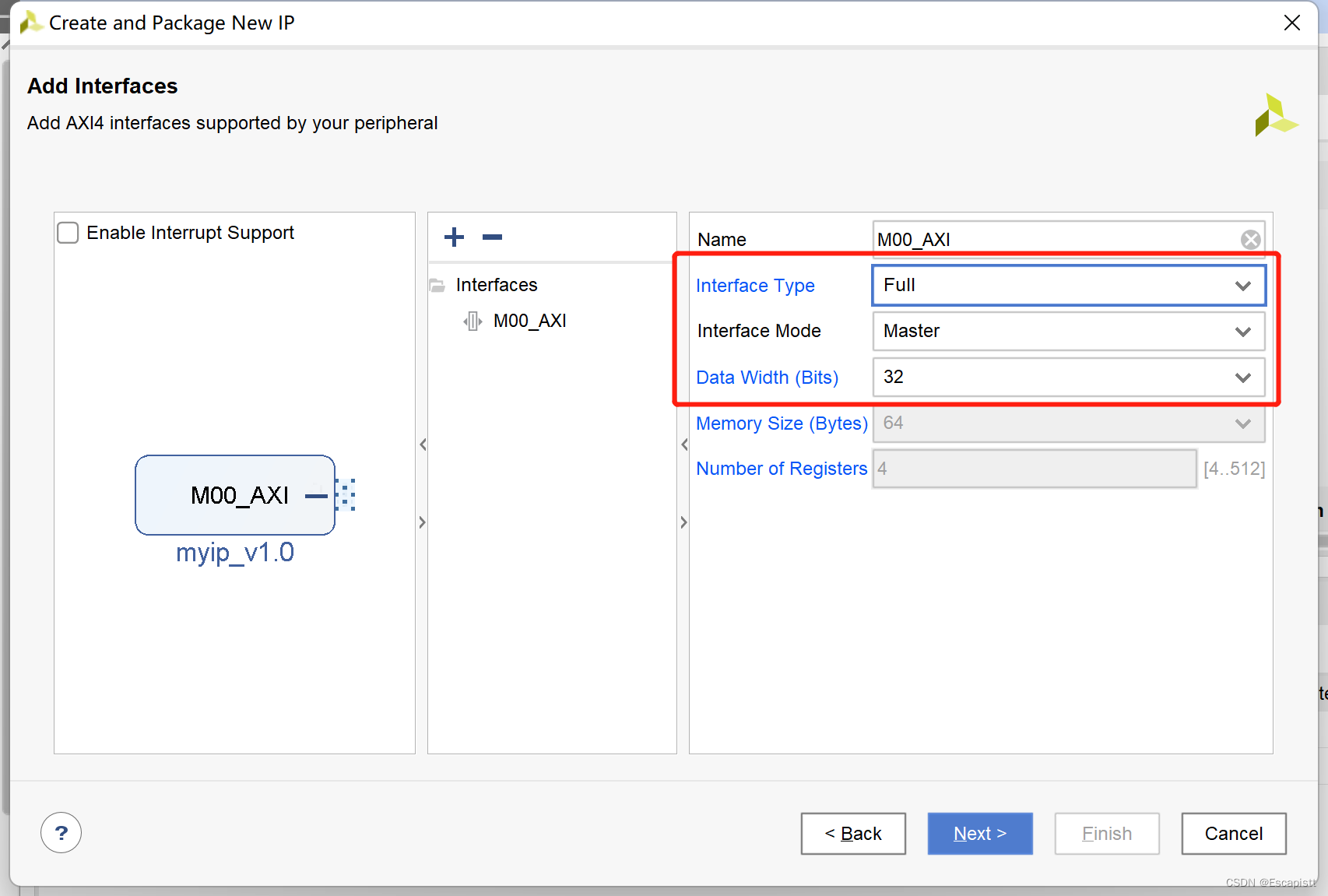
Interface Mode 选择 Master,Interface Type 选择 Full, Date Width自行设定,这里选择32.
选择edit IP.
本文整理了master的部分代码,后续有时间会整理master部分剩下的代码和slave的代码,因为学习协议去看文档非常枯燥,还是与代码结合比较有效,当做一个学习笔记。
1. AXI 的时钟与复位
1.1 时钟
Each AXI component uses a single clock signal, ACLK. All input signals are sampled on the rising edge of ACLK.
All output signal changes must occur after the rising edge of ACLK.
代码:
// Global Clock Signal.input wire M_AXI_ACLK,
1.2 复位
The AXI protocol uses a single active LOW reset signal, ARESETn. The reset signal can be asserted
asynchronously, but deassertion must be synchronous with a rising edge of ACLK.
引脚定义:
master:
// Global Reset Singal. This Signal is Active Lowinput wire M_AXI_ARESETN,
复位的作用引脚为:
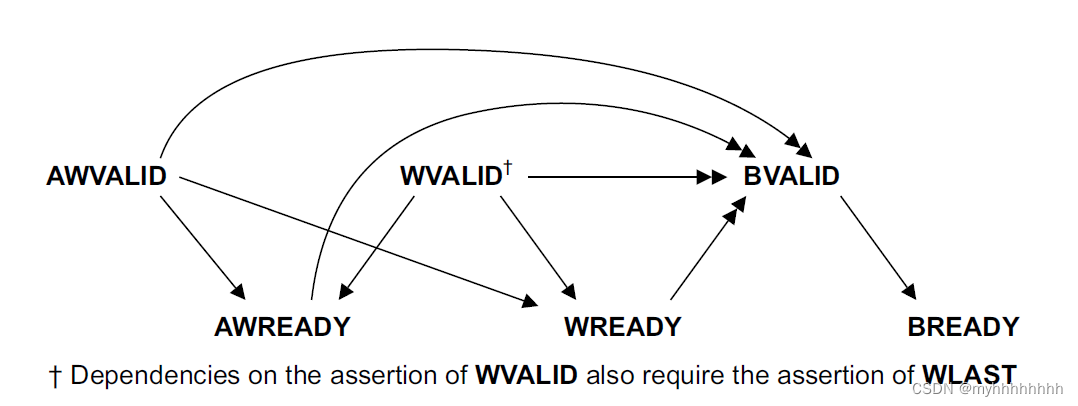
a master interface must drive ARVALID, AWVALID, and WVALID LOW
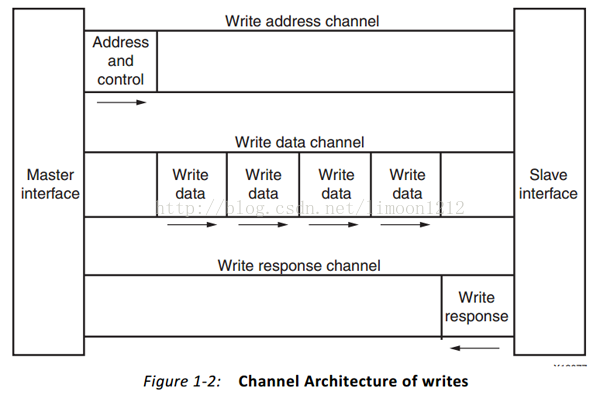
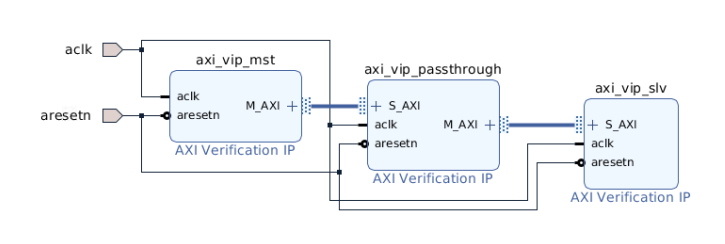
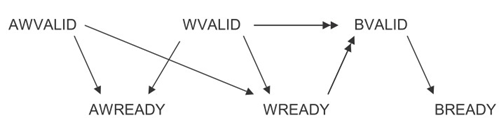
2. 五个通道
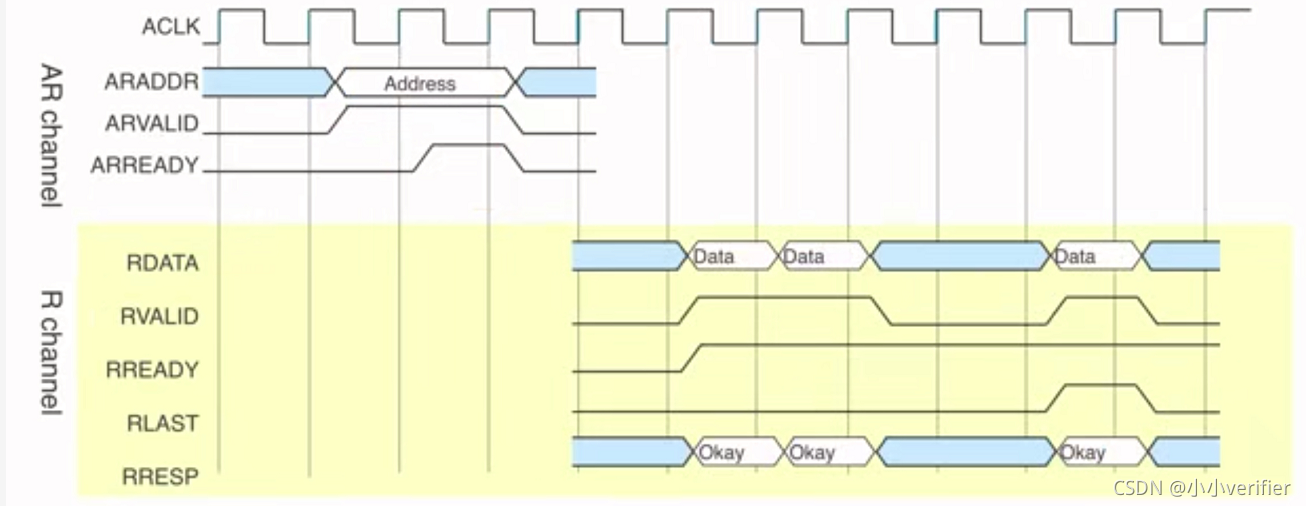
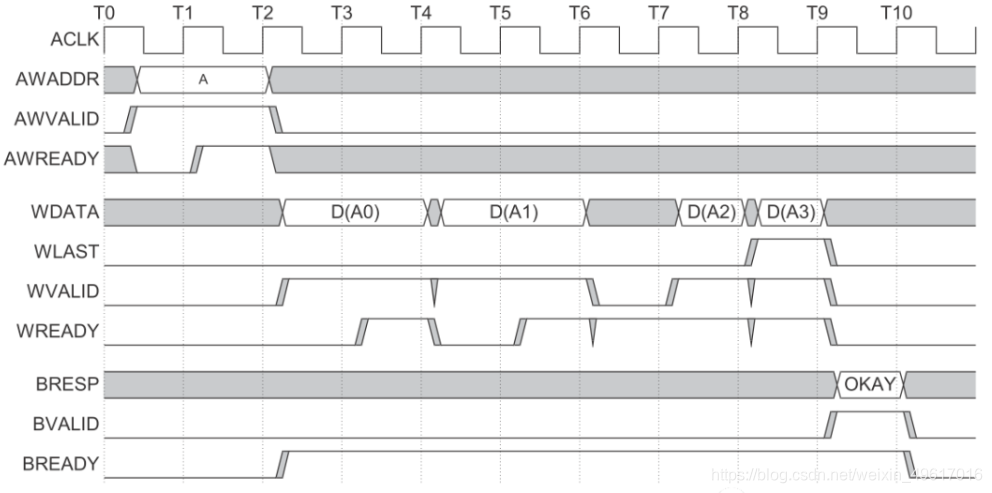
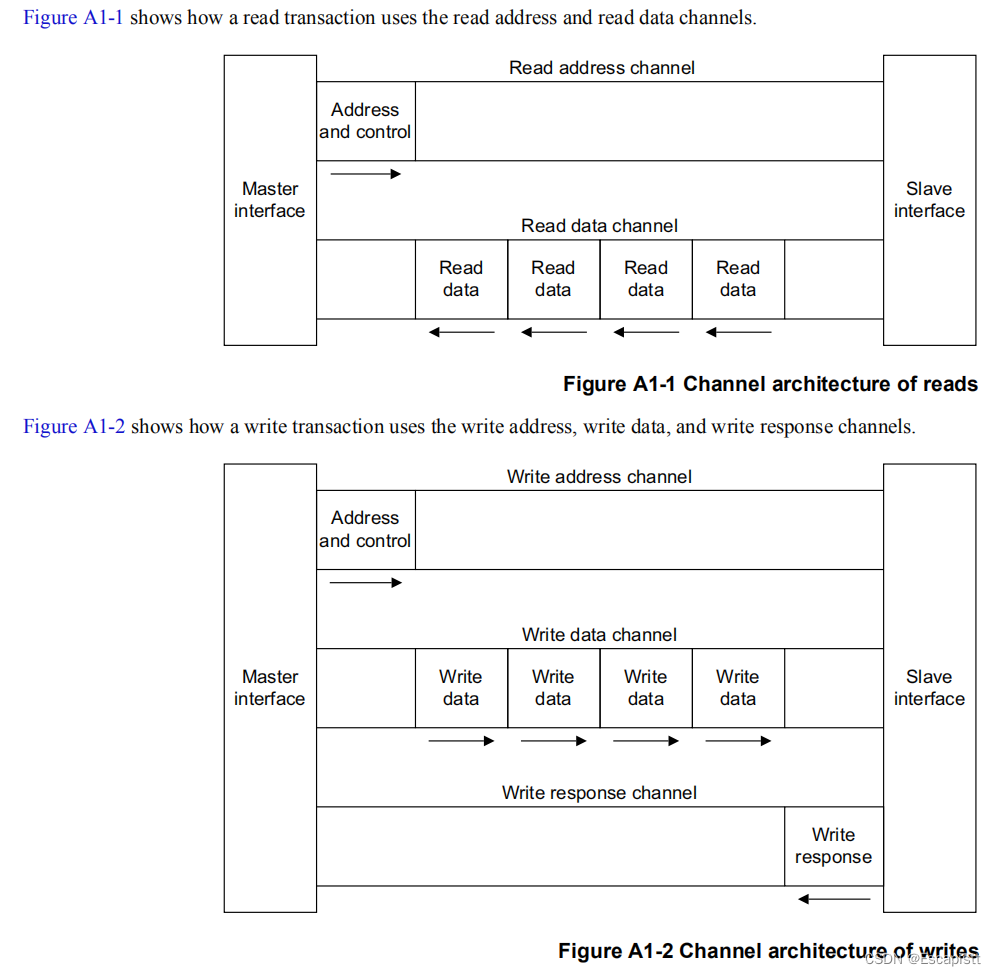
如图所示:
2.1 Write Address Channel
相关信号:
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| AWVALID | master | Write address valid. This signal indicates that the channel is signaling valid write address and control information. |
| AWREADY | slave | Write address valid. This signal indicates that the channel is signaling valid write address and control information. |
| AWADDR | master | Write address. The write address gives the address of the first transfer in a write burst transaction. |
代码:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_awvalid <= 1'b0; end // If previously not valid , start next transaction else if (~axi_awvalid && start_single_burst_write) begin axi_awvalid <= 1'b1; end /* Once asserted, VALIDs cannot be deasserted, so axi_awvalid must wait until transaction is accepted */ else if (M_AXI_AWREADY && axi_awvalid) begin axi_awvalid <= 1'b0; end else axi_awvalid <= axi_awvalid; end
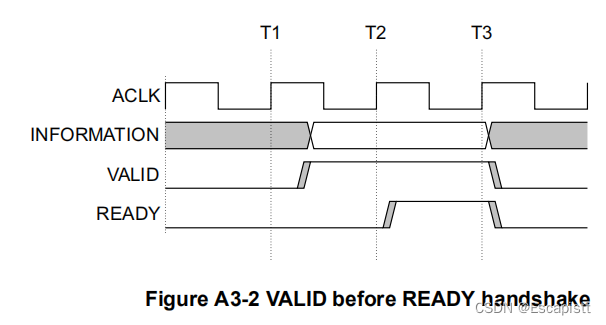
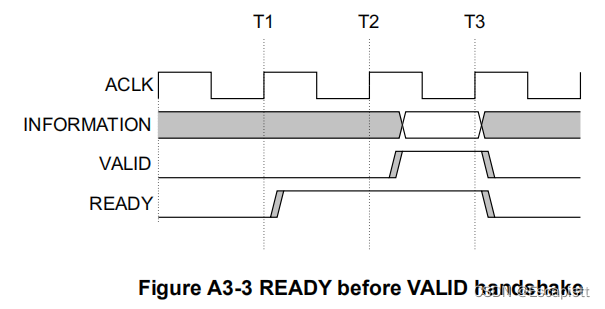
这一段代码即为握手过程:
Once VALID is asserted it must remain asserted until the handshake occurs, at a rising clock edge at which VALID and READY are both asserted.
代码:
// Next address after AWREADY indicates previous address acceptance always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1) begin axi_awaddr <= 'b0; end else if (M_AXI_AWREADY && axi_awvalid) begin axi_awaddr <= axi_awaddr + burst_size_bytes; end else axi_awaddr <= axi_awaddr; end
这里init_txn_pulse是初始标志,将axi_awvalid清零和axi_awaddr地址归到起始。
如前面所说,AWADDR是每次burst传输的首地址,因此每次加一个burst_size_bytes。
burst_size_bytes定义为:
assign burst_size_bytes = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN * C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8;
即长度×宽度/8(字节),这里涉及到突发传输的长度宽度,可以看3.1。
2.2 Write Data Channel
相关信号:
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| WVALID | master | Write valid. This signal indicates that valid write data and strobes are available. |
| WREADY | slave | Write ready. This signal indicates that the slave can accept the write data. |
| WLAST | master | Write last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a write burst. |
| WDATA | master | Write data. |
代码:
// WVALID logic, similar to the axi_awvalid always block above always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_wvalid <= 1'b0; end // If previously not valid, start next transaction else if (~axi_wvalid && start_single_burst_write) begin axi_wvalid <= 1'b1; end /* If WREADY and too many writes, throttle WVALID Once asserted, VALIDs cannot be deasserted, so WVALID must wait until burst is complete with WLAST */ else if (M_AXI_WREADY & axi_wvalid&& axi_wlast) axi_wvalid <= 1'b0; else axi_wvalid <= axi_wvalid; end
这一段和上面的握手过程类似,不同的是WVALID需要在axi_wlast为1时清零。
代码:
//WLAST generation on the MSB of a counter underflow // WVALID logic, similar to the axi_awvalid always block above always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_wlast <= 1'b0; end // axi_wlast is asserted when the write index // count reaches the penultimate count to synchronize // with the last write data else if (((write_index == C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-2 && C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN >= 2) && M_AXI_WREADY & axi_wvalid) || (C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN == 1 ))begin axi_wlast <= 1'b1; end // Deassrt axi_wlast when the last write data has been // accepted by the slave with a valid response else if (M_AXI_WREADY & axi_wvalid) axi_wlast <= 1'b0; else if (axi_wlast && C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN == 1) axi_wlast <= 1'b0; else axi_wlast <= axi_wlast; end
C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN为burst的长度,在长度大于等于2时,write_index为C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-2时wlast置1,如果长度为1则直接置1。在最后一个数据被接收后wlast清零。
代码,write_index:
/* Burst length counter. Uses extra counter register bit to indicate terminal count to reduce decode logic */ always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 || start_single_burst_write == 1'b1) begin write_index <= 0; end else if (wnext && (write_index != C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-1)) begin write_index <= write_index + 1; end else write_index <= write_index; end
代码,write data,这里给出的是简单的每次增加1的data
/* Write Data Generator Data pattern is only a simple incrementing count from 0 for each burst */ always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1) axi_wdata <= 'b1; //else if (wnext && axi_wlast) // axi_wdata <= 'b0; else if (wnext) axi_wdata <= axi_wdata + 1; else axi_wdata <= axi_wdata; end
2.3 Write Response (B) Channel
相关信号:
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| BVALID | slave | Write response valid. This signal indicates that the channel is signaling a valid write response. |
| BREADY | master | Response ready. This signal indicates that the master can accept a write response. |
代码:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_bready <= 1'b0; end // accept/acknowledge bresp with axi_bready by the master // when M_AXI_BVALID is asserted by slave else if (M_AXI_BVALID && ~axi_bready) begin axi_bready <= 1'b1; end // deassert after one clock cycle else if (axi_bready) begin axi_bready <= 1'b0; end // retain the previous value else axi_bready <= axi_bready; end
这是握手过程,是上面两段握手的反过程,valid由slave发送,ready由master发送。ready仅发送一个时钟。
2.4 Read Address Channel
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| ARVALID | master | Read address valid. This signal indicates that the channel is signaling valid read address and control information. |
| ARREADY | salve | Read address ready. This signal indicates that the slave is ready to accept an address and associated control signals. |
| ARADDR | master | Read address. The read address gives the address of the first transfer in a read burst transaction. |
握手机制代码:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_arvalid <= 1'b0; end // If previously not valid , start next transaction else if (~axi_arvalid && start_single_burst_read) begin axi_arvalid <= 1'b1; end else if (M_AXI_ARREADY && axi_arvalid) begin axi_arvalid <= 1'b0; end else axi_arvalid <= axi_arvalid; end
地址增加代码,这里和写地址十分类似:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1) begin axi_araddr <= 'b0; end else if (M_AXI_ARREADY && axi_arvalid) begin axi_araddr <= axi_araddr + burst_size_bytes; end else axi_araddr <= axi_araddr; end
2.5 Read Data (and Response) Channel
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| RLAST | slave | Read last. This signal indicates the last transfer in a read burst. |
| RVALID | salve | Read valid. This signal indicates that the channel is signaling the required read data. |
| RREADY | master | Read ready. This signal indicates that the master can accept the read data and response information. |
握手机制代码:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 ) begin axi_rready <= 1'b0; end // accept/acknowledge rdata/rresp with axi_rready by the master // when M_AXI_RVALID is asserted by slave else if (M_AXI_RVALID) begin if (M_AXI_RLAST && axi_rready) begin axi_rready <= 1'b0; end else begin axi_rready <= 1'b1; end end // retain the previous value end
3 突发传输机制
3.1 突发传输长度和宽度
相关信号:
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| AWLEN | master | Burst length. The burst length gives the exact number of transfers in a burst. This information determines the number of data transfers associated with the address. |
| AWSIZE | master | Burst size. This signal indicates the size of each transfer in the burst. |
| ARLEN | master | 同AWLEN |
| ARSIZE | master | 同ARSIZE |
引脚定义(master):
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_AWLEN,
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_AWSIZE,
output wire [7 : 0] M_AXI_ARLEN,
output wire [2 : 0] M_AXI_ARSIZE,
assign M_AXI_ARLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
assign M_AXI_ARSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
assign M_AXI_AWLEN = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN - 1;
assign M_AXI_AWSIZE = clogb2((C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8)-1);
ARLEN/AWLEN:
The burst length for AXI4 is defined as,
Burst_Length = AxLEN[7:0] + 1, to accommodate the extended burst length of the INCR burst type in AXI4.
ARSIZE/AWSIZE如下表所示:
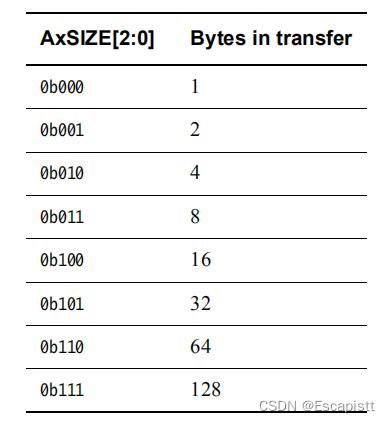
都与代码是一致的。
C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH定义与之前定义的width是一致的:
parameter integer C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH = 32,
一次传输的字节数:
assign burst_size_bytes = C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN * C_M_AXI_DATA_WIDTH/8;
读数据通道的突发传输长度计数:
突发传输方式计数:
always @(posedge M_AXI_ACLK) begin if (M_AXI_ARESETN == 0 || init_txn_pulse == 1'b1 || start_single_burst_read) begin read_index <= 0; end else if (rnext && (read_index != C_M_AXI_BURST_LEN-1)) begin read_index <= read_index + 1; end else read_index <= read_index; end
3.2 突发传输类型
相关信号:
| signal | source | description |
|---|---|---|
| ARBURST | master | Burst type. The burst type and the size information determine how the address for each transfer within the burst is calculated. |
| AWBURST | master | 同ARBURST |
引脚定义(master):
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_AWBURST,
output wire [1 : 0] M_AXI_ARBURST
不同的ARBURST/AWBURST对应的突发传输类型如下表,具体的机制需要分析slave的代码 (slave的代码后续有时间也会整理)。
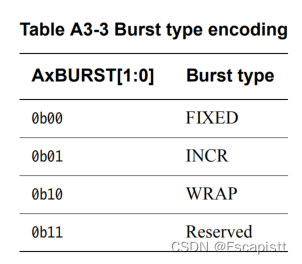
同时突发传输长度也与突发传输类型有关,突发传输长度的规定:
AXI4 extends burst length support for the INCR burst type to 1 to 256 transfers. Support for all other burst types in AXI4 remains at 1 to 16 transfers.