二分图Bipartite graph
有没有可能通过数学过程找到你的灵魂伴侣?大概让我们一起探索吧!
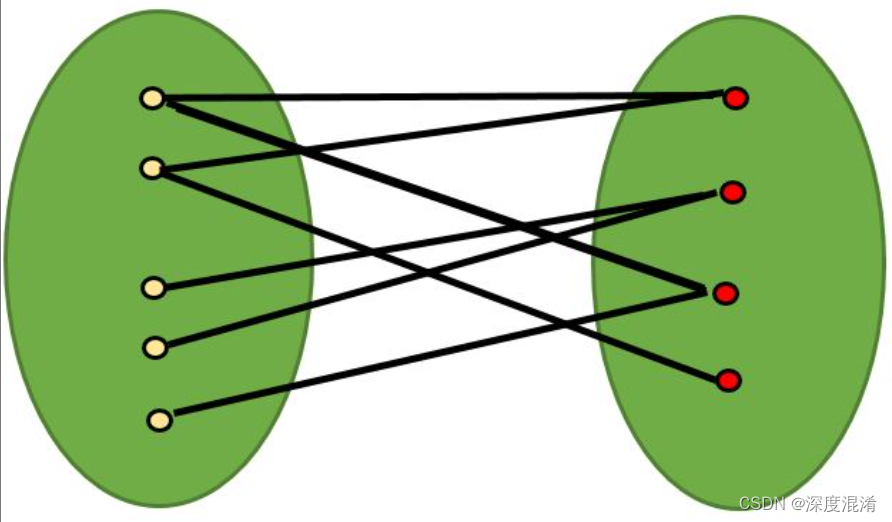
假设有两组人注册了约会服务。在他们注册后,会向他们展示另一组人的图像并给出他们的描述。他们被要求选择他们愿意与之匹配的人。
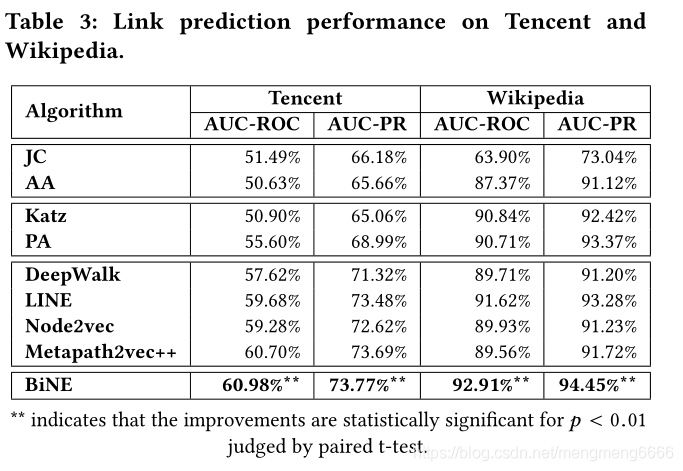
所有信息都被输入计算机,计算机以图形的形式对其进行组织。图中的顶点是人,如果他们都表示愿意与另一个人匹配,那么他们之间就有一条边。
请注意,该图由两组顶点(组1和组2)组成,因此同一组中的顶点之间没有边。在数学上,这被称为二部图,这是一个图,其中顶点可以被分成两个单独的组,这样只有边在这两个组之间,而同一组中的顶点之间没有边。
图论中另一个有趣的概念是图的匹配。这个概念在二部图的各种应用中特别有用。让我们讨论什么是图的匹配,以及我们如何在数学上寻找灵魂伴侣的过程中使用它。
再考虑一下约会者。显然,每个人只能与一个人匹配。根据每组成员的选择,这家约会服务公司想看看他们是否能想出一个方案,让每个人都与他们说他们会满意的人匹配。
就代表成员选择的二部图而言,这意味着我们正在寻找一组边,以便每个顶点只有一条边。从数学上讲,这称为匹配。图的匹配是图中没有两条边共享一个顶点的一组边。也就是说,在匹配中,每个顶点只有一条连接到它的边。
此外,当一个匹配是这样的,如果我们试图向它添加一条边,那么它将不再是一个匹配,那么我们称之为最大匹配。最大匹配是包含最大数量边的匹配。需要注意的是,一个图可以有多个最大匹配。因此,我们在我们的二部图中寻找一个最大匹配,以便以这样一种方式匹配每个人,使他们最终都与他们说他们会满意的人匹配。嗯……让我们试着弄清楚。
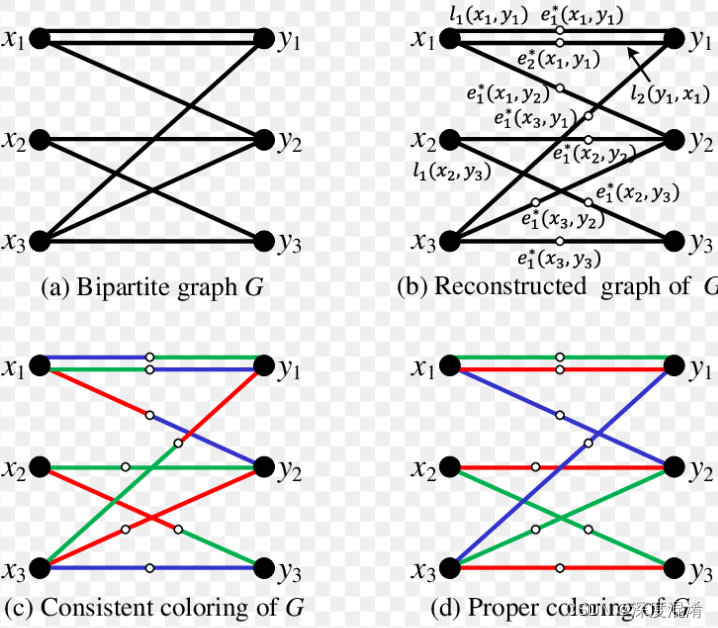
A bipartite graph, also called a bigraph, is a set of graph vertices decomposed into two disjoint sets such that no two graph vertices within the same set are adjacent. A bipartite graph is a special case of a k-partite graph with k=2. The illustration above shows some bipartite graphs, with vertices in each graph colored based on to which of the two disjoint sets they belong.
Bipartite graphs are equivalent to two-colorable graphs. All acyclic graphs are bipartite. A cyclic graph is bipartite iff all its cycles are of even length (Skiena 1990, p. 213)
----
Bipartite Graph - If the vertex-set of a graph G can be split into two disjoint sets, V1 and V2 , in such a way that each edge in the graph joins a vertex in V1 to a vertex in V2 , and there are no edges in G that connect two vertices in V1 or two vertices in V2 , then the graph G is called a bipartite graph.
二部图-如果图G的顶点集可以拆分为两个不相交集V1和V2,使得图中的每条边将V1中的一个顶点连接到V2中的一个顶点,并且G中没有连接V1中的两个顶点或V2中的两个顶点的边,则图G称为二部图。
Complete Bipartite Graph - A complete bipartite graph is a bipartite graph in which each vertex in the first set is joined to every single vertex in the second set. The complete bipartite graph is denoted by Kx,y where the graph G contains x vertices in the first set and y vertices in the second set.
完全二部图-完全二部图是一个二部图,其中第一个集中的每个顶点都连接到第二个集中的每个顶点。完整的二部图用Kx,y表示,其中图G在第一个集中包含x个顶点,在第二个集中包含y个顶点。
Hopcroft-Karp算法
二部图中的匹配是一组边的选择方式,使两条边不共享一个端点。最大匹配是最大大小(最大边数)的匹配。在最大匹配中,如果向其添加任何边,则该边不再是匹配。对于给定的二部图,可以有多个最大匹配。
在前一篇文章中,我们讨论了最大匹配的重要性以及基于Ford-Fulkerson的最大二部匹配方法。基于Ford-Fulkerson算法的时间复杂度为O(V×E)。
Hopcroft-Karp算法是在O(√V x E)时间。在讨论算法之前,让我们先定义几个术语
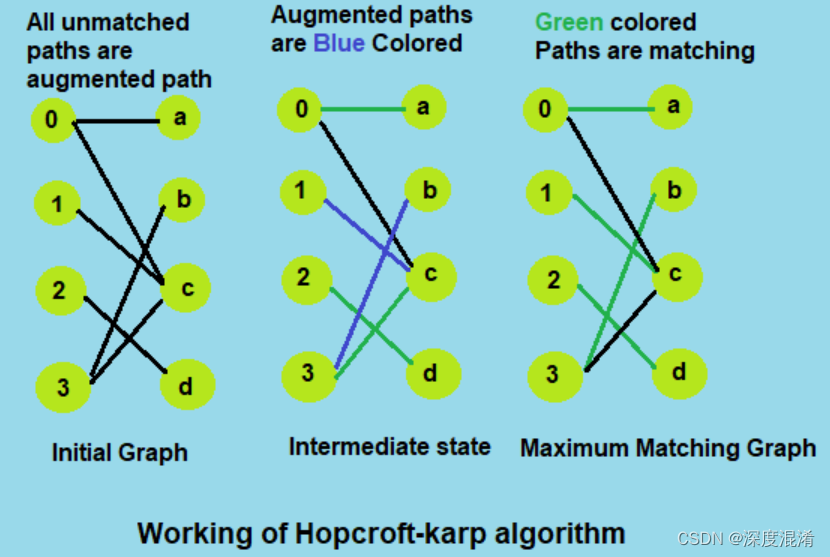
自由节点或顶点:给定匹配的M,不属于匹配的节点称为自由节点。最初,所有顶点都是自由的(请参见下图的第一个图形)。在第二个图中,u2和v2是自由的。在第三个图中,没有顶点是自由的。
匹配和不匹配边:给定匹配M,属于匹配的边称为匹配边,不属于M(或连接自由节点)的边称为不匹配边。在第一个图中,所有边都是不匹配的。在第二个图中,(u0,v1),(u1,v0)和(u3,v3)是匹配的,其他的不匹配。
交替路径:给定一个匹配的M,交替路径是一条边交替属于匹配和不匹配的路径。所有单条边路径都是交替路径。中间图中交替路径的示例有u0-v1-u2和u2-v1-u0-v2。
扩充路径:给定一个匹配的M,扩充路径是一个从自由顶点开始到自由顶点结束的交替路径。所有以自由顶点开始和结束的单边路径都是扩充路径。在下图中,增强路径以蓝色突出显示。请注意,扩充路径始终有一条额外的匹配边。
Hopcroft-Karp算法基于以下概念。
如果存在扩充路径,则匹配的M不是最大值。另一方面也是如此,即如果不存在增广路径,则匹配是最大的
因此,我们的想法是一个接一个地寻找扩充路径。并将找到的路径添加到当前匹配。
Hopcroft-Karp算法
1) 将最大匹配M初始化为空。
2) 而存在一条增广路径p
从M中删除p的匹配边,并将p的不匹配边添加到M
(当p以自由顶点开始和结束时,M的大小会增加1)
3) 返回M。
源代码(POWER BY TRUFFER):
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace Legalsoft.Truffer.Algorithm
{public class Bipartite_Graph{private int M { get; set; } = 0;private int N { get; set; } = 0;private List<int>[] adj { get; set; }private int[] pairU { get; set; } = null;private int[] pairV { get; set; } = null;private int[] distance { get; set; } = null;public Bipartite_Graph(int m, int n){this.M = m;this.N = n;adj = new List<int>[M + 1];for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++){adj[i] = new List<int>();}pairU = new int[M + 1];pairV = new int[N + 1];distance = new int[M + 1];for (int i = 0; i < M + 1; i++){pairU[i] = 0;}for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++){pairV[i] = 0;}}public void AddEdge(int u, int v){adj[u].Add(v);}public int Hopcroft_Karp_Algorithm(){int result = 0;while (BFS()){for (int u = 1; u <= M; u++){if (pairU[u] == 0 && DFS(u)){result++;}}}return result;}private bool BFS(){Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();for (int u = 1; u <= M; u++){if (pairU[u] == 0){distance[u] = 0;queue.Enqueue(u);}else{distance[u] = Int32.MaxValue;}}distance[0] = Int32.MaxValue;while (queue.Count != 0){int u = queue.Dequeue();if (distance[u] < distance[0]){foreach (int i in adj[u]){int v = i;if (distance[pairV[v]] == Int32.MaxValue){distance[pairV[v]] = distance[u] + 1;queue.Enqueue(pairV[v]);}}}}return (distance[0] != Int32.MaxValue);}private bool DFS(int u){if (u != 0){foreach (int i in adj[u]){int v = i;if (distance[pairV[v]] == distance[u] + 1){if (DFS(pairV[v]) == true){pairV[v] = u;pairU[u] = v;return true;}}}distance[u] = Int32.MaxValue;return false;}return true;}}public static partial class GraphDrives{public static string Hopcroft_Karp(){Bipartite_Graph g = new Bipartite_Graph(4, 4);g.AddEdge(1, 2);g.AddEdge(1, 3);g.AddEdge(2, 1);g.AddEdge(3, 2);g.AddEdge(4, 2);g.AddEdge(4, 4);return ("Size of maximum matching is " + g.Hopcroft_Karp_Algorithm());}}
}![[VLDB 2022]Butterfly Counting on Uncertain Bipartite Graphs](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/1b73ccd0e116142bc0cca4fe865cd11b.png)
![二分匹配大总结——Bipartite Graph Matchings[LnJJF]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f12f5708538c44c08101ac60cf3d8342.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZHJvaWRzYW5zZmFsbGJhY2s,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBATG5KSkY=,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)