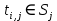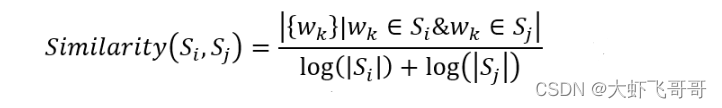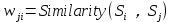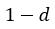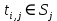利用TextRank提取关键词
TextRank 是一种基于 PageRank 的算法,常用于关键词提取和文本摘要。在本文中,我将通过一个关键字提取示例帮助您了解 TextRank 如何工作,并展示 Python 的实现。

1.PageRank简介
关于 PageRank 的文章有很多,我只简单介绍一下 PageRank。这将有助于我们稍后理解 TextRank,因为它是基于 PageRank 的。
PageRank (PR) 是一种用于计算网页权重的算法。我们可以把所有的网页看成一个大的有向图。在此图中,节点是网页。如果网页 A 有指向网页 B 的链接,则它可以表示为从 A 到 B 的有向边。
构建完整个图后,我们可以通过以下公式为网页分配权重。


这是一个示例,可以更好地理解上面的符号。我们有一个图表来表示网页如何相互链接。每个节点代表一个网页,箭头代表边。我们想得到网页 e 的权重。
我们可以将上述函数中的求和部分重写为更简单的版本。

我们可以通过下面的函数得到网页 e 的权重。

我们可以看到网页 e 的权重取决于其入站页面的权重。我们需要多次运行此迭代才能获得最终权重。初始化时,每个网页的重要性为 1。
2.PageRank实现

我们可以用一个矩阵来表示图中 a、b、e、f 之间的入站和出站链接。

一行中的每个节点表示来自其他节点的入站链接。例如,对于 e 行,节点 a 和 b 具有指向节点 e 的出站链接。本演示文稿将简化更新权重的计算。
根据 1 ∣ O u t ( V i ) ∣ \frac{1}{|Out(Vi)|} ∣Out(Vi)∣1,从函数中,我们应该规范化每一列。

我们使用这个矩阵乘以所有节点的权重。

这只是一次没有阻尼系数 d 的迭代。

我们可以使用 Python 进行多次迭代。
import numpy as np
g = [[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[1, 0.5, 0, 0],[0, 0.5, 0, 0]]g = np.array(g)
pr = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1]) # initialization for a, b, e, f is 1
d = 0.85for iter in range(10):pr = 0.15 + 0.85 * np.dot(g, pr)print(iter)print(pr)
0
[0.15 0.15 1.425 0.575]
1
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
2
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
3
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
4
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
5
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
6
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
7
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
8
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
9
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
10
[0.15 0.15 0.34125 0.21375]
所以 e 的权重(PageRank值)为 0.34125。
如果我们把有向边变成无向边,我们就可以相应地改变矩阵。

规范化。

我们应该相应地更改代码。
import numpy as np
g = [[0, 0, 0.5, 0],[0, 0, 0.5, 1],[1, 0.5, 0, 0],[0, 0.5, 0, 0]]g = np.array(g)
pr = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1]) # initialization for a, b, e, f is 1
d = 0.85for iter in range(10):pr = 0.15 + 0.85 * np.dot(g, pr)print(iter)print(pr)
0
[0.575 1.425 1.425 0.575]
1
[0.755625 1.244375 1.244375 0.755625]
2
[0.67885937 1.32114062 1.32114062 0.67885937]
3
[0.71148477 1.28851523 1.28851523 0.71148477]
4
[0.69761897 1.30238103 1.30238103 0.69761897]
5
[0.70351194 1.29648806 1.29648806 0.70351194]
6
[0.70100743 1.29899257 1.29899257 0.70100743]
7
[0.70207184 1.29792816 1.29792816 0.70207184]
8
[0.70161947 1.29838053 1.29838053 0.70161947]
9
[0.70181173 1.29818827 1.29818827 0.70181173]
所以 e 的权重(PageRank值)为 1.29818827。
3.TextRank原理
TextRank 和 PageTank 有什么区别呢?
简而言之 PageRank 用于网页排名,TextRank 用于文本排名。 PageRank 中的网页就是 TextRank 中的文本,所以基本思路是一样的。
我们将一个文档分成几个句子,我们只存储那些带有特定 POS 标签的词。我们使用 spaCy 进行词性标注。
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')content = '''
The Wandering Earth, described as China’s first big-budget science fiction thriller, quietly made it onto screens at AMC theaters in North America this weekend, and it shows a new side of Chinese filmmaking — one focused toward futuristic spectacles rather than China’s traditionally grand, massive historical epics. At the same time, The Wandering Earth feels like a throwback to a few familiar eras of American filmmaking. While the film’s cast, setting, and tone are all Chinese, longtime science fiction fans are going to see a lot on the screen that reminds them of other movies, for better or worse.
'''doc = nlp(content)
for sents in doc.sents:print(sents.text)
我们将段落分成三个句子。
The Wandering Earth, described as China’s first big-budget science fiction thriller, quietly made it onto screens at AMC theaters in North America this weekend, and it shows a new side of Chinese filmmaking — one focused toward futuristic spectacles rather than China’s traditionally grand, massive historical epics.At the same time, The Wandering Earth feels like a throwback to a few familiar eras of American filmmaking.While the film’s cast, setting, and tone are all Chinese, longtime science fiction fans are going to see a lot on the screen that reminds them of other movies, for better or worse.
因为句子中的大部分词对确定重要性没有用,我们只考虑带有 NOUN、PROPN、VERB POS 标签的词。这是可选的,你也可以使用所有的单词。
candidate_pos = ['NOUN', 'PROPN', 'VERB']
sentences = []
for sent in doc.sents:selected_words = []for token in sent:if token.pos_ in candidate_pos and token.is_stop is False:selected_words.append(token)sentences.append(selected_words)
print(sentences)
[[Wandering, Earth, described, China, budget, science, fiction, thriller, screens, AMC, theaters, North, America, weekend, shows, filmmaking, focused, spectacles, China, epics],
[time, Wandering, Earth, feels, throwback, eras, filmmaking],
[film, cast, setting, tone, science, fiction, fans, going, lot, screen, reminds, movies]]
每个词都是 PageRank 中的一个节点。我们将窗口大小设置为 k。

[ w 1 , w 2 , … , w k ] , [ w 2 , w 3 , … , w k + 1 ] , [ w 3 , w 4 , … , w k + 2 ] [w1, w2, …, w_k], [w2, w3, …, w_{k+1}], [w3, w4, …, w_{k+2}] [w1,w2,…,wk],[w2,w3,…,wk+1],[w3,w4,…,wk+2] 是窗口。窗口中的任何两个词对都被认为具有无向边。
我们以 [time, wandering, earth, feels, throwback, era, filmmaking] 为例,设置窗口大小 k = 4 k=4 k=4,所以得到 4 个窗口,[time, Wandering, Earth, feels],[Wandering, Earth, feels, throwback],[Earth, feels, throwback, eras],[feels, throwback, eras, filmmaking]。
对于窗口 [time, Wandering, Earth, feels],任何两个词对都有一条无向边。所以我们得到 (time, Wandering),(time, Earth),(time, feels),(Wandering, Earth),(Wandering, feels),(Earth, feels)。
基于此图,我们可以计算每个节点(单词)的权重。最重要的词可以用作关键字。
4.TextRank提取关键词
这里我用 Python 实现了一个完整的例子,我们使用 spaCy 来获取词的词性标签。
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
import spacy
from spacy.lang.en.stop_words import STOP_WORDSnlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')class TextRank4Keyword():"""Extract keywords from text"""def __init__(self):self.d = 0.85 # damping coefficient, usually is .85self.min_diff = 1e-5 # convergence thresholdself.steps = 10 # iteration stepsself.node_weight = None # save keywords and its weightdef set_stopwords(self, stopwords): """Set stop words"""for word in STOP_WORDS.union(set(stopwords)):lexeme = nlp.vocab[word]lexeme.is_stop = Truedef sentence_segment(self, doc, candidate_pos, lower):"""Store those words only in cadidate_pos"""sentences = []for sent in doc.sents:selected_words = []for token in sent:# Store words only with cadidate POS tagif token.pos_ in candidate_pos and token.is_stop is False:if lower is True:selected_words.append(token.text.lower())else:selected_words.append(token.text)sentences.append(selected_words)return sentencesdef get_vocab(self, sentences):"""Get all tokens"""vocab = OrderedDict()i = 0for sentence in sentences:for word in sentence:if word not in vocab:vocab[word] = ii += 1return vocabdef get_token_pairs(self, window_size, sentences):"""Build token_pairs from windows in sentences"""token_pairs = list()for sentence in sentences:for i, word in enumerate(sentence):for j in range(i+1, i+window_size):if j >= len(sentence):breakpair = (word, sentence[j])if pair not in token_pairs:token_pairs.append(pair)return token_pairsdef symmetrize(self, a):return a + a.T - np.diag(a.diagonal())def get_matrix(self, vocab, token_pairs):"""Get normalized matrix"""# Build matrixvocab_size = len(vocab)g = np.zeros((vocab_size, vocab_size), dtype='float')for word1, word2 in token_pairs:i, j = vocab[word1], vocab[word2]g[i][j] = 1# Get Symmeric matrixg = self.symmetrize(g)# Normalize matrix by columnnorm = np.sum(g, axis=0)g_norm = np.divide(g, norm, where=norm!=0) # this is ignore the 0 element in normreturn g_normdef get_keywords(self, number=10):"""Print top number keywords"""node_weight = OrderedDict(sorted(self.node_weight.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True))for i, (key, value) in enumerate(node_weight.items()):print(key + ' - ' + str(value))if i > number:breakdef analyze(self, text, candidate_pos=['NOUN', 'PROPN'], window_size=4, lower=False, stopwords=list()):"""Main function to analyze text"""# Set stop wordsself.set_stopwords(stopwords)# Pare text by spaCydoc = nlp(text)# Filter sentencessentences = self.sentence_segment(doc, candidate_pos, lower) # list of list of words# Build vocabularyvocab = self.get_vocab(sentences)# Get token_pairs from windowstoken_pairs = self.get_token_pairs(window_size, sentences)# Get normalized matrixg = self.get_matrix(vocab, token_pairs)# Initionlization for weight(pagerank value)pr = np.array([1] * len(vocab))# Iterationprevious_pr = 0for epoch in range(self.steps):pr = (1-self.d) + self.d * np.dot(g, pr)if abs(previous_pr - sum(pr)) < self.min_diff:breakelse:previous_pr = sum(pr)# Get weight for each nodenode_weight = dict()for word, index in vocab.items():node_weight[word] = pr[index]self.node_weight = node_weight
这个 TextRank4Keyword 实现了前文描述的相关功能。我们可以看到一段的输出。
text = '''
The Wandering Earth, described as China’s first big-budget science fiction thriller, quietly made it onto screens at AMC theaters in North America this weekend, and it shows a new side of Chinese filmmaking — one focused toward futuristic spectacles rather than China’s traditionally grand, massive historical epics. At the same time, The Wandering Earth feels like a throwback to a few familiar eras of American filmmaking. While the film’s cast, setting, and tone are all Chinese, longtime science fiction fans are going to see a lot on the screen that reminds them of other movies, for better or worse.
'''
tr4w = TextRank4Keyword()
tr4w.analyze(text, candidate_pos = ['NOUN', 'PROPN'], window_size=4, lower=False)
tr4w.get_keywords(10)
science - 1.717603106506989
fiction - 1.6952610926181002
filmmaking - 1.4388798751402918
China - 1.4259793786986021
Earth - 1.3088154732297723
tone - 1.1145002295684114
Chinese - 1.0996896235078055
Wandering - 1.0071059904601571
weekend - 1.002449354657688
America - 0.9976329264870932
budget - 0.9857269586649321
North - 0.9711240881032547