ResNet介绍
1 简要概括
ResNet(Residual Neural Network)由微软研究院的Kaiming He等四名华人提出,通过使用ResNet Unit成功训练出了152层的神经网络,并在ILSVRC2015比赛中取得冠军,在top5上的错误率为3.57%,同时参数量比VGGNet低,效果非常突出。ResNet的结构可以极快的加速神经网络的训练,模型的准确率也有比较大的提升。同时ResNet的推广性非常好,甚至可以直接用到InceptionNet网络中。
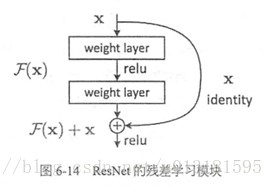
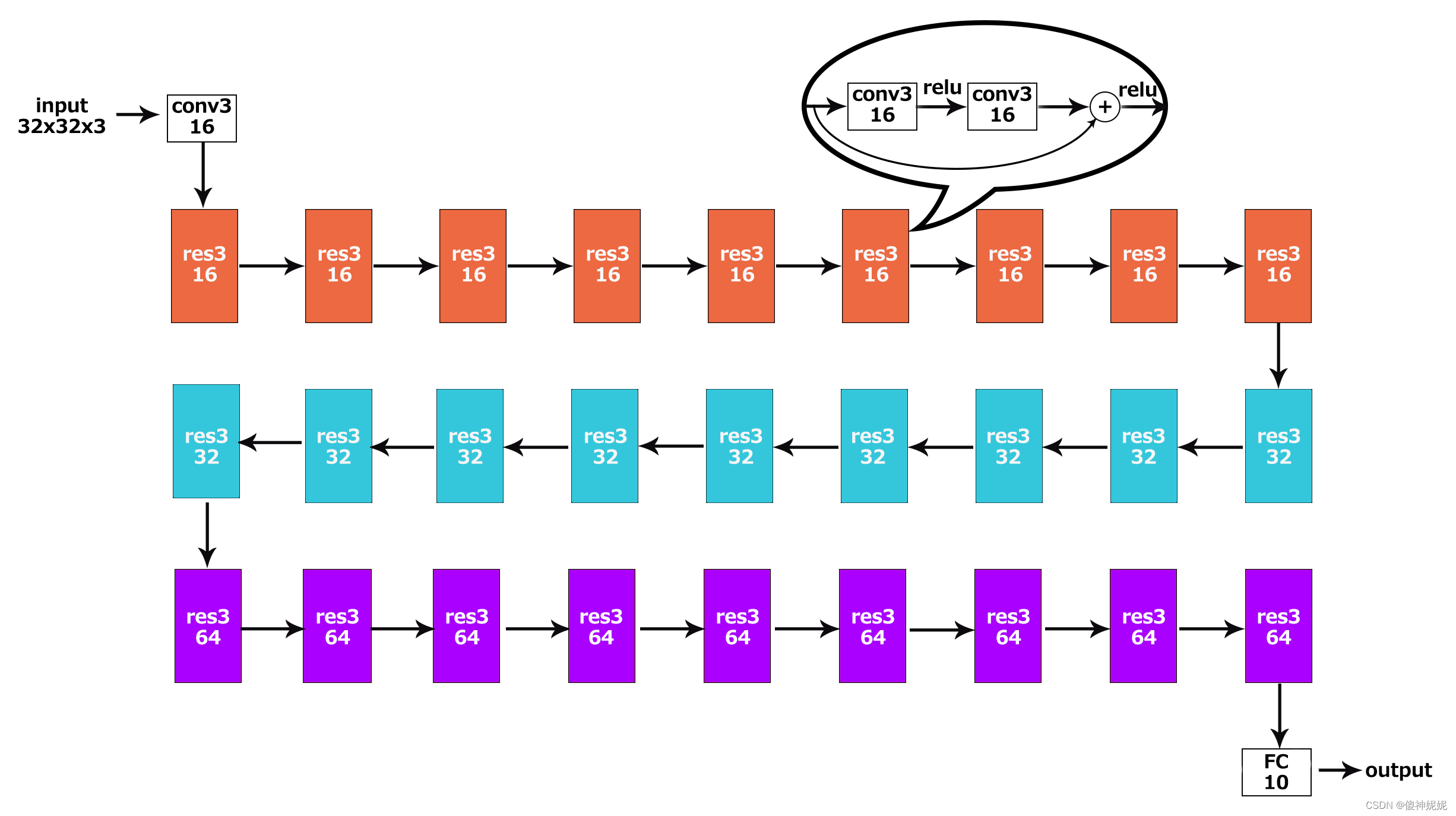
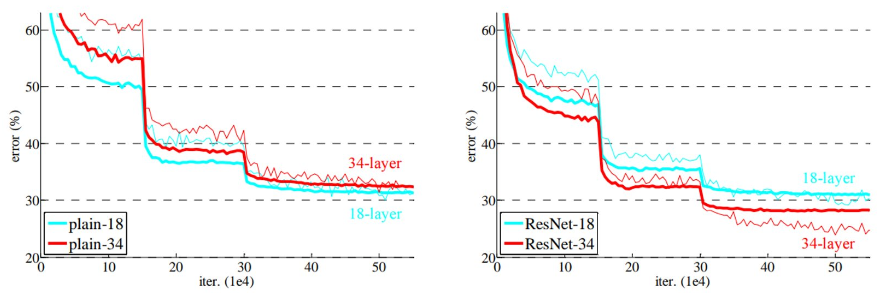
ResNet的主要思想是在网络中增加了直连通道,即Highway Network的思想。此前的网络结构是性能输入做一个非线性变换,而Highway Network则允许保留之前网络层的一定比例的输出。ResNet的思想和Highway Network的思想也非常类似,允许原始输入信息直接传到后面的层中,如下图所示。
这样的话这一层的神经网络可以不用学习整个的输出,而是学习上一个网络输出的残差,因此ResNet又叫做残差网络。
2 创新点
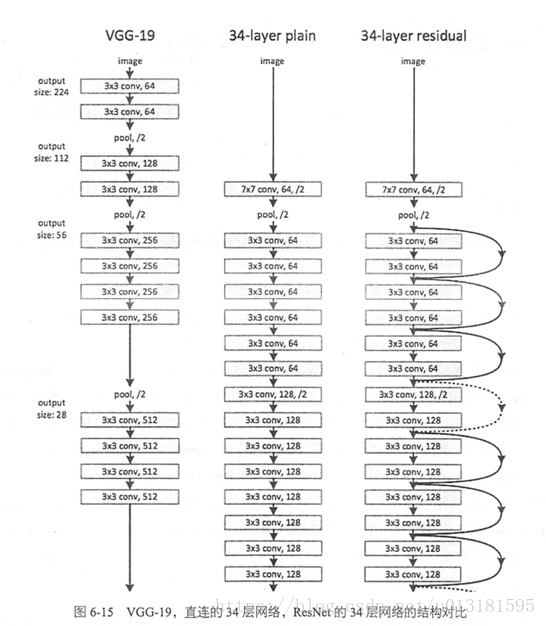
提出残差学习的思想。传统的卷积网络或者全连接网络在信息传递的时候或多或少会存在信息丢失,损耗等问题,同时还有导致梯度消失或者梯度爆炸,导致很深的网络无法训练。ResNet在一定程度上解决了这个问题,通过直接将输入信息绕道传到输出,保护信息的完整性,整个网络只需要学习输入、输出差别的那一部分,简化学习目标和难度。VGGNet和ResNet的对比如下图所示。ResNet最大的区别在于有很多的旁路将输入直接连接到后面的层,这种结构也被称为shortcut或者skip connections。
3 网络结构
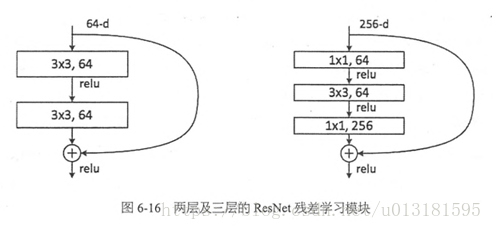
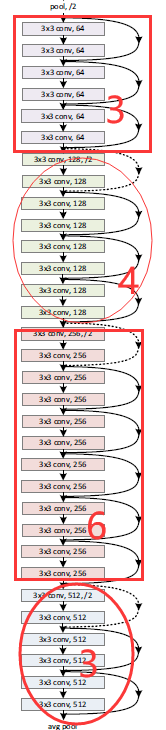
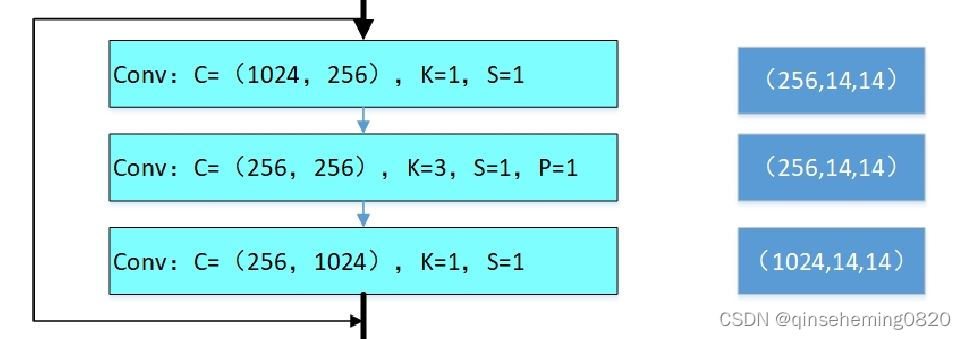
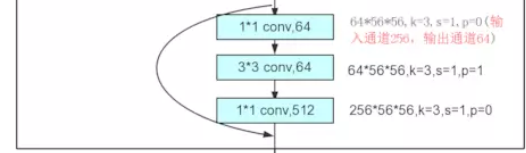
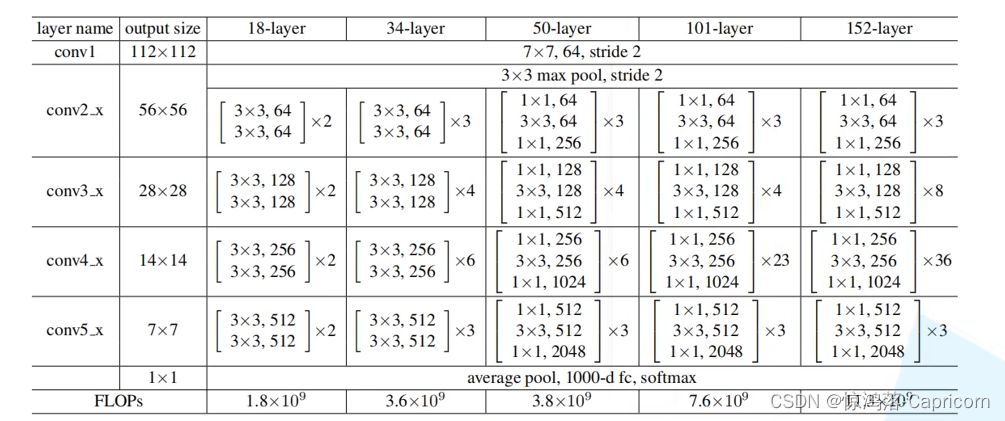
在ResNet网络结构中会用到两种残差模块,一种是以两个3*3的卷积网络串接在一起作为一个残差模块,另外一种是1*1、3*3、1*1的3个卷积网络串接在一起作为一个残差模块。他们如下图所示。
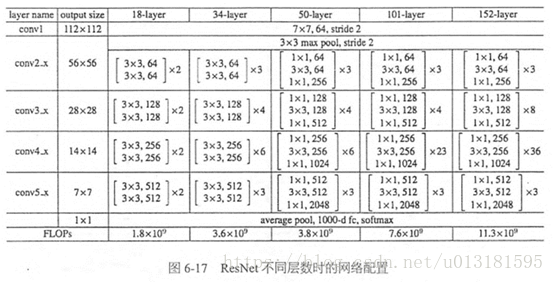
ResNet有不同的网络层数,比较常用的是50-layer,101-layer,152-layer。他们都是由上述的残差模块堆叠在一起实现的。
4 代码实现
#%%
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Typical use:from tensorflow.contrib.slim.nets import resnet_v2ResNet-101 for image classification into 1000 classes:# inputs has shape [batch, 224, 224, 3]with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(is_training)):net, end_points = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_101(inputs, 1000)ResNet-101 for semantic segmentation into 21 classes:# inputs has shape [batch, 513, 513, 3]with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v2.resnet_arg_scope(is_training)):net, end_points = resnet_v2.resnet_v2_101(inputs,21,global_pool=False,output_stride=16)
"""
import collections
import tensorflow as tf
slim = tf.contrib.slim#namedtuple是一个函数,它用来创建一个自定义的tuple对象,并且规定了tuple元素的个数,
#并可以用属性而不是索引来引用tuple的某个元素
#相当于创建了一个Block类,有scope,unit_fn,args属性
class Block(collections.namedtuple('Block', ['scope', 'unit_fn', 'args'])):"""A named tuple describing a ResNet block.Its parts are:scope: The scope of the `Block`.unit_fn: The ResNet unit function which takes as input a `Tensor` andreturns another `Tensor` with the output of the ResNet unit.args: A list of length equal to the number of units in the `Block`. The listcontains one (depth, depth_bottleneck, stride) tuple for each unit in theblock to serve as argument to unit_fn."""def subsample(inputs, factor, scope=None):"""Subsamples the input along the spatial dimensions.Args:inputs: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].factor: The subsampling factor.scope: Optional variable_scope.Returns:output: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels] with theinput, either intact (if factor == 1) or subsampled (if factor > 1)."""if factor == 1:return inputselse:return slim.max_pool2d(inputs, [1, 1], stride=factor, scope=scope)def conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride, scope=None):"""Strided 2-D convolution with 'SAME' padding.When stride > 1, then we do explicit zero-padding, followed by conv2d with'VALID' padding.Note thatnet = conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=stride)is equivalent tonet = slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=1, padding='SAME')net = subsample(net, factor=stride)whereasnet = slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=stride, padding='SAME')is different when the input's height or width is even, which is why we add thecurrent function. For more details, see ResnetUtilsTest.testConv2DSameEven().Args:inputs: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].num_outputs: An integer, the number of output filters.kernel_size: An int with the kernel_size of the filters.stride: An integer, the output stride.rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution.scope: Scope.Returns:output: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels] withthe convolution output."""#conv2d_same是一个卷积后输入和输出图片大小相同的函数#步长为1可以直接卷积,不为1,需要计算在图片周围padding的大小再卷积if stride == 1:return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=1,padding='SAME', scope=scope)else:#kernel_size_effective = kernel_size + (kernel_size - 1) * (rate - 1)pad_total = kernel_size - 1pad_beg = pad_total // 2pad_end = pad_total - pad_beginputs = tf.pad(inputs,[[0, 0], [pad_beg, pad_end], [pad_beg, pad_end], [0, 0]])return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=stride,padding='VALID', scope=scope)@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks,outputs_collections=None):"""Stacks ResNet `Blocks` and controls output feature density.First, this function creates scopes for the ResNet in the form of'block_name/unit_1', 'block_name/unit_2', etc.Args:net: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height, width, channels].blocks: A list of length equal to the number of ResNet `Blocks`. Eachelement is a ResNet `Block` object describing the units in the `Block`.outputs_collections: Collection to add the ResNet block outputs.Returns:net: Output tensor """#生成残差网络所有的堆叠,并存放在net中for block in blocks:with tf.variable_scope(block.scope, 'block', [net]) as sc:for i, unit in enumerate(block.args):with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i + 1), values=[net]):unit_depth, unit_depth_bottleneck, unit_stride = unitnet = block.unit_fn(net,depth=unit_depth,depth_bottleneck=unit_depth_bottleneck,stride=unit_stride)net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, net)return netdef resnet_arg_scope(is_training=True,weight_decay=0.0001,batch_norm_decay=0.997,batch_norm_epsilon=1e-5,batch_norm_scale=True):"""Defines the default ResNet arg scope.TODO(gpapan): The batch-normalization related default values above areappropriate for use in conjunction with the reference ResNet modelsreleased at https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networks. Whentraining ResNets from scratch, they might need to be tuned.Args:is_training: Whether or not we are training the parameters in the batchnormalization layers of the model.weight_decay: The weight decay to use for regularizing the model.batch_norm_decay: The moving average decay when estimating layer activationstatistics in batch normalization.batch_norm_epsilon: Small constant to prevent division by zero whennormalizing activations by their variance in batch normalization.batch_norm_scale: If True, uses an explicit `gamma` multiplier to scale theactivations in the batch normalization layer.Returns:An `arg_scope` to use for the resnet models."""batch_norm_params = {'is_training': is_training,'decay': batch_norm_decay,'epsilon': batch_norm_epsilon,'scale': batch_norm_scale,'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,}with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d],weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm,normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], **batch_norm_params):# The following implies padding='SAME' for pool1, which makes feature# alignment easier for dense prediction tasks. This is also used in# https://github.com/facebook/fb.resnet.torch. However the accompanying# code of 'Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition' uses# padding='VALID' for pool1. You can switch to that choice by setting# slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='VALID').with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='SAME') as arg_sc:return arg_sc@slim.add_arg_scope
def bottleneck(inputs, depth, depth_bottleneck, stride,outputs_collections=None, scope=None):"""Bottleneck residual unit variant with BN before convolutions.This is the full preactivation residual unit variant proposed in [2]. SeeFig. 1(b) of [2] for its definition. Note that we use here the bottleneckvariant which has an extra bottleneck layer.When putting together two consecutive ResNet blocks that use this unit, oneshould use stride = 2 in the last unit of the first block.Args:inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height, width, channels].depth: The depth of the ResNet unit output.depth_bottleneck: The depth of the bottleneck layers.stride: The ResNet unit's stride. Determines the amount of downsampling ofthe units output compared to its input.rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution.outputs_collections: Collection to add the ResNet unit output.scope: Optional variable_scope.Returns:The ResNet unit's output."""with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'bottleneck_v2', [inputs]) as sc:depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(), min_rank=4)preact = slim.batch_norm(inputs, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='preact')if depth == depth_in:shortcut = subsample(inputs, stride, 'shortcut')else:shortcut = slim.conv2d(preact, depth, [1, 1], stride=stride,normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None,scope='shortcut')residual = slim.conv2d(preact, depth_bottleneck, [1, 1], stride=1,scope='conv1')residual = conv2d_same(residual, depth_bottleneck, 3, stride,scope='conv2')residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth, [1, 1], stride=1,normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None,scope='conv3')output = shortcut + residualreturn slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,sc.name,output)def resnet_v2(inputs,blocks,num_classes=None,global_pool=True,include_root_block=True,reuse=None,scope=None):"""Generator for v2 (preactivation) ResNet models.This function generates a family of ResNet v2 models. See the resnet_v2_*()methods for specific model instantiations, obtained by selecting differentblock instantiations that produce ResNets of various depths.Args:inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].blocks: A list of length equal to the number of ResNet blocks. Each elementis a resnet_utils.Block object describing the units in the block.num_classes: Number of predicted classes for classification tasks. If Nonewe return the features before the logit layer.include_root_block: If True, include the initial convolution followed bymax-pooling, if False excludes it. If excluded, `inputs` should be theresults of an activation-less convolution.reuse: whether or not the network and its variables should be reused. To beable to reuse 'scope' must be given.scope: Optional variable_scope.Returns:net: A rank-4 tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels_out].If global_pool is False, then height_out and width_out are reduced by afactor of output_stride compared to the respective height_in and width_in,else both height_out and width_out equal one. If num_classes is None, thennet is the output of the last ResNet block, potentially after globalaverage pooling. If num_classes is not None, net contains the pre-softmaxactivations.end_points: A dictionary from components of the network to the correspondingactivation.Raises:ValueError: If the target output_stride is not valid."""with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'resnet_v2', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, bottleneck,stack_blocks_dense],outputs_collections=end_points_collection):net = inputsif include_root_block:# We do not include batch normalization or activation functions in conv1# because the first ResNet unit will perform these. Cf. Appendix of [2].with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d],activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None):net = conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1')net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool1')net = stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks)# This is needed because the pre-activation variant does not have batch# normalization or activation functions in the residual unit output. See# Appendix of [2].net = slim.batch_norm(net, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='postnorm')if global_pool:# Global average pooling.net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name='pool5', keep_dims=True)if num_classes is not None:net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None,normalizer_fn=None, scope='logits')# Convert end_points_collection into a dictionary of end_points.end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection)if num_classes is not None:end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope='predictions')return net, end_pointsdef resnet_v2_50(inputs,num_classes=None,global_pool=True,reuse=None,scope='resnet_v2_50'):"""ResNet-50 model of [1]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""blocks = [Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 5 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)def resnet_v2_101(inputs,num_classes=None,global_pool=True,reuse=None,scope='resnet_v2_101'):"""ResNet-101 model of [1]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""blocks = [Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 3 + [(512, 128, 2)]),Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 22 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)def resnet_v2_152(inputs,num_classes=None,global_pool=True,reuse=None,scope='resnet_v2_152'):"""ResNet-152 model of [1]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""blocks = [Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 7 + [(512, 128, 2)]),Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)def resnet_v2_200(inputs,num_classes=None,global_pool=True,reuse=None,scope='resnet_v2_200'):"""ResNet-200 model of [2]. See resnet_v2() for arg and return description."""blocks = [Block('block1', bottleneck, [(256, 64, 1)] * 2 + [(256, 64, 2)]),Block('block2', bottleneck, [(512, 128, 1)] * 23 + [(512, 128, 2)]),Block('block3', bottleneck, [(1024, 256, 1)] * 35 + [(1024, 256, 2)]),Block('block4', bottleneck, [(2048, 512, 1)] * 3)]return resnet_v2(inputs, blocks, num_classes, global_pool,include_root_block=True, reuse=reuse, scope=scope)from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):num_steps_burn_in = 10total_duration = 0.0total_duration_squared = 0.0for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):start_time = time.time()_ = session.run(target)duration = time.time() - start_timeif i >= num_steps_burn_in:if not i % 10:print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))total_duration += durationtotal_duration_squared += duration * durationmn = total_duration / num_batchesvr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mnsd = math.sqrt(vr)print ('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))batch_size = 32
height, width = 224, 224
inputs = tf.random_uniform((batch_size, height, width, 3))
with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=False)):net, end_points = resnet_v2_152(inputs, 1000)init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
num_batches=100
time_tensorflow_run(sess, net, "Forward")
5 参考文献
[1]黄文坚,唐源.TensorFlow实战[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2017.
[2]https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
[3]https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/resnet_v2.py
插播:
阿里云-城市大脑团体需要NLP算法工程师,校招/社招/实习均可,可私信或联系wuwen.lw@alibaba-inc.com