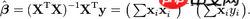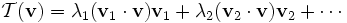One-dimensional linear regression
给定数据集(点集),我们希望优化出一个好的函数f(x),使得f(xi)= wxi+b。有均方差损失函数可得E(w,b)。如下图:
为什么要求出outputs(即f(xi))?因为梯度下降需要用到梯度,求梯度要求偏导(详见最优化之梯度下降法 计算公式及举例),求偏导必然要求函数值E(w,b),故必须求得f(xi)。
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython import display# Hyper-parameters 超参数是在开始学习过程之前设置值的参数,而不是通过训练得到的参数数据
input_size = 1 #输入维度
output_size = 1 #输出维度
num_epochs = 100 #迭代次数
learning_rate = 0.01 #学习率 : 决定了参数移动到最优值的速度快慢。#如果学习率过大,很可能会越过最优值;反而如果学习率过小,优化的效率可能过低,长时间算法无法收敛。#所以学习率对于算法性能的表现至关重要。#给出一些点(存在数组中)
x_train = np.array([[3.3], [4.4], [5.5], [6.71], [6.93], [4.168],[9.779], [6.182], [7.59], [2.167], [7.042],[10.791], [5.313], [7.997], [3.1]], dtype=np.float32)y_train = np.array([[1.7], [2.76], [2.09], [3.19], [1.694], [1.573],[3.366], [2.596], [2.53], [1.221], [2.827],[3.465], [1.65], [2.904], [1.3]], dtype=np.float32)# Convert numpy arrays to torch tensors
#将numpy的array转换为pytorch的tensor,他们都可以表示多维数组,
#区别在于numpy只能在CPU上运行,而pytorch可以在GPU运行。
# x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
# y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train)# Linear regression model
# model = nn.Linear(input_size, output_size)#定义一个 LinearRegression 类 继承 父类nn.Module
#self指的是类实例对象本身
class LinearRegression(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LinearRegression,self).__init__()self.linear=nn.Linear(input_size,output_size)def forward(self,x):out=self.linear(x)return out# if torch.cuda.is_available():
# model = LinearRegression().cuda()
# else:
# model = LinearRegression()model = LinearRegression()# Loss and optimizer
#均方误差(Mean Square Error)函数计算的是预测值与真实值之差的期望值,
#可用于评价数据的变化程度,其得到的值越小,则说明模型的预测值具有越好的精确度。
#SGD:Stochastic Gradient Descent ,使用随机梯度下降的优化方法
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)# Train the model
# range返回一个序列的数,num_epochs = 100 ,所以循环100次
# 判断是否可以使用GPU计算
# 将tensor 转换为 variable。variable是神经网络里特有的一个概念,它提供了自动求导功能。
# variable 和 tensor 的区别在于,variable会放入一个计算图中,进行前向传播,反向传播,自动求导。
for epoch in range(num_epochs):inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)target = torch.from_numpy(y_train)# Forward passoutputs = model(inputs) #前向传播,为什么要求出outputs?因为梯度下降需要用到梯度,求梯度要求偏导,求偏导要求函数值loss = criterion(outputs, target) #损失函数,均方差函数E(w,b),自变量为 w,b# Backward and optimizeoptimizer.zero_grad() #梯度归零,否则梯度会累加在一 起,造成结果不收敛loss.backward() #反向传播,均方差函数E(w,b),用梯度下降求出新的w,boptimizer.step() #更新参数w,b#每隔5个,输出损失函数的值看看,确保模型误差越来越小。
#每隔5个,绘制一张图像,图像中包括Original data(原始数据)和Fitted line(拟合线)if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train)).detach().numpy()plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'ro', label='Original data')plt.plot(x_train, predicted, label='Fitted line')plt.xlim((0, 12))plt.ylim((0, 6))plt.legend()plt.savefig('1.png')plt.show()display.clear_output(wait=True)plt.pause(1)print('Epoch [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, loss.item()))# Plot the graph
predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train)).detach().numpy()
plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(x_train, predicted, label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()# Save the model checkpoint (保存模型的参数,保存对象是模型的状态.P31)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.ckpt')(DATA.csv)One-dimensional linear regression
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import csv
import pandas as pd
import time
from IPython import display
import torch.autograd.variable as variable# Hyper-parameters 超参数是在开始学习过程之前设置值的参数,而不是通过训练得到的参数数据
input_size = 1 #输入维度
output_size = 1 #输出维度
num_epochs = 2000 #迭代次数
learning_rate = 0.0001 #学习率 : 决定了参数移动到最优值的速度快慢。#如果学习率过大,很可能会越过最优值;反而如果学习率过小,优化的效率可能过低,长时间算法无法收敛。#所以学习率对于算法性能的表现至关重要。#给出一些点(存在数组中)
with open('D:/PyCharm/untitled6/data.csv','r') as csvfile:reader = csv.reader(csvfile)x_data = [row[0]for row in reader]x_data = list(map(float, x_data))x_data_npy = np.asarray(x_data).reshape(-1,1)with open('D:/PyCharm/untitled6/data.csv','r') as csvfile1:reader = csv.reader(csvfile1)y_data = [row[1] for row in reader]y_data = list(map(float, y_data))y_data_npy = np.asarray(y_data).reshape(-1, 1)x_train=np.array(x_data_npy,dtype=np.float32)
y_train=np.array(y_data_npy,dtype=np.float32)# Convert numpy arrays to torch tensors
#将numpy的array转换为pytorch的tensor,他们都可以表示多维数组,
#区别在于numpy只能在CPU上运行,而pytorch可以在GPU运行。
# x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
# y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train)# Linear regression model
# model = nn.Linear(input_size, output_size)#定义一个 LinearRegression 类 继承 父类nn.Module
#self指的是类实例对象本身
class LinearRegression(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LinearRegression,self).__init__()self.linear=nn.Linear(input_size,output_size)def forward(self,x):out=self.linear(x)return out# if torch.cuda.is_available():
# model = LinearRegression().cuda()
# else:
# model = LinearRegression()model = LinearRegression()# Loss and optimizer
#均方误差(Mean Square Error)函数计算的是预测值与真实值之差的期望值,
#可用于评价数据的变化程度,其得到的值越小,则说明模型的预测值具有越好的精确度。
#SGD:Stochastic Gradient Descent ,使用随机梯度下降的优化方法
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)# Train the model
# range返回一个序列的数,num_epochs = 100 ,所以循环100次
# 判断是否可以使用GPU计算
# 将tensor 转换为 variable。variable是神经网络里特有的一个概念,它提供了自动求导功能。
# variable 和 tensor 的区别在于,variable会放入一个计算图中,进行前向传播,反向传播,自动求导。
for epoch in range(num_epochs):# if torch.cuda.is_available():# inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train).cuda()# target = torch.from_numpy(y_train).cuda()# else:# inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)# target = torch.from_numpy(y_train)inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)target = torch.from_numpy(y_train)# Forward passoutputs = model(inputs) #前向传播loss = criterion(outputs, target) #损失函数# Backward and optimizeoptimizer.zero_grad() #梯度归零,否则梯度会累加在一起,造成结果不收敛loss.backward() #反向传播optimizer.step() #更新参数#每隔5个,输出损失函数的值看看,确保模型误差越来越小。
#每隔5个,绘制一张图像,图像中包括Original data(原始数据)和Fitted line(拟合线)if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train)).detach().numpy()plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'ro', label='Original data')plt.plot(x_train, predicted, label='Fitted line')plt.xlim((0, 100))plt.ylim((0, 150))plt.legend()plt.savefig('1.png')plt.show()display.clear_output(wait=True)plt.pause(1)print('Epoch [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, loss.item()))# Plot the graph
predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train)).detach().numpy()
plt.plot(x_train, y_train, 'ro', label='Original data')
plt.plot(x_train, predicted, label='Fitted line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()# Save the model checkpoint
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.ckpt')polynomial regression
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef make_features(x):# 将原来长度为3的tensor数组,变成大小为(3,1)的矩阵(列向量)x = x.unsqueeze(1)#range(1,4),0123,从1开始到3.#torch.cat((A,B), 1),第二个参数,0代表行(竖着拼),1代表列(横着拼)return torch.cat([x ** i for i in range(1,4)], 1)#将原来长度为3的tensor数组,变成大小为(3,1)的矩阵(列向量)
w_target = torch.FloatTensor([0.5, 3, 2.4]).unsqueeze(1)
b_target = torch.FloatTensor([0.9])def f(x):return x.mm(w_target) + b_target[0] #x.mm()是作矩阵乘法def get_batch(batch_size=32):random = torch.randn(batch_size) #生成32个随机数x = make_features(random) #首先生成(32,1)的矩阵,然后拼接为(32,3)的矩阵'''Compute the actual results'''y = f(x) #矩阵相乘,即(32,3)的矩阵乘以(3,1)的列向量,得到y是(32,1)的列向量return np.array(x), np.array(y)class poly_model(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(poly_model, self).__init__()self.poly = nn.Linear(3, 1) #因为每一个神经元其实模拟的是wx+b的计算过程,无法模拟幂运算,#所以显然我们需要将x,x的平方,x的三次方,所以输入变为3.def forward(self, x):out = self.poly(x)return outmodel = poly_model()criterion = nn.MSELoss() #均方误差损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 1e-3) #随机梯度下降优化方法epoch = 0
while True:batch_x,batch_y = get_batch()output = model(torch.from_numpy(batch_x))loss = criterion(output,torch.from_numpy(batch_y))print_loss = loss.item()optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()if (epoch + 1) % 50 == 0:print('Epoch [{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1,loss.item()))epoch+=1if print_loss < 1e-3:breakprint('Epoch [{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, loss.item()))#%% 绘制真值和拟合结果曲线
#np.linspace(-1,1,30) 起始点-1,结束点1,取30个元素
x = np.linspace(-1,1,30)
x_sample = torch.from_numpy(x)
x_sample = x_sample.unsqueeze(1) #转换为列向量
x_sample = torch.cat([x_sample ** i for i in range(1,4)] , 1) #3个列向量拼接为一个(3,3)矩阵
x_sample = x_sample.float()
y_actural = f(x_sample) #获得真值
y_predict = model(x_sample) #获得拟合结果
plt.plot(x,y_actural.numpy(),'ro',x,y_predict.data.cpu().numpy())
plt.legend(['real point','fit'])
plt.show()# Save the model checkpoint(保存模型的参数,保存对象是模型的状态.P31)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.ckpt')