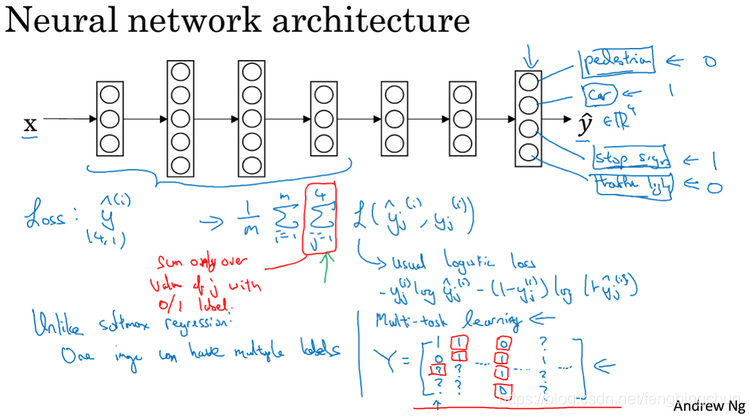
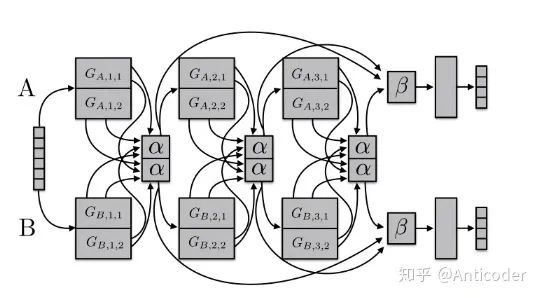
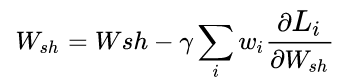多任务学习MTL的简单实现,主要是为了理解MTL
代码写得挺烂的,有时间回来整理一下
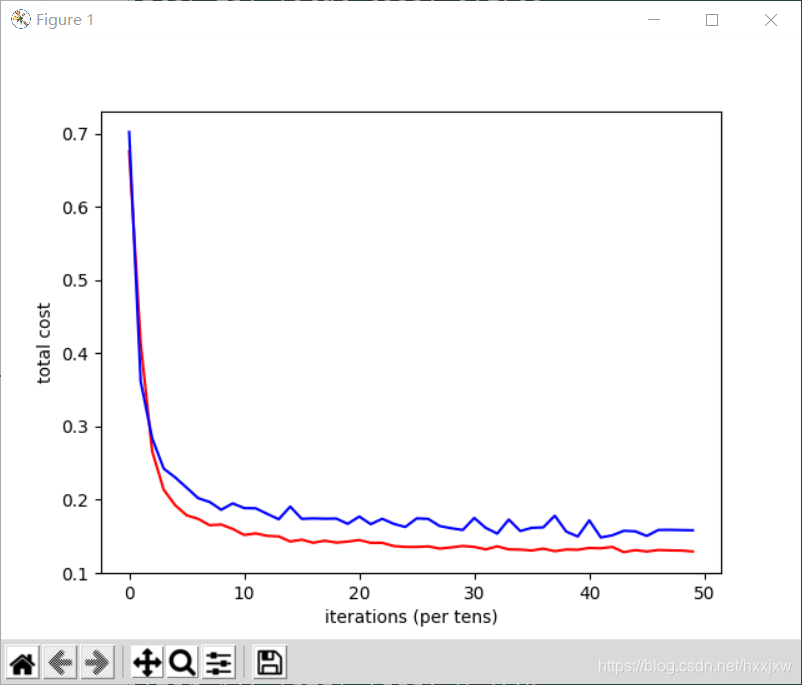
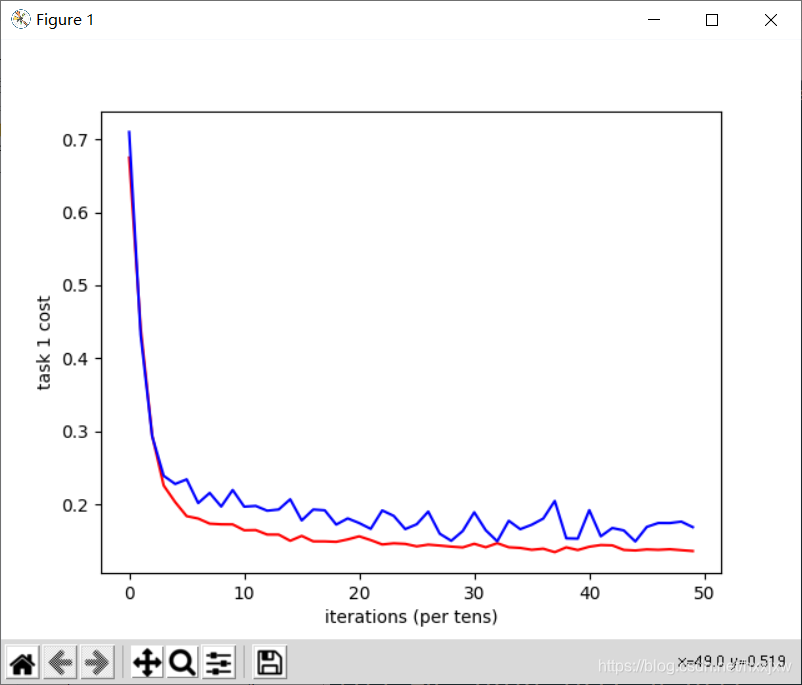
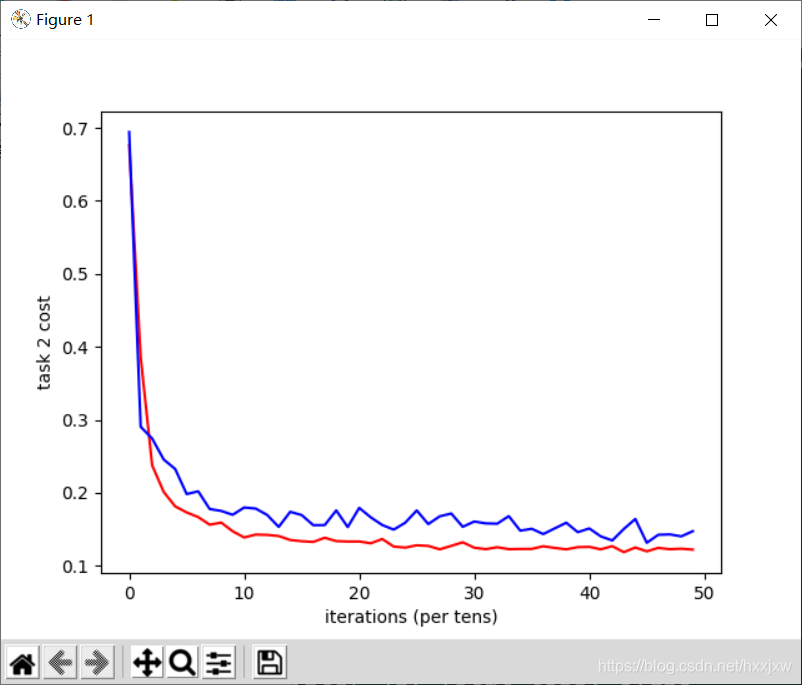
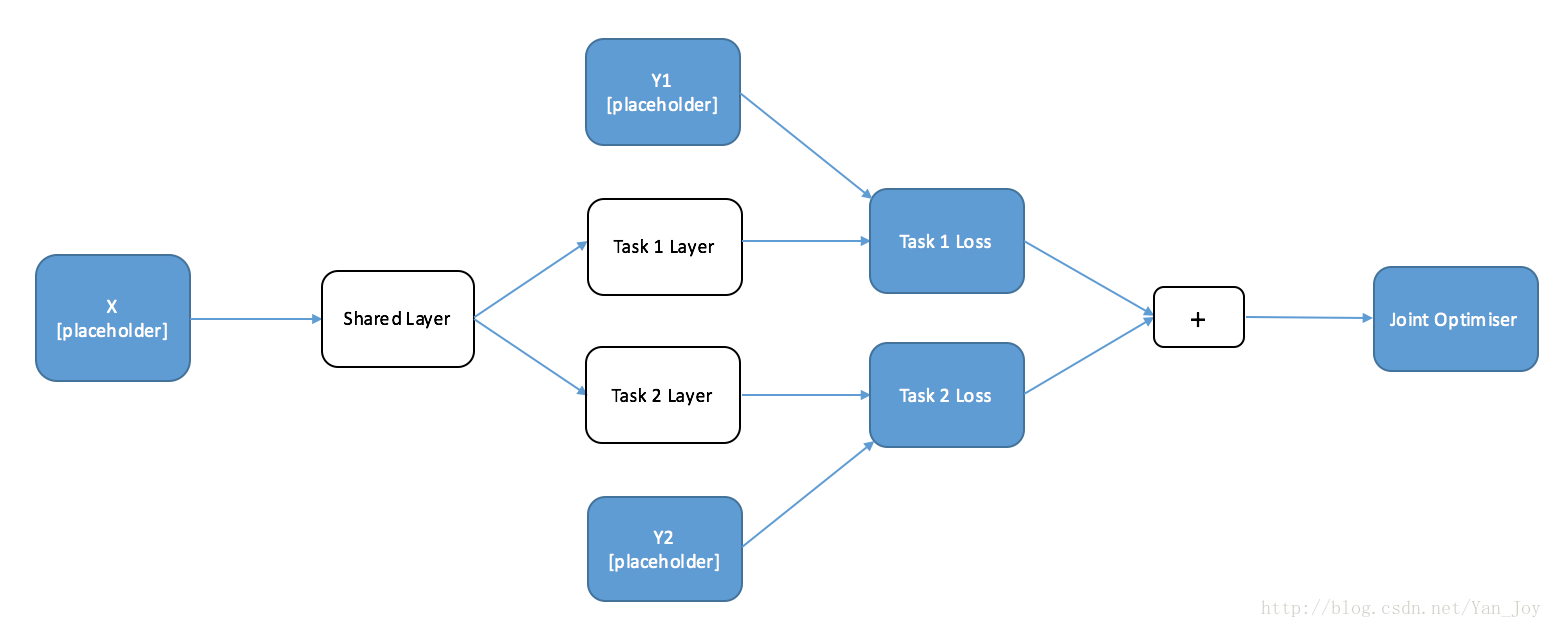
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec import os from torch.autograd import Variable import pandas as pd import math import sklearn.preprocessing as sk from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter import seaborn as sns from sklearn.model_selection import KFold from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import randomseed = 42 random.seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)N = 10000 M = 100 c = 0.5 p = 0.9 k = np.random.randn(M) u1 = np.random.randn(M) u1 -= u1.dot(k) * k / np.linalg.norm(k)**2 u1 /= np.linalg.norm(u1) k /= np.linalg.norm(k) u2 = k w1 = c*u1 w2 = c*(p*u1+np.sqrt((1-p**2))*u2) X = np.random.normal(0, 1, (N, M)) eps1 = np.random.normal(0, 0.01) eps2 = np.random.normal(0, 0.01) Y1 = np.matmul(X, w1) + np.sin(np.matmul(X, w1))+eps1 Y2 = np.matmul(X, w2) + np.sin(np.matmul(X, w2))+eps2 split = list(np.random.permutation(N))X_train = X[split[0:8000],:] Y1_train = Y1[split[0:8000]] Y2_train = Y2[split[0:8000]] X_valid = X[8000:9000,:] Y1_valid = Y1[8000:9000] Y2_valid = Y2[8000:9000] X_test = X[9000:10000,:] Y1_test = Y1[9000:10000] Y2_test = Y2[9000:10000] print(X_train.shape) print(X_valid.shape) print(X_test.shape) print(Y1_train.shape) print(Y2_train.shape) print(Y1_valid.shape) print(Y2_valid.shape) print(Y1_test.shape) print(Y2_test.shape)X_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train) X_train = X_train.float() Y1_train = torch.tensor(Y1_train) Y1_train = Y1_train.float() Y2_train = torch.tensor(Y2_train) Y2_train = Y2_train.float()X_valid = torch.from_numpy(X_valid) X_valid = X_valid.float() Y1_valid = torch.tensor(Y1_valid) Y1_valid = Y1_valid.float() Y2_valid = torch.tensor(Y2_valid) Y2_valid = Y2_valid.float()X_test = torch.from_numpy(X_test) X_test = X_test.float() Y1_test = torch.tensor(Y1_test) Y1_test = Y1_test.float() Y2_test = torch.tensor(Y2_test) Y2_test = Y2_test.float()print(X_train.shape) print(X_valid.shape) print(X_test.shape) print(Y1_train.shape) print(Y2_train.shape) print(Y1_valid.shape) print(Y2_valid.shape) print(Y1_test.shape) print(Y2_test.shape)input_size, feature_size = X.shape shared_layer_size = 64 tower_h1 = 32 tower_h2 = 16 output_size = 1 LR = 0.001 epoch = 50 mb_size = 100 cost1tr = [] cost2tr = [] cost1D = [] cost2D = [] cost1ts = [] cost2ts = [] costtr = [] costD = [] costts = []class MTLnet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(MTLnet, self).__init__()self.sharedlayer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(feature_size, shared_layer_size),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout())self.tower1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(shared_layer_size, tower_h1),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(tower_h1, tower_h2),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(tower_h2, output_size))self.tower2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(shared_layer_size, tower_h1),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(tower_h1, tower_h2),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(tower_h2, output_size)) def forward(self, x):h_shared = self.sharedlayer(x)out1 = self.tower1(h_shared)out2 = self.tower2(h_shared)return out1, out2def random_mini_batches(XE, R1E, R2E, mini_batch_size = 10, seed = 42): # Creating the mini-batchesnp.random.seed(seed) m = XE.shape[0] mini_batches = []permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))shuffled_XE = XE[permutation,:]shuffled_X1R = R1E[permutation]shuffled_X2R = R2E[permutation]num_complete_minibatches = math.floor(m/mini_batch_size)for k in range(0, int(num_complete_minibatches)):mini_batch_XE = shuffled_XE[k * mini_batch_size : (k+1) * mini_batch_size, :]mini_batch_X1R = shuffled_X1R[k * mini_batch_size : (k+1) * mini_batch_size]mini_batch_X2R = shuffled_X2R[k * mini_batch_size : (k+1) * mini_batch_size]mini_batch = (mini_batch_XE, mini_batch_X1R, mini_batch_X2R)mini_batches.append(mini_batch)Lower = int(num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size)Upper = int(m - (mini_batch_size * math.floor(m/mini_batch_size)))if m % mini_batch_size != 0:mini_batch_XE = shuffled_XE[Lower : Lower + Upper, :]mini_batch_X1R = shuffled_X1R[Lower : Lower + Upper]mini_batch_X2R = shuffled_X2R[Lower : Lower + Upper]mini_batch = (mini_batch_XE, mini_batch_X1R, mini_batch_X2R)mini_batches.append(mini_batch)return mini_batchesMTL = MTLnet() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(MTL.parameters(), lr=LR) loss_func = nn.MSELoss()for it in range(epoch):epoch_cost = 0epoch_cost1 = 0epoch_cost2 = 0num_minibatches = int(input_size / mb_size) minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y1_train, Y2_train, mb_size)for minibatch in minibatches:XE, YE1, YE2 = minibatch Yhat1, Yhat2 = MTL(XE)l1 = loss_func(Yhat1, YE1.view(-1,1)) l2 = loss_func(Yhat2, YE2.view(-1,1))loss = (l1 + l2)/2optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()epoch_cost = epoch_cost + (loss / num_minibatches)epoch_cost1 = epoch_cost1 + (l1 / num_minibatches)epoch_cost2 = epoch_cost2 + (l2 / num_minibatches)costtr.append(torch.mean(epoch_cost))cost1tr.append(torch.mean(epoch_cost1))cost2tr.append(torch.mean(epoch_cost2))with torch.no_grad():Yhat1D, Yhat2D = MTL(X_valid)l1D = loss_func(Yhat1D, Y1_valid.view(-1,1))l2D = loss_func(Yhat2D, Y2_valid.view(-1,1))cost1D.append(l1D)cost2D.append(l2D)costD.append((l1D+l2D)/2)print('Iter-{}; Total loss: {:.4}'.format(it, loss.item()))plt.plot(np.squeeze(costtr), '-r',np.squeeze(costD), '-b') plt.ylabel('total cost') plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') plt.show() plt.plot(np.squeeze(cost1tr), '-r', np.squeeze(cost1D), '-b') plt.ylabel('task 1 cost') plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') plt.show() plt.plot(np.squeeze(cost2tr),'-r', np.squeeze(cost2D),'-b') plt.ylabel('task 2 cost') plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') plt.show()
参考:
https://github.com/hosseinshn/Basic-Multi-task-Learning