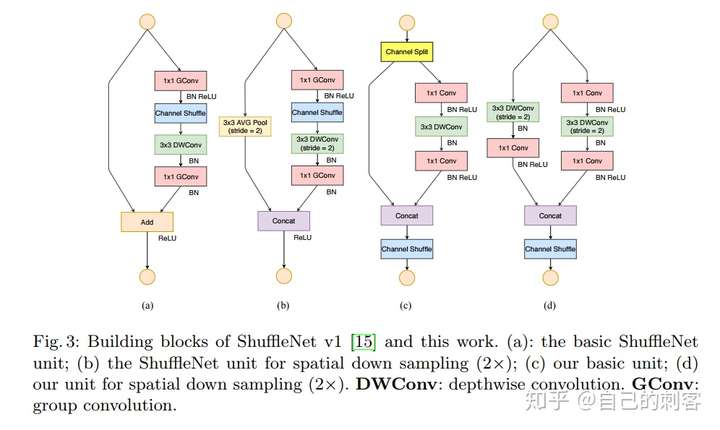
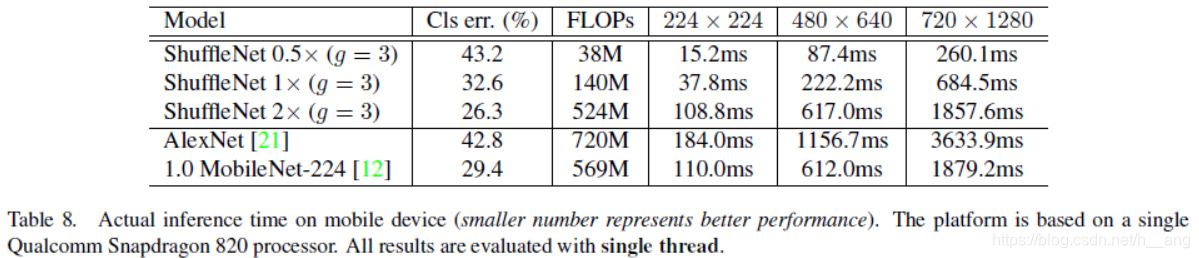
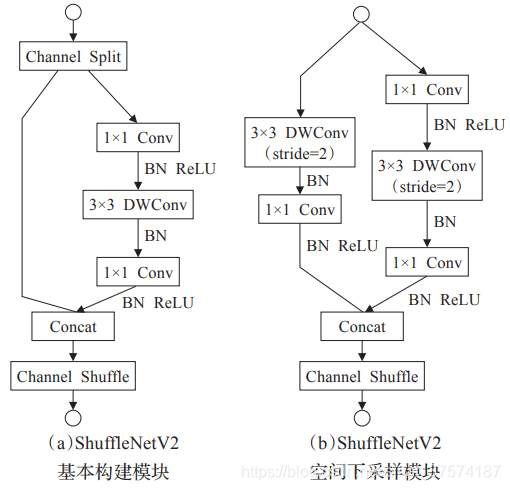
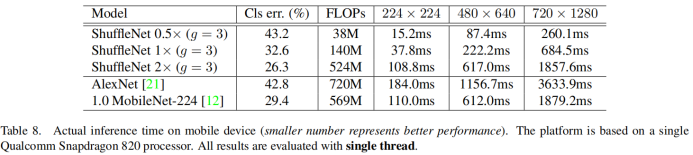
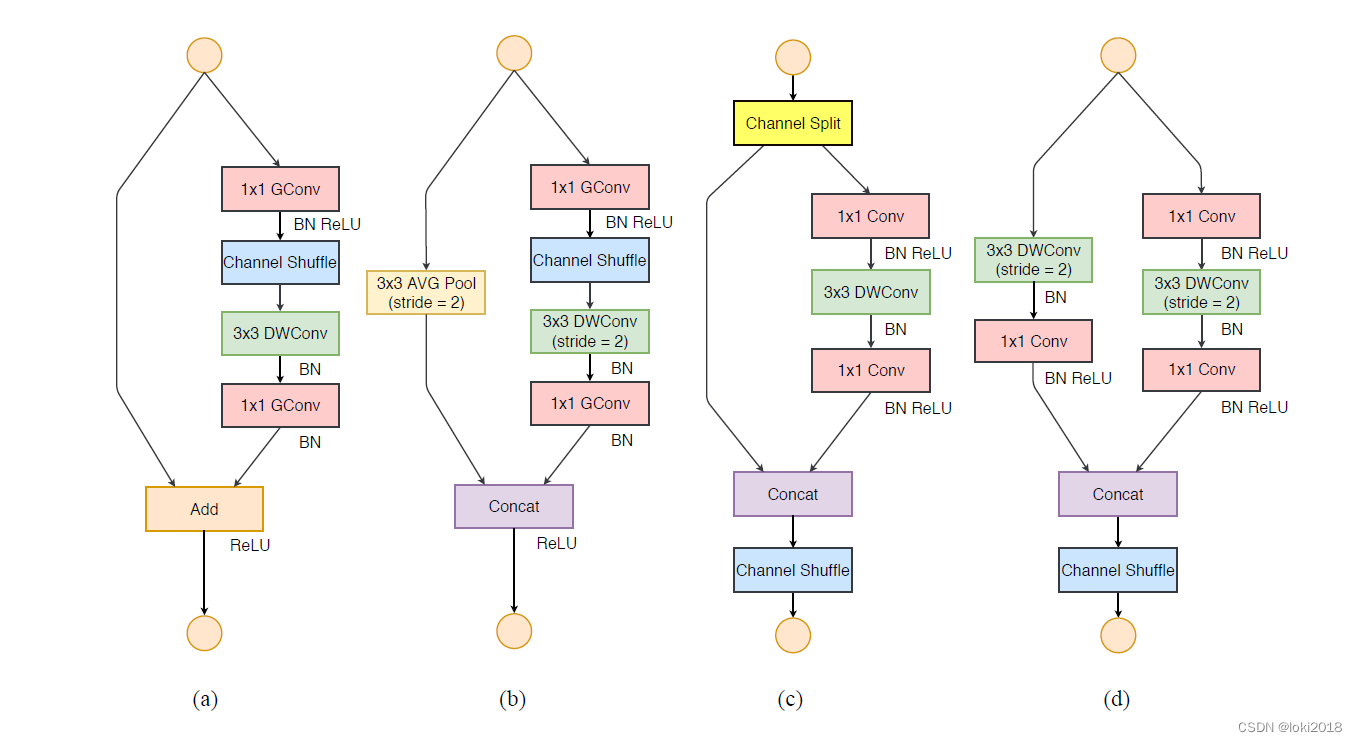
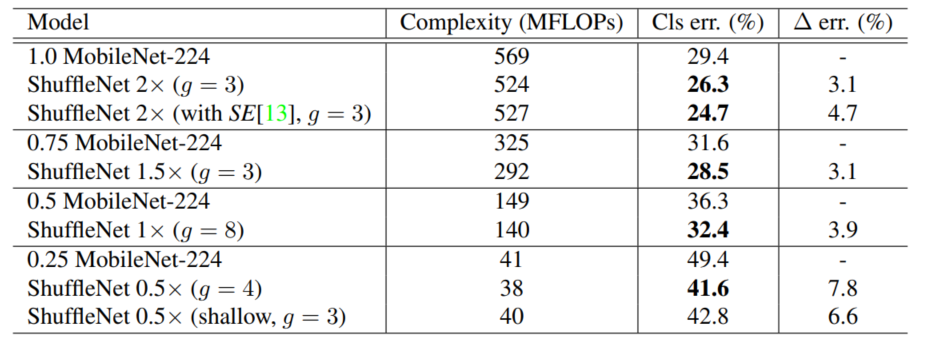
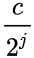channel shuffle:
1)利用group ,再组间进行深度卷积。
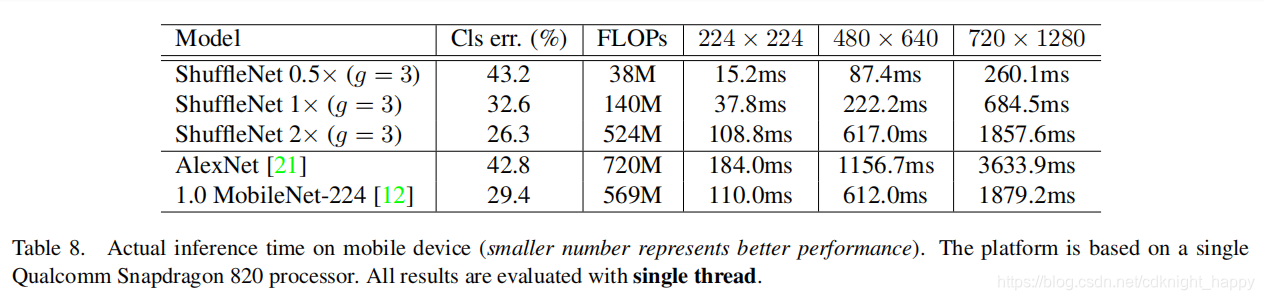
优点:1)极大减小计算量(FLOPS)
由于每个filter不再是和输入的全部feature map做卷积,而是仅仅和一个group的feature map做卷积。
缺点:边界效应产生,即某个输出channel仅仅来自输入channel的一小部分
细节:一般卷积操作中比如输入feature map的数量是N,该卷积层的filter数量是M,那么M个filter中的每一个filter都要和N个feature map的某个区域做卷积,然后相加作为一个卷积的结果。假设你引入group操作,设group为g,那么N个输入feature map就被分成g个group,M个filter就被分成g个group,然后在做卷积操作的时候,第一个group的M/g个filter中的每一个都和第一个group的N/g个输入feature map做卷积得到结果,第二个group同理,直到最后一个group.
2)为了抵消边界效应,提出channel shuffle
本质; 即进行GConv2之前,对其输入feature map做一个分配,使得GConv2的每一个group都能卷积输入的所有group的feature map
def _shuffle(x, groups):def shuffle_layer(x):_, w, h, n = K.int_shape(x)nb_chan_per_grp = n // groupsx = K.reshape(x, (-1, w, h, nb_chan_per_grp, groups))x = K.permute_dimensions(x, (0, 1, 2, 4, 3)) # Transpose only grps and chs(按照给定的模式重排一个张量的轴)x = K.reshape(x, (-1, w, h, n)return x
附代码:
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import *
from keras.activations import *
from keras.callbacks import *
import keras.backend as K
from keras.engine.topology import get_source_inputs
count=0
def _info(groups):return {1: [24, 144, 288, 576],2: [24, 200, 400, 800],3: [24, 240, 480, 960],4: [24, 272, 544, 1088],8: [24, 384, 768, 1536]}[groups], [None, 3, 7, 3]def basemodel(input_tensor=None, input_shape=None,groups=8):if input_tensor is None:img_input = Input(shape=input_shape)else:if not K.is_keras_tensor(input_tensor):img_input = Input(tensor=input_tensor, shape=input_shape)else:img_input = input_tensorbn_axis = 3 if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_last' else 1x = Conv2D(24,kernel_size=(3, 3),strides=2,use_bias=False,padding='same')(img_input)x = BatchNormalization()(x)x = Activation('relu')(x)x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3),strides=2,padding='same',)(x)x = Activation('relu',name='pool1')(x)channels_list, repeat_list = _info(groups) # [24, 200, 400, 800],[None, 3, 7, 3]# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()for i, (out_channels, repeat) in enumerate(zip(channels_list[1:], repeat_list[1:]), start=1):x = _stage(x, groups, channels_list[i-1], out_channels, repeat)#8if input_tensor is not None:inputs = get_source_inputs(input_tensor)else:inputs = img_inputmodel = Model(inputs, x, name='basemodel_dense')return modeldef _stage(tensor, groups, in_channels, out_channels, repeat):#repeat=repeat_list[1:],[None, 3, 7, 3]x = _shufflenet_unit(tensor, groups, in_channels, out_channels, 2) #2for _ in range(repeat):x = _shufflenet_unit(x, groups, out_channels, out_channels, 1)return x#out_i=[4,12,16]
#(name='stage%s'% k[0])def _pw_group(tensor, groups, in_channels, out_channels): #一个组,分通道卷积操作,之后cancat"""Pointwise grouped convolution."""nb_chan_per_grp = in_channels // groupspw_convs = []for grp in range(groups):x = Lambda(lambda x: x[:, :, :, nb_chan_per_grp * grp: nb_chan_per_grp * (grp + 1)])(tensor)grp_out_chan = int(out_channels / groups + 0.5)pw_convs.append(Conv2D(grp_out_chan,kernel_size=(1, 1),padding='same',use_bias=False,strides=1)(x))return Concatenate(axis=-1)(pw_convs)def _shuffle(x, groups): #通道间的打乱def shuffle_layer(x):_, w, h, n = K.int_shape(x)nb_chan_per_grp = n // groupsx = K.reshape(x, (-1, w, h, nb_chan_per_grp, groups))x = K.permute_dimensions(x, (0, 1, 2, 4, 3)) # Transpose only grps and chs(按照给定的模式重排一个张量的轴)x = K.reshape(x, (-1, w, h, n))return xreturn Lambda(shuffle_layer)(x)def _shufflenet_unit(tensor, groups, in_channels, out_channels, strides, shuffle=True, bottleneck=4):bottleneck_channels = out_channels // bottleneckx = _pw_group(tensor, groups, in_channels, bottleneck_channels) #深度可分离卷积x = BatchNormalization()(x)x = Activation('relu')(x)if shuffle:x = _shuffle(x, groups) #通道间的打乱x = DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size=(3, 3), #深度卷积padding='same',use_bias=False,strides=strides)(x)x = BatchNormalization()(x)x = _pw_group(x, groups, bottleneck_channels,out_channels if strides < 2 else out_channels - in_channels)x = BatchNormalization()(x)if strides < 2:x = Add()([tensor, x])else:avg = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3),strides=2,padding='same')(tensor)x = Concatenate(axis=-1)([avg, x])global countcount+=1x = Activation('relu',name='stage%s'% count)(x)return x