搬运自:Raushan Roy-TEMPORAL CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS
Learning sequences efficiently and effectively
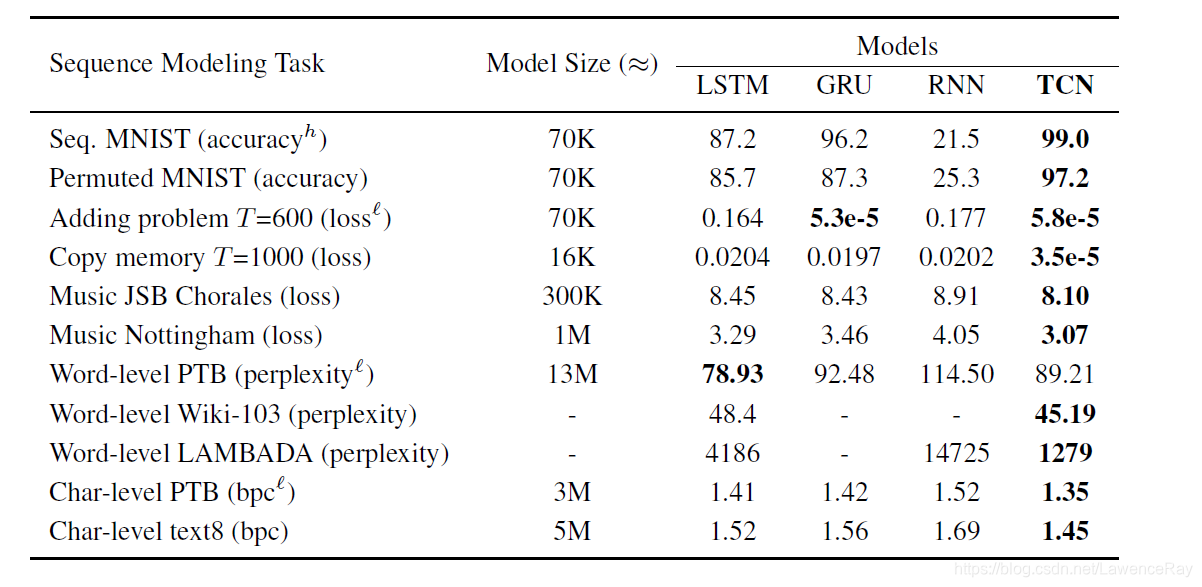
Until recently the default choice for sequence modeling task was RNNs because of their great ability to capture temporal dependencies in sequential data. There are several variants of RNNs such as LSTM, GRU capable of capturing long term dependencies in sequences and have achieved state of art performances in seq2seq modeling tasks.
Recently, Deep Learning practitioners have been using a variation of Convolutional Neural Network architecture for the sequence modelling tasks, Temporal Convolutional Networks. This is a simple descriptive term to refer to a family of architectures.
Google DeepMind published a paper Pixel Recurrent Neural Network where the authors introduced the notion of using CNN as sequence model with fixed dependency range, by using masked convolutions. The idea was to convolve only on the elements from current timestamp or earlier in the previous layer. Google DeepMind published another paper Neural Machine Translation in Linear Time inspired from the above idea which achieved state-of -the-art performance on English-to-German translation task surpassing the recurrent networks with attentional pooling.
The distinguishing characteristics of TCNs are:
- The architecture can take a sequence of any length and map it to an output sequence of the same length, just as with an RNNs.
- The convolutions in the architecture are causal, meaning that there is no information “leakage” from future to past.
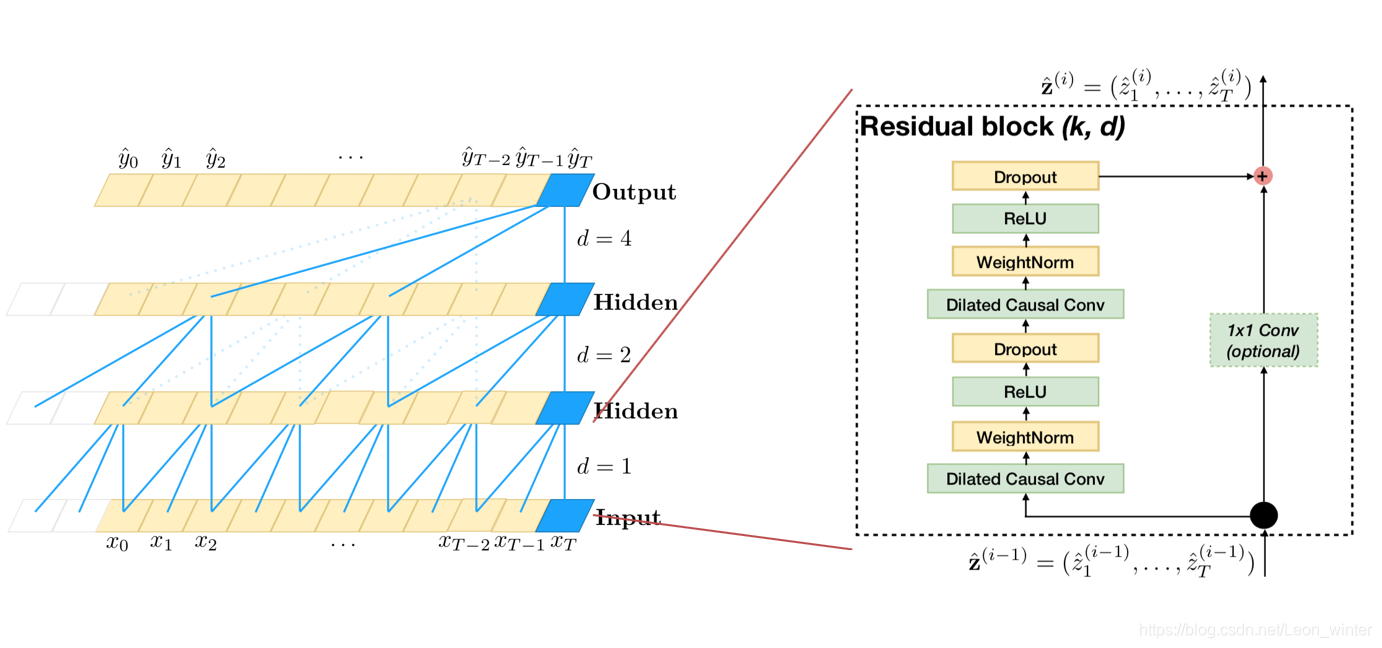
To accomplish the first point, the TCN uses a 1D fully-convolutional network (FCN) architecture, where each hidden layer is the same length as the input layer, and zero padding of length (kernel size − 1) is added to keep subsequent layers the same length as previous ones. To achieve the second point, the TCN uses causal convolutions, convolutions where an output at time t is convolved only with elements from time t and earlier in the previous layer.
To put it simply: TCN= 1D FCN + causal convolutions
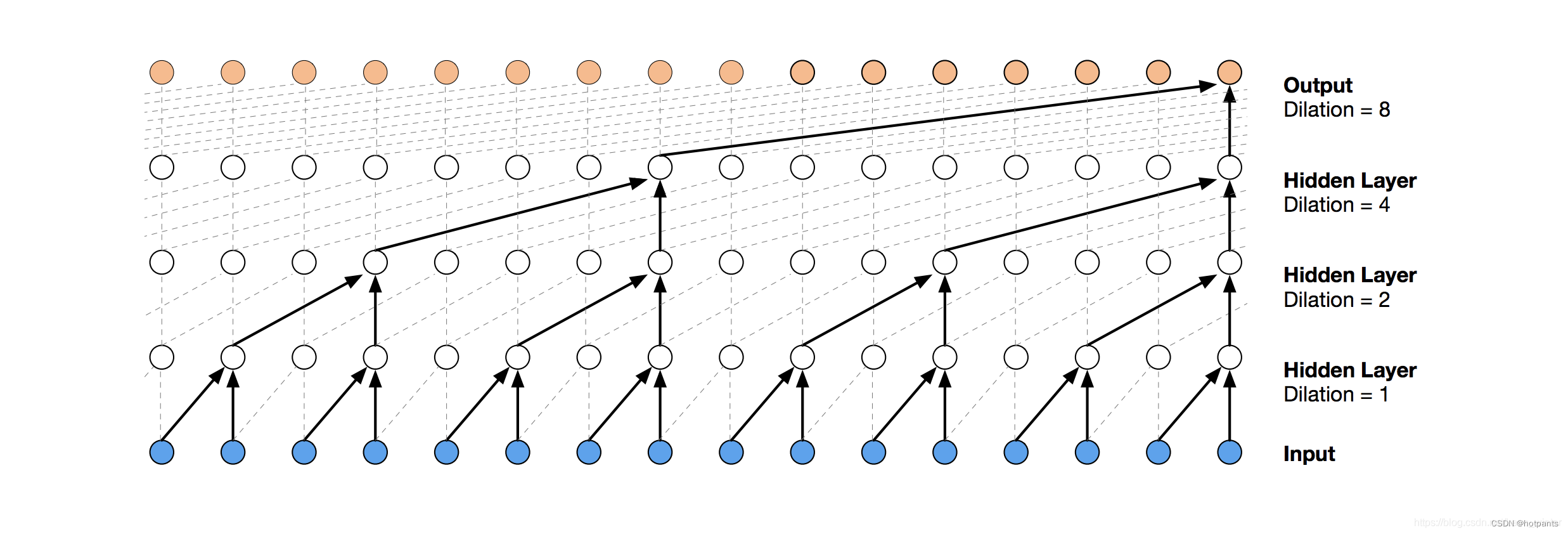
This basic architecture can look back at history with size linear in the depth of the network and the filter size. Hence, capturing long term dependencies becomes really challenging. One simple solution to overcome this problem is to use dilated convolutions.
Dilated Convolutions
For a 1-D sequence input x ∈ R^n and a filter f: {0,…,k-1} → R, the dilated convolution operation F on element s of the sequence is defined as(Image from paper):
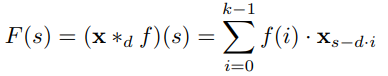
In above formula the causal convolution criteria is also taken care of by using only non-negative values of i. It is evident that the normal convolution is nothing but a 1 dilated convolution. For more on dilated convolution you can refer to this blog.
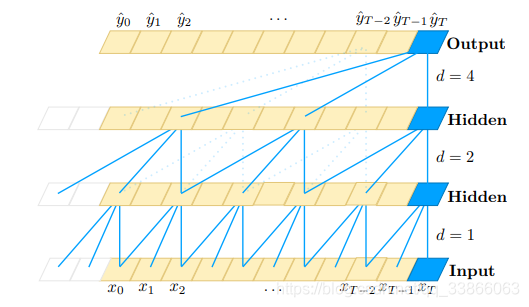
A dilated causal convolution with dilation factors d = 1, 2, 4 and filter size k = 3
Advantages of using TCNs for sequence modeling
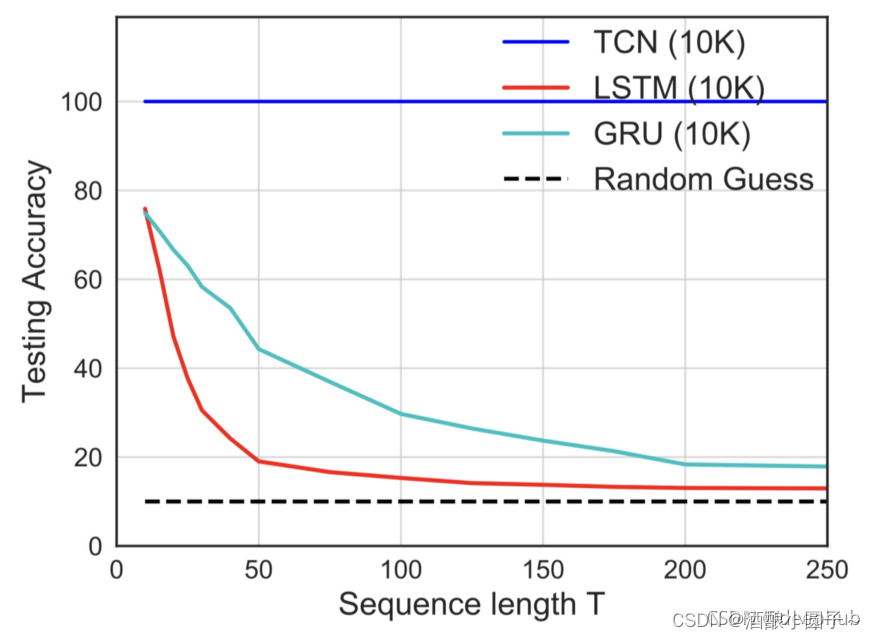
- Parallelism: Unlike in RNNs where the predictions for later time-steps must wait for their predecessors to complete, convolutions can be done in parallel since the same filter is used in each layer. Therefore, in both training and evaluation, a long input sequence can be processed as a whole in TCN, instead of sequentially as in RNN.
- Flexible receptive field size: A TCN can change its receptive field size in multiple ways. For instance, stacking more dilated (causal) convolutional layers, using larger dilation factors, or increasing the filter size are all viable options (with possibly different interpretations). TCNs thus afford better control of the model’s memory size, and are easy to adapt to different domains.
- Low memory requirement for training: Especially in the case of a long input sequence, LSTMs and GRUs can easily use up a lot of memory to store the partial results for their multiple cell gates. However, in a TCN the filters are shared across a layer, with the back-propagation path depending only on network depth. Therefore in practice, gated RNNs are likely to use up to a multiplicative factor more memory than TCNs.
- Capturing local information: Using convolution operation helps in capturing local information along with temporal information.
Departing Words:
Performing BackProp for dilated convolutions is nothing but transpose convolution operation.
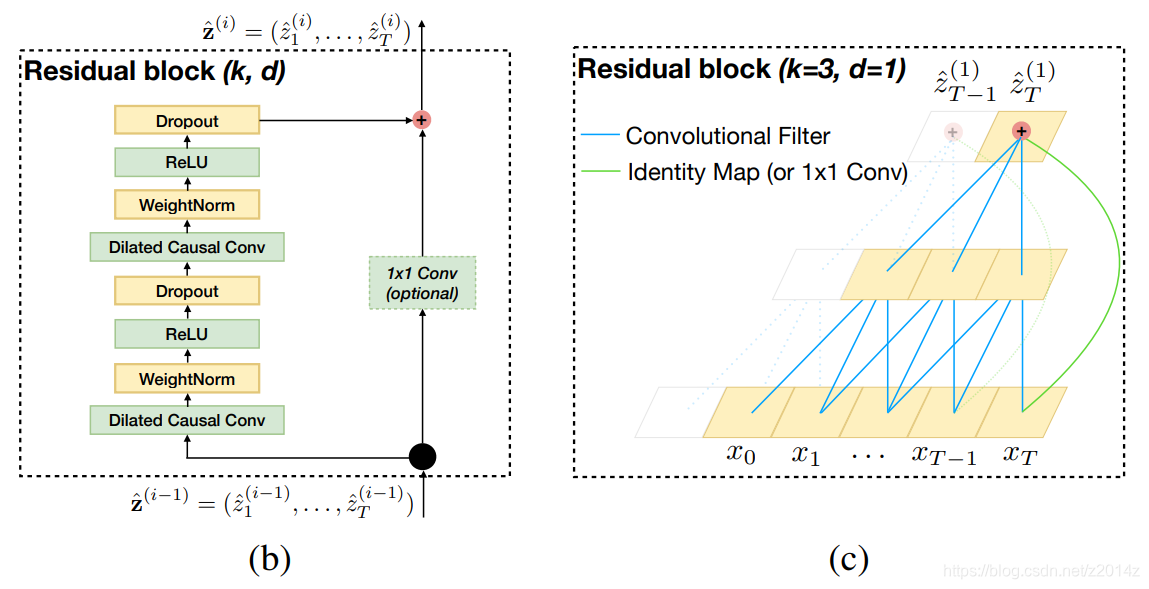
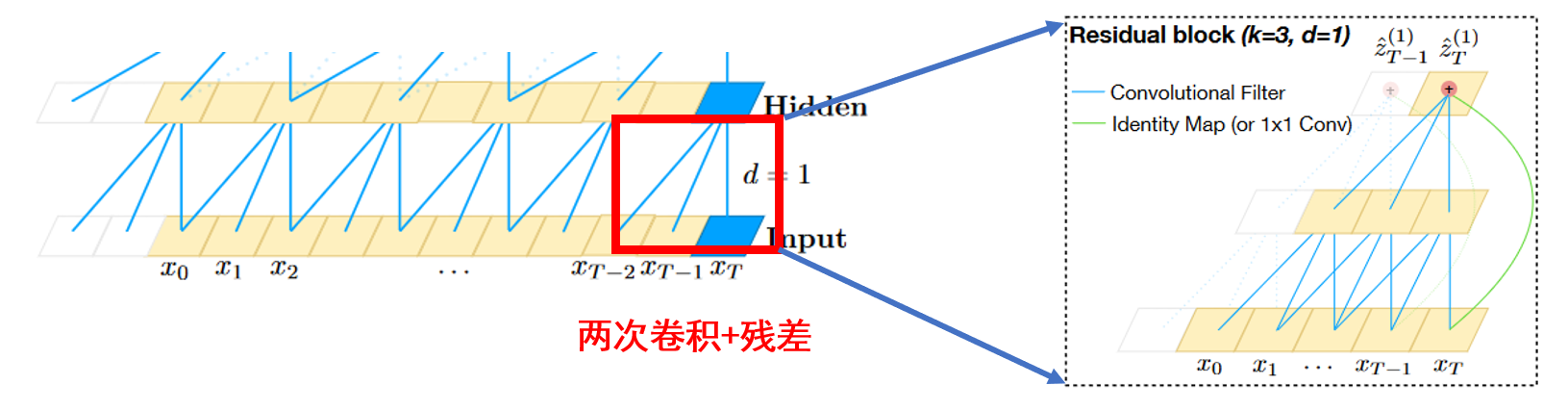
Since a TCN’s receptive field depends on the network depth n as well as filter size k and dilation factor d, stabilization of deeper and larger TCNs becomes important. Therefore, a generic residual module in place of a convolutional layer.
References:
- Bai, S., Kolter, J. Z., & Koltun, V. (2018). An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.01271.
- Lea, C., Vidal, R., Reiter, A., & Hager, G. D. (2016, October). Temporal convolutional networks: A unified approach to action segmentation. In European Conference on Computer Vision(pp. 47–54). Springer, Cham.
- Kalchbrenner, N., Espeholt, L., Simonyan, K., Oord, A. V. D., Graves, A., & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016). Neural machine translation in linear time. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.10099.
补充:
https://blog.csdn.net/Kuo_Jun_Lin/article/details/80602776