文章目录
- 决策树
- 数据集
- 代码
- 实验分析
决策树
决策树(Decision Tree)是一种基本的分类与回归方法,当决策树用于分类时称为分类树,用于回归时称为回归树。主要介绍分类树。
决策树由结点和有向边组成。结点有两种类型:内部结点和叶结点,其中内部结点表示一个特征或属性,叶结点表示一个类。
决策树学算法通常是一个递归地选择最优特征,并根据该特征对训练数据进行分割,使得对各个子数据集有一个最好的分类的过程。根据信息增益准则的特征选择方法:对于训练数据集(或子集),计算其每个特征的信息增益,并比较它们的大小,选择信息增益最大的特征。
数据集
代码
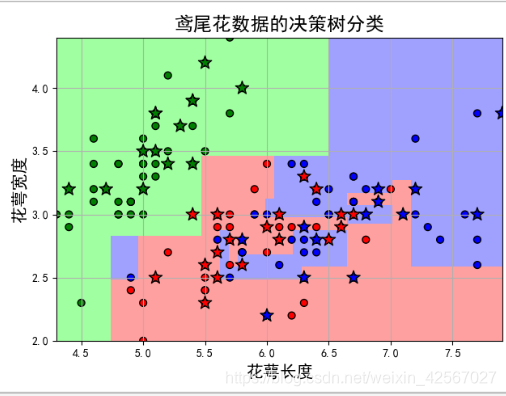
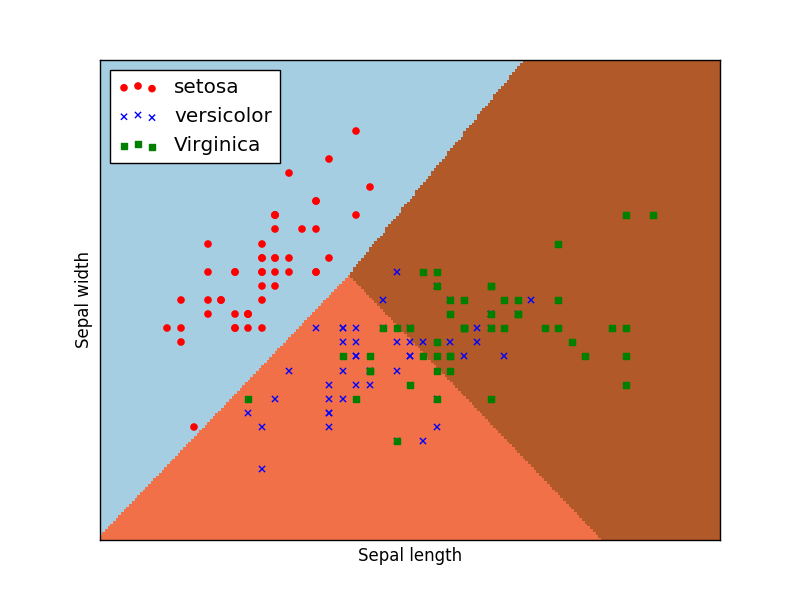
不同深度情况下的分类
// An highlighted block
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 花萼长度、花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度
iris_feature_E = 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width'
iris_feature = u'花萼长度', u'花萼宽度', u'花瓣长度', u'花瓣宽度'
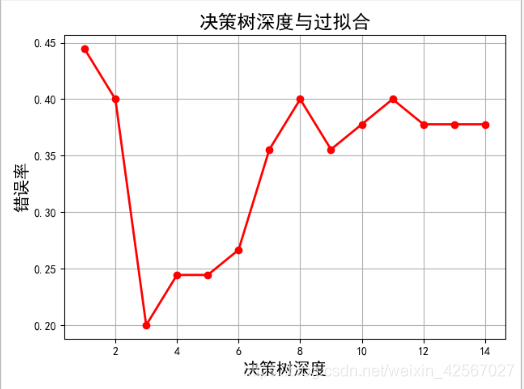
iris_class = 'Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'if __name__ == "__main__":mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei']mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False'''加载数据'''data = pd.read_csv('F:\pythonlianxi\shuju\iris.data', header=None)#print(data)#样本集x = data[range(4)]#标签集y = pd.Categorical(data[4]).codes# 为了可视化,仅使用前两列特征x = x.iloc[:, :2]#样本集,标签集分为测试集和验证集x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.7, random_state=1)#print(y_test.shape)print('开始训练模型....')#'''决策树'''# 决策树参数估计# min_samples_split = 10:如果该结点包含的样本数目大于10,则(有可能)对其分支# min_samples_leaf = 10:若将某结点分支后,得到的每个子结点样本数目都大于10,则完成分支;否则,不进行分支#建立决策树模型model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')model.fit(x_train, y_train)#测试数据y_test_hat = model.predict(x_test) # 测试数据# 横纵各采样值N, M = 50, 50 x1_min, x2_min = x.min()x1_max, x2_max = x.max()t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N)t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M)# 生成网格采样点x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) # 测试点x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) #图形颜色cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF'])cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r', 'b'])# 预测值y_show_hat = model.predict(x_show) # 使之与输入的形状相同y_show_hat = y_show_hat.reshape(x1.shape) # print (y_show_hat)'''绘图'''plt.figure(facecolor='w')plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_show_hat, cmap=cm_light) # 预测值的显示plt.scatter(x_test[0], x_test[1], c=y_test.ravel(), edgecolors='k', s=150, zorder=10, cmap=cm_dark, marker='*') # 测试数据plt.scatter(x[0], x[1], c=y.ravel(), edgecolors='k', s=40, cmap=cm_dark) # 全部数据plt.xlabel(iris_feature[0], fontsize=15)plt.ylabel(iris_feature[1], fontsize=15)plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max)plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max)plt.grid(True)plt.title(u'鸢尾花数据的决策树分类', fontsize=17)plt.show()#'''测试样本'''# 训练集上的预测结果y_test = y_test.reshape(-1)print( y_test_hat)print (y_test)result = (y_test_hat == y_test) # True则预测正确,False则预测错误#取平均acc = np.mean(result)print('准确度: %.2f%%' % (100 * acc))'''过拟合'''# 过拟合:错误率#给定深度14层depth = np.arange(1, 15)err_list = []#每个深度进行测试for d in depth:clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=d)clf.fit(x_train, y_train)y_test_hat = clf.predict(x_test) # 测试数据result = (y_test_hat == y_test) # True则预测正确,False则预测错误if d == 1:print (result)err = 1 - np.mean(result)err_list.append(err)print (d, ' 错误率: %.2f%%' % (100 * err))'''绘图'''plt.figure(facecolor='w')plt.plot(depth, err_list, 'ro-', lw=2)plt.xlabel(u'决策树深度', fontsize=15)plt.ylabel(u'错误率', fontsize=15)plt.title(u'决策树深度与过拟合', fontsize=17)plt.grid(True)plt.show()
实验分析
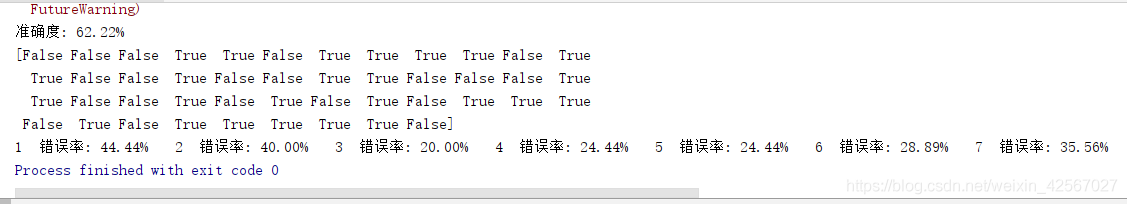
准确度: 62.22%,决策树深度为3时可以达到较高的识别率。