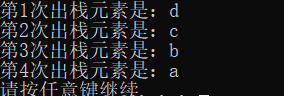
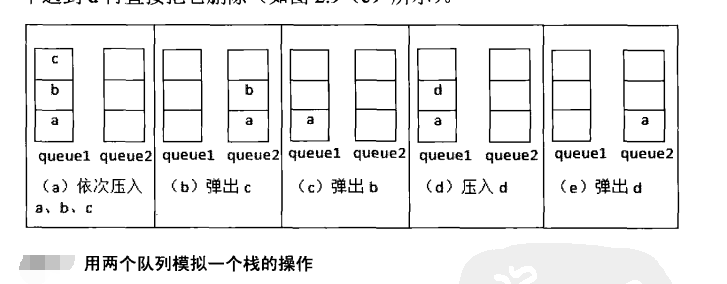
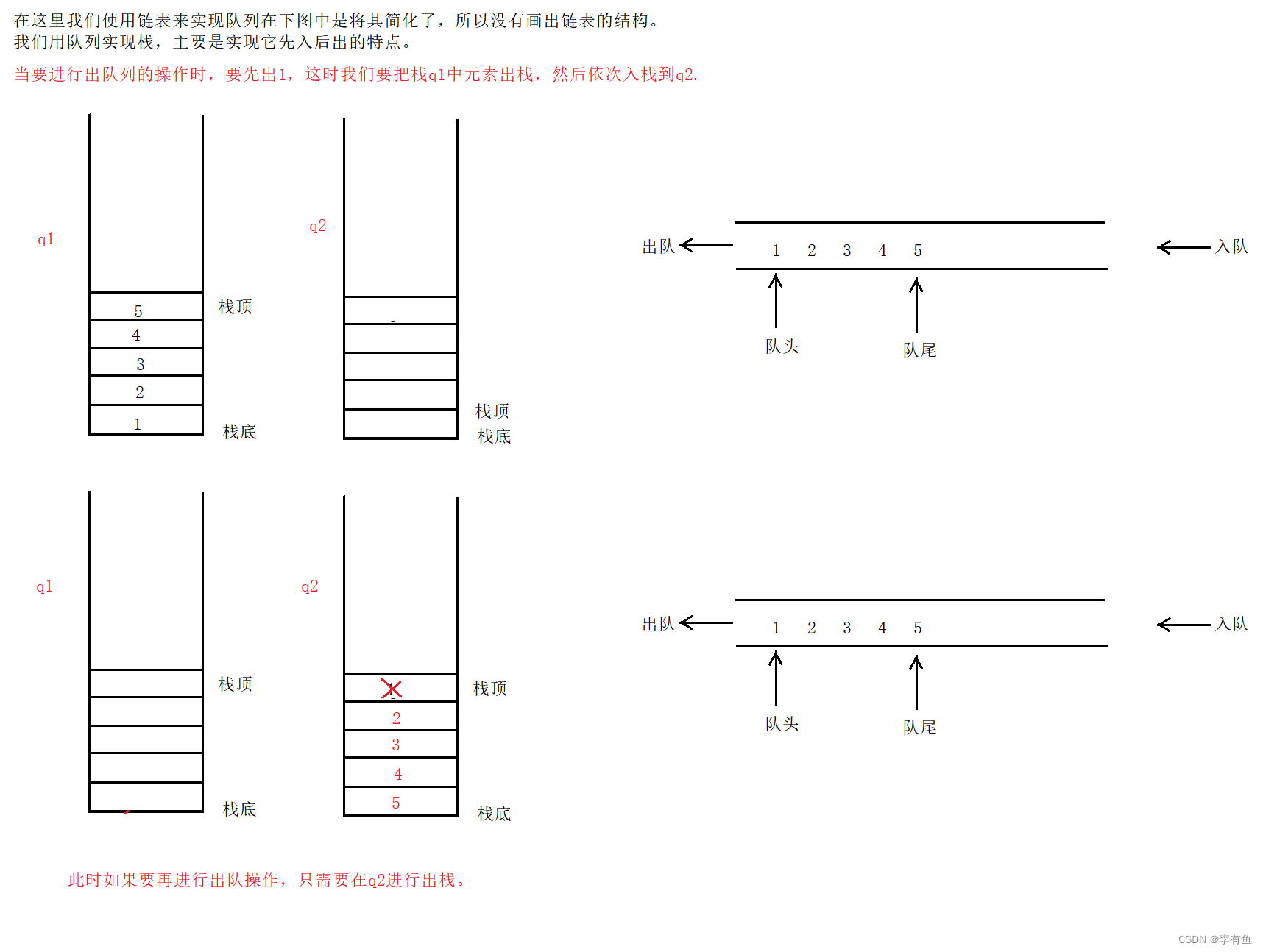
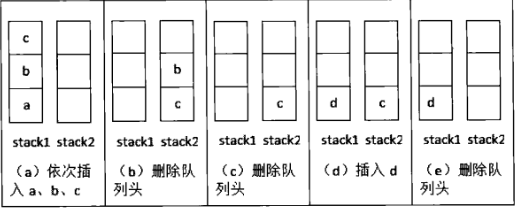
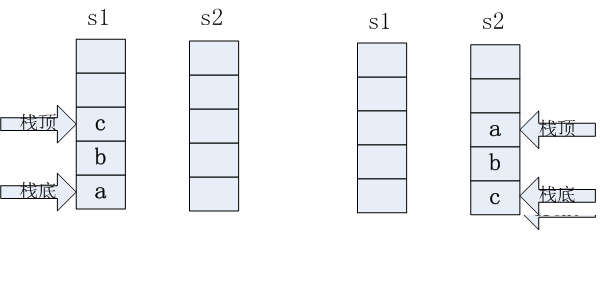
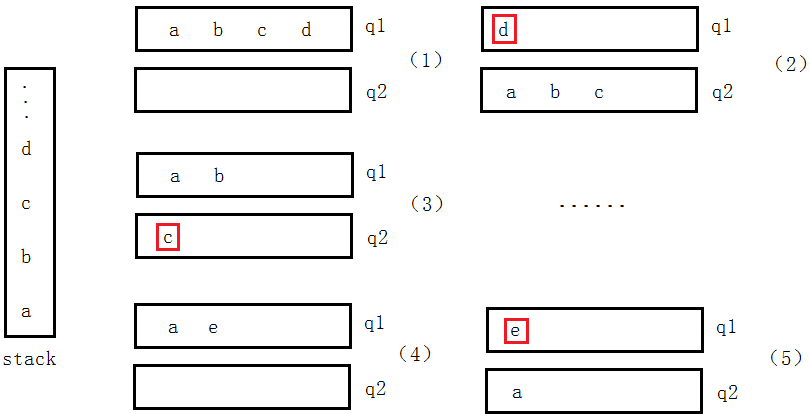
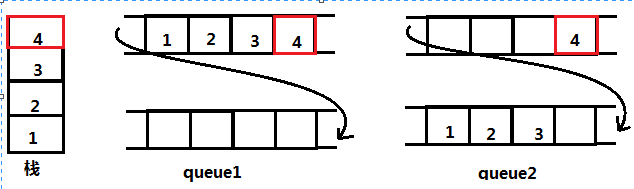
Two queue to stack规则:(重点理解规则)
如何入栈:直接向q2里边入
如何出栈:首先判断q2里面有没有值,如果q2不空,将q2除了最后一个数据外,剩余数据全部放在q1中,这时候q2仅仅剩下一个数据,这时候就可以出出来了;如果q2为空,代表着值都在q1里,将q1除了最后一个数据外,剩余数据全部放在q2中,这时候q1仅仅剩下一个数据,这时候就可以出出来了。
先写头文件two_queue_to_stack.h(这个依旧是用了链式队列的头文件list_queue.h链式队列-基础数据结构_hi332516_1的博客-CSDN博客)
#pragma once
#include"list_queue.h" //用两个队列模拟实现的栈的结构体声明
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;//用两个队列实现的栈的结构体声明
typedef struct Two_queue_stack
{struct LQueue q1;//是之前自己实现过的顺序栈struct LQueue q2;
}Two_queue_stack, * PTwo_queue_stack;//初始化
void my_Init_two_queue_stack(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);//入栈
bool my_Push(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE val);//出栈(还需要一个输出参数,帮助将出栈的值带出来)
bool my_Pop(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE* rtval);//获取队头元素值(还需要一个输出参数,帮助将出队的值带出来)
bool my_Top(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE* rtval);//判空
bool my_IsEmpty(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);//有效元素个数
int my_Get_length(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);//打印
void my_Show(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);//清空
void my_Clear(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);//销毁
void my_Destroy(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs);再写two_queue_to_stack.cpp文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"list_queue.h"
#include"two_queue_to_stack.h"//初始化
void my_Init_two_queue_stack(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{Init_LQueue(&tqs->q1);//直接调用q1和q2自身的初始化函数即可Init_LQueue(&tqs->q2);
}//入栈
bool my_Push(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE val)
{return Push(&tqs->q2, val);
}//出栈(还需要一个输出参数,帮助将出栈的值带出来)
bool my_Pop(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE* rtval)
{//assertif (my_IsEmpty(tqs))//确保了自己模拟实现的栈里一定有数据,只是要么在左边,要么在右边{return false;}if (!IsEmpty(&tqs->q2))//q2不空,直接出(仅剩一个元素,其他的全部挪到另一个中){int len = Get_length(&tqs->q2);while (len > 1){ELEM_TYPE tmp;Pop(&tqs->q2, &tmp);//直接调用q1和q2自身的入队函数即可Push(&tqs->q1, tmp);len--;}return Pop(&tqs->q2, rtval);}else//如果q2为空,确定值都在q1中{int len = Get_length(&tqs->q2);while (len > 1){ELEM_TYPE tmp;Pop(&tqs->q1, &tmp);//直接调用q1和q2自身的入队函数即可Push(&tqs->q2, tmp);len--;}return Pop(&tqs->q1, rtval);}
}//获取队头元素值(还需要一个输出参数,帮助将出队的值带出来)
bool my_Top(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs, ELEM_TYPE* rtval)
{//assertif (my_IsEmpty(tqs))//确保了自己模拟实现的栈里一定有数据,只是要么在左边,要么在右边{return false;}if (!IsEmpty(&tqs->q2))//q2不空,直接出(仅剩一个元素,其他的全部挪到另一个中){int len = Get_length(&tqs->q2);while (len > 1){ELEM_TYPE tmp;Pop(&tqs->q2, &tmp);//直接调用q1和q2自身的入队函数即可Push(&tqs->q1, tmp);len--;}Pop(&tqs->q2, rtval);Push(&tqs->q1, *rtval);return true;}else//如果q2为空,确定值都在q1中{int len = Get_length(&tqs->q2);while (len > 1){ELEM_TYPE tmp;Pop(&tqs->q1, &tmp);//直接调用q1和q2自身的入队函数即可Push(&tqs->q2, tmp);len--;}Pop(&tqs->q1, rtval);Push(&tqs->q2, *rtval);return true;}
}//判空
bool my_IsEmpty(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{if (IsEmpty(&tqs->q1) && IsEmpty(&tqs->q2)){return true;}return false;
}//有效元素个数
int my_Get_length(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{return Get_length(&tqs->q1) + Get_length(&tqs->q2);
}//打印
void my_Show(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{Show(&tqs->q1);Show(&tqs->q2);
}//清空
void my_Clear(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{Clear(&tqs->q1);Clear(&tqs->q2);
}//销毁
void my_Destroy(struct Two_queue_stack* tqs)
{Destroy(&tqs->q1);Destroy(&tqs->q2);
}在主函中测试所写代码的正确性
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<vld.h>
#include"two_queue_to_stack.h"//两个队列模拟实现一个栈的测试用例
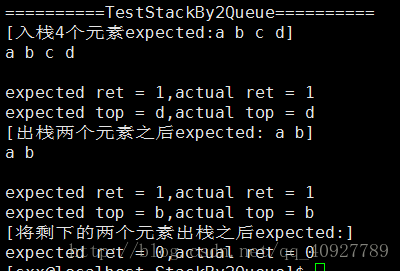
int main()
{struct Two_queue_stack head;my_Init_two_queue_stack(&head);for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){my_Push(&head, i);}my_Show(&head);ELEM_TYPE flag;bool tag = my_Pop(&head, &flag);if (tag){printf("Pop = %d\n", flag);}my_Show(&head);for (int i = 4; i <= 6; i++){my_Push(&head, i);}my_Show(&head);my_Pop(&head, &flag);printf("Pop = %d\n", flag);my_Pop(&head, &flag);printf("Pop = %d\n", flag);my_Pop(&head, &flag);printf("Pop = %d\n", flag);my_Pop(&head, &flag);printf("Pop = %d\n", flag);printf("length = %d\n", my_Get_length(&head));my_Top(&head, &flag);printf("Top = %d\n", flag);printf("length = %d\n", my_Get_length(&head));my_Destroy(&head);return 0;
}测试结果