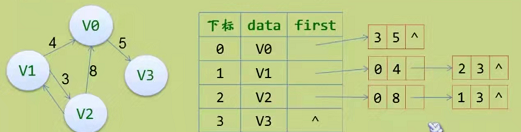
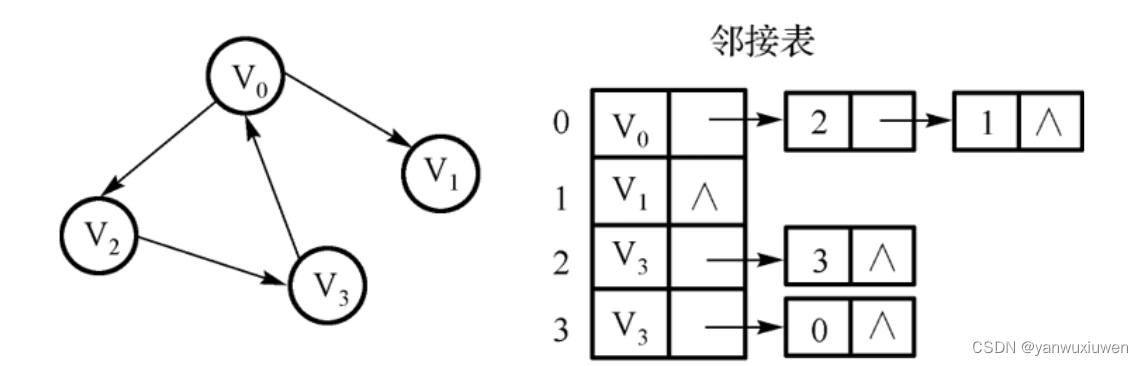
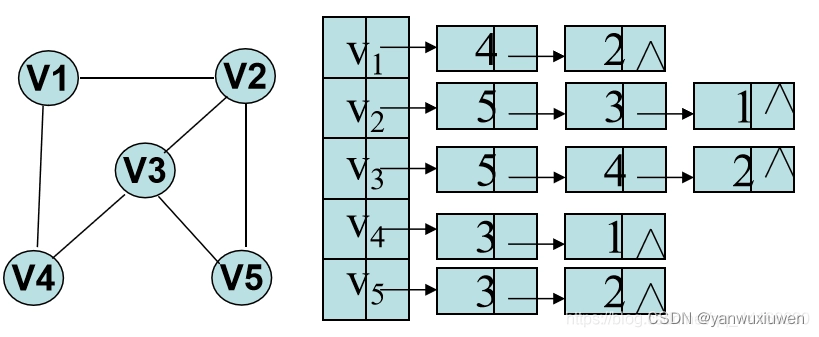
邻接表
图的邻接表存储方法跟树的孩子链表示法相类似,是一种顺序分配和链式分配相结合的存储结构。如这个表头结点所对应的顶点存在相邻顶点,则把相邻顶点依次存放于表头结点所指向的单向链表中。如词条概念图所示,表结点存放的是邻接顶点在数组中的索引。对于无向图来说,使用邻接表进行存储也会出现数据冗余,表头结点A所指链表中存在一个指向C的表结点的同时,表头结点C所指链表也会存在一个指向A的表结点。 [1]
邻接表是图的一种最主要存储结构,用来描述图上的每一个点。对图的每个顶点建立一个容器(n个顶点建立n个容器),第i个容器中的结点包含顶点Vi的所有邻接顶点。实际上我们常用的邻接矩阵就是一种未离散化每个点的边集的邻接表。
在有向图中,描述每个点向别的节点连的边(点a->点b这种情况)。
在无向图中,描述每个点所有的边(点a-点b这种情况)
与邻接表相对应的存图方式叫做边集表,这种方法用一个容器存储所有的边。
总代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define QUEUE_SIZE 10int* visitedPtr;typedef struct Graph{int** connections;int numNodes;
} *GraphPtr;//初始化
GraphPtr initGraph(int paraSize, int** paraData) {int i, j;GraphPtr resultPtr = (GraphPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));resultPtr -> numNodes = paraSize;//resultPtr -> connections = (int**)malloc(paraSize * paraSize * sizeof(int));resultPtr -> connections = (int**)malloc(paraSize * sizeof(int*));for (i = 0; i < paraSize; i ++) {resultPtr -> connections[i] = (int*)malloc(paraSize * sizeof(int));for (j = 0; j < paraSize; j ++) {resultPtr -> connections[i][j] = paraData[i][j];}//Of for j}//Of for ireturn resultPtr;
}//Of initGraph//创建队列
typedef struct GraphNodeQueue{int* nodes;int front;int rear;
}GraphNodeQueue, *QueuePtr;//初始化队列
QueuePtr initQueue(){QueuePtr resultQueuePtr = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphNodeQueue));resultQueuePtr->nodes = (int*)malloc(QUEUE_SIZE * sizeof(int));resultQueuePtr->front = 0;resultQueuePtr->rear = 1;return resultQueuePtr;
}//Of initQueue//判断队列是否为空
bool isQueueEmpty(QueuePtr paraQueuePtr){if ((paraQueuePtr->front + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE == paraQueuePtr->rear) {return true;}return false;
}//Of isQueueEmpty//入队
void enqueue(QueuePtr paraQueuePtr, int paraNode){if ((paraQueuePtr->rear + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE == paraQueuePtr->front % QUEUE_SIZE) {printf("Error, trying to enqueue %d. queue full.\r\n", paraNode);return;}//Of ifparaQueuePtr->nodes[paraQueuePtr->rear] = paraNode;paraQueuePtr->rear = (paraQueuePtr->rear + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE;
}//Of enqueue//出队
int dequeue(QueuePtr paraQueuePtr){if (isQueueEmpty(paraQueuePtr)) {printf("Error, empty queue\r\n");return NULL;}paraQueuePtr->front = (paraQueuePtr->front + 1) % QUEUE_SIZE;return paraQueuePtr->nodes[paraQueuePtr->front];
}typedef struct AdjacencyNode {int column;struct AdjacencyNode* next;
}AdjacencyNode, *AdjacentNodePtr;typedef struct AdjacencyList {int numNodes;AdjacencyNode* headers;
}AdjacencyList, *AdjacencyListPtr;AdjacencyListPtr graphToAdjacentList(GraphPtr paraPtr) {int i, j, tempNum;AdjacentNodePtr p, q;tempNum = paraPtr->numNodes;AdjacencyListPtr resultPtr = (AdjacencyListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct AdjacencyList));resultPtr->numNodes = tempNum;resultPtr->headers = (AdjacencyNode*)malloc(tempNum * sizeof(struct AdjacencyNode));//Fill the data.for (i = 0; i < tempNum; i ++) {//初始化头节点 p = &(resultPtr->headers[i]);p->column = -1;p->next = NULL;for (j = 0; j < tempNum; j ++) {if (paraPtr->connections[i][j] > 0) {//Create a new node.q = (AdjacentNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct AdjacencyNode));q->column = j;q->next = NULL;//Link.p->next = q;p = q;}}}return resultPtr;
}void printAdjacentList(AdjacencyListPtr paraPtr) {int i;AdjacentNodePtr p;int tempNum = paraPtr->numNodes;printf("This is the graph:\r\n");for (i = 0; i < tempNum; i ++) {p = paraPtr->headers[i].next;while (p != NULL) {printf("%d, ", p->column);p = p->next;}printf("\r\n");}
}//广度优先
void widthFirstTranverse(AdjacencyListPtr paraListPtr, int paraStart){printf("width first \r\n");//Use a queue to manage the pointersint i, j, tempNode;AdjacentNodePtr p;i = 0;//Initialize datavisitedPtr = (int*) malloc(paraListPtr->numNodes * sizeof(int));for (i = 0; i < paraListPtr->numNodes; i ++) {visitedPtr[i] = 0;}//Of for iQueuePtr tempQueuePtr = initQueue();printf("%d\t", paraStart);visitedPtr[paraStart] = 1;enqueue(tempQueuePtr, paraStart);while (!isQueueEmpty(tempQueuePtr)) {tempNode = dequeue(tempQueuePtr);for (p = &(paraListPtr->headers[tempNode]); p != NULL; p = p->next) {j = p->column;if (visitedPtr[j]) continue;printf("%d\t", j);visitedPtr[j] = 1;enqueue(tempQueuePtr, j);}}printf("\r\n");
}void testGraphTranverse() {int i, j;int myGraph[5][5] = { {0, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}};int** tempPtr;printf("Preparing data\r\n");tempPtr = (int**)malloc(5 * sizeof(int*));for (i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {tempPtr[i] = (int*)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));}for (i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {for (j = 0; j < 5; j ++) {tempPtr[i][j] = myGraph[i][j];}}printf("Data ready\r\n");GraphPtr tempGraphPtr = initGraph(5, tempPtr);AdjacencyListPtr tempListPtr = graphToAdjacentList(tempGraphPtr);printAdjacentList(tempListPtr);widthFirstTranverse(tempListPtr, 4);
}int main(){testGraphTranverse();return 1;
}
测试结果
Preparing data
Data ready
This is the graph:
1, 3,
0, 2, 4,
1, 3, 4,
0, 2,
1, 2,
width first
4 1 2 0 3