1、背景
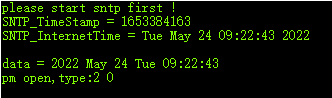
由于项目中的数据对时间比较敏感,目前常常出现校时问题,导致时间偏差,出现曲线数据丢失和曲线数据重复等问题。
因此对sntp源码进行深入分析。
要了解SNTP,首先需要了解NTP协议。SNTP是NTP的子集,简化了NTP的许多算法和步骤,得到了效率,但时间的精度不如NTP,可是对于民用时间来说足够了,大概最多差距几秒的样子。NTP(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)是由RFC 1305定义的时间同步协议,用来在分布式时间服务器和客户端之间进行时间同步。NTP基于UDP报文进行传输,使用的UDP端口号为123。使用NTP的目的是对网络内所有具有时钟的设备进行时钟同步,使网络内所有设备的时钟保持一致,从而使设备能够提供基于统一时间的多种应用。
NTP原理,就是4个时间,假设A时客户端侧,B时服务器
报文离开A时A的时间戳T1,到达B时B的时间戳T2,离开B时B的时间戳T3,到达A时A的时间戳T4,那么在A和B之间来回传输的时间差&T=(T4-T1) - (T3-T2).
那么A和B之间时钟的差=(T2-T1) - &T= (T2-T1)- ((T4-T1)-(T3-T2))/2 = ((T2-T1)+(T3-T4))/2
1.1 参考文档
SNTP简介_PUSONG568的博客-CSDN博客_sntp端口要了解SNTP,首先需要了解NTP协议。SNTP是NTP的子集,简化了NTP的许多算法和步骤,得到了效率,但时间的精度不如NTP,可是对于民用时间来说足够了,大概最多差距几秒的样子。 NTP(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)是由RFC 1305定义的时间同步协议,用来在分布式时间服务器和客户端之间进行时间同步。NTP基于UDP报文进行传输,使用的UDP端口号为123。 使...https://blog.csdn.net/PUSONG568/article/details/80845458
2、SNTP源码分析
一旦时间同步,ESP32将使用内置定时器来执行记时。
RTC时钟用于芯片处于深度睡眠模式时保持准确的时间。
High-resolution定时器用于在ESP32运行时提供微妙精度的时间。

2.1 设置操作模式
/** The operating mode */
static u8_t sntp_opmode;/** The UDP pcb used by the SNTP client */
static struct udp_pcb *sntp_pcb;.....
/*** @ingroup sntp* Sets the operating mode.* @param operating_mode one of the available operating modes*/
void sntp_setoperatingmode(u8_t operating_mode)
{LWIP_ASSERT("Invalid operating mode", operating_mode <= SNTP_OPMODE_LISTENONLY);LWIP_ASSERT("Operating mode must not be set while SNTP client is running", sntp_pcb == NULL);sntp_opmode = operating_mode;
}可选的模式就两种:轮询SNTP_OPMODE_POLL和只监听SNTP_OPMODE_LISTENONLY。
2.2 设置服务器hostname
/*** Initialize one of the NTP servers by name** @param numdns the index of the NTP server to set must be < SNTP_MAX_SERVERS* @param dnsserver DNS name of the NTP server to set, to be resolved at contact time*/
void sntp_setservername(u8_t idx, char *server)
{if (idx < SNTP_MAX_SERVERS){sntp_servers[idx].name = server;}
}支持设置多个NTP服务器时间同步源。
2.3 初始化SNTP模块,并发出请求
/*** @ingroup sntp* Initialize this module.* Send out request instantly or after SNTP_STARTUP_DELAY(_FUNC).*/
void sntp_init(void)
{
#ifdef SNTP_SERVER_ADDRESS
#if SNTP_SERVER_DNSsntp_setservername(0, SNTP_SERVER_ADDRESS);
#else
#error SNTP_SERVER_ADDRESS string not supported SNTP_SERVER_DNS==0
#endif
#endif /* SNTP_SERVER_ADDRESS */if (sntp_pcb == NULL){sntp_pcb = udp_new_ip_type(IPADDR_TYPE_ANY);LWIP_ASSERT("Failed to allocate udp pcb for sntp client", sntp_pcb != NULL);if (sntp_pcb != NULL){udp_recv(sntp_pcb, sntp_recv, NULL);if (sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_POLL){SNTP_RESET_RETRY_TIMEOUT();
#if SNTP_STARTUP_DELAYsys_timeout((u32_t)SNTP_STARTUP_DELAY_FUNC, sntp_request, NULL);
#elsesntp_request(NULL);
#endif}else if (sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_LISTENONLY){ip_set_option(sntp_pcb, SOF_BROADCAST);udp_bind(sntp_pcb, IP_ANY_TYPE, SNTP_PORT);}}}
}上述源码中有创建udp client和设置udp的接收回调函数为sntp_recv,该回调函数具体实现见之后的说明。
2.4 接收回调函数
/** UDP recv callback for the sntp pcb */
static void
sntp_recv(void *arg, struct udp_pcb *pcb, struct pbuf *p, const ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t port)
{u8_t mode;u8_t stratum;u32_t receive_timestamp[SNTP_RECEIVE_TIME_SIZE];err_t err;LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(pcb);/* packet received: stop retry timeout */sys_untimeout(sntp_try_next_server, NULL);sys_untimeout(sntp_request, NULL);err = ERR_ARG;
#if SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 1/* check server address and port */if (((sntp_opmode != SNTP_OPMODE_POLL) || ip_addr_cmp(addr, &sntp_last_server_address)) &&(port == SNTP_PORT))
#else /* SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 1 */LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(addr);LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(port);
#endif /* SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 1 */{/* process the response */if (p->tot_len == SNTP_MSG_LEN){pbuf_copy_partial(p, &mode, 1, SNTP_OFFSET_LI_VN_MODE);mode &= SNTP_MODE_MASK;/* if this is a SNTP response... */if (((sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_POLL) && (mode == SNTP_MODE_SERVER)) ||((sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_LISTENONLY) && (mode == SNTP_MODE_BROADCAST))){pbuf_copy_partial(p, &stratum, 1, SNTP_OFFSET_STRATUM);if (stratum == SNTP_STRATUM_KOD){/* Kiss-of-death packet. Use another server or increase UPDATE_DELAY. */err = SNTP_ERR_KOD;LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_STATE, ("sntp_recv: Received Kiss-of-Death\n"));}else{
#if SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 2/* check originate_timetamp against sntp_last_timestamp_sent */u32_t originate_timestamp[2];pbuf_copy_partial(p, &originate_timestamp, 8, SNTP_OFFSET_ORIGINATE_TIME);if ((originate_timestamp[0] != sntp_last_timestamp_sent[0]) ||(originate_timestamp[1] != sntp_last_timestamp_sent[1])){LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_WARN, ("sntp_recv: Invalid originate timestamp in response\n"));}else
#endif /* SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 2 *//* @todo: add code for SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 3 and >= 4 here */{/* correct answer */err = ERR_OK;pbuf_copy_partial(p, &receive_timestamp, SNTP_RECEIVE_TIME_SIZE * 4, SNTP_OFFSET_TRANSMIT_TIME);}}}else{LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_WARN, ("sntp_recv: Invalid mode in response: %" U16_F "\n", (u16_t)mode));/* wait for correct response */err = ERR_TIMEOUT;}}else{LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_WARN, ("sntp_recv: Invalid packet length: %" U16_F "\n", p->tot_len));}}
#if SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 1else{/* packet from wrong remote address or port, wait for correct response */err = ERR_TIMEOUT;}
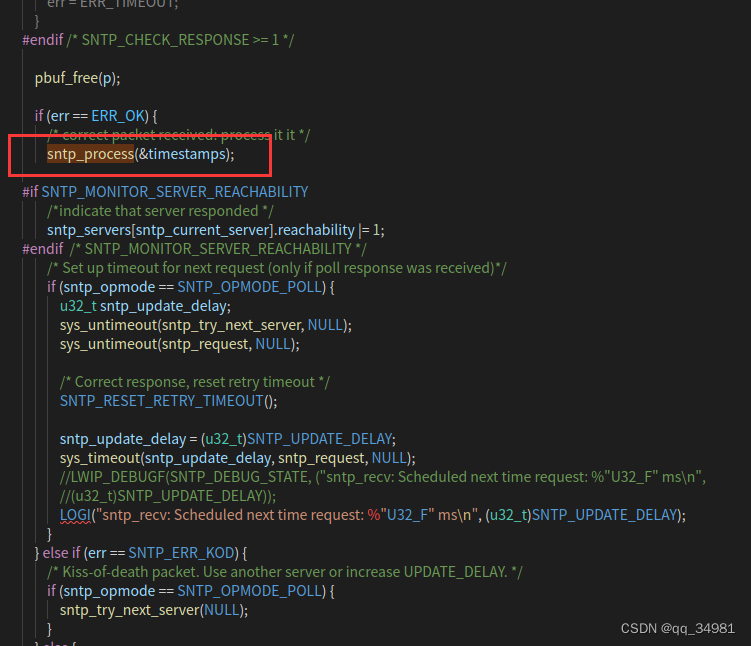
#endif /* SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE >= 1 */pbuf_free(p);if (err == ERR_OK){sntp_process(receive_timestamp);/* Set up timeout for next request (only if poll response was received)*/if (sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_POLL){/* Correct response, reset retry timeout */SNTP_RESET_RETRY_TIMEOUT();sys_timeout((u32_t)SNTP_UPDATE_DELAY, sntp_request, NULL);LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_STATE, ("sntp_recv: Scheduled next time request: %" U32_F " ms\n",(u32_t)SNTP_UPDATE_DELAY));}}else if (err != ERR_TIMEOUT){/* Errors are only processed in case of an explicit poll response */if (sntp_opmode == SNTP_OPMODE_POLL){if (err == SNTP_ERR_KOD){/* Kiss-of-death packet. Use another server or increase UPDATE_DELAY. */sntp_try_next_server(NULL);}else{/* another error, try the same server again */sntp_retry(NULL);}}}
}/** Main packet buffer struct */
struct pbuf {/** next pbuf in singly linked pbuf chain */struct pbuf *next;/** pointer to the actual data in the buffer */void *payload;/*** total length of this buffer and all next buffers in chain* belonging to the same packet.** For non-queue packet chains this is the invariant:* p->tot_len == p->len + (p->next? p->next->tot_len: 0)*/u16_t tot_len;/** length of this buffer */u16_t len;/** pbuf_type as u8_t instead of enum to save space */u8_t /*pbuf_type*/ type;/** misc flags */u8_t flags;/*** the reference count always equals the number of pointers* that refer to this pbuf. This can be pointers from an application,* the stack itself, or pbuf->next pointers from a chain.*/u16_t ref;#if ESP_LWIPstruct netif *l2_owner;void *l2_buf;
#endif
}; 
这里有对NTP报文的解析
1.LI 闰秒标识器,占用2bits
2.VN版本号,占用3bits,标识NTP的版本号,现为3
3.Mode模式,占用3bit,标识模式,具体如下
检查总长度==SNTP_MSG_LEN(48字节),解析Mode字段---首字节的低三bits---指示协议模式。
| Mode | 定义 |
| 0 | 保留 |
| 1 | 对称主动 |
| 2 | 对称被动 |
| 3 | 客户 |
| 4 | 服务器 |
| 5 | 广播 |
| 6 | 保留为NTP控制信息 |
| 7 | 保留为用户定义 |
在单播或多播模式时,客户请求把这个字段设置为3,服务器在响应时把这个字段设置为4.
广播时,服务器把这个字段设置为5。
4.stratum(层),占用8bits
解析Stratum---->SNTP_STRATUM_KOD
其他则
pbuf_copy_partial(p, &receive_timestamp, SNTP_RECEIVE_TIME_SIZE * 4, SNTP_OFFSET_TRANSMIT_TIME);
获取Transmit Timestamp,即服务器向客户发时间戳的时间
recv的不是ntp应答报文,如果错误原因是SNTP_ERR_KOD,则尝试下一个时间同步源;
其他错误,则重新尝试一次。
/** Sanity check:* Define this to* - 0 to turn off sanity checks (default; smaller code)* - >= 1 to check address and port of the response packet to ensure the* response comes from the server we sent the request to.* - >= 2 to check returned Originate Timestamp against Transmit Timestamp* sent to the server (to ensure response to older request).* - >= 3 @todo: discard reply if any of the LI, Stratum, or Transmit Timestamp* fields is 0 or the Mode field is not 4 (unicast) or 5 (broadcast).* - >= 4 @todo: to check that the Root Delay and Root Dispersion fields are each* greater than or equal to 0 and less than infinity, where infinity is* currently a cozy number like one second. This check avoids using a* server whose synchronization source has expired for a very long time.*/
#if !defined SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE || defined __DOXYGEN__
#define SNTP_CHECK_RESPONSE 0
#endif5.Poll测试间隔,占用8bits,标识连续信息之间的最大间隔
6.Precision精度,占用8bits,标识本地时钟精度
7.Root Delay根时延,占用8bits,标识在主参考源之间往返的总共时延
8.Root Dispersion根离散,占用8bits,标识在主参考源有关的名义错误
9.Reference Identifier参考时钟标识符,占用8bits,用来标识特殊的参考源
10.参考时间戳,64bit时间戳,本地时钟被修改的最新时间
11、原始时间戳,客户端发送的时间,64bits
12、接收时间戳,服务端接收到的时间,64bits
13、发送时间戳,服务端发送应答的时间,64bits
14、认证符(可选)
2.5 NTP请求
/*** Send out an sntp request.** @param arg is unused (only necessary to conform to sys_timeout)*/
static void
sntp_request(void *arg)
{ip_addr_t sntp_server_address;err_t err;LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);/* initialize SNTP server address */
#if SNTP_SERVER_DNSif (sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].name){/* always resolve the name and rely on dns-internal caching & timeout */ip_addr_set_zero(&sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].addr);err = dns_gethostbyname(sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].name, &sntp_server_address,sntp_dns_found, NULL);if (err == ERR_INPROGRESS){/* DNS request sent, wait for sntp_dns_found being called */LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_STATE, ("sntp_request: Waiting for server address to be resolved.\n"));return;}else if (err == ERR_OK){sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].addr = sntp_server_address;}}else
#endif /* SNTP_SERVER_DNS */{sntp_server_address = sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].addr;err = (ip_addr_isany_val(sntp_server_address)) ? ERR_ARG : ERR_OK;}if (err == ERR_OK){LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_TRACE, ("sntp_request: current server address is %s\n",ipaddr_ntoa(&sntp_server_address)));sntp_send_request(&sntp_server_address);}else{/* address conversion failed, try another server */LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_WARN_STATE, ("sntp_request: Invalid server address, trying next server.\n"));sys_timeout((u32_t)SNTP_RETRY_TIMEOUT, sntp_try_next_server, NULL);}
}2.6 重试或下一个时间同步源
/*** Retry: send a new request (and increase retry timeout).** @param arg is unused (only necessary to conform to sys_timeout)*/
static void
sntp_retry(void *arg)
{LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_STATE, ("sntp_retry: Next request will be sent in %" U32_F " ms\n",sntp_retry_timeout));/* set up a timer to send a retry and increase the retry delay */sys_timeout(sntp_retry_timeout, sntp_request, NULL);#if SNTP_RETRY_TIMEOUT_EXP{u32_t new_retry_timeout;/* increase the timeout for next retry */new_retry_timeout = sntp_retry_timeout << 1;/* limit to maximum timeout and prevent overflow */if ((new_retry_timeout <= SNTP_RETRY_TIMEOUT_MAX) &&(new_retry_timeout > sntp_retry_timeout)){sntp_retry_timeout = new_retry_timeout;}}
#endif /* SNTP_RETRY_TIMEOUT_EXP */
}static void
sntp_try_next_server(void *arg)
{u8_t old_server, i;LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);old_server = sntp_current_server;for (i = 0; i < SNTP_MAX_SERVERS - 1; i++){sntp_current_server++;if (sntp_current_server >= SNTP_MAX_SERVERS){sntp_current_server = 0;}if (!ip_addr_isany(&sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].addr)
#if SNTP_SERVER_DNS|| (sntp_servers[sntp_current_server].name != NULL)
#endif){LWIP_DEBUGF(SNTP_DEBUG_STATE, ("sntp_try_next_server: Sending request to server %" U16_F "\n",(u16_t)sntp_current_server));/* new server: reset retry timeout */SNTP_RESET_RETRY_TIMEOUT();/* instantly send a request to the next server */sntp_request(NULL);return;}}/* no other valid server found */sntp_current_server = old_server;sntp_retry(NULL);
}4、问题解决
参考SDK4.1内的代码,处理时延和使用adjtime函数加快或减慢时钟来靠近目标时间。adjtime在35Min内调用成功,否则失败。由于这个调整是一个长时间的操作,只有直接设置系统时间才可以结束时钟调整。如需加快,用户需要自己设置结束条件,达到结束条件后,直接调用设置系统时间函数结束调整。
校时源不稳定,导致校时不准。推荐使用商业NTP公共服务器,国内推荐使用阿里/腾讯的。如无特殊需要,24小时校时一次即可。