1.虚基类的作用
类B与类C都为类D的基类,而类A为类B与类C的基类,因此类D会继承类B与类C的多份同名成员。如下图所示:
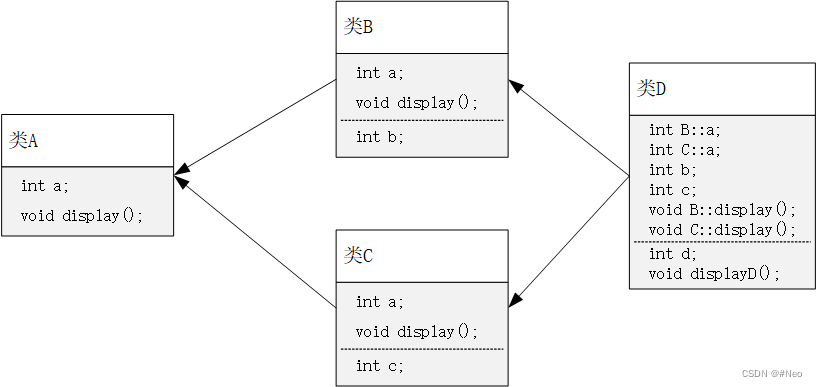
在引用这些同名成员时,必须在派生类对象后增加直接基类名,以避免产生二义性,如:D d; d.B::display();
在这种继承方式下,会保留多份数据成员的拷贝,不仅占用内存还会增加访问成员时的困难。
C++提供了虚基类使得在继承共同间接基类时只保留一份成员。
2.虚基类的声明
因为类B与类C都继承自类A,因此将类A声明为虚基类,这样类D通过类B与类C间接继承的类A只继承一次,即只保留类A的一份成员。
声明类A为虚基类:
class A
{…};
class B:virtual public A
{…};
class C:virtual public A
{…};
虚基类并不是在声明基类时声明的,而是在声明派生类时,指定继承方式声明的。
声明虚基类的一般形式为:
class 派生类名:virtual 继承方式 基类名
3.虚基类的初始化
如果在虚基类中定义了带参数的构造函数,而且没有定义默认构造函数,则在其所有派生类(直接派生或间接派生)中,通过构造函数的初始化表对虚基类进行初始化。
在最后的派生类中不仅要负责对其直接基类进行初始化,还要负责对虚基类的初始化。
C++编译系统只执行最后的派生类对虚基类的构造函数的调用,而忽略基类的其它派生类(如类B与类C)对虚基类的构造函数的调用,这就保证了虚基类的数据成员不会被多次初始化。
4.虚基类实例代码
Person类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_PERSON_H
#define PROJECT5_PERSON_H#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;class Person {
protected:string name;char gender;
public:Person(string n, char g) : name(n), gender(g) {}void display() {cout << "name: " << name << endl;cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;}
};#endif //PROJECT5_PERSON_HStudent类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#define PROJECT5_STUDENT_H#include <string>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;class Student : virtual public Person {
protected:double score;
public:Student(string n, char g, double s) : Person(n, g), score(s) {};
};#endif //PROJECT5_STUDENT_HTeacher类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#define PROJECT5_TEACHER_H#include <string>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;class Teacher : virtual public Person {
protected:string title;
public:Teacher(string n, char g, string t) : Person(n, g), title(t) {};
};#endif //PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
Graduate类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#define PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H#include "Teacher.h"
#include "Student.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;class Graduate : public Teacher, public Student{
private:double wage;
public:Graduate(string n, char g, double s, string t, double w) : Person(n, g), Student(n, g, s), Teacher(n, g, t), wage(w) {};void display() {Person::display();cout << "score: " << score << endl;cout << "title: " << title << endl;cout << "wages: " << wage << endl;};
};#endif //PROJECT5_GRADUATE_Hmain:
#include <iostream>
#include "Graduate.h"
using namespace std;int main() {Graduate grad1("neo",'f',88,"教授",1234.5);grad1.display();return 0;
}