目的:
前几天在开发过程中遇到一个需求: 读取一个大约5G的csv文件内容,将其转化为对象然后存储到redis中, 想着直接开大内存直接load 进入到内存中就行了,结果可想而知,5G的文件 ,Xmx 开到10G都没有解决,直接out of Memory 异常

1、读入大文件
① 直接load 进入到内存中
这种处理大文件很容易造成 内存不够的问题
String path = "F:\\originData\\snapshotDepth\\2022-06-20\\sh_stock_now.csv";File testFile = new File(path);List<String> file = FileUtil.readLines(testFile, Charset.defaultCharset());这种 500M的文件,堆内存一般会占用2.5G ,那么如果你去读一个5G的文件,那么内存直接起飞,所以这种不建议使用
② 按照行读取文件
String path = "F:\\originData\\snapshotDepth\\2022-06-20\\sh_stock_now.csv";Scanner scanner = null;try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path)) {scanner = new Scanner(fileInputStream);while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {String line = scanner.nextLine();log.info("对应的行的信息---{}", line);}} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("捕获到异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}这种因为是有按照一行行读取到内存当中, 所以耗时肯定增加
③ 使用common io 中的函数
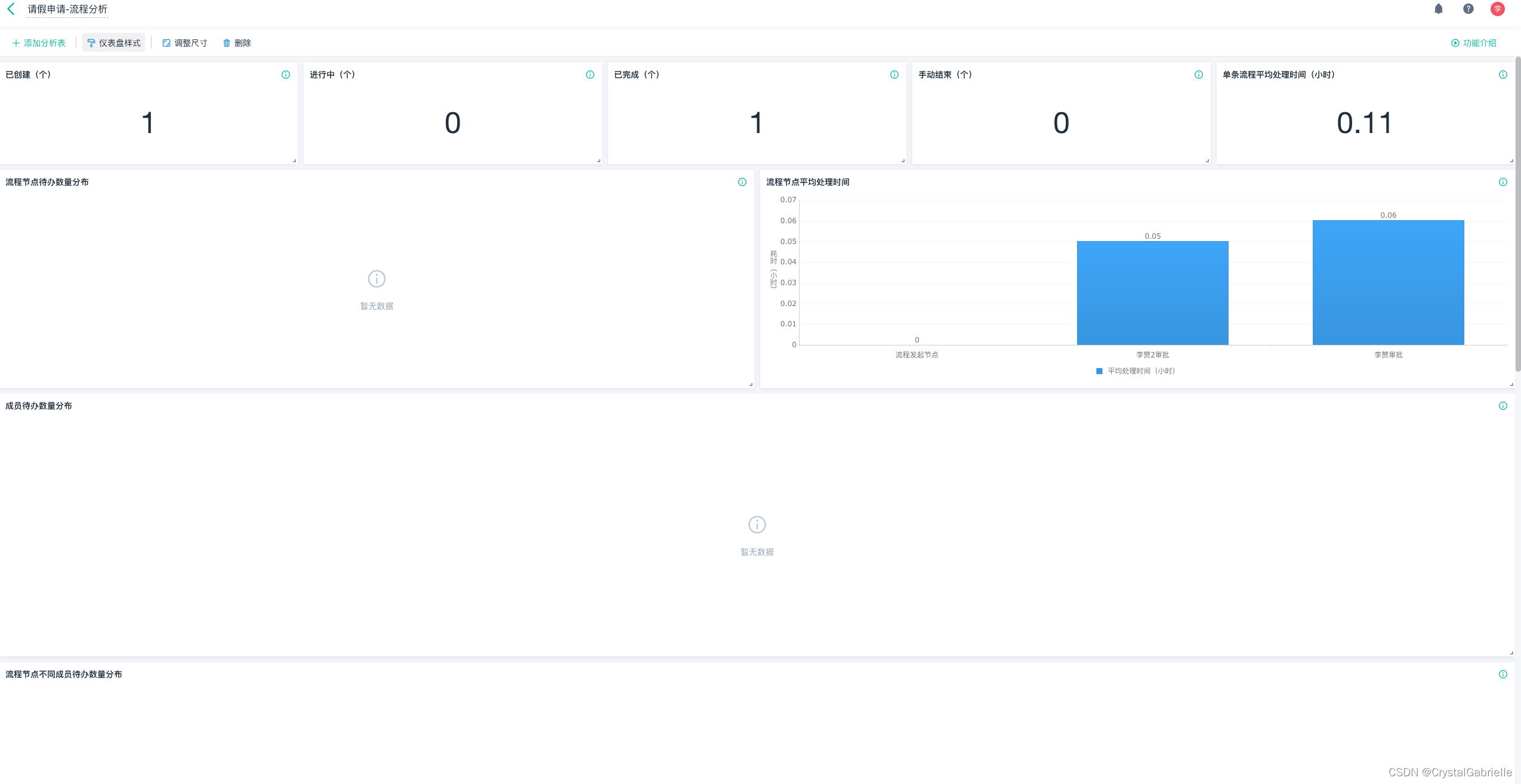
public void testCommon() {String path = "F:\\originData\\snapshotDepth\\2022-06-20\\sh_stock_now.csv";File file = new File(path);try {Integer count = 0;Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();final LineIterator lineIterator = FileUtils.lineIterator(file, "utf-8");while (lineIterator.hasNext()) {count++;String line = lineIterator.nextLine();if (count % 1000000 == 0) {Long stepTime = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("读取100w 数据耗时为---{}", stepTime - startTime);startTime = stepTime;}}} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("读取文件异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}}运行结果:
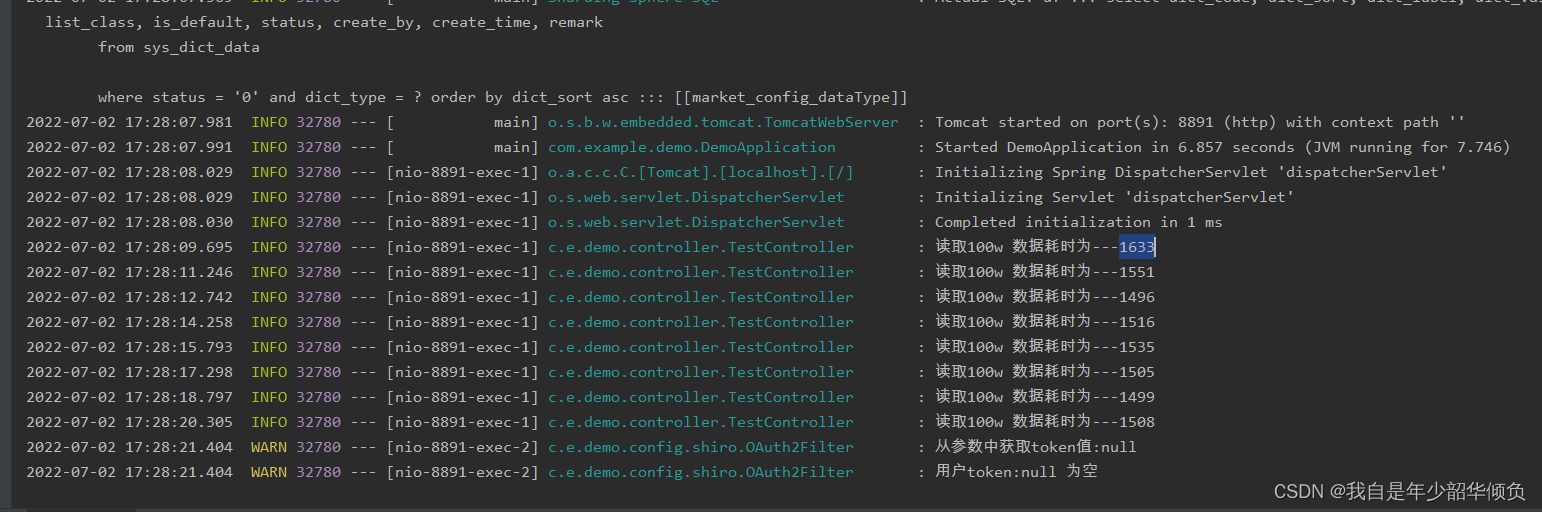
每100w行的数据 大概耗时为1.5秒, 这个是在我的笔记本上运行的结果,如果在性能更好的机器上速度应该更快。
2、写入文件
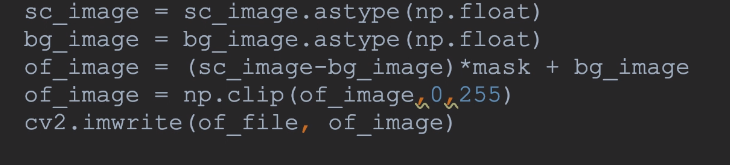
log.info("开始对FileWriter 写入文件进行计时");Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();String path = "F:\\originData\\test.txt";String content = "12312313";for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(path, true)) {fileWriter.append(content);} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("捕获到异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}}Long stepEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("FileWriter 耗时为----{}", stepEnd - startTime);String path2 = "F:\\originData\\test2.txt";log.info("开始对 BufferedWriter 写入文件进行计时");for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {try (BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(path2, true))) {bufferedWriter.append(content);} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("捕获到异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}}Long stepNextEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("BufferedWriter 耗时为----{}", stepNextEnd - stepEnd);log.info("开始对 BufferedOutputStream 写入文件进行计时");String path3 = "F:\\originData\\test3.txt";for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {try (BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path3, true))) {bufferedOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("捕获到异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}}Long stepNextStream = System.currentTimeMillis();log.info("BufferedWriter 耗时为----{}", stepNextStream - stepNextEnd);String path4 = "F:\\originData\\test4.txt";File file = new File(path4);try {if (!file.exists()) {file.createNewFile();}for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {FileUtils.write(file, content, true);}log.info("FileUtils 耗时为----{}", System.currentTimeMillis() - stepNextStream);} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("捕获到异常---{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);}运行结果
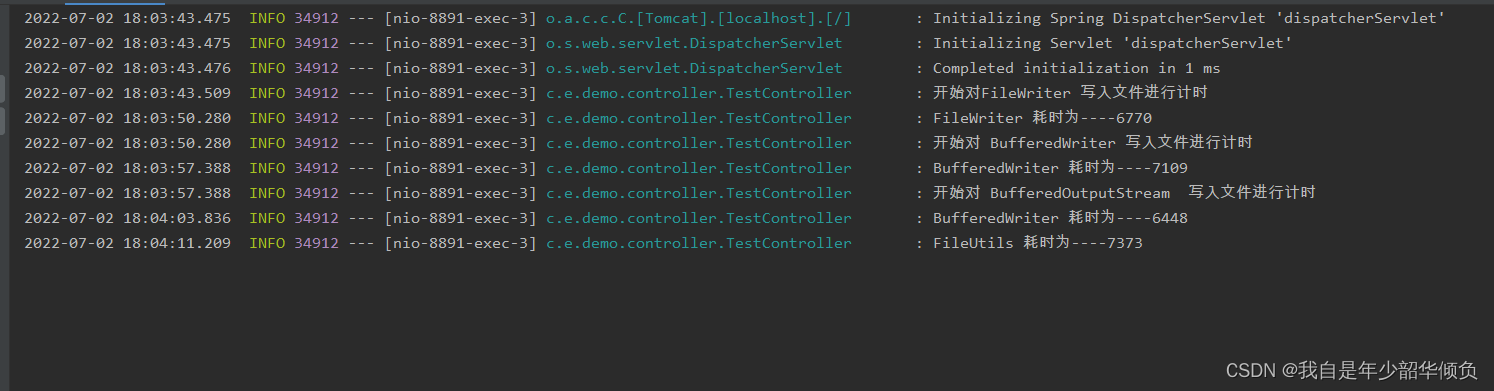
如果是写入字符串的话 还是建议使用BuffereOutputStream