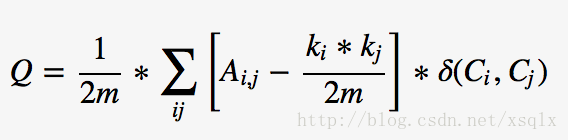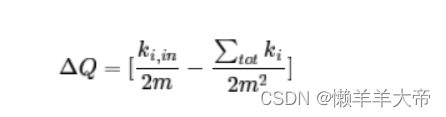Louvain社区划分算法及Java语言实现
- 社区划分算法处理的对象
- Louvain社区发现算法
- 全局模块度
- 单层算法过程
- 多层算法过程
- Java代码实现
- 图实现
- 模块度计算
- 单层louvain实现
- 多层louvain实现
- 运行入口,使用方法
社区划分算法处理的对象
社区划分算法又称社区发现算法,针对网络数据结构,把联系紧密度比较高的节点划分为一个组。一个社区可以代表“物以类聚人以群分”、“家族”、“流量”、“属性相似”等概念,有很大的应用前景。
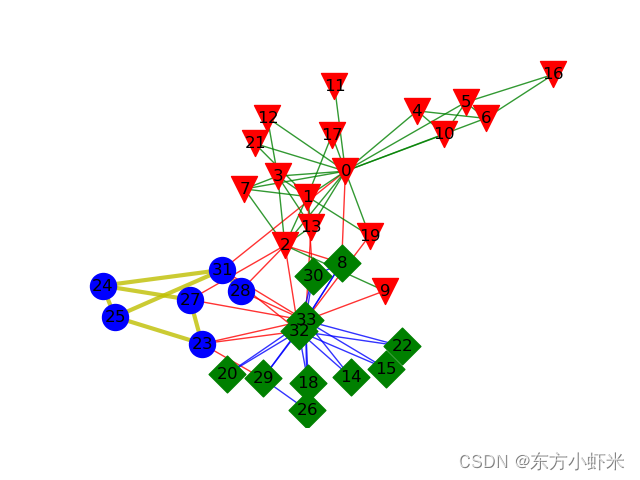
Louvain社区发现算法
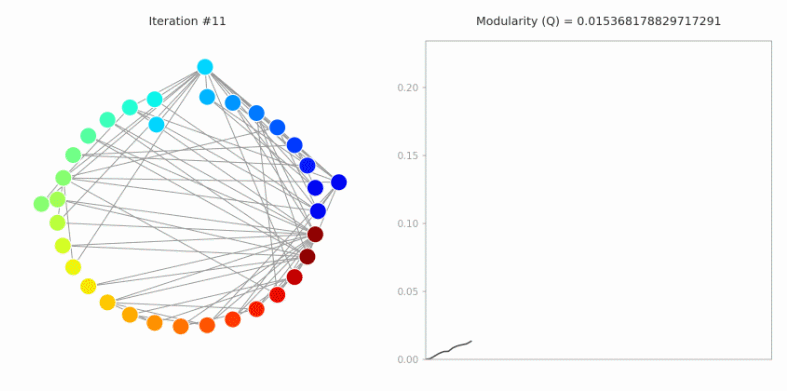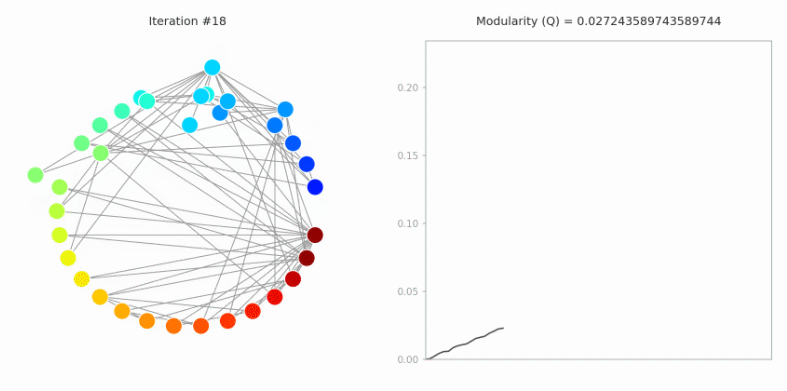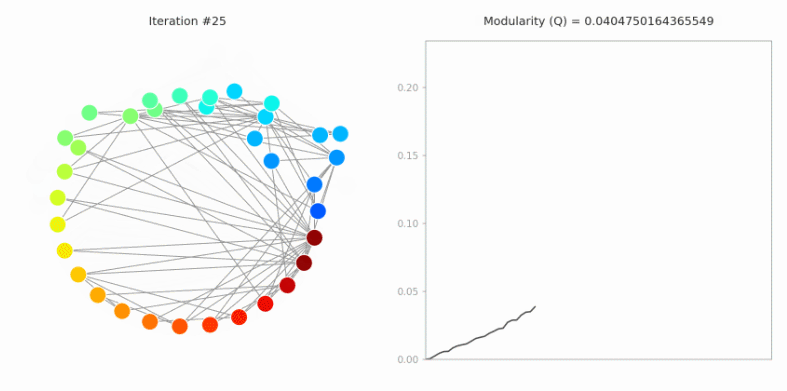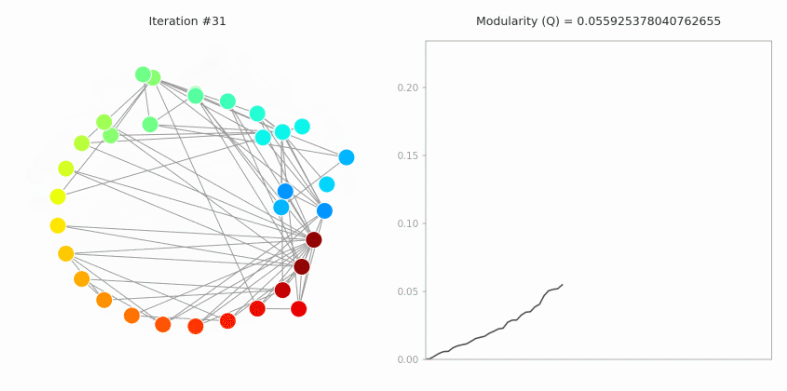
Louvain社区发现算法是一种基于模块度的社区发现算法。模块度是一种评价网络划分好坏的指标,后续会详细介绍。Louvain算法最终目标是得到最优的模块度
全局模块度

-
对于图中任意两点i,j
- A(i,j)表示两点之间的边的权重,不考虑方向
- 2m表示所有边的权重和
- k(i)表示点i所有边的权重和(度中心性)
- c(i,j)表示两者是否在一个社区,如果在则为1否为为0
(为了写方便,和图中符号有点差异)
-
含义:
- A(i,j) * c(i,j) / 2m表示社区内边的权重与图中总权重的比值,社区对内边越多,对外边越少,模块度越大
- -k(i) * k(j) * c(i,j) / 2m给度中心性较大的节点一个排斥的效果 ,减缓社区的增大速度
-
缺点:全图计算,运算速度较慢
单层算法过程
-
过程A:
-
为图中每个节点生成社区编号,如果有n个节点就有n个社区。

如图所示,为A~J节点分配了10个社区编号,这里用10中颜色表示 -
处理一个节点,它的社区编号依次分配为相邻节点的社区编号。计算模块度,选择模块度最大且为△Q为正的社区编号(一个节点的社区编号由相邻节点决定)

举个例子来说,分别把A的社区号分配为C,D,E的社区号(图中橙色、黄色和绿色),分别计算模块度。由于例子中的图十分对称,且边权重为1,所以三种情况的模块度Q都是相同的,但都比A自己一个社区好,这时颜色随便选一个就可以(程序上的比较法工厂选择第一个)。但如果网络拓扑结构比较复杂,情况会有所不同。 -
遍历所有节点,重复步骤2,完成一轮(后面的社区编号分配会依赖前面的结果)
-
-
过程B:重复过程A,直到所有节点社区编号不再变化(收敛)
因为每一轮的结果可能不同,也就是不稳定。可以重复直到所有节点社区编号都不变化或者一定比例的节点社区编号不变化。因为图如果很大,有时为了提升效率这么做。
多层算法过程
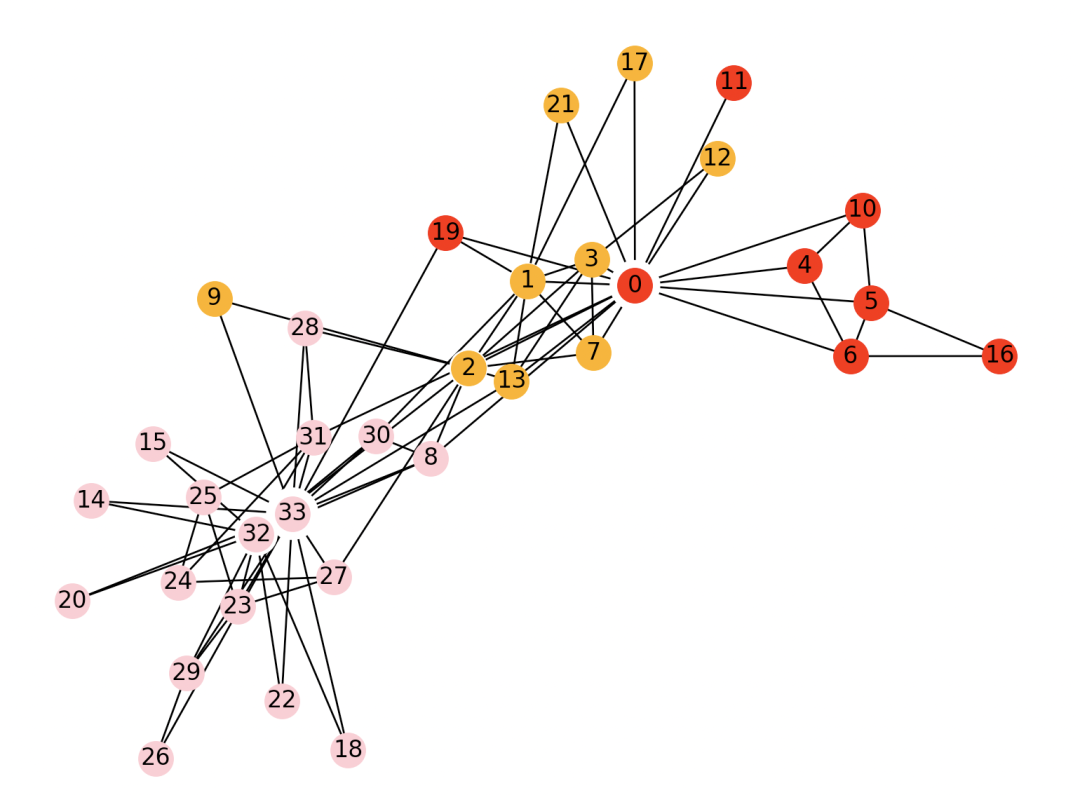
运行完过程A,B后可以把一个社区的节点融合成为一个节点,对新的图形结构再次进行单层划分,即完成了第二层。

如图中所示,节点融合时,忽略社区内部的边(不考虑指向自身的边),社区之间的边合并(权重合并),然后对新的图进行单层louvain即可。
可以重复达到n层,层数越多,社区数量越少,效果更好,但时间也会增加。因此要选择合适的层数。
Java代码实现
参考我的实现:https://github.com/ghostorsoul/louvain这是一种基于内存的单线程计算方法
图实现
- com.wjj.community.louvain.graph.entity包内封装了图的实现:Graph是图定义,Link是边定义。
- 采用了邻接表和逆邻接表的方式存储图,因为图通常不是很稠密,邻接矩阵的存储空间达到了O(n^2),而且求权重、临边和临接节点效率都比较低下;而邻接表和逆邻接表优势更加明显,尽管求两点之间的边效率略低,但后期会有优化手段。个人认为优势比劣势大。
模块度计算
- com.wjj.community.louvain.graph.algo.LouvainCalculator中包括了缓存、模块度计算、单层划分和多层划分功能。
- 缓存存储节点权重、图总权重和社区编号分配情况
/*** 缓存总权重*/private double totalW;/*** 节点社区编号*/private int[] nodeCommunityNo;/*** 缓存节点度中心性(带权重版,无向)*/private double[] nodeBothWeight;
- 基于上述缓存计算全局模块度,整个过程使用了之前提到的公式,但计算还有优化的空间。
/*** 计算当前模块度(全局模块度)** @return ModuleQ值*/private double getModuleQ() {System.out.println("comm status: " + Arrays.toString(nodeCommunityNo));System.out.println("total weight: " + totalW);double q = 0.0;Set<Integer> nodeIds = graph.getNodes();for (int id1 : nodeIds) {for (int id2 : nodeIds) {if (id1 == id2) {continue;}double A = 0.0;for (Link link : graph.getLinksBetweenTwoNodes(id1, id2)) {A += link.weight;}q += c(id1, id2) * (A - nodeBothWeight[id1] * nodeBothWeight[id2] / totalW * stickingK);System.out.printf("id1: %s,id2: %s, A: %s, c: %s, k1: %s, k2: %s%n", id1, id2, A, c(id1, id2),nodeBothWeight[id1], nodeBothWeight[id2]);}}return q / totalW;}
单层louvain实现
/*** 单层louvain社区划分算法** @return 社区划分结果*/public CommunityInfo findCommunitiesSingleLevel() {while (true) {int[] copy = nodeCommunityNo.clone();double Q = getModuleQ();if (Double.isNaN(Q)) {break;}System.out.println(String.format("initQ: %s", Q));for (int id1 : graph.getNodes()) {System.out.println("deal id: " + id1);int bestCommunityNo = -1;double deltaQ = 0.0;int id1OriginNo = nodeCommunityNo[id1];for (int id2 : graph.getBothNodes(id1)) {if (c(id1, id2) == 1) {continue;}nodeCommunityNo[id1] = nodeCommunityNo[id2];double currentQ = getModuleQ();if (Double.isNaN(currentQ)) {continue;}System.out.println(String.format("currentQ: %s", currentQ));if (currentQ - Q > 0.00001 && currentQ - Q > deltaQ) {deltaQ = currentQ - Q;bestCommunityNo = nodeCommunityNo[id2];}}if (bestCommunityNo == -1) {nodeCommunityNo[id1] = id1OriginNo;System.out.println(String.format("no best communityNo. id: %s", id1));} else {nodeCommunityNo[id1] = bestCommunityNo;System.out.println(String.format("set best communityNo. id: %s, comm: %s", id1, bestCommunityNo));Q = getModuleQ();}}if (Arrays.equals(nodeCommunityNo, copy)) {break;}}Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < nodeCommunityNo.length; i++) {int commNum = nodeCommunityNo[i];List<Integer> integers = map.get(commNum);if (integers == null) {integers = new ArrayList<>();map.put(commNum, integers);}integers.add(i);}CommunityInfo communityInfo = new CommunityInfo();communityInfo.communitiesNo = map.size();communityInfo.communityNodeIds = new int[map.size()][];AtomicInteger nextCommNum = new AtomicInteger(0);map.forEach((commNum, ids) -> {communityInfo.communityNodeIds[nextCommNum.get()] = new int[ids.size()];for (int i = 0; i < ids.size(); i++) {communityInfo.communityNodeIds[nextCommNum.get()][i] = ids.get(i);}nextCommNum.incrementAndGet();});communityInfo.nodeCommunityNo = new int[nodeCommunityNo.length];for (int c = 0; c < communityInfo.communityNodeIds.length; c++) {for (int nodeId : communityInfo.communityNodeIds[c]) {communityInfo.nodeCommunityNo[nodeId] = c;}}return communityInfo;}
- 第一个while表示执行多轮,等到所有节点的社区编号都稳定后,就退出循环
- 第一个for循环代表寻找一个节点的最优社区划分结果
- 第二个for循环代表为一个节点分配社区编号和比较模块度的过程
- 后面的过程是一些社区编号转换(读者可以PASS…)
多层louvain实现
/*** 多层louvain社区划分算法** @param level 层数* @return 社区划分结果*/public CommunityInfo findCommunitiesMultiLevel(int level) {CommunityInfo[] levelResult = new CommunityInfo[level + 1];Graph currentGraph = graph;while (level > 0) {System.out.println("current level: " + level);CommunityInfo communityInfo;if (currentGraph == this.graph) {communityInfo = findCommunitiesSingleLevel();} else {communityInfo = new LouvainCalculator(currentGraph).findCommunitiesSingleLevel();}levelResult[level] = communityInfo;System.out.println(String.format("levelResult: %s, level: %s", communityInfo, level));Graph newGraph = new Graph();for (int c1 = 0; c1 < communityInfo.communitiesNo; c1++) {boolean ac = true;for (int c2 = 0; c2 < communityInfo.communitiesNo; c2++) {if (c1 == c2) {continue;}int[] c1NodeIds = communityInfo.communityNodeIds[c1];int[] c2NodeIds = communityInfo.communityNodeIds[c2];List<Link> links = new ArrayList<>();for (int c1OneNode : c1NodeIds) {for (int c2OneNode : c2NodeIds) {Link tempLink = currentGraph.getLinkFromOneToAnother(c1OneNode, c2OneNode);if (tempLink != null) {links.add(tempLink);}}}if (!links.isEmpty()) {Link newLink = new Link(c1, c2, 0.0);links.forEach(link -> newLink.weight += link.weight);newGraph.addLinks(Arrays.asList(newLink));ac = false;}}if (ac) {newGraph.addAcNodes(Arrays.asList(c1));}}currentGraph = newGraph;level--;}CommunityInfo finalComm = new CommunityInfo();Map<Integer, Integer> commNoFinalCommNoMap = new HashMap<>();int cCommNum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo.length; i++) {for (int j = levelResult.length - 2; j >= 1; j--) {int c = levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo[i];int newC = levelResult[j].nodeCommunityNo[c];levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo[i] = newC;}int c = levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo[i];if (!commNoFinalCommNoMap.containsKey(c)) {commNoFinalCommNoMap.put(c, cCommNum++);}levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo[i] = commNoFinalCommNoMap.get(c);}finalComm.nodeCommunityNo = levelResult[levelResult.length - 1].nodeCommunityNo;finalComm.communitiesNo = cCommNum;Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < cCommNum; i++) {map.put(i, new ArrayList<>());}for (int id = 0; id < finalComm.nodeCommunityNo.length; id++) {map.get(finalComm.nodeCommunityNo[id]).add(id);}finalComm.communityNodeIds = new int[cCommNum][];map.forEach((cId, nodeIds) -> {int[] ids = new int[nodeIds.size()];for (int i = 0; i < nodeIds.size(); i++) {ids[i] = nodeIds.get(i);}finalComm.communityNodeIds[cId] = ids;});return finalComm;}
多层划分基于单层划分,重点是:
- 划分结果进行节点融合,进入下次划分
- 最后一层划分完成后,由于节点编号已经不是原来的,需要还原回去
- 第一个while循环用于保证n层的划分
- 第一个双层for循环完成了节点的融合和生成新图的功能
- while循环后面的内容代表节点编号的还原过程,还包括一些转换功能。
运行入口,使用方法
这个程序没有写main类,而是使用了junit单元测试,展示了使用方法
/*** 单层划分*/@Testpublic void testSingle() {Graph g = new Graph();// 0->1->2->0g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(0, 1, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(1, 2, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(2, 0, 1.0)));// 3->4->5->3g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(3, 4, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(4, 5, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(5, 3, 1.0)));// 构造计算器LouvainCalculator louvainCalculator = new LouvainCalculator(g);// 执行划分CommunityInfo communityInfo = louvainCalculator.findCommunitiesSingleLevel();// 输出结果System.out.println(communityInfo);}/*** 多层划分*/@Testpublic void testMultiple() {Graph g = new Graph();// 0->1->2->0g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(0, 1, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(1, 2, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(2, 0, 1.0)));// 3->4->5->3g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(3, 4, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(4, 5, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(5, 3, 1.0)));// 6->7->8->6->5g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(6, 7, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(7, 8, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(8, 9, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(9, 6, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(6, 8, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(7, 9, 1.0)));g.addLinks(Arrays.asList(new Link(6, 5, 1.0)));// 构造计算器LouvainCalculator louvainCalculator = new LouvainCalculator(g);// 执行划分CommunityInfo communityInfo = louvainCalculator.findCommunitiesMultiLevel(2);// 输出结果System.out.println(communityInfo);}
步骤如下:
- 创建Graph对象g
- 向图g添加边和孤立点
- 点ID用int表示,要求是从0开始连续的编号
- 边的权重不能为0
- 如果有孤立点,必须通过addAcNodes( List )方法添加
- 创建LouvainCalculator对象(louvain算法计算对象)执行findCommunitiesSingleLevel进行单层划分或者findCommunitiesMultiLevel( int )进行多层划分,返回对象类型为CommunityInfo能详细表明社区分布情况。