1.lseek函数的介绍
(1)文件指针:当我们对一个文件读写时,一定需要打开这个文件,所以我们操作的都是动态文件,动态文件在内存中的形态就是流的形式。
(2)文件流很长,里面有很多字节。那我们操作的是哪一个位置,GUI模式下就是用光标来标识,在动态文件中,我们通过文件指针来表示正在操作的位置。文件指针其实就是vnode里的一个元素。这个指针表示我们操作的位置,在linux中用lseek来访问这个指针。
(3)write和read函数本身自带移动文件指针的功能,所以打开一个有n字节的文件,read/write会自动从n字节后读写,如果要人为改变这个文件指针就用lssek函数。
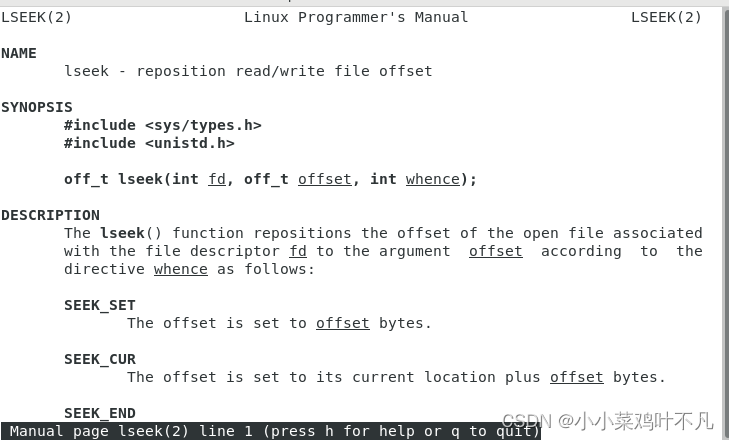
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
fd:文件描述符
offset:偏移字节数
whence:文件指针所在位置(SEEK_SET:起始位置、SEEK_CUR:当前位置、SEEK_END:末尾地址)
返回值:返回偏移量
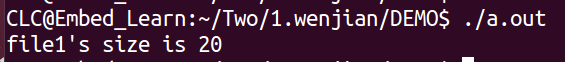
2.用lseek计算文件的大小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc ,char *argv[])
{int fd = -1;int ret = -1;if(argc != 2){printf("usage: %s filename\n",argv[0]);_exit(-1);}fd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);if(-1 == fd){printf("打开文件出错\n");_exit(-1);}else{printf("打开成功,fd = %d\n",fd);}//此时文件指针指向文件开头,我们用lseek将文件指针移动到末尾//然后返回值就是文件指针距离文件开头的偏移量,也就是文件的长度ret = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);printf("文件长度是%d个字节\n",ret);return 0;
}将求文件大小大小这个功能封装成一个函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int cal_len(const char *pathname)
{int fd = -1;int ret = -1;fd = open(pathname,O_RDONLY);if(-1 == fd){printf("打开文件出错\n");return -1;}//此时文件指针指向文件开头,我们用lseek将文件指针移动到末尾//然后返回值就是文件指针距离文件开头的偏移量,也就是文件的长度ret = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);return ret;}int main(int argc ,char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){printf("usage:%s filename\n",argv[0]);_exit(-1);}printf("文件长度是%d个字节\n",cal_len(argv[1]));return 0;
}
3.用lseek构建空洞文件
(1)空洞文件就是这个文件有一段是空的
(2)普通文件时不能为空的,因为我们write时文件指针是从前到后去移动的,不能绕过前面到后面
(3)我们打开一个文件后,用lseek往后跳过一段,在write写入一段,就会构成一个空洞文件。
(4)空洞文件对多线程共同操作文件是及其有用的,有时候我们创建一个很大的文件。如果从头依次构建是非常慢的,有一种思路将文件分为多段,然后多线程来操作每个线程负责其中一段写入。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>int main()
{int fd = -1;int ret = -1;char writeBuf[10] = "asdqwe";fd = open("123.txt",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0666);if(fd == -1){//printf("创建文件失败\n");perror("创建失败");_exit(-1);}else{printf("创建成功fd = %d\n",fd);}ret = lseek(fd,10,SEEK_SET);int n = write(fd,writeBuf,strlen(writeBuf));printf("写入了%d个字节\n",n);printf("偏移了%d个字节\n",ret);close(fd);return 0;
}