目录
一.lseek函数简介:
1.包含的头文件
2.函数原型
3.函数参数说明:
4.lseek函数描述
5.函数返回值
二.运用lseek移动光标,代码demo:
几种lseek移动光标的操作方法:
三.利用lseek函数的返回值,巧妙计算文件的大小:
一.lseek函数简介:
1.包含的头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
2.函数原型
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
3.函数参数说明:
- int fd :文件描述符
- off_t offset:偏移多少个字节
- int whence:光标偏移位置
【整个函数的意思是:将文件读写指针相对whence移动offset个字节位置】
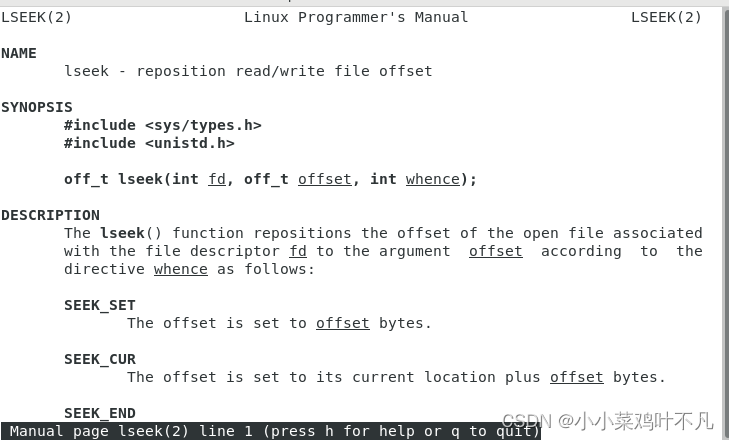
4.lseek函数描述
The lseek() function repositions the offset of the open file associated with the file descriptor fd to the argument offset according to the directive whence as follows:
SEEK_SET
The offset is set to offset bytes.SEEK_CUR
The offset is set to its current location plus offset bytes.SEEK_END
The offset is set to the size of the file plus offset bytes.
给whence参数设定偏移位置:SEEK_SET:光标偏移到头
SEEK_CUR:光标为当前位置
SEEK_END:光标偏移到末尾
5.函数返回值
RETURN VALUE
Upon successful completion, lseek() returns the resulting offset location as measured in bytes from the beginning of the file. On error, the value (off_t) -1 is returned and errno is set to indicate the error.成功完成后,Iseek()返回从文件开始的偏移位置(以字节为单位)【就是返回偏移了多少个字节】。发生错误时,返回值(off_t) -1,并设置errno来指示错误。
二.运用lseek移动光标,代码demo:
open打开文件:此时的光标是在头位置。
write写入操作:写入操作后,光标的位置在尾巴。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
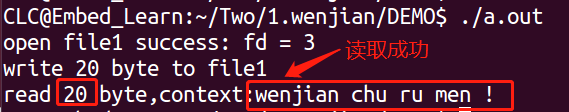
{int fd;char *buf = "wenjian chu ru men !";fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR); //打开文件if(fd == -1){printf("open file1 fail \n");fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0600); //如果没有文件,创建文件if(fd > 0){printf("creat file1 success \n");}}printf("open file1 success: fd = %d \n",fd);//write函数原型:ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));printf("write %d byte to file1 \n",n_write);lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET); //将光标移动到头后,相对头偏移0个字节位置char *readbuf;readbuf = (char *)malloc(strlen(buf)+1);//read函数原型:ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);int n_read = read(fd,readbuf,n_write);printf("read %d byte,context:%s\n",n_read,readbuf);close(fd);return 0;
}
几种lseek移动光标的操作方法:
- lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET); //将光标移动到头后,相对头偏移0个字节位置(常用一种就好啦)
- lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END; //常用于计算文件大小
- lseek(fd,-20,SEEK_END); //将光标移动到尾巴后,相对尾巴向头偏移,也就是往前偏移20个字节位置
- lseek(fd,-n_write,SEEK_END); //将光标移动到尾巴后,相对尾巴向头偏移,也就是往前偏移写入操作write之后的(返回值,实际就是20)个字节位置
- lseek(fd,-20,SEEK_CUR); //将光标移动到当前位置(上面代码也就是尾巴),相对当前位置(尾巴)向头偏移,也就是往前偏移20个字节位置
- lseek(fd,-n_write,SEEK_CUR); //将光标移动到当前位置(上面代码也就是尾巴),也就是往前偏移写入操作write之后的(返回值,实际就是20)个字节
三.利用lseek函数的返回值,计算文件的大小:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
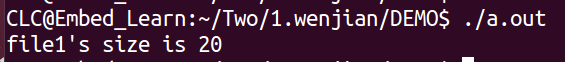
{int fd;fd = open("./file1",O_RDWR);// off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);int n_lseek = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);printf("file1's size is %d \n",n_lseek);close(fd);return 0;
}