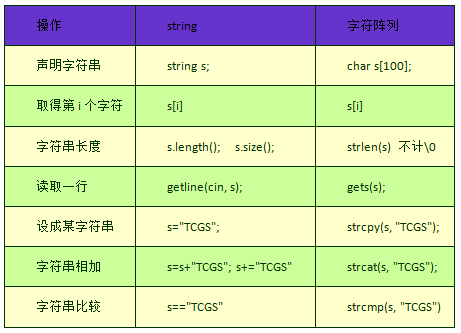
目录
标准库中的string类
string类(了解)
编码介绍
string类的常用接口说明
Member functions
测试一:创建对象
测试二:遍历字符串
Iterators
测试三:反向迭代器(Iterators)
Capacity
测试四:容器相关(Capacity)
测试五:自动扩容
测试六:resize的不同情况
Element access
测试七:字符获取函数(Element access)
Modifiers
测试八:修改类(Modifiers)
测试九:insert与erase
测试十:assign与replace
find的使用
将空格替换成%20
operations
测试十一:c_str
测试十二:substr取一段字符
find_first_of
Non-member function overloads
relational operators (string)
一些题目
917. 仅仅反转字母
415. 字符串相加
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
HJ1 字符串最后一个单词的长度
125. 验证回文串
541. 反转字符串 II
557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
43. 字符串相乘
HJ59 找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
结束语
标准库中的string类
string从发展历史上来说,比STL创建的更早,我们现在通常把它归类到STL里面,但是从发展历史上来看其实不算,这一点从string的实现中可以看出来,相比标准的STL容器,string更加杂乱,标准化不高。
string类(了解)
string类的文档介绍 -- 链接
1. 字符串是表示字符序列的类
2. 标准的字符串类提供了对此类对象的支持,其接口类似于标准字符容器的接口,但添加了专门用于操作单字节字符字符串的设计特性。
3. string类是使用char(即作为它的字符类型,使用它的默认char_traits和分配器类型(关于模板的更多信息,请参阅basic_string)。
4. string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例,它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类,并用char_traits和allocator作为basic_string的默认参数(根于更多的模板信息请参basic_string)。
5. 注意,这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列,这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器,将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。编码的本质其实是计算机里面存的值(0、1组成,我们人一般看不懂,所以就有了ASCLL码(256个)来存一些常用的文字字符,建立对应关系,我们在使用的时候就无需知道字符对应的二进制码了,计算机可以帮助我们自己去寻找)
总结:
1. string是表示字符串的字符串类
2. 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。3. string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>string;
4. 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
编码介绍
ASCII_百度百科 (baidu.com)
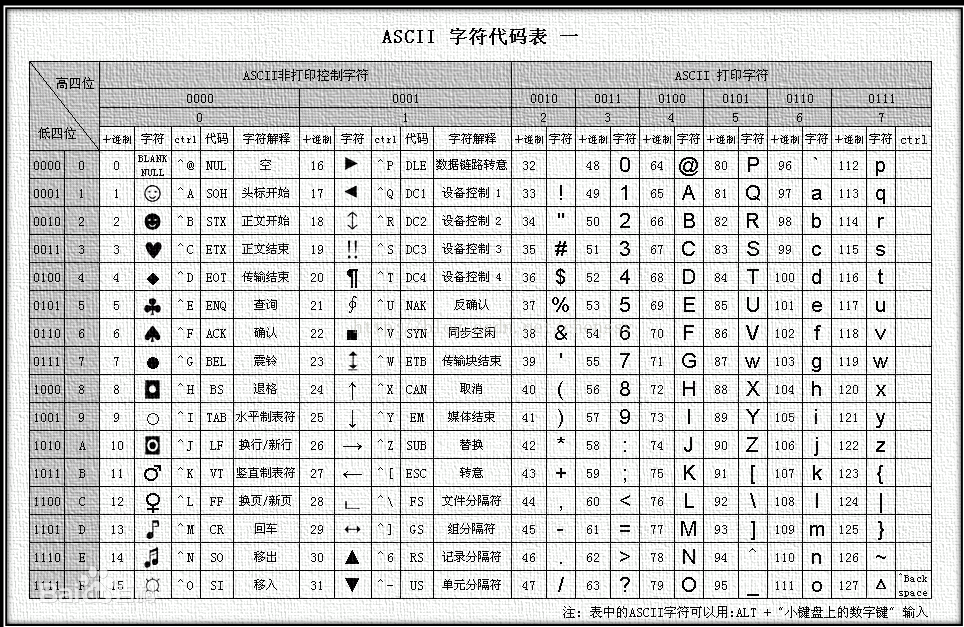
后面为了解决计算机流通的问题,又引入了Unicode(万国码)
统一码_百度百科 (baidu.com)

而我们中文也有自己的编码,这里面收录了全面的汉字,包括繁体字、生僻字这类较少用到的
GBK字库_百度百科 (baidu.com)

默认下Linux系统是使用UTF-8,VS是使用GBK,我们在高级保存选项中可以看到,不过有可能看不到这个选项,需要自己调整出来
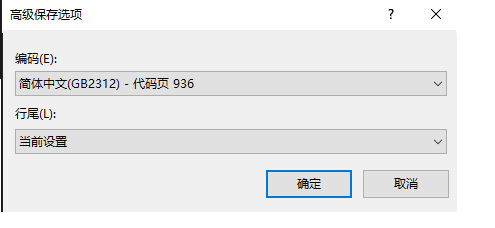
在调试下我们会发现GBK编码的一些小细节

通常我们使用的就是string这一个,不过C++11之后也有其他的类型了

string类的常用接口说明
Member functions
测试一:创建对象
string::string - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接

string::npos - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接
//string 使用
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;//typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>string; 库里面是重命名过了
void test_test1()
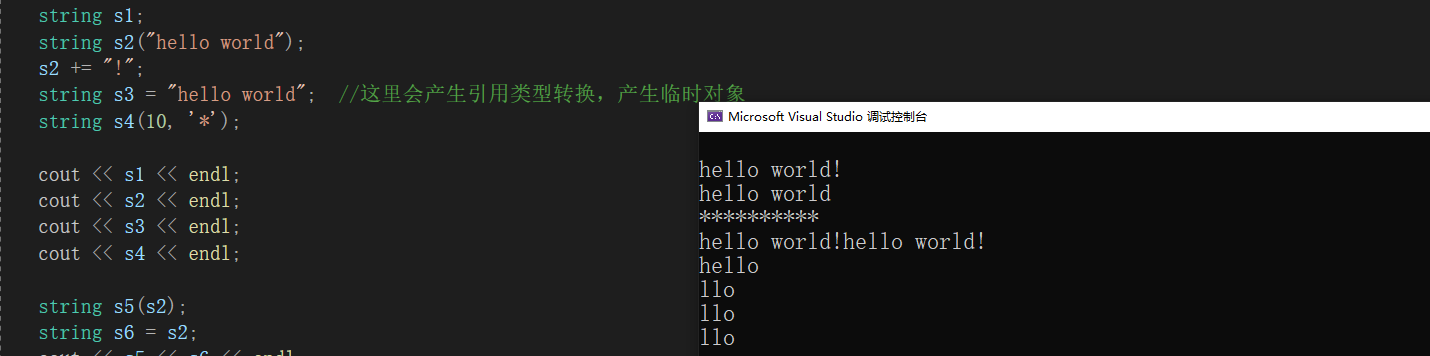
{//basic_string<char> s1; 这种写法与下面写法是一样的string s1;string s2("hello world");s2 += "!";string s3 = "hello world"; //这里会产生引用类型转换,产生临时对象string s4(10, '*');cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;cout << s3 << endl;cout << s4 << endl;string s5(s2);string s6 = s2;cout << s5 << s6 << endl;string s7("hello world", 5);cout << s7 <<endl;string s8(s7, 2, 3);cout << s8 << endl;string s9(s7, 2, 30); //字符串太小,会直接取到最后一个cout << s9 << endl;string s9(s7, 2); //不给参数,会直接使用npos(是一个静态成员变量-1,不过因为是无符号所以很大)cout << s9 << endl; //基本上是取到结尾,因为大概没有4G长的字符串吧}
int main()
{test_test1();return 0;
}
测试二:遍历字符串
void test_tring2()
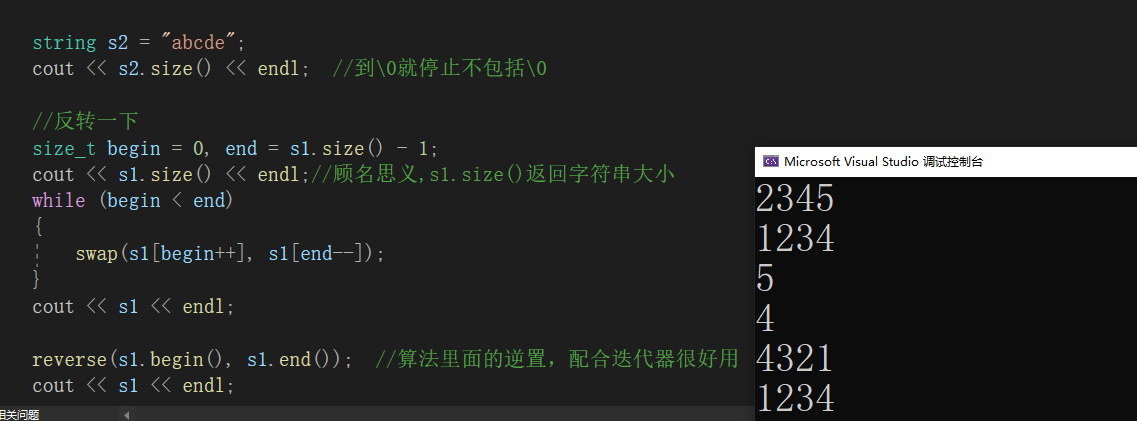
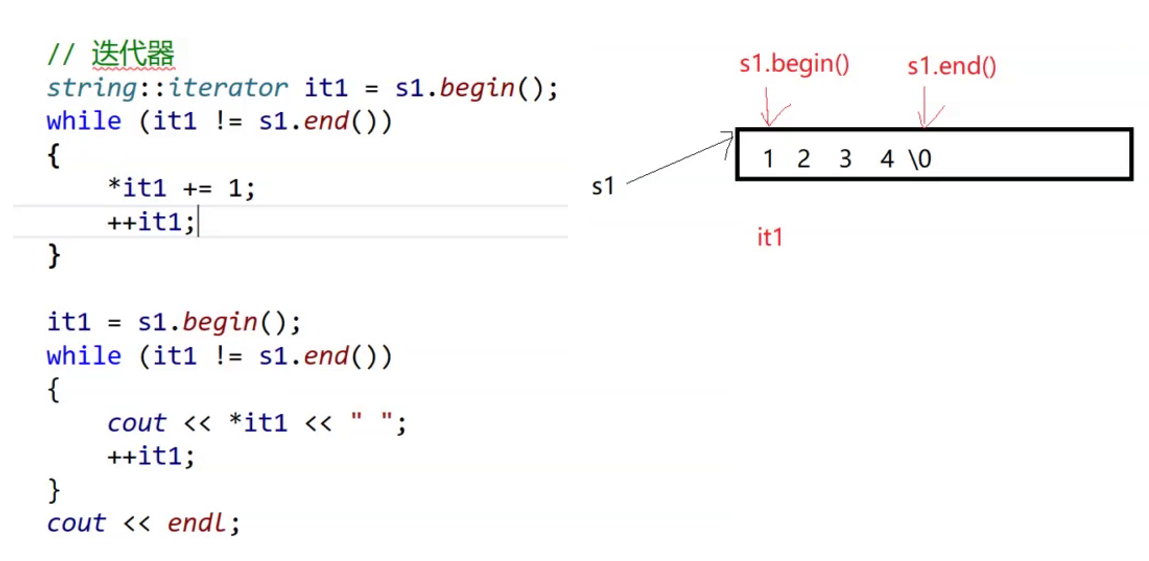
{string s1("1234"); //会自动加\0//遍历//1、下标 []for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){s1[i]++;}//s1[10]; 这里是重载,所以这里会检查越界cout << s1 << endl;//2、范围forfor (auto& e : s1){e--;}cout << s1 << endl;string s2 = "abcde";cout << s2.size() << endl; //到\0就停止不包括\0//反转一下size_t begin = 0, end = s1.size() - 1; cout << s1.size() << endl;//顾名思义,s1.size()返回字符串大小while (begin < end){swap(s1[begin++], s1[end--]);}cout << s1 << endl;reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); //算法里面的逆置,配合迭代器很好用cout << s1 << endl;//迭代器(通用的访问形式,不仅仅是在string里面可以用) -- 一个像指针但是不一定就是指针string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){*it1 += 1;++it1;}it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << end;//vector 我们会发现基本上使用方式是一样的vector<int> v;vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin();while (vit != v.end()){*vit += 1;++vit;}cout << end;//listlist<int> lt;list<int>::iterator ltit = lt.begin();while (ltit != lt.end()){*ltit += 1;++ltit;}}
int main()
{//test_tring1();test_tring2();return 0;
}
Iterators
迭代器(Iterators)
测试三:反向迭代器(Iterators)
string - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接

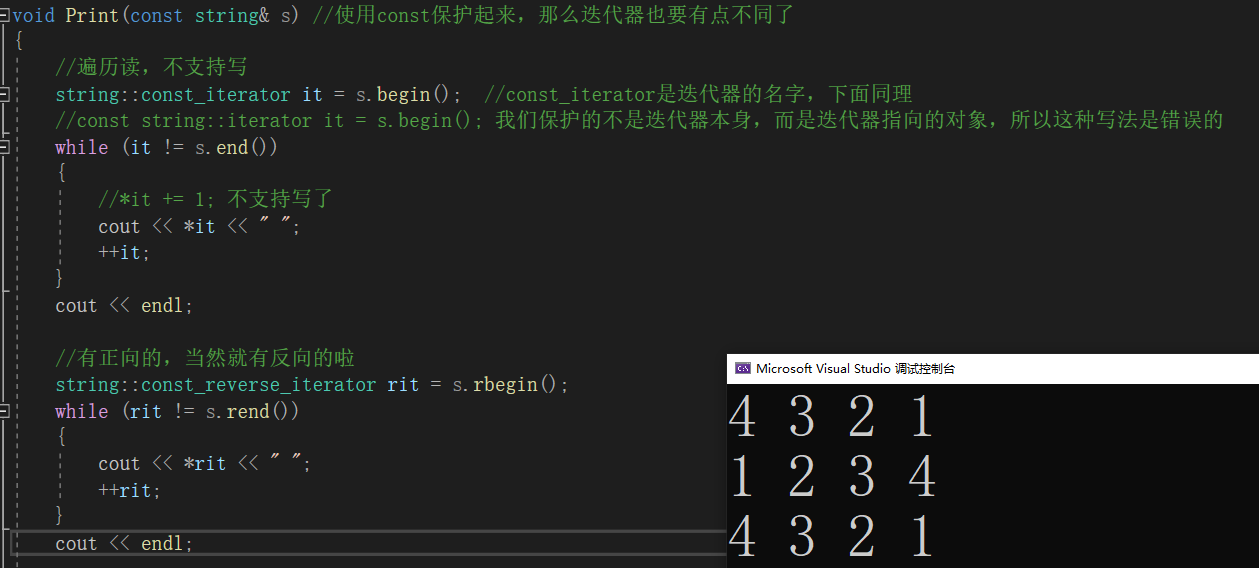
//反向迭代器void Print(const string& s) //使用const保护起来,那么迭代器也要有点不同了
{//遍历读,不支持写string::const_iterator it = s.begin(); //const_iterator是迭代器的名字,下面同理//const string::iterator it = s.begin(); 我们保护的不是迭代器本身,而是迭代器指向的对象,所以这种写法是错误的while (it != s.end()){ //*it += 1; 不支持写了cout << *it << " "; ++it;}cout << endl;//有正向的,当然就有反向的啦string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();while (rit != s.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;
}
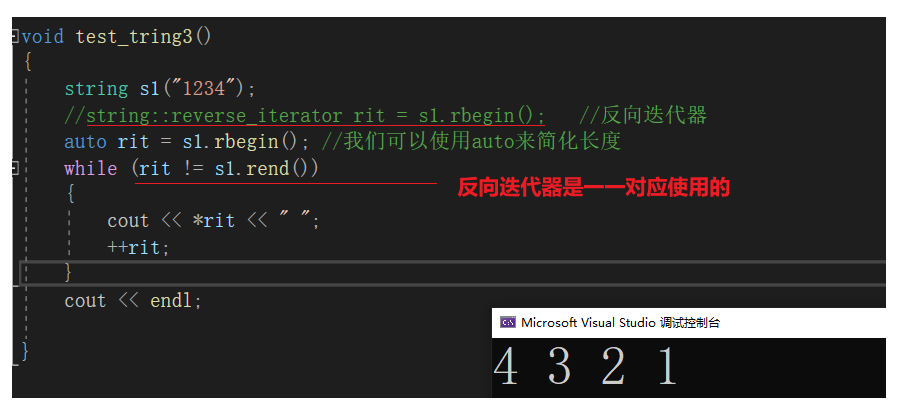
void test_tring3()
{string s1("1234");//string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); //反向迭代器auto rit = s1.rbegin(); //我们可以使用auto来简化长度while (rit != s1.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;Print(s1); //传引用
}
不修改内容的迭代器
当然了过长是可以使用auto来自动确定类型的
基于上面的情况,我们发现有些函数提供了两种版本,而有些函数则只能读或者只能写,那么如何区别呢?
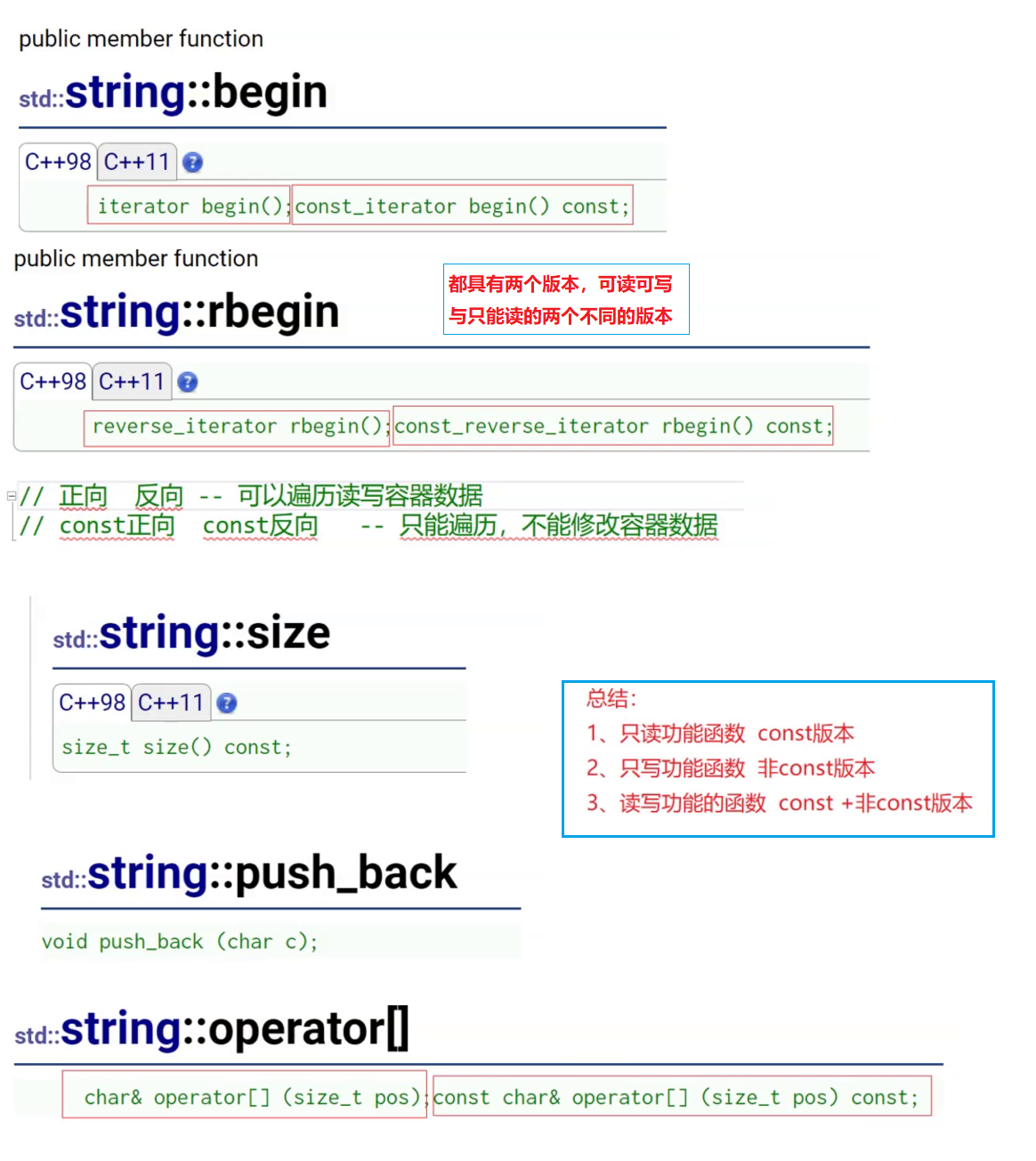
Capacity
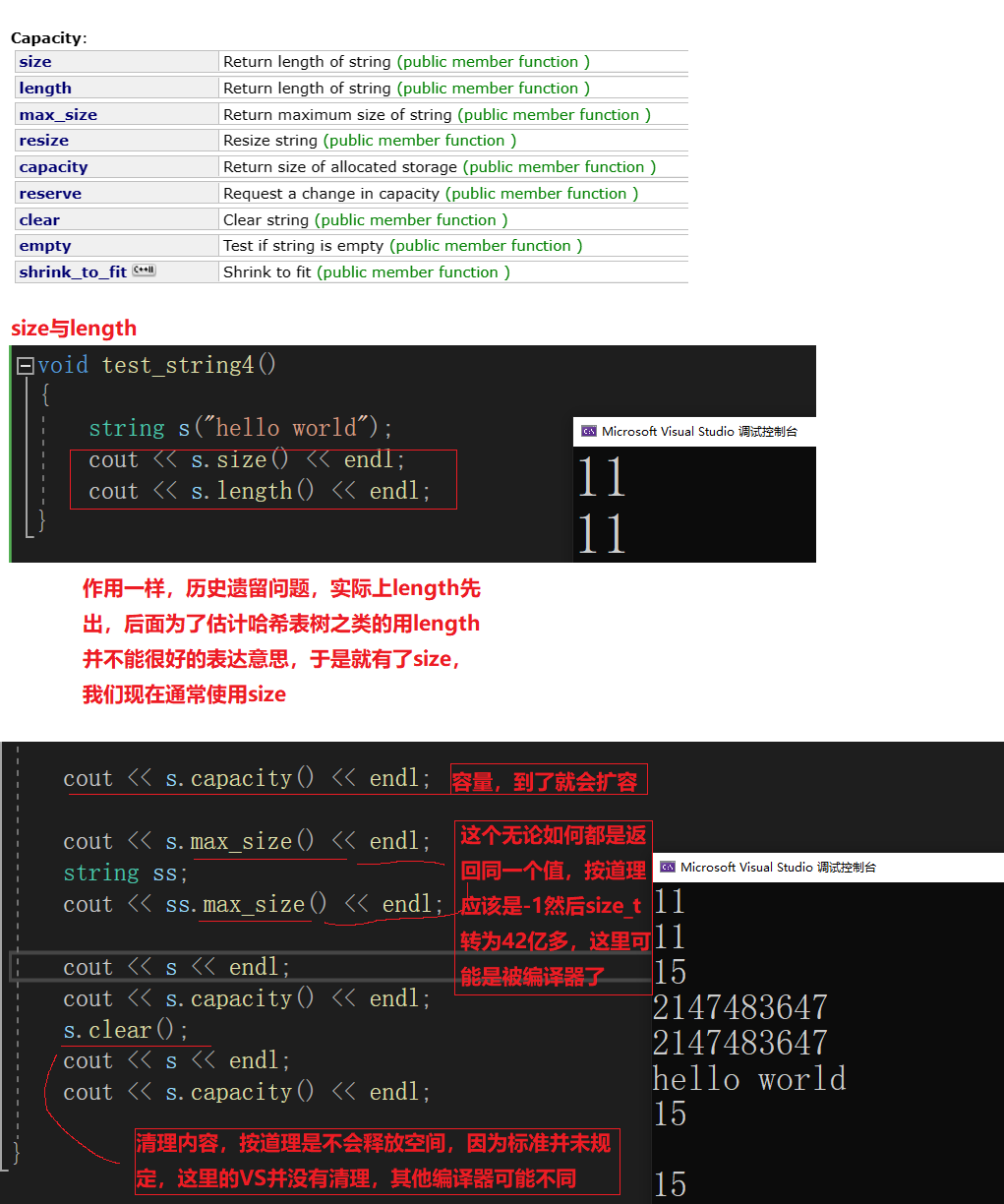
测试四:容器相关(Capacity)
string::empty - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接
empty判断是否为空,是就返回ture,否则返回false
测试五:自动扩容

利用reserve提高插入数据的效率,避免增容带来的开销
string::reserve - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接

测试六:resize的不同情况
string::resize - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com) -- 链接
//resize
void test_string6()
{string s1("hello world");s1.resize(5);cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1 << endl << endl;string s2("hello world");s2.resize(15);cout << s2.size() << endl;cout << s2.capacity() << endl;cout << s2 << endl << endl;string s3("hello world");s3.resize(30);cout << s3.size() << endl;cout << s3.capacity() << endl;cout << s3 << endl << endl;
}
Element access
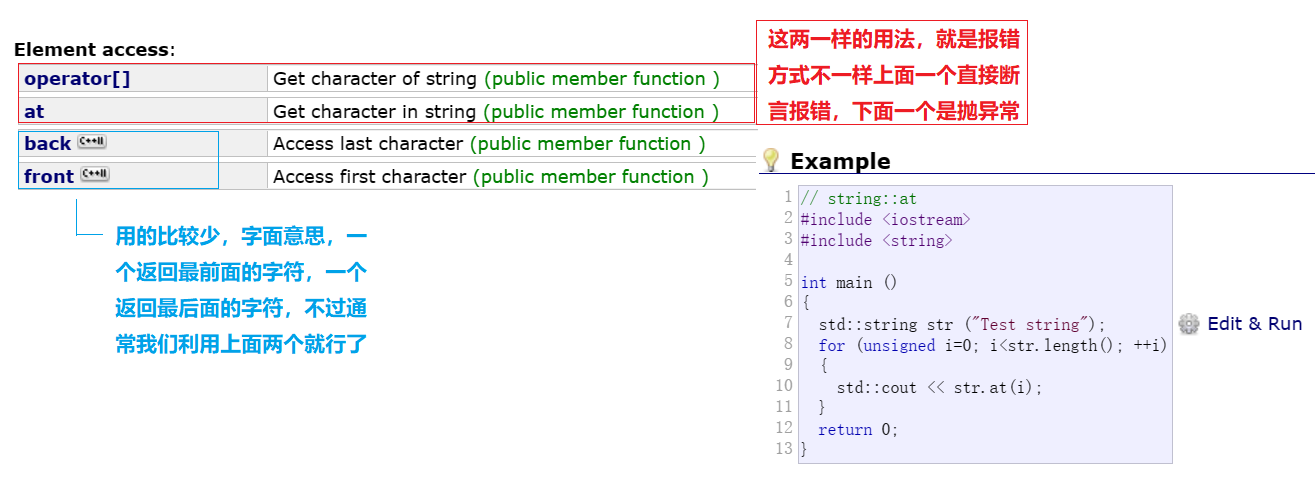
测试七:字符获取函数(Element access)
string::at - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
Modifiers

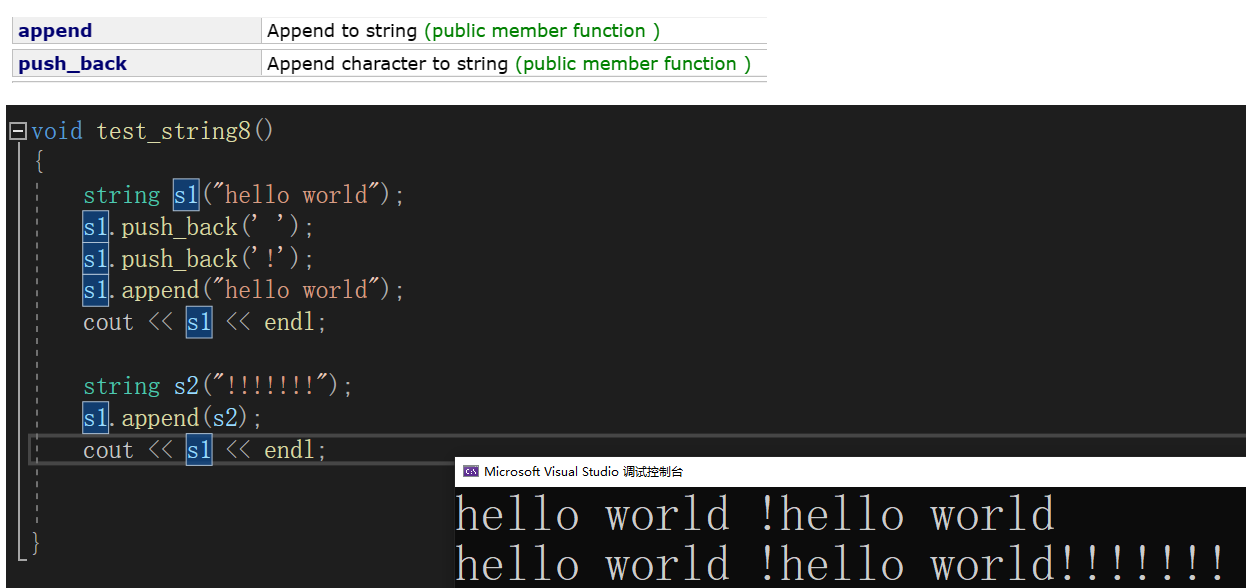
测试八:修改类(Modifiers)
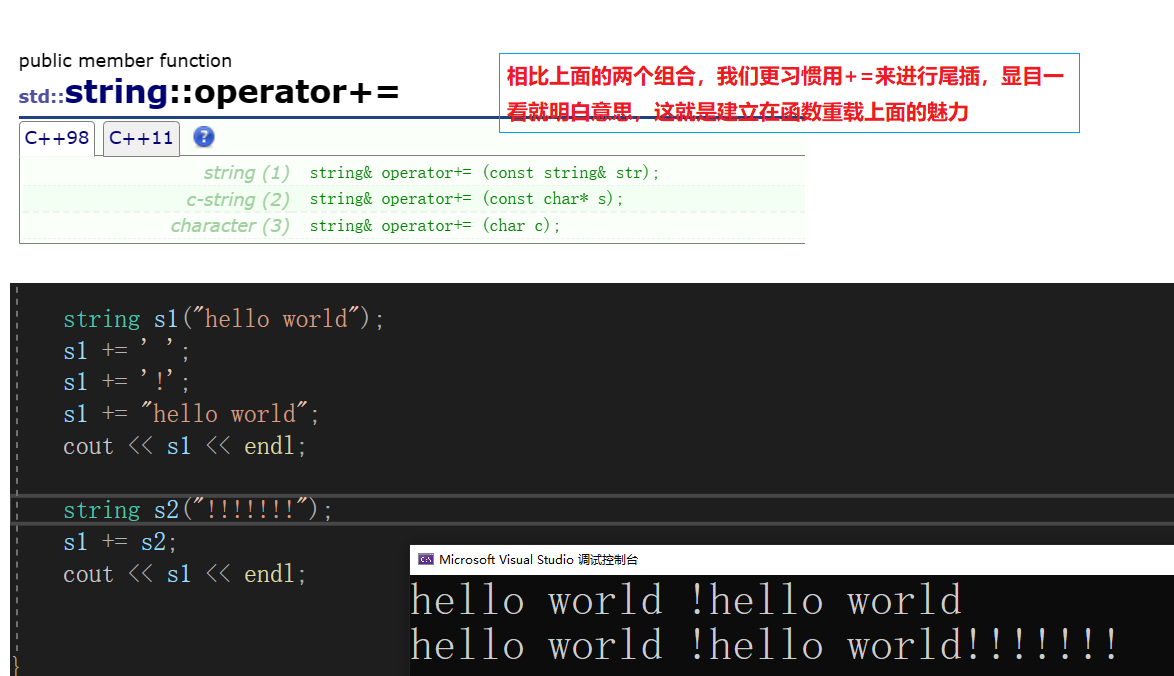
//修改类(Modifiers)
void test_string8()
{//string s1("hello world");//s1.push_back(' ');//s1.push_back('!');//s1.append("hello world");//cout << s1 << endl;////string s2("!!!!!!!");//s1.append(s2);//cout << s1 << endl;string s1("hello world");s1 += ' ';s1 += '!';s1 += "hello world";cout << s1 << endl;string s2("!!!!!!!");s1 += s2;cout << s1 << endl;
}
+=的使用
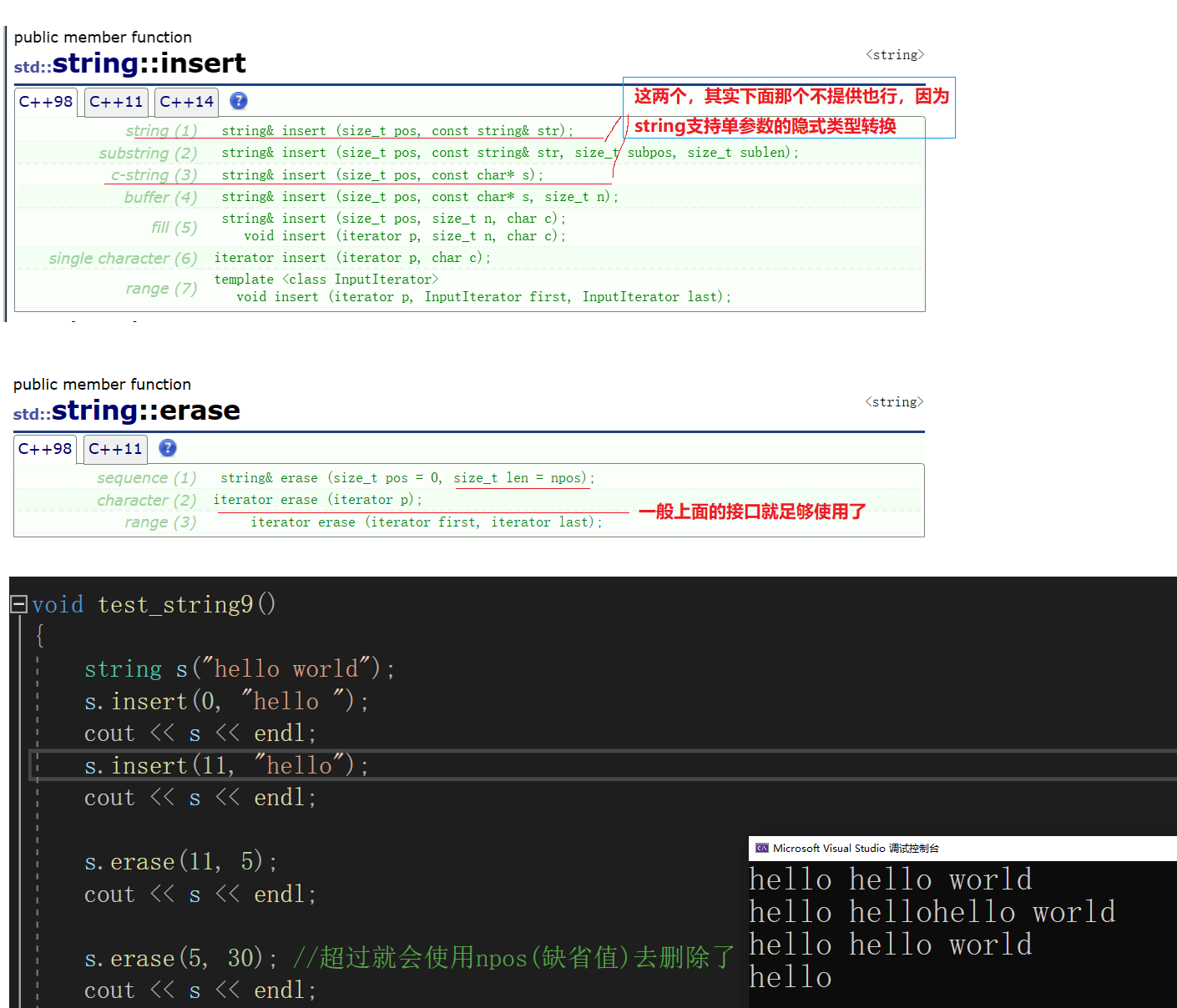
测试九:insert与erase
//insert与erase
void test_string9()
{string s("hello world");s.insert(0, "hello ");cout << s << endl;s.insert(11, "hello");cout << s << endl;s.erase(11, 5);cout << s << endl;s.erase(5, 30); //超过就会使用npos(缺省值)去删除了cout << s << endl;
}
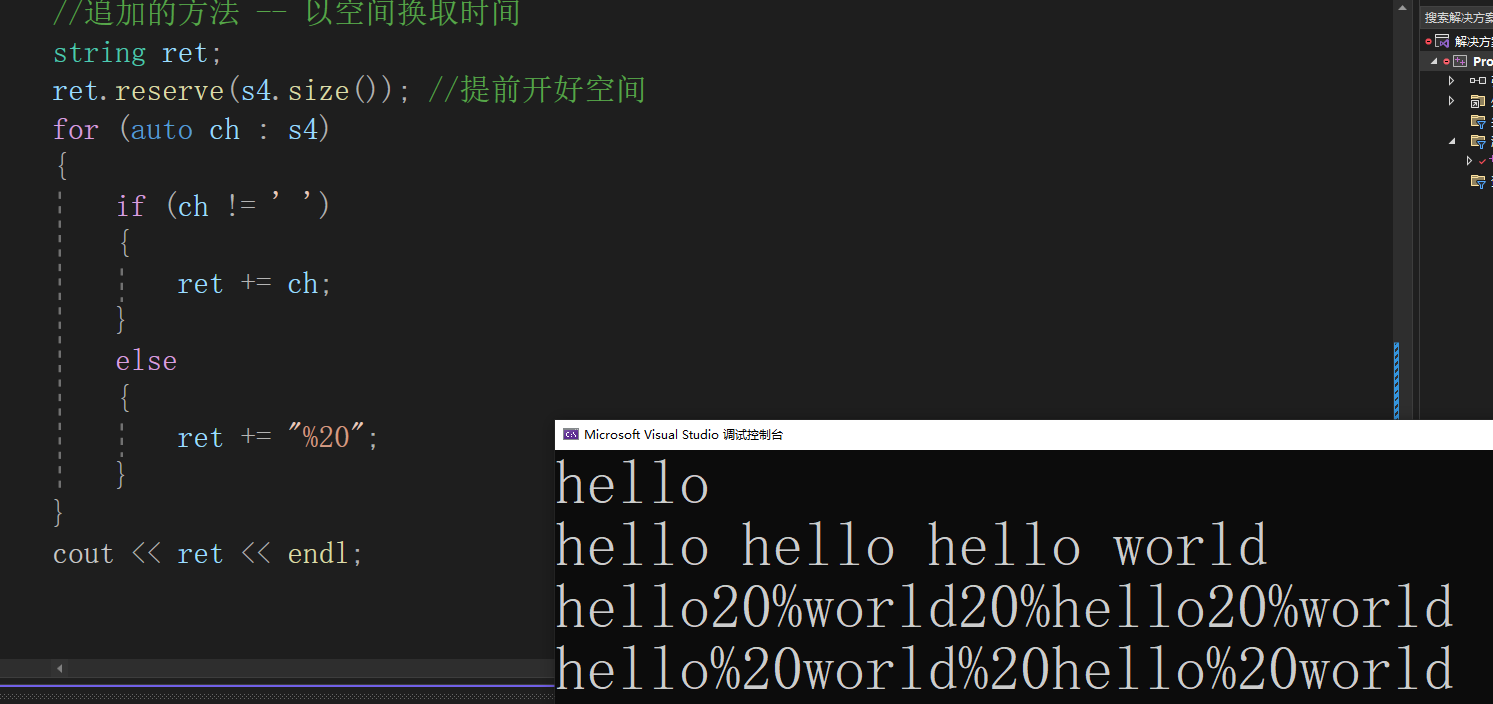
测试十:assign与replace
void test_string10()
{string s1("hello world hello world");string s2("hello world hello world");string s3(s2);s1.assign("hello world", 5);cout << s1 << endl;s2.replace(6, 5, "hello");cout << s2 << endl;//将 ' ' 替换成%20size_t pos = s3.find(' ');while (pos!=string::npos) //这样写任何平台都可以使用{s3.replace(pos,1,"20%");pos = s3.find(' ', pos + 3); //加三跳过%20}cout << s3 << endl;
}
find的使用

将空格替换成%20
operations
测试十一:c_str
void test_string11()
{string file("test.cpp");FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "r");assert(fout);char ch = fgetc(fout);while (ch != EOF){cout << ch;ch = fgetc(fout);}fclose(fout);
}
测试十二:substr取一段字符
//substr -- 取一串字符
void test_string12()
{//test.cppstring file;cin >> file;//要求取后缀//size_t pos = file.find('.'); 从头开始找size_t pos = file.rfind('.'); //这里从尾部开始找更好点if (pos != string::npos){//string suffix = file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos);string suffix = file.substr(pos);cout << suffix;}
}
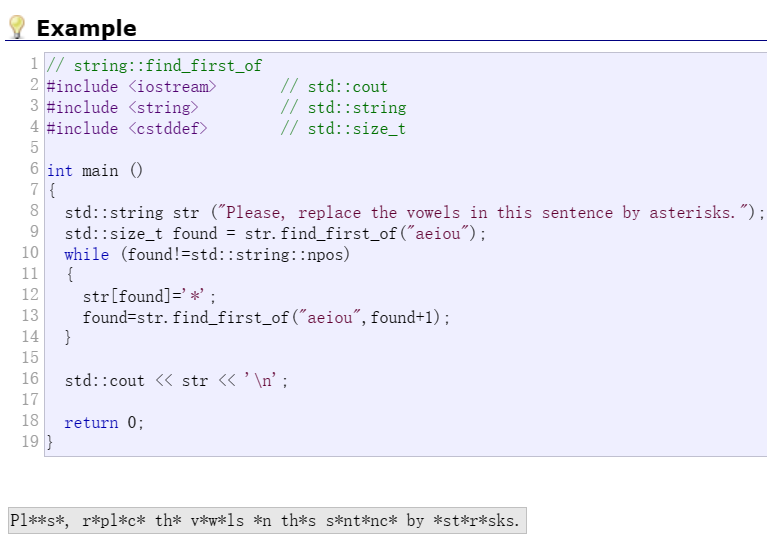
find_first_of
string::find_first_of - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
并不是字面意思,而是找到单词中的某一个字母
Non-member function overloads
relational operators (string)
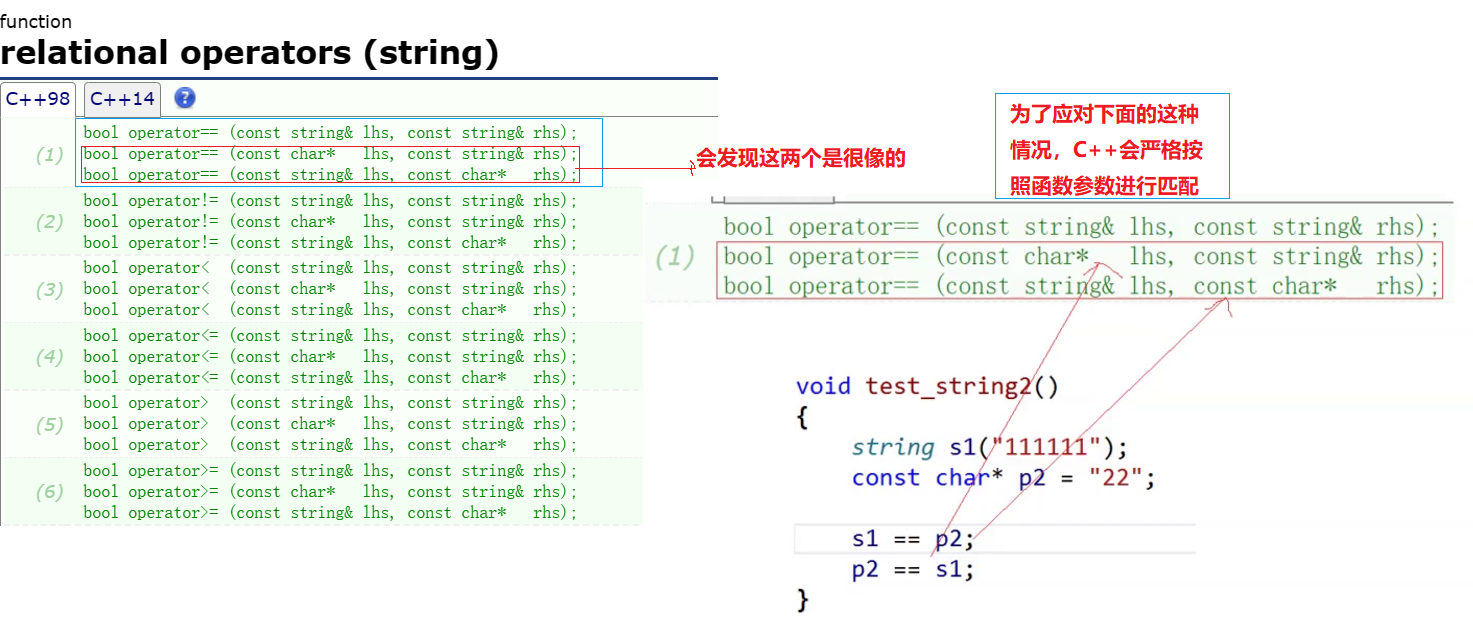
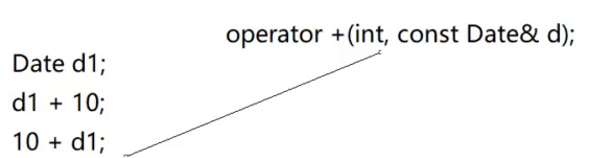
基于这一点可以知道,最下面的一种情况得特殊处理,不过我们得知道,Date类里面的成员函数左参数会被this抢占无法实现这一项,所以得使用友元函数进行处理
一些题目
917. 仅仅反转字母
class Solution {
public:string reverseOnlyLetters(string s) {int begin = 0;int end = s.size()-1;if(end == 1)return s;while(begin < end){//从左找字母while(begin < end && !isalpha(s[begin])){++begin;}//从右找左字母while(begin < end && !isalpha(s[end])){--end;}//左右交换swap(s[begin],s[end]);//再向后走++begin;--end;}return s;}
};415. 字符串相加
class Solution {
public:string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {int end1 = num1.size()-1 , end2 = num2.size()-1;int carry = 0;string retStr;retStr.reserve(max(num1.size(),num2.size())+1); while(end1 >= 0 || end2 >= 0){int ret1 = end1 >= 0 ? num1[end1]-'0' : 0;int ret2 = end2 >= 0 ? num2[end2]-'0' : 0;int ret = ret1 + ret2 + carry;carry = ret/10;ret%=10;retStr+= (ret + '0');end1--;end2--;}if(carry == 1)retStr+='1';reverse(retStr.begin(),retStr.end());return retStr;}
};387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {int tmp[26] = {0};size_t sz = s.size();for(auto ch : s){tmp[ch - 'a']++;}for(size_t i = 0; i<sz; ++i){if(tmp[s[i] - 'a'] == 1)return i;}return -1;}
};HJ1 字符串最后一个单词的长度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {string s;getline(cin,s,'\n'); //默认结束符合为\n,当然也可以自己给定int pos = s.rfind(' ');cout<<s.size() - pos - 1 <<endl;return 0;
}125. 验证回文串
class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(string s) {string tmp;int sz = s.size();tmp.reserve(sz+1);for(int i = 0; i<sz; ++i){if(isalnum(s[i])) //字母和数字都属于字母数字字符,所以使用这个才可以tmp+=tolower(s[i]);}cout<<tmp<<endl;int end = tmp.size()-1;int begine = 0;while(begine<end){if( begine<end && (tmp[begine] != tmp[end]) )return false;begine++;end--;}return true;}
};541. 反转字符串 II
class Solution {
public:string reverseStr(string s, int k) {int sz = s.size();for(int i = 0; i < sz; i += 2*k)reverse(s.begin()+i, s.begin()+min(i+k,sz)); //迭代器可以跳过return s;}
};557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
class Solution {
public:string reverseWords(string s) {int sz = s.size();int i = 0;while(i < sz){int start = i;while(i<sz && s[i] != ' ')++i;int left = start, right = i;while(left<right){swap(s[left],s[right-1]);left++;right--;}++i;//跳过空格}return s;}
};我倾向于这种写法
class Solution {
public:string reverseWords(string s) {int length = s.length();int pos = 0;for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){if (s[i] == ' '){std::reverse(s.begin() + pos, s.begin() + i);pos = i + 1;}}std::reverse(s.begin() + pos, s.end());return s;}
};43. 字符串相乘
class Solution {
public:string multiply(string num1, string num2) {if(num1 == "0" || num2 == "0") return "0";if(num1 == "1" && num2 != "1") return num2;if(num1 != "1" && num2 == "1") return num1;if(num1.length()<num2.length())swap(num1,num2);int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length();string ret(m+n,'0');for(int i = n-1; i>=0; --i){if(num2[i] == '0')continue;int carry = 0;for(int j = m-1; j>=0; --j){int new_num = (num1[j]-'0')*(num2[i]-'0') + (ret[i+j+1]-'0') + carry;carry = new_num/10;new_num %=10;ret[i+j+1]=(new_num + '0'); }if(carry>0)ret[i]=(carry + '0');}int i = 0;while(ret[i] == '0')i++;return ret.substr(i,m+n-i);}
};HJ59 找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;int main() {string s;cin >> s;unordered_map<char, int> Hash;for (auto ch : s) {Hash[ch]++;}int i = 0;for(auto it : s){if(Hash[it] == 1){cout<<it;return 0;}}cout<<-1;return 0;
}结束语
我最怜君中宵舞,道男儿到死心如铁。看试手,补天裂。
《贺新郎·同父见和再用韵答之》