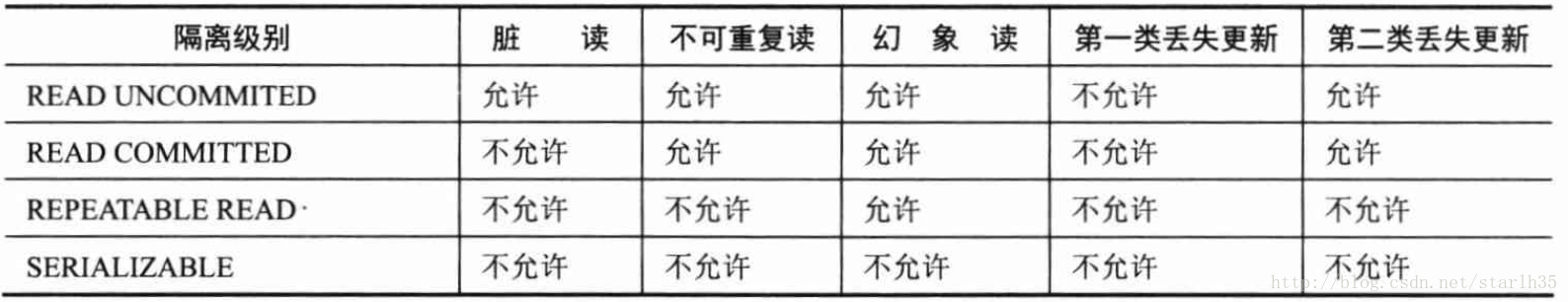
概述
基于上一篇文章提到的DFS算法和BFS算法
A星算法属于图这种数据结构的搜索算法,对比于树的遍历搜索,需要考虑到的问题是:同一个节点的重复访问,所以需要对于已经访问过的节点进行标记。
曼哈顿距离:
在几何度量空间中,用以标明两个点在标准坐标系上的绝对轴距总和。
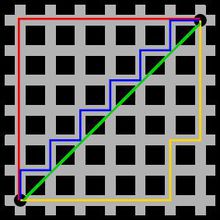
图1中绿色代表欧氏距离(直线距离),蓝色和黄色代表等价的曼哈顿距离。
d( i , j ) = |Xi - Xj| + |Yi - Yj|
优势:计算机图形学中,欧氏距离需要进行浮点运算,曼哈顿距离只涉及到加减法,运算速度大大提高。
我们假设无人车需要从A点(左下侧浅绿色)移动到B点(右上侧浅黄色),但是两点之间被障碍物隔开,我们使用矩阵的形式来构建地图,其中元素为0的矩阵坐标视为可走的,值为1的视为不可走的。
clear;
clc;
clf;
figure(1);
map =[
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 .3 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 .7 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
];
pcolor(map)
colormap summer
[row,col] = size(map);
[start_px,start_py] = find(map == .3);
[end_px,end_py] = find(map == .7);close = struct([]);
closelen = 0;
open = struct([]);
openlen = 0;%% 将起点添加到open列表
open(1).row = start_px;
open(1).col = start_py;
open(1).g = 0;
open(1).h = abs(end_py - start_py) + abs(end_px - start_px);
openlen = openlen + 1;
%% 四种运动格式
sport = [0,1;0,-1;-1,0;1,0];
backNum = 0;
prev = [];
while openlen > 0%% 获取代价最小的值for i = 1:openlenf(i,:) = [i,open(i).g + open(i).h]; endf1 = sortrows(f,2);current = open(f1(1));choose = 0;chooseArr = [];%% 回溯将走过的点标记出来if current.row == end_px && current.col == end_pyi = 1;while(i<=size(prev,1))if prev(i,3) == current.row && prev(i,4) == current.colchoose = choose +1;chooseArr(choose,1) = prev(i,1);chooseArr(choose,2) = prev(i,2);current.row = prev(i,1);current.col = prev(i,2);i = 1;elsei = i + 1;endend for j = 1: size(chooseArr,1)map(chooseArr(j,1),chooseArr(j,2)) = 0.5;endfigure(2);pcolor(map);colormap winter;return; endcloselen = closelen + 1;close(closelen).row = open(f1(1)).row;close(closelen).col = open(f1(1)).col;close(closelen).g = open(f1(1)).g;close(closelen).h = open(f1(1)).h; open(f1(1)) = [];openlen = openlen -1; for i = 1:4dimNormal = all([current.row,current.col]+sport(i,:)>0) ...&& current.row+sport(i,1)<=row && current.col+sport(i,2)<=col;neighbor.row = current.row + sport(i,1);neighbor.col = current.col + sport(i,2);neighbor.g = abs(start_px - neighbor.row) + abs(start_py - neighbor.col);neighbor.h = abs(end_px - neighbor.row) + abs(end_py - neighbor.col);if dimNormalinCloseFlag = 0; if closelen ==0elsefor j = 1:closelenif close(j).row == neighbor.row && close(j).col ==neighbor.colinCloseFlag = 1;break;endendendif inCloseFlagcontinue;endtemp_g = current.g + abs(current.row - neighbor.row) + abs(current.col - neighbor.col);inOpenFlag = 0;for j =1:openlenif open(j).row == neighbor.row && open(j).col ==neighbor.colinOpenFlag = 1;break;endend if ~inOpenFlag && map(neighbor.row,neighbor.col) ~= 1openlen = openlen + 1;open(openlen).row = neighbor.row;open(openlen).col = neighbor.col;open(openlen).g = abs(start_px - neighbor.row) + abs(start_py - neighbor.col);open(openlen).h = abs(end_px - neighbor.row) + abs(end_py - neighbor.col); elseif temp_g >= neighbor.gcontinue;endbackNum = backNum +1;prev(backNum,:) = [current.row ,current.col,neighbor.row ,neighbor.col];neighbor.g = temp_g; elsecontinue;endend
end
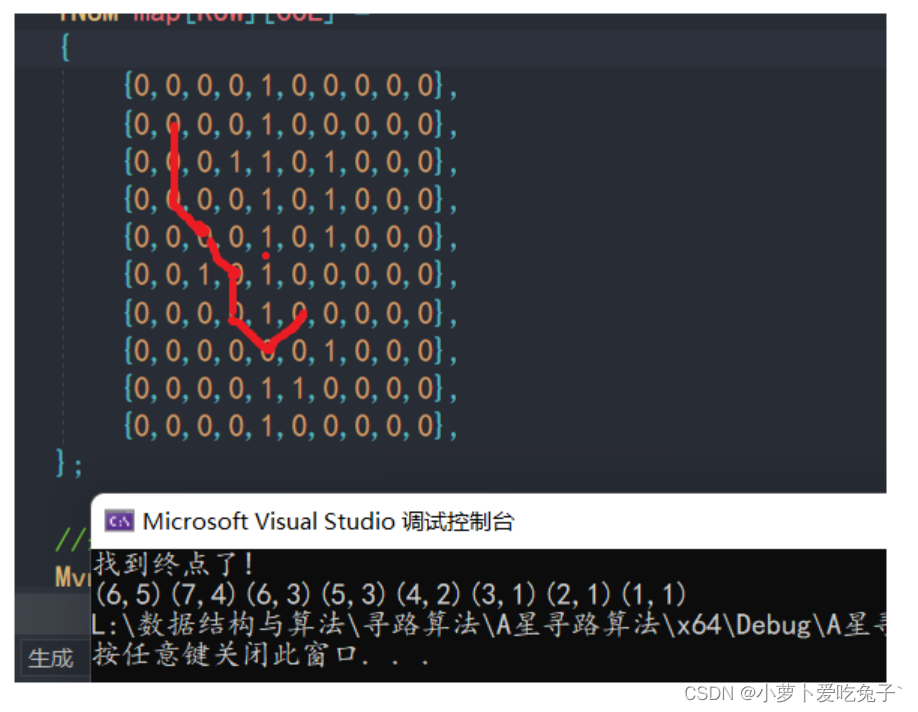
生成初始图:

开始搜索
我们已经完成地图搜寻区域的准备工作,下面我们基于可以移动的四个动作(上、下、左、右)来进行搜索,我们使用openList来维护需要展开的待搜索的节点,在最开始的时候,只有起点这一项。之后,openList里面的元素可能是会经过的,也有可能是不经过的,但是经过的点都应该在openList中存在或者曾经存在。另外,对于我们已经访问过的点,我们使用closeList来进行记录,避免多次访问。
代价函数:
f(v) = g(v) + h(v)
g(v)表示由起始点到当前节点的最小cost;
h(v)表示由当前结点到目标节点的最小cost的估计值;
这里,为方便计算,笔者统一选取了曼哈顿距离用来计算g(v)和h(v)的cost值。
算法伪码:
function AStar_Routing(Gragh(V,E),src,dst)create vertex List openListcreate vertex List closeListcreate prev_mapinsert src into openListwhile(openList.isNotEmpty)current = the node v in openList s.t. min(f[v]) in openListif current = dstreturn reconstruction_route(prev_map,current)endifremove current from openListinsert current into closeListfor each neighbor u of currentif u in closeListcontinue;endiftemp_u = g[current] + h(current,u)if u not in openListinsert u into openListelseif temp_u >= g[u]continue;endifprev_map[u] = current g[u] = temp_costf[u] = g[u] + h(current,dst)endwhile
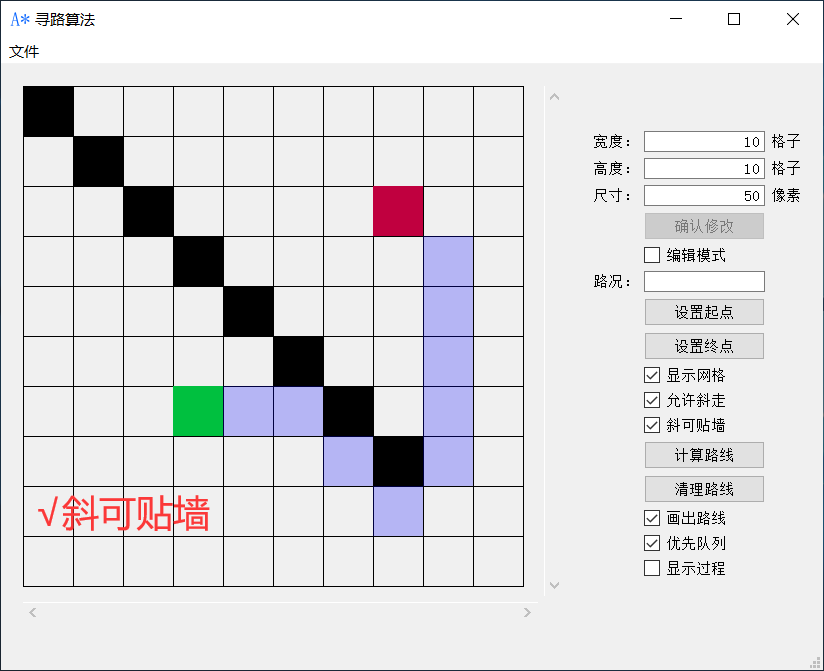
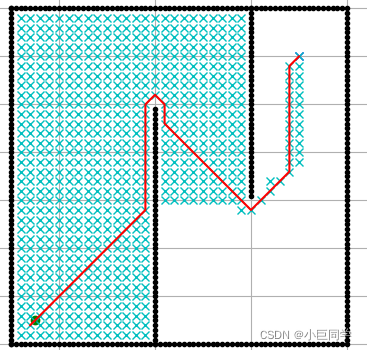
回溯后,整体PATH效果如下:










![[Database] 脏读、幻读这些都是什么?事务隔离级别又是什么?MySQL数据库的事务隔离级别都有哪些?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0b42b3bc46874658a5c93fe5e8c41c09.png)
