A星算法理解
1.选择A星算法的原因
为了进行路径规划算法是不可回避的:启发式搜索算法是比较常规的一类算法就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无谓的搜索路径,提高了效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。启发中的估价是用估价函数表示的,如:f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 。g(n)为起点到当前位置的实际路径长度,h(n)为所在位置到终点的最佳路径的估计距离。前面说每次会优先向终点方向进行移动,就是因为估价函数所导致的。h(n)=0时,意味着此时是盲目搜索,当h(n)越复杂,即约束的条件越多,耗费的时间就越多,而减少约束条件,则可能得到的并不是最优路线。在A算法中,估价函数为f(n)=g(n)+h*(n)。这里面的h*(n)的附加条件为h*(n)<=h‘(n),h’(n)为n到目标的直线最短距离,也就说A*算法中挑选的启发函数是最优的,也正是如此,所找到的路径是最短路径。
2.启发函数的选择问题
有时候经过简单的对比,很容易得出曼哈顿距离作为启发函数,搜索效率最高,并得出曼哈顿距离最好的结论。可是在实际情况下,我们不仅要考虑搜索效率,也要考虑最优性,所以大多情况下选择対角距离作为启发函数。
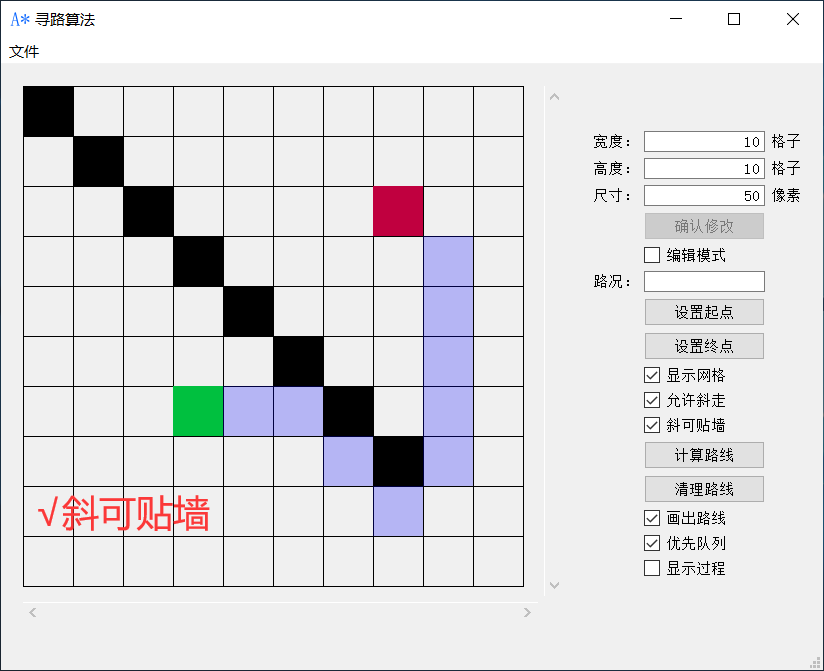
3.算法流程图

4.算法实现步骤
- 启发式函数
double Manhattan_dist,Euclidean_dist,Diagonal_dist;Eigen::Vector3i diff=node2->index-node1->index;double dx,dy,dz;dx=abs(diff(0));dy=abs(diff(1));dz=abs(diff(2));Manhattan_dist=dx+dy+dz;Euclidean_dist=sqrt(diff.dot(diff));float dmin = min(dx, min(dy, dz));float dmax = max(dx, max(dy, dz));float dmid = dx + dy + dz - dmin - dmax;Diagonal_dist=(1.732 - 1.414) * dmin + (1.414 - 1) * dmid + dmax;// tie breakerhue=Diagonal_dist*1.00001;return Euclidean_dist;- 将起始节点放入OPEN表里
startPtr -> gScore = 0;startPtr -> fScore = getHeu(startPtr,endPtr);//STEP 1: finish the AstarPathFinder::getHeu , which is the heuristic functionstartPtr -> id = 1; startPtr -> coord = start_pt;openSet.insert( make_pair(startPtr -> fScore, startPtr) );
- 当主循环不为空时
while ( !openSet.empty() )
- 将代价值最小的点从open表转移到close表中,并将原表中的点删除
// openSet.begin()->second->cameFrom=currentPtr;currentPtr=openSet.begin()->second;//acending order//move it to closeset at oncecurrentPtr->id=-1;// closeSet.insert(make_pair(openSet.begin()->first,openSet.begin()->second));openSet.erase(openSet.begin());GridNodeMap[currentPtr->index[0]][currentPtr->index[1]][currentPtr->index[2]]=currentPtr;- 如果当前点是目标点,路径成功结束。
// if the current node is the goal if( currentPtr->index == goalIdx ){ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();terminatePtr = currentPtr;ROS_WARN("[A*]{sucess} Time in A* is %f ms, path cost if %f m", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() * 1000.0, currentPtr->gScore * resolution ); return;}//get the succetion
- 对扩展节点进行扩展子节点
* */ for(int i = 0; i < (int)neighborPtrSets.size(); i++){/***Judge if the neigbors have been expandedplease write your code belowIMPORTANT NOTE!!!neighborPtrSets[i]->id = -1 : expanded, equal to this node is in close setneighborPtrSets[i]->id = 1 : unexpanded, equal to this node is in open set* */neighborPtr=neighborPtrSets[i];if(neighborPtr -> id == 0){ //discover a new node, which is not in the closed set and open set/***STEP 6: As for a new node, do what you need do ,and then put neighbor in open set and record itplease write your code below* */neighborPtr -> gScore=edgeCostSets[i];neighborPtr -> fScore = getHeu(neighborPtr,endPtr)+edgeCostSets[i];neighborPtr ->id=1;//openneighborPtr->cameFrom=currentPtr;openSet.insert( make_pair(neighborPtr -> fScore, neighborPtr) );//update mapGridNodeMap[neighborPtr->index[0]][neighborPtr->index[1]][neighborPtr->index[2]]=neighborPtr;continue;}else if(neighborPtr -> id ==1){ //this node is in open set and need to judge if it needs to update, the "0" should be deleted when you are coding/***STEP 7: As for a node in open set, update it , maintain the openset ,and then put neighbor in open set and record itplease write your code below* */if(neighborPtr->gScore>edgeCostSets[i])neighborPtr->gScore=edgeCostSets[i];neighborPtr -> fScore = getHeu(neighborPtr,endPtr)+neighborPtr->gScore;continue;}else if(neighborPtr -> id ==-1){//this node is in closed set: it is impossible that node in closeset will be suceession/**please write your code below* */
// ROS_ERROR("NOOOO");continue;}}}
- 由当前点获取路径上的所有点
while(terminatePtr!=nullptr){gridPath.push_back(terminatePtr);terminatePtr=terminatePtr->cameFrom;if(gridPath.size()>100){ROS_ERROR("dead loop!!");break;}}for (auto ptr: gridPath)path.push_back(ptr->coord);reverse(path.begin(),path.end());return path;
一个具有注脚的文本。1
注脚的解释
小白一枚 ↩︎







![[Database] 脏读、幻读这些都是什么?事务隔离级别又是什么?MySQL数据库的事务隔离级别都有哪些?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0b42b3bc46874658a5c93fe5e8c41c09.png)