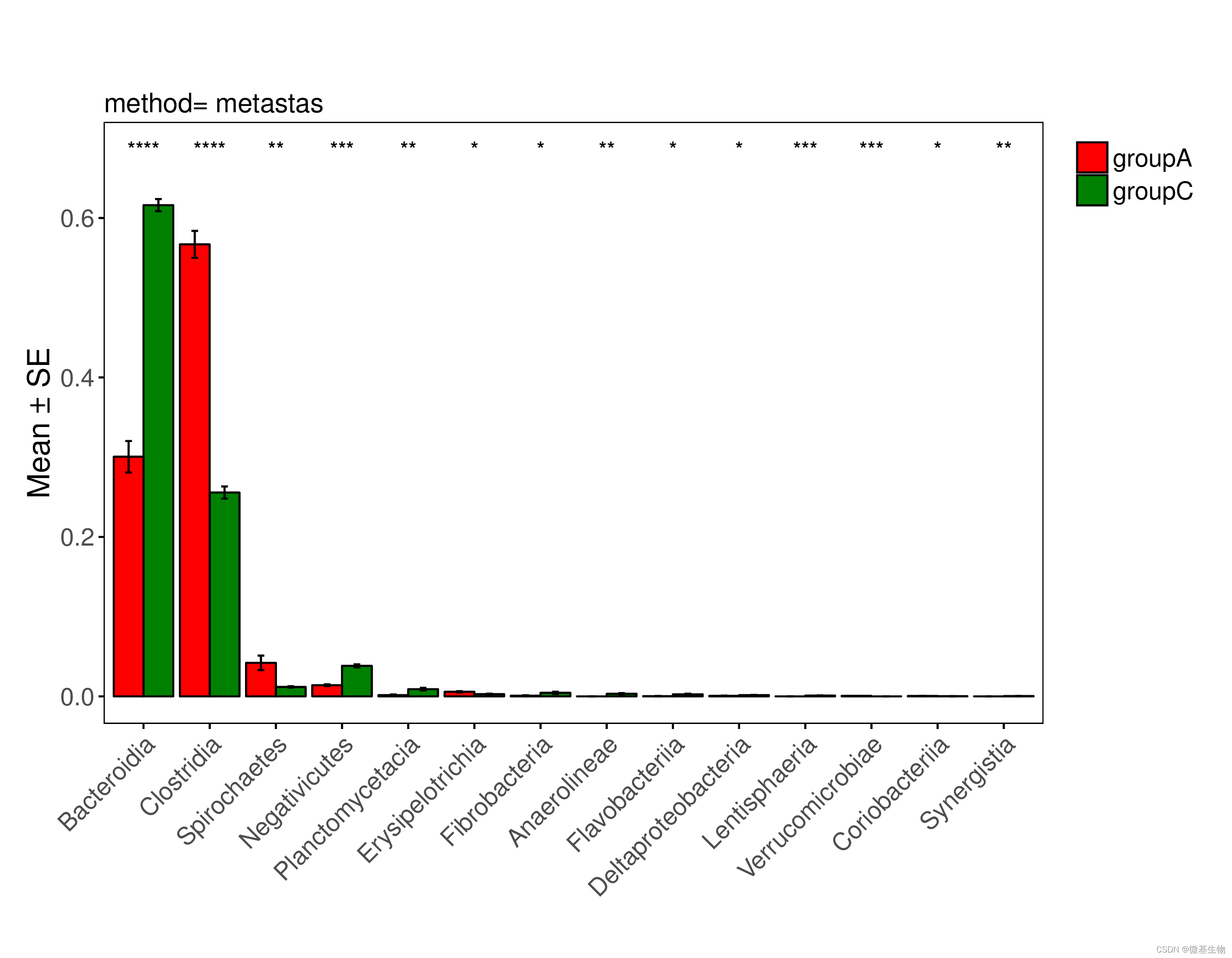
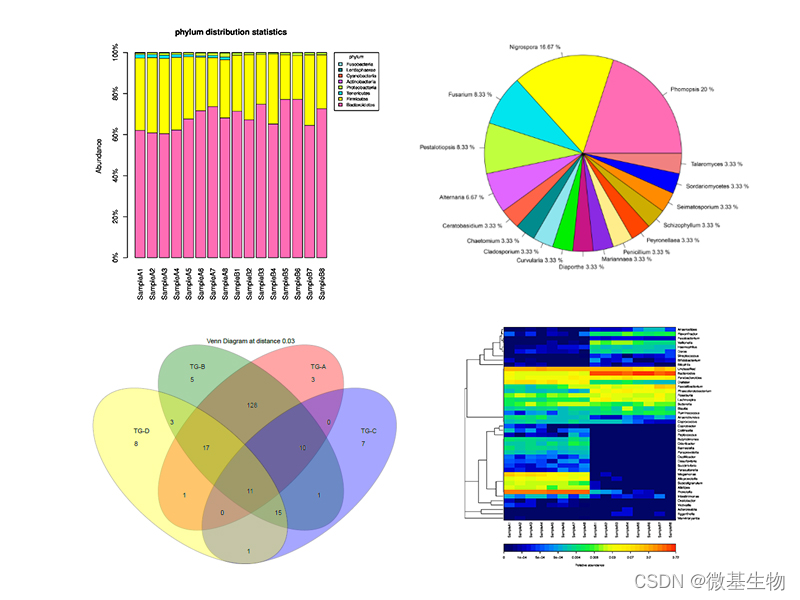
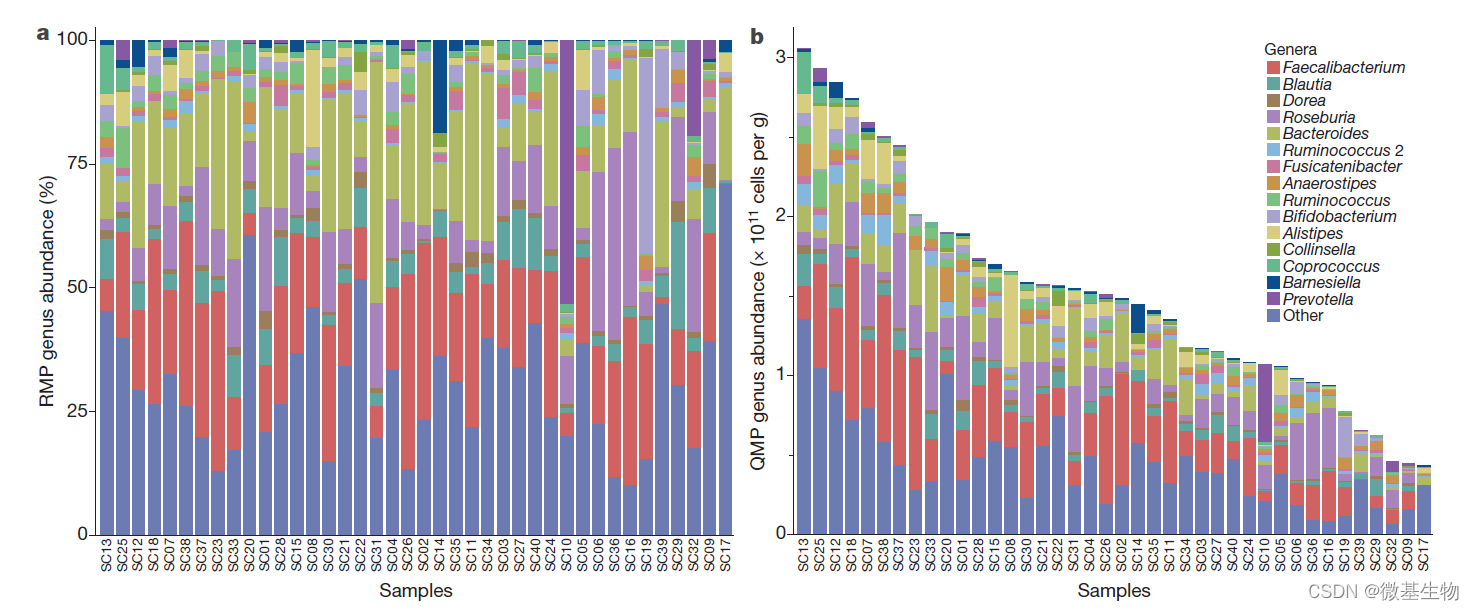
PICRUSt2分析实战:16S扩增子OTU或ASV预测宏基因组、新增KEGG层级
更新时间:2021年7月8日
PICRUSt推出了近8年,引用5000余次。

现推出PICRUSt2,202年再次霸气发表于顶级期刊Nature Biotechnology,原文解读详见:
NBT:PICRUSt2预测宏基因组功能
主页:https://github.com/picrust/picrust2
具有以下三大优势:
任何OTU/ASV直接预测功能;
数据库扩大10倍;
一条命令完成全部分析。
使用中的不足:
需要至少16G内存的Linux环境下使用,我们正在搭web server;
官方起始输入文件为biom格式,我们提供了由txt制作biom的方法,详见:BIOM:生物观测矩阵——微生物组数据通用数据格式;其实软件默认也是支持txt格式的特征表,我们提供了演示。
输出KEGG只有KO,缺少PICRUSt中分类合并为Pathway的三、二、一级的功能,这里我们引用了一个脚本并整理了KEGG的层级数据来实现此功能;
简介
https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki
PICRUSt2 (Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States)是一款基于标记基因序列来预测功能丰度的软件。
“功能”通常指的是基因家族,如KEGG同源基因和酶分类号,但可以预测任何一个任意的特性。同样,预测通常基于16S rRNA基因测序数据,但也可以使用其他标记基因。
在这个帮助文档中,您可以找到脚本、安装说明和工作流的描述。有关详细信息,请参见github wiki的右侧栏。
PICRUSt2包括这些改进以及与原始版本相比的其他改进:
允许用户预测任何16S序列的功能。
来自OTU或扩增序列变体(amplicon sequence variants,ASV,例如DADA2和Deblur输出)的代表性序列可通过序列放置方法用作输入。
用于预测的参考基因组数据库扩大了10倍以上。
从Castor R包中添加隐藏状态预测算法。
允许输出MetaCyc 本体预测,这将可与普通宏基因组学的结果比较。
通路丰度的推断现在依赖于MinPath,这使得这些预测更加严格。
工作流程
PICRUSt2 Flowchart
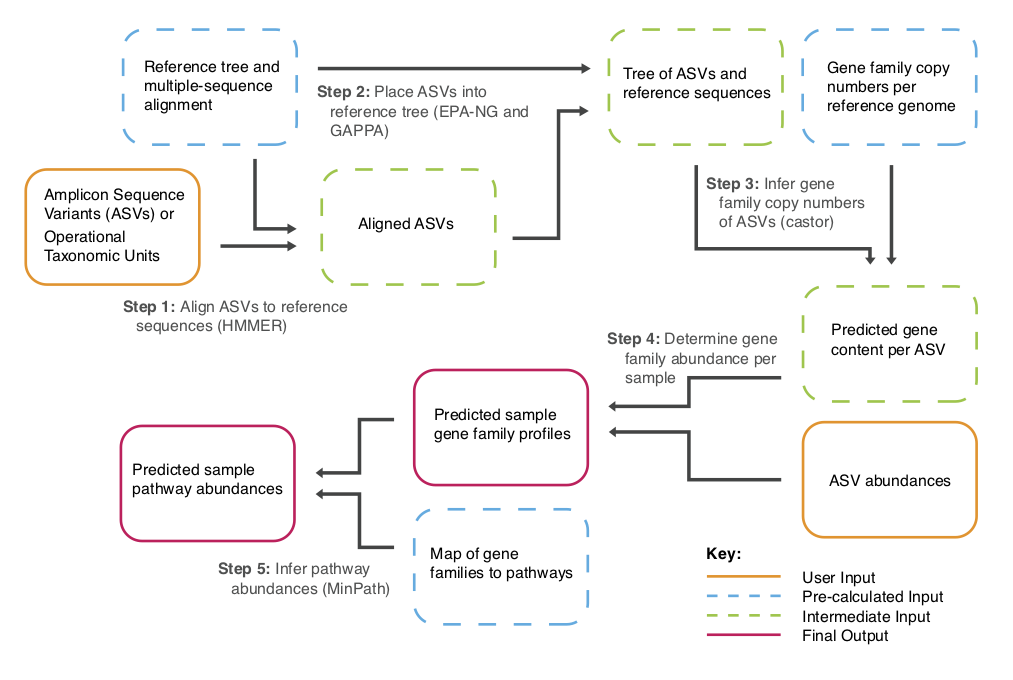
引用主要软件
确定读长的进化位置 For phylogenetic placement of reads:
HMMER (paper, website)
EPA-NG (paper, website)
gappa (pre-print, website).
隐性状态预测 For hidden state prediction:
castor (paper, website)
For pathway inference:
MinPath (paper, website)
主要使用限制
https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki/Key-Limitations
分析PICRUSt2输出时要牢记一些限制,这主要与预测仅限于现有参考基因组的基因内容有关。评估此局限性如何影响数据集中任何解释的最佳方法是与样本子集上的宏基因组的功能谱进行比较 https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki/Validation-with-paired-metagenomes 。
差异丰度的结果可能与基于随机宏基因组学数据所发现的结果大不相同。尽管基随机宏基因组学测序数据的基于扩增子的预测可能与功能谱高度相关,但被识别为明显不同的实际功能可能存在显着差异。查看此 https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki/Major-Bug-Reports-and-Announcements#updated-biorxiv-pre-print-and-major-caveats-highlighted 以获取更多详细信息。
预测受研究序列如何放置在参考树中的限制。默认情况下,EPA-NG用于放置研究序列,这需要考虑多个因素。最重要的是,取决于还同时放置了哪些其他序列,放置可能无法完全重现。在实践中,每个样本的最终预测往往非常相似,但是可能会有重要的差异,尤其是在解释基于单个ASV或功能的情况下。目前,我们正在尝试在PICRUSt2的Beta版中尝试解决使用不同组输入ASV完全重现放置步骤的问题。
任何给定样品类型的准确性将在很大程度上取决于适当的参考基因组的可用性。您可以通过计算每个ASV和样本加权最近排序的分类单元指数(NSTI)值来部分评估此问题,这将使您大致了解参考数据库对ASV的表示程度(请参见下面教程)。但是,16S rRNA基因序列通常无法解析物种内的菌株变异。原核生物菌株的基因含量可以有不同程度的变化,而远距离相关的类群之间也经常发生水平基因转移,因此,应始终将信将疑地持保留态度(taken with a grain of salt)。
一个相关的问题是,参考基因组比其他环境更好地代表了某些环境。例如,即使实际的16S序列本身非常相似,也希望PICRUSt2在人肠的16S序列上比牛瘤胃表现更好。原因是默认参考基因组中缺少许多重要的瘤胃特异性酶。解决此问题的一种潜在方法是创建一个特定于您感兴趣的环境的基因组定制参考数据库,以进行预测。值得注意的是,我们在非人类相关环境上的验证表明,整体预测的效果要好于随机的预测,但尽管如此,我们仍希望许多特定生境功能无法得到很好的体现。
默认情况下,NSTI值大于2的输入序列将从分析中排除。与其他样本相比,这可能会对某些样本产生更大的影响,因此应该对其进行评估(即,您可以确定每个样本中群落相对丰度所占的比例是多少(通常很少)。
PICRUSt2仅能预测输入功能表中的基因(默认情况下,它们对应于KEGG直系同源基因和酶分类号)。尽管这些基因家族是有用的,但它们通常只占宏基因组内总遗传变异的一小部分,而且可能会被错误注释。
PICRUSt2到高级功能(例如路径)的映射完全取决于所使用的映射文件。因此,在通路注释或基因功能分配中的任何缺口或不准确之处仍将存在。例如,许多KEGG直系同源物被列为参与与“人类疾病”有关的途径。在许多情况下,这仅仅是由于细菌中含有(远距离)酶同系物的细菌,这些酶在例如哺乳动物的途径中起着重要的作用。因此,值得仔细检查KEGG路径注释,以确保它们对您的系统合理,并过滤掉所有不相关的通路。
预测仅限于引物靶向的生物所贡献的完整基因组的一部分。如果引物偏离某些分类单元而不是自然地偏向,则这些分类单元贡献的功能将在预测的基因组中较少代表。
安装
https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki/Installation
仅支持Linux或Mac,且运行至少16G内存。
推荐conda安装,自动解决依赖关系。
conda create -n picrust2 -c bioconda -c conda-forge picrust2=2.3.0_b
conda activate picrust2(可选)可选源码安装、pip安装(不推荐),详见上方原始网页链接。
# 官方源下载
wget https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/archive/refs/tags/v2.4.1.tar.gz
tar xvzf v2.4.1.tar.gz
cd picrust2-2.4.1/
conda env create -f picrust2-env.yaml
source activate picrust2
pip install --editable .
# 测试命令(bioconda安装不可用)
pytest分析流程
https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/wiki/Workflow
一条命令完成分析
全部流程已经封装为1个脚本,可以实现上面流程图中的4个主要步骤:
进化树中的序列位置确定;
预测基因组;
预测宏基因组;
通路预测;
输入文件为fasta文件的代表性序列,可以是OTU或ASV,如下面的study_seqs.fna。还需要一个biom格式或制表符分隔的文本格式的特征表study_seqs.biom。
输出文件为基于16S rRNA基因数据预测的宏基因组。
计算每条序列的最近序列物种索引(NTSI),如果ASV的NTSI > 2将被在分析中排除。--stratified参数将计算层化的输出,但将会极大增加计算时间。
picrust2_pipeline.py -s study_seqs.fna \-i study_seqs.biom \-o picrust2_out_pipeline \-p 1比如基于我们常用的代表序列otus.fa和特征表otutab.txt,测试数据见:https://github.com/YongxinLiu/MicrobiomeStatPlot/tree/master/Data/Science2019,手动下载以个otutab.txt和otus.fa两个文件
# 运行流程
picrust2_pipeline.py -s otus.fa -i otutab.txt \-o picrust2 -p 48
# 1线程42分钟,8线程12分钟,流程将产生所有结果,包括中间文件(方便用于解决中间出现的问题)将会输出在picrust2_out_pipeline目录中。注意这是默认的输出,你可以指定不同的注释数据库,或自定义的参考数据库(包括非16S数据库)。
核心输出结果
注:结果表全为gz压缩文件,可用less/zless查看,可用gunzip解压。
EC_metagenome_out - 目录包括非分层的预测宏基因组EC数量 (pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv), 基于预测16S拷贝数校正的特征表 (seqtab_norm.tsv), 每个样本的NSTI权重 (weighted_nsti.tsv)
KO_metagenome_out - 和 EC_metagenome_out 类似, 但为宏基因组KO表
pathways_out - 文件夹包括预测的通路丰度和覆盖度,基于EC数量丰度,一般仅有400多行
额外输出文件
可能对进一步分析的经验用户更有用:
EC_predicted.tsv - 每个ASV/OTU中预测的EC数量;
intermediate - 目录包括MinPath中间文件(minpath_running),用序列取代流程的文件(包括JPLACE文件: intermediate/place_seqs/epa_out/epa_result.jplace).
KO_predicted.tsv - 和EC_predicted.tsv类似, 每个ASV/OTU中预测的KO数量; 为KO 预测中间文件.
marker_nsti_predicted.tsv - 16S预测的拷贝数和NSTI
out.tre - 参考序列的树文件,这个树应该比你自己建的树更专业
结果注释
cd picrust2在第一列后面添加一列注释,结果表也方便在STAMP中进行差异比较。
添加EC的注释
add_descriptions.py -i EC_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz -m EC \-o EC_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat_descrip.tsv.gzEC注释结果
function description KO1 KO2 KO3 KO4
EC:1.1.1.1 Alcohol dehydrogenase 82528.85999999997
EC:1.1.1.100 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase
EC:1.1.1.102 3-dehydrosphinganine reductase 156.32999999KO添加注释
add_descriptions.py -i KO_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz -m KO \-o KO_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat_descrip.tsv.gzKO注释结果
function description KO1 KO2 KO3 KO4
K00001 E1.1.1.1, adh; alcohol dehydrogenase [EC:1.1.1.1]
K00002 AKR1A1, adh; alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP+) [EC:1.1.1.2]
K00003 E1.1.1.3; homoserine dehydrogenase [EC:1.1.1.3] 29262.5
K00004 BDH, butB; (R,R)-butanediol dehydrogenase / meso-butanepathway添加注释,基于MetaCyc数据库
add_descriptions.py -i pathways_out/path_abun_unstrat.tsv.gz -m METACYC \-o pathways_out/path_abun_unstrat_descrip.tsv.gzpathway注释结果
pathway description KO1 KO2 KO3 KO4 KO5
1CMET2-PWY N10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis
3-HYDROXYPHENYLACETATE-DEGRADATION-PWY 4-hydroxyphenylacetate
AEROBACTINSYN-PWY aerobactin biosynthesis 116.8037
ALL-CHORISMATE-PWY superpathway of chorismate metabolism
KEGG通路层级汇总
KO层级通常有7、8千的功能条目。我们更多是汇总对KEGG的3级通路(Pathway),仅剩500多个条目,方便比较和描述。
此步分析在PICRUSt中存在categorize_by_function.py命令,但在第二版中变没有更新此脚本及配套的数据库。我们编写相关脚本和数据库,分别位于 https://github.com/yongxinliu/db 中的script/summarizeAbundance.py (Python3环境) 和 kegg/KO1-4.txt
zcat KO_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz > KEGG.KO.txtpython3 ${db}/script/summarizeAbundance.py \-i KEGG.KO.txt \-m ${db}/kegg/KO1-4.txt \-c 2,3,4 -s ',+,+,' -n raw \-o KEGG统计各层级特征数量
wc -l KEGG*6707 KEGG.KO.txt9 KEGG.PathwayL1.raw.txt55 KEGG.PathwayL2.raw.txt474 KEGG.Pathway.raw.txtPathway(三级结果预览)
Pathway KO1 KO2 KO3 KO4 KO5 KO6 OE1 OE2 14- and 16-membered macrolides [PATH:ko00522] 149.93 173.93 206.8 aspartate and glutamate metabolism [PATH:ko00250] 279378.68999999diarylheptanoid and gingerol biosynthesis [PATH:ko00945] 1078.88kanamycin and gentamicin biosynthesis [PATH:ko00524] 18801.210000000leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis [PATH:ko00290] 170318.89 leucine and isoleucine degradation [PATH:ko00280] 367934.48999999piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis [PATH:ko00960] 38850.8secretion and action [PATH:ko04928] 139.53 66.17 79.350000000000secretion and action [PATH:ko04935] 3.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 serine and threonine metabolism [PATH:ko00260] 381260.81000000006 suberine and wax biosynthesis [PATH:ko00073] 26.0 6.0 14.0 tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis [PATH:ko00400] 217654.89000000附录
分步计算详细
将扩增子序列插入参考进化树中,结果为epa_result_parsed.newick
mkdir -p picrust2/
place_seqs.py -s otus.fa \-o picrust2/ -p 24 \--intermediate placement_working预测16S的拷贝数,-n计算NSTI,预测基因组的E.C.编号,KO相度
hsp.py -i 16S -t picrust2/epa_result_parsed.newick -o picrust2/marker_nsti_predicted.tsv.gz -p 8 -n预测16S的酶学委员会EC编号
hsp.py -i EC -t picrust2/epa_result_parsed.newick -o picrust2/EC_predicted.tsv.gz -p 8预测16S的基因同源簇KO编号(时间长)
hsp.py -i KO -t picrust2/epa_result_parsed.newick -o picrust2/KO_predicted.tsv.gz -p 8预测E.C.和KO的丰度,—strat_out输出分层结果(极大的增加计算时间)
metagenome_pipeline.py -i otutab.txt \-m picrust2/marker_nsti_predicted.tsv.gz \-f picrust2/EC_predicted.tsv.gz \-o picrust2/EC_metagenomemetagenome_pipeline.py -i otutab.txt \-m picrust2/marker_nsti_predicted.tsv.gz \-f picrust2/KO_predicted.tsv.gz \-o KO_metagenome --strat_outMetaCyc通路丰度,基于EC结果汇总
pathway_pipeline.py -i picrust2/EC_metagenome/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz \-o picrust2/pathways \--intermediate pathways_working \-p 8KEGG通路,基于KO
~/miniconda2/envs/picrust2/lib/python3.6/site-packages/picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/KEGG_pathways_to_KO.tsv
pathway_pipeline.py -i picrust2/KO_metagenome/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz -o picrust2/KEGG_pathways --no_regroup --map ~/miniconda2/envs/picrust2/lib/python3.6/site-packages/picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/KEGG_pathways_to_KO.tsv通路的结果:picrust2/KEGG_pathways/path_abun_unstrat.tsv.gz,但缺少注释,add_descriptions.py中KO查不到通路的注释
—coverage 可计算覆盖度
—per_sequence_contrib 可计算每个序列的贡献度,需要指定—per_sequence_abun和—per_sequence_function指定特征表,和具体序列的功能,极大的增加计算时间
流程picrust2_pipeline.py参数
picrust2_pipeline.py -h[-h] -s PATH -i PATH -o PATH [-p PROCESSES]
[-r PATH] [—in_traits IN_TRAITS]
[—custom_trait_tables PATH]
[—marker_gene_table PATH] [—pathway_map MAP]
[—reaction_func MAP] [—no_pathways]
[—regroup_map ID_MAP] [—no_regroup]
[—stratified] [—max_nsti FLOAT]
[—min_reads INT] [—min_samples INT]
[-m {mp,emp_prob,pic,scp,subtree_average}]
[—min_align MIN_ALIGN] [—skip_nsti]
[—skip_minpath] [—no_gap_fill] [—coverage]
[—per_sequence_contrib] [—wide_table]
[—skip_norm] [—remove_intermediate] [—verbose]
[-v]
完整PICRUSt2管道的包装器。使用EPA-NG和GAPPA进行序列放置,以将研究序列(即OTU和ASV)放置到参考树中。然后使用蓖麻R包运行隐藏状态预测,以预测每个研究序列的基因组。然后生成元基因组图谱,可以通过贡献序列对其进行分层。最后,基于元基因组图谱预测途径的丰度。默认情况下,输出文件包括对酶分类(EC)编号,KEGG直系同源物(KO)和MetaCyc途径丰度的预测。但是,此脚本使用户可以使用自定义参考和特征表自定义分析。
-s PATH - OTU或ASV的序列文件
-i PATH - 序列丰度表 (BIOM, TSV, or mothur shared file format)
-o PATH - 输出目录
-p INT - 线程数 (默认: 1).
—ref_dir DIRECTORY: 参数用于指定非标准参考序列文件,需要文件夹中包括四个文件如下:
—in_traits IN_TRAITS - 逗号分隔列表(无空格),包括来自以下数据集的基因家族: COG, EC, KO, PFAM, TIGRFAM。注意,这些EC数据默认预测,可用--no_pathways关闭 (默认: EC,KO).
—custom_trait_tables PATH - 可选的目录用于存放性状表,要求包括基因组为行,基因家族为列 (优先级高于 —in_traits setting),用于hidden-state预测。多个表可以用逗号分隔输入,第一个自定义的表用于推断通路丰度。此命令通常还需要一个标记基因表 (—marker_gene_table)
—marker_gene_table PATH - 标记基因拷贝数表 (默认16S 拷贝数).
—pathway_map MAP - 最小通路表 MinPath mapfile. 默认为件为原核生物通路的MetaCyc反应 The default mapfile maps MetaCyc reactions to prokaryotic pathways (default: picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/metacyc_path2rxn_struc_filt_pro.txt).
—no_pathways - 不进行推断通路,默认为计算的 Flag to indicate that pathways should NOT be inferred (otherwise they will be inferred by default). Predicted E.C. number abundances are used to infer pathways when default reference files are used.
—regroup_map ID_MAP - 基因ID与基因家族对应表,默认的EC编号与MetaCyc反应的对应表 Mapfile of ids to regroup gene families to before running MinPath. The default mapfile is for regrouping E. C. numbers to MetaCyc reactions (default: picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/ec_level4_to_metacyc_rxn.tsv).
—no_regroup - 不进行基因家族的按反应归类。当你使用自定义数据时,推荐使用此参数 Do not regroup input gene families to reactions as specified in the regrouping mapfile. This option should only be used if you are using custom reference and/or mapping files.
—stratified - 在各层级产生分层的表,即功能对应物种来源,这步需要较多计算时间 Flag to indicate that stratified tables should be generated at all steps (will increase run-time).
-a {hmmalign,papara} - 比对序列至多序列比对的程序,默认为hmmalign。Which program to use for aligning query sequences to reference MSA prior to EPA-NG step (default: hmmalign).
—max_nsti INT - 序列与参考序列的相似度阈值,大于2认为没有相近基因组将排除在分析之外 Sequences with NSTI values above this value will be excluded (default: 2).
—min_reads INT - 每个ASV的最低丰度,默认为1。即低于此丰度的在层化中被视稀释分类, Minimum number of reads across all samples for each input ASV. ASVs below this cut-off will be counted as part of the “RARE” category in the stratified output (default: 1).
—min_samples INT - ASV在样品中出现的频率,默认1。。即低于此频率的在层化中被视为稀释分类, Minimum number of samples that an ASV needs to be identfied within. ASVs below this cut-off will be counted as part of the “RARE” category in the stratified output (default: 1).
-m {mp,emp_prob,pic,scp,subtree_average} - HSP方法选择,mp预测离散性状使用最大简约法,emp_prob预测离散性状使用经验概率,subtree_average预测连续性状使用子树平均,pic预测连续性状使用进化独立比较,scp预测连续性状使用简约平方变换;HSP method to use. “mp”: predict discrete traits using max parsimony. “emp_prob”: predict discrete traits based on empirical state probabilities across tips. “subtree_average”: predict continuous traits using subtree averaging. “pic”: predict continuous traits with phylogentic independent contrast. “scp”: reconstruct continuous traits using squared-change parsimony (default: mp).
—skip_nsti - 不计算最近序列分类索引NSTI,默认在预测拷贝数表marker_nsti_predicted.tsv中添加列;Do not calculate nearest-sequenced taxon index (NSTI), which is added as a column in the predicted marker-gene copy-number table by default (marker_nsti_predicted.tsv).
—no_gap_fill - 预测前不进行空白填充。默认进行空白填充。Do not perform gap filling before predicting pathway abundances (Gap filling is on otherwise by default).
—coverage - 计算通路的覆盖度,这计算通路有无的另一种方法。这些值只对实验和高级用户有用。这处与HUMAnN2中计算的方法一致。Calculate pathway coverages as well as abundances, which are an alternative way to identify which pathway are present. Note that these values are experimental and only useful for advanced users. Coverage is also calculated using the same approach as HUMAnN2.
—skip_minpath - 跳过最小通路计算,默认使用MinPath Do not run MinPath to identify which pathways are present as a first pass (MinPath is run by default).
—per_sequence_contrib - 计算每条序列的贡献,即将计算每个个体的通路,只有当—coverage打开时才计算分层的覆盖度。Option to specify that stratified abundances should be reported in terms of the contribution by each predicted genome rather than how much each genome is contributing to the overall community abundance. In other words, pathway abundances will be calculated for each individual predicted genome. Stratified coverages will only be reported when this option is used (and —coverage is set).
—verbose - 输出计算过程的代码 If specified, print out wrapped commands to screen.
建树place_seqs.py参数
运行EPA-ng和GAPPA以将研究序列(即OTU或ASV)放入参考树的脚本。通常这样做是为了准备使用PICRUSt2进行后续的隐藏状态预测。需要未比对的研究序列FASTA。用户可以根据需要指定非默认参考文件。
-h, --help 帮助 show this help message and exit
-s PATH, --study_fasta PATH输入序列,非对齐FASTA of unaligned study sequences.
-r PATH, --ref_dir PATH参考序列目录,系统默认 Directory containing reference sequence files(default: ~/miniconda2/envs/picrust2/lib/python3.6/site-packages/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/pro_ref).Please see the online documentation for how to namethe files in this directory in order to use customreference files.
-o PATH, --out_tree 输出文件 PATHName of final output tree.
-p PROCESSES, --processes PROCESSES线程数 Number of processes to run in parallel (default: 1).Note that this refers to multithreading rather thanmultiprocessing when running EPA-ng and GAPPA.
--intermediate PATH 中间文件位置 Output folder for intermediate files (will be deletedotherwise).
--min_align MIN_ALIGN比对长度 Proportion of the total length of an input querysequence that must align with reference sequences. Anysequences with lengths below this value after makingan alignment with reference sequences will be excludedfrom the placement and all subsequent steps. (default:0).
--chunk_size CHUNK_SIZE每批读长数量 Number of query seqs to read in at once for EPA-ng(default: 5000).
--verbose 输出计算过程 If specified, print out wrapped commands and otherdetails to screen.
-v, --version 版本 show program's version number and exitUsage example:
place_seqs.py -s study_seqs.fna -o placed_seqs.tre --processes 1 --intermediate placement_working拷贝数、功能预测hsp.py参数
该脚本根据特征树值未知的输入树中的提示执行隐藏状态预测。通常,给定一棵树和一组已知的性状值,该脚本用于预测每个扩增子序列变体在预测基因组中存在的基因家族的拷贝数。该脚本输出特征预测表。
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t PATH, --tree PATH 指定刚生成的树文件 The full reference tree in newick format containingboth study sequences (i.e. ASVs or OTUs) and referencesequences.
-o PATH, --output PATH输出文件 Output table with predicted abundances per studysequence in input tree. If the extension ".gz" isadded the table will automatically be gzipped.
-i {16S,COG,EC,KO,PFAM,TIGRFAM,PHENO}, --in_trait {16S,COG,EC,KO,PFAM,TIGRFAM,PHENO}指定预测类别,包括16S,COG,EC,KO,PAFM,TIGRFAM,PHENO等7种。Specifies which default trait table should be used.Use the --observed_trait_table option to input a non-default trait table.
--observed_trait_table PATH个性输入文件 The input trait table describing directly observedtraits (e.g. sequenced genomes) in tab-delimitedformat. Necessary if you want to use a custom table.
--chunk_size CHUNK_SIZENumber of functions to run at a time on one processor.Note that you should consider how many processes youhave specified before changing this option. E.g. ifyou specify the chunk_size to be the total number offunctions, 1 processor will be used even if youspecified more so the job will be substantially slower(default: 500).
-m {mp,emp_prob,pic,scp,subtree_average}, --hsp_method {mp,emp_prob,pic,scp,subtree_average}树类型 HSP method to use."mp": predict discrete traits usingmax parsimony. "emp_prob": predict discrete traitsbased on empirical state probabilities across tips."subtree_average": predict continuous traits usingsubtree averaging. "pic": predict continuous traitswith phylogentic independent contrast. "scp":reconstruct continuous traits using squared-changeparsimony (default: mp).
-n, --calculate_NSTI 计算NSTI Calculate NSTI and add to output file.
--check Check input trait table before HSP.
-p PROCESSES, --processes PROCESSES线程数 Number of processes to run in parallel (default: 1).
--seed SEED 种子数使用结果可重复 Seed to make output reproducible, which is necessaryfor the emp_prob method (default: 100).
--verbose If specified, print out wrapped commands and otherdetails to screen.
-v, --version show program's version number and exitUsage example:
hsp.py -n -t out.tre -i 16S -o 16S_predicted_and_nsti.tsv.gz --processes 1宏基因组表计算metagenome_pipeline.py参数
基于每个研究序列的预测功能,生成每个样本的宏基因组功能组成文件。注意,这些序列通常对应于OTU或ASV。默认情况下,在输出最终文件之前,将通过标记基因拷贝的预测数量对指定的序列丰度表进行标准化。通过贡献ASV分层的样本宏基因组表也可以选择输出。
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i PATH, --input PATH输入特征表,BIOM或文本均可 Input table of sequence abundances (BIOM, TSV, ormothur shared file format).
-f PATH, --function PATHKO/EC功能注释表 Table of predicted gene family copy numbers (output ofhsp.py).
-m PATH, --marker PATH拷贝数文件Table of predicted marker gene copy numbers (output ofhsp.py - typically for 16S).
--max_nsti FLOAT 准确性过滤阈值 Sequences with NSTI values above this value will beexcluded (default: 2).
--min_reads INT 丰度过滤 Minimum number of reads across all samples for eachinput ASV. ASVs below this cut-off will be counted aspart of the "RARE" category in the stratified output(default: 1).
--min_samples INT 频率过滤 Minimum number of samples that an ASV needs to beidentfied within. ASVs below this cut-off will becounted as part of the "RARE" category in thestratified output (default: 1).
--strat_out 输出分层结果 Output table stratified by sequences as well. Bydefault this will be in "contributional" format (i.e.long-format) unless the "--wide_table" option is set.The startified outfile is named"metagenome_contrib.tsv.gz" when in long-format.
--wide_table 输出分层结果 Output wide-format stratified table of metagenomepredictions when "--strat_out" is set. This is thedeprecated method of generating stratified tablessince it is extremely memory intensive. The startifiedoutfile is named "pred_metagenome_strat.tsv.gz" whenthis option is set.
--skip_norm Skip normalizing sequence abundances by predictedmarker gene copy numbers (typically 16S rRNA genes).This step will be performed automatically unless thisoption is specified.
-o PATH, --out_dir PATHOutput directory for metagenome predictions. (default:metagenome_out).
-v, --version show program's version number and exitUsage example:
metagenome_pipeline.py -i seqabun.biom -f predicted_EC.tsv.gz -m predicted_16S.tsv.gz --max_nsti 2.0 -o metagenome_out通路计算pathway_pipeline.py
基于样本中基因家族丰度推断通路存在和丰度的脚本。默认情况下,该脚本需要一个EC数量丰度表(由PICRUSt2输出)。但是,也可以指定对通路映射文件的替代反应。默认情况下,EC号首先重新分组为MetaCyc反应,然后通过默认数据库链接到MetaCyc通路。
仅当输入分层的基因组(或设置了—per_sequence_contrib)时,才会输出分层输出。请注意,默认情况下,分层丰度是基于预测的基因组(例如序列)对整个群落的丰度有多大贡献,而不是仅基于该基因组中预测基因的途径的丰度。换句话说,一个预测的基因组可能对整个群落的通路丰度做出了很大的贡献,这仅仅是因为该通路的一个所需基因在该基因组中的丰度非常高,即使该通路没有其他所需的基因。相反,应使用—per_sequence_contrib选项基于每个基因组中的预测基因家族来获得每个途径的预测丰度和覆盖率。请注意,使用—per_sequence_contrib选项可以大大增加运行时间。
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i IN_TABLE, --input IN_TABLE输入metagenome生成的层化或非层化结果 Input TSV table of gene family abundances (either theunstratified or stratified output ofmetagenome_pipeline.py).
-o DIRECTORY, --out_dir DIRECTORYOutput folder for pathway abundance output.
-m MAP, --map MAP Mapping of pathways to reactions. The default mapfilemaps MetaCyc reactions to prokaryotic MetaCyc pathways(default: /mnt/bai/yongxin/miniconda2/envs/picrust2/lib/python3.6/site-packages/picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/metacyc_path2rxn_struc_filt_pro.txt).
--skip_minpath Do not run MinPath to identify which pathways arepresent as a first pass (on by default).
--no_gap_fill Do not perform gap filling before predicting pathwayabundances (Gap filling is on otherwise by default.
--intermediate DIR Output folder for intermediate files (will be deletedotherwise).
-p PROCESSES, --processes PROCESSESNumber of processes to run in parallel (default: 1).
--no_regroup Do not regroup input gene families to reactions asspecified in the regrouping mapfile.
--coverage Calculate pathway coverages as well as abundances,which are experimental and only useful for advancedusers.
-r ID_MAP, --regroup_map ID_MAPMapfile of ids to regroup gene families to beforerunning MinPath. The default mapfile is for regroupingEC numbers to MetaCyc reactions (default: /mnt/bai/yongxin/miniconda2/envs/picrust2/lib/python3.6/site-packages/picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/ec_level4_to_metacyc_rxn.tsv).
--per_sequence_contribFlag to specify that MinPath is run on the genescontributed by each sequence (i.e. a predicted genome)individually. Note this will greatly increase theruntime. The output will be the predicted pathwayabundance contributed by each individual sequence.This is in contrast to the default stratified output,which is the contribution to the community-widepathway abundances. Experimental pathway coveragestratified by contributing sequence will also beoutput when --coverage is set. Options--per_sequence_contrib and --per_sequence_functionneed to be set when this option is used (default:False).
--per_sequence_abun PATHPath to table of sequence abundances across samplesnormalized by marker copy number (typically thenormalized sequence abundance table output at themetagenome pipeline step). This input is required whenthe --per_sequence_contrib option is set. (default:None).
--per_sequence_function PATHPath to table of function abundances per sequence,which was outputted at the hidden-state predictionstep. This input is required when the--per_sequence_contrib option is set. Note that thisfile should be the same input table as used for themetagenome pipeline step (default: None).
--wide_table Flag to specify that wide-format stratified tableshould be output rather than metagenome contributiontable. This is the deprecated method of generatingstratified tables since it is extremely memoryintensive (default: False).
--verbose If specified, print out wrapped commands and otherdetails to screen.
-v, --version show program's version number and exitUsage examples:Default mapping of predicted EC number abundances to MetaCyc pathways:
pathway_pipeline.py -i EC_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz -o pathways_out --processes 1Mapping predicted KO abundances to legacy KEGG pathways (with stratified output that represents contributions to community-wide abundances):
pathway_pipeline.py -i KO_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_strat.tsv.gz -o KEGG_pathways_out --no_regroup --map picrust2/picrust2/default_files/pathway_mapfiles/KEGG_pathways_to_KO.tsvMap EC numbers to MetaCyc pathways and get stratified output corresponding to contribution of predicted gene family abundances within each predicted genome:
pathway_pipeline.py -i EC_metagenome_out/pred_metagenome_unstrat.tsv.gz -o pathways_out_per_seq --per_sequence_contrib --per_sequence_abun EC_metagenome_out/seqtab_norm.tsv.gz --per_sequence_function EC_predicted.tsv.gz注释add_descriptions.py
该脚本将描述列添加到功能丰富度表并输出一个新文件。用户需要指定输入文件以及输入表中的功能类型。如果有id重名,将显示错误,否则将在函数表中而不是mapfile中的id描述中填写“ not_found”。
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i PATH, --input PATHInput function abundance table.
-o PATH, --output PATHOutput function abundance table with added descriptioncolumn. If the extension ".gz" is added the table willautomatically be gzipped.
-m {METACYC,COG,EC,KO,PFAM,TIGRFAM}, --map_type {METACYC,COG,EC,KO,PFAM,TIGRFAM}注释类型,但没有KEGG_pathway Specifies which default mapping table should be used.Use the --custom_map_table option to input a non-default mapping table.
--custom_map_table PATH手动指定注释列表 An input map table linking function ids todescriptions for each function.
-v, --version show program's version number and exitUsage:
add_descriptions.py -i IN_TABLE -m KO -o OUT_TABLE猜你喜欢
10000+:菌群分析 宝宝与猫狗 梅毒狂想曲 提DNA发Nature Cell专刊 肠道指挥大脑
系列教程:微生物组入门 Biostar 微生物组 宏基因组
专业技能:学术图表 高分文章 生信宝典 不可或缺的人
一文读懂:宏基因组 寄生虫益处 进化树
必备技能:提问 搜索 Endnote
文献阅读 热心肠 SemanticScholar Geenmedical
扩增子分析:图表解读 分析流程 统计绘图
16S功能预测 PICRUSt FAPROTAX Bugbase Tax4Fun
在线工具:16S预测培养基 生信绘图
科研经验:云笔记 云协作 公众号
编程模板: Shell R Perl
生物科普: 肠道细菌 人体上的生命 生命大跃进 细胞暗战 人体奥秘
写在后面
为鼓励读者交流、快速解决科研困难,我们建立了“宏基因组”专业讨论群,目前己有国内外5000+ 一线科研人员加入。参与讨论,获得专业解答,欢迎分享此文至朋友圈,并扫码加主编好友带你入群,务必备注“姓名-单位-研究方向-职称/年级”。PI请明示身份,另有海内外微生物相关PI群供大佬合作交流。技术问题寻求帮助,首先阅读《如何优雅的提问》学习解决问题思路,仍未解决群内讨论,问题不私聊,帮助同行。

学习16S扩增子、宏基因组科研思路和分析实战,关注“宏基因组”
 点击阅读原文,跳转最新文章目录阅读
点击阅读原文,跳转最新文章目录阅读