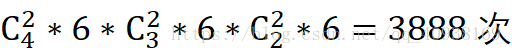原理
暴力枚举所有的情况,运算符号4个,加减乘除 + - * / ,整数数字4个(易扩展为5个数或者更多)。所需要枚举的次数:
- 数字顺序:4个数的全排列,4! = 24。
- 运算符号:4个数需要3个符号,每个可选4种,43 = 64。
- 加括号方式:((AB)C)D、(A(BC))D、(AB)(CD)、A((BC)D)、A(B(CD)),共5种。
- 枚举次数 24*64*5
实现细节
- 全排列枚举由库函数
next_permutation来完成枚举 - 64种运算符号搭配由一个整数状压(0—63)来完成枚举
- 加括号方式由后缀表达式来完成,运算对象用0表示,运算符用1表示,由右向左开始,以
(A-(B+C))*D为例,转成后缀表达式为ABC+-D*,改成由右向左阅读的顺序,*D-+CBA,再转成用01标记的二进制数1011000,为了在代码中便于对运算符和运算对象同时操作,去掉最后一个0,变为101100,去掉的那个在初始时提前压栈,这样就正好3个0、3个1了,同理,((AB)C)D->101010、(AB)(CD)->110010、A((BC)D)->110100、A(B(CD))->111000 - 由于运算过程中含有除法,用double又不是我风格,所以写个小结构体表示有理数。包含分子和分母。
- 验证是否有解和打印解分开,更灵活。
代码
运算过程和模拟计算后缀表达式差不多,一个原理。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define top_and_pop(stack, var) var=stack.top();stack.pop()
using namespace std;
//运算 + - * / , 数量 num_n = 4
const int num_n = 4, max_oper = 1 << (2*num_n - 2);
struct Num {int a, b;Num(int ta = 0, int tb = 1) : a(ta), b(tb) {if(b < 0)a = -a, b = -b;int g = __gcd(abs(a), b);a /= g, b /= g;}
};
// 候选的后缀表达式所代表的整数值
int methods[5] = {0b101010, 0b101100, 0b110010, 0b110100, 0b111000};
bool hasAnswer(int* arr, int oper_code, int method) {stack<int> ops;stack<Num> nums;int arr_pos = 0;nums.push(Num(arr[arr_pos++]));while(method) {if(method & 1) {Num x,y;top_and_pop(nums, y);top_and_pop(nums, x);switch(ops.top()) {case 0: // +nums.push({x.a * y.b + x.b * y.a, x.b * y.b});break;case 1: // -nums.push({x.a * y.b - x.b * y.a, x.b * y.b});break;case 2: // *nums.push({x.a * y.a, x.b * y.b});break;case 3: // /if(y.a == 0)return false;nums.push({x.a * y.b, x.b * y.a});break;}ops.pop();} else {nums.push(Num(arr[arr_pos++]));ops.push(oper_code & 3);oper_code >>= 2;}method >>= 1;}return nums.top().a == 24 && nums.top().b == 1;
}
void printAnswer(int* arr, int oper_code, int method) {const char* operstr = "+-*/";string zuo = "(", you = ")", s1, s2;stack<char> ops;stack<string> str;int arr_pos = 0;str.push(to_string(arr[arr_pos++]));while(method) {if(method & 1) {top_and_pop(str, s2);top_and_pop(str, s1);str.push(zuo + s1 + ops.top() + s2 + you);ops.pop();} else {str.push(to_string(arr[arr_pos++]));ops.push(operstr[oper_code & 3]);oper_code >>= 2;}method >>= 1;}string res = str.top();cout << res.substr(1, res.length() - 2) << endl;
}
int arr[num_n]; // 4 个数字
int main() {int t;cin >> t;
outer_loop:while(t--) {for(int i = 0; i < num_n; i++) {cin >> arr[i];}sort(arr, arr + num_n);do {for(int meth : methods) {for(int oper = 0; oper < max_oper; oper++) {if(hasAnswer(arr, oper, meth)) {printAnswer(arr, oper, meth);goto outer_loop; // break multiloop}}}} while(next_permutation(arr, arr + num_n));cout << "No solution" << endl;}
}
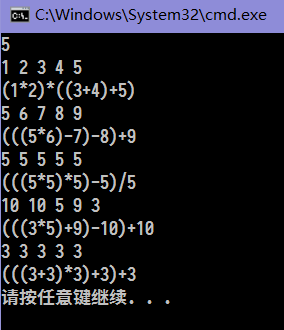
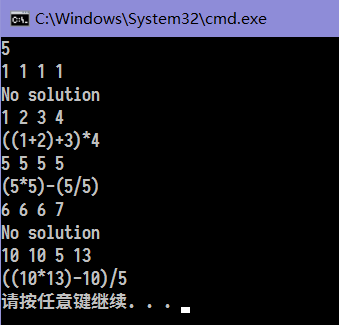
测试
注: 第一个数是测试组数
扩展
上述代码可以很容易的扩展成多个数字,比如对5个数字进行24点计算。把 num_n 改为5,然后再修改一下 methods 数组为
int methods[14] = {0b10101010,0b10101100,0b10110010,0b10110100,0b10111000,0b11001010,0b11001100,0b11010010,0b11010100,0b11011000,0b11100010,0b11100100,0b11101000,0b11110000};
其中14就是5个数字加括号一共的种类数,他是卡特兰数。其实上面那一串二进制数是有规律的,所以可以写代码来生成,而不需要手算。
其实,也可以写成递归版的,就不需要算这些后缀表达式了。改天写一写。
5个数24点测试