背景
下载地址:https://rrc.cvc.uab.es/?ch=4&com=downloads
注意:该数据为开源数据,但需要注册一个账号,简单注册下即可下载;
介绍:用于文本检测任务,数据包含1000张训练样本以及500张测试样本;
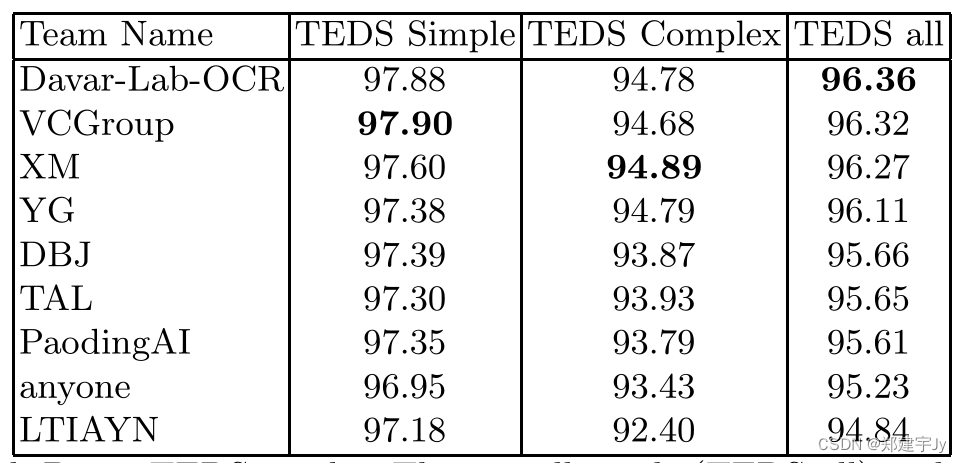
所需数据展示
首先,该数据是用于EAST算法,需要处理成模型所需的数据格式;
原始标签数据:

可以看出,每张图像对应一个文本,其中有多个框的标注信息,分别表示四个坐标点和类别;
所需数据格式:

需要的数据分为三个部分,Score map、d_map、θ_map,取文本位置中的每个像素点作为标签样本;
代码实现
主函数实现
class custom_dataset(data.Dataset):# scale表示图像缩放到原来的1/4,图像大小缩放为512x512def __init__(self, img_path, gt_path, scale=0.25, length=512):super(custom_dataset, self).__init__()# 因为图片和标签数据都是对应的,并且在Linux系统下是乱序读入,所以需要排序self.img_files = [os.path.join(img_path, img_file) for img_file in sorted(os.listdir(img_path))]self.gt_files = [os.path.join(gt_path, gt_file) for gt_file in sorted(os.listdir(gt_path))]self.scale = scaleself.length = length# 返回数据数量def __len__(self):return len(self.img_files)# __getitem__这个函数好用,可以建立个类,然后用下标来调用# 所有数据处理的调用都在这里进行def __getitem__(self, index):# 读取标签文件中所有文本with open(self.gt_files[index], 'r', encoding='utf-8-sig') as f:lines = f.readlines()# 提取点和标签的函数vertices, labels = extract_vertices(lines)# 每次取得时候,都是随机取得,所以这样安排,[动态数据增强],注意到,动态得增强,省了不少空间 img = Image.open(self.img_files[index])# 为什么要随机缩放高度[0.8--1.2]:应该是数据增强img, vertices = adjust_height(img, vertices) # 数据增强,旋转角度img, vertices = rotate_img(img, vertices)# 随机剪切(缩放)512x512的图片img, vertices = crop_img(img, vertices, labels, self.length) # 函数功能:修改亮度、对比度和饱和度# 这里均值和方差都设置为0.5,实际上不太合理,但对后续影响不大transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ColorJitter(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.25),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5,0.5,0.5),std=(0.5,0.5,0.5))])# 得到所需要的训练数据,geo_map包括d1-d4和θ,ignored_map表示忽略部分score_map, geo_map, ignored_map = get_score_geo(img, vertices, labels, self.scale, self.length)return transform(img), score_map, geo_map, ignored_map
拓展:
- Pytorch中的transforms有多种用法,下面是一篇总结博客;
文章:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38533896/article/details/86028509
- 图像缩放到原来的1/4是什么原因?
结合网络的结构分析可知,EAST模型通过编解码的形式,先下采样后上采样,最终输出特征图为输入的1/4,所以标签也需要和模型的输出相匹配;

可以看出,下采样的倍数为32倍,上采样的倍数为8倍,总体缩小了四倍,也就是输出特征图为原图的1/4;
extract_vertices函数
作用:得到标签文本中的点和类别信息
def extract_vertices(lines):'''Input:lines : list of string infoOutput:vertices: vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>labels : 1->valid, 0->ignore, <numpy.ndarray, (n,)>'''labels = []vertices = []for line in lines:# 消除一些无用信息,取出前八个数作为点坐标信息vertices.append(list(map(int,line.rstrip('\r\n').lstrip('\xef\xbb\xbf').split(',')[:8])))label = 0 if '###' in line else 1labels.append(label)return np.array(vertices), np.array(labels)
拓展:
-
字符串的一些处理技巧:
首先map函数可用于类型转换,例如:map(int,str[]),对于数组中的所有元素都转成int类型;
rstrip(’\r\n’):表示去除右边的空格和换行符 lstrip(’\xef\xbb\xbf’):消除左端一个UTF-8 BOM字符
adjust_height函数
作用:随机缩放高度[0.8,1.2],数据增强的操作;
def adjust_height(img, vertices, ratio=0.2):'''Input:img : PIL Imagevertices : vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>ratio : height changes in [0.8, 1.2]Output:img : adjusted PIL Imagenew_vertices: adjusted vertices'''# np.random.rand()生成一个0-1的随机数,所以这里的范围是0.8到1.2ratio_h = 1 + ratio * (np.random.rand() * 2 - 1)old_h = img.height# np.around表示四舍五入new_h = int(np.around(old_h * ratio_h))# 对图像的高度进行缩放img = img.resize((img.width, new_h), Image.BILINEAR)new_vertices = vertices.copy()if vertices.size > 0:# 这里是只对坐标点y的值进行处理# 注意:切片操作需要熟练一些,在数据处理时很常用new_vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] = vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] * (new_h / old_h)return img, new_vertices
rotate_img函数
作用:旋转角度,数据增强的作用;
def rotate_img(img, vertices, angle_range=10):'''Input:img : PIL Imagevertices : vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>angle_range : rotate rangeOutput:img : rotated PIL Imagenew_vertices: rotated vertices'''# 取出中心点坐标center_x = (img.width - 1) / 2center_y = (img.height - 1) / 2# 这里还是将旋转范围定位-10到10angle = angle_range * (np.random.rand() * 2 - 1)# 采用PIL Image中的旋转函数rotateimg = img.rotate(angle, Image.BILINEAR)# 生成对应点想同纬度的全为0数组new_vertices = np.zeros(vertices.shape)for i, vertice in enumerate(vertices):# 这里对每个顶点也要进行翻转new_vertices[i,:] = rotate_vertices(vertice, -angle / 180 * math.pi, np.array([[center_x],[center_y]]))return img, new_vertices# 对顶点进行旋转,这里传入的角度表示弧度,1度等于Π/180弧度
def rotate_vertices(vertices, theta, anchor=None):'''Input: vertices: vertices of text region <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>theta : angle in radian measureanchor : fixed position during rotationOutput:rotated vertices <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>'''v = vertices.reshape((4,2)).Tif anchor is None:anchor = v[:,:1] rotate_mat = get_rotate_mat(theta)# 点和矩阵进行点乘res = np.dot(rotate_mat, v - anchor)return (res + anchor).T.reshape(-1)# 直接根据affine变换来把旋转矩阵填上
def get_rotate_mat(theta):# 返回一个旋转矩阵return np.array([[math.cos(theta), -math.sin(theta)], [math.sin(theta), math.cos(theta)]])
拓展:
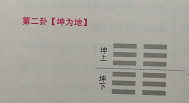
- 旋转矩阵是怎样的?实际上是由初中所学的公式推导出来的,具体如下图所示:

crop_img函数
作用:进行图像裁剪;
首先需要了解一下这个裁剪的流程:
第一步:先选出左上角的候选区域,作为点的选取,这里其实就是做一个范围内的裁剪;

第二步,判断裁剪框是否横跨文本框;

def crop_img(img, vertices, labels, length):'''Input:img : PIL Imagevertices : vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>labels : 1->valid, 0->ignore, <numpy.ndarray, (n,)>length : length of cropped image regionOutput:region : cropped image regionnew_vertices: new vertices in cropped region'''h, w = img.height, img.width# confirm the shortest side of image >= length# 如果短边小于512,将短边放大到512if h >= w and w < length:img = img.resize((length, int(h * length / w)), Image.BILINEAR)elif h < w and h < length:img = img.resize((int(w * length / h), length), Image.BILINEAR)# 计算缩放后的比例ratio_w = img.width / wratio_h = img.height / h# 断言(在程序判断中起重要作用)assert(ratio_w >= 1 and ratio_h >= 1)new_vertices = np.zeros(vertices.shape)if vertices.size > 0:# 文本框的标签x,y需要乘以一定比例new_vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] = vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] * ratio_wnew_vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] = vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] * ratio_h# find random position# 找到随机裁剪初始点的位置,也就是第一步中的候选区域remain_h = img.height - lengthremain_w = img.width - lengthflag = Truecnt = 0# crop图片的时候,不能把文本前切为两半。# 尝试1000次while flag and cnt < 1000:cnt += 1start_w = int(np.random.rand() * remain_w)start_h = int(np.random.rand() * remain_h)# 判断是否横跨文本框flag = is_cross_text([start_w, start_h], length, new_vertices[labels==1,:])box = (start_w, start_h, start_w + length, start_h + length)region = img.crop(box)if new_vertices.size == 0:return region, new_vertices # 标准化标签的坐标new_vertices[:,[0,2,4,6]] -= start_wnew_vertices[:,[1,3,5,7]] -= start_hreturn region, new_vertices# 作用:判断裁剪是否横跨文本框
def is_cross_text(start_loc, length, vertices):'''Input:start_loc: left-top positionlength : length of crop imagevertices : vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>Output:True if crop image crosses text region'''if vertices.size == 0:return False# 裁剪框的长和宽start_w, start_h = start_loca = np.array([start_w, start_h, start_w + length, start_h, \start_w + length, start_h + length, start_w, start_h + length]).reshape((4,2))# p1表示矩阵a表示的矩形框p1 = Polygon(a).convex_hullfor vertice in vertices:p2 = Polygon(vertice.reshape((4,2))).convex_hull# 可以算出两个矩形框的重叠区域(也就是IOU的值)inter = p1.intersection(p2).area# 0.0和1.0均不算横跨(包含或无交集的情况)p2_area = p2.areaif p2.area == 0:p2_area = 0.00000001if 0.01 <= inter / p2_area <= 0.99: return Truereturn False
拓展:
-
如何判断裁剪框是否横框文本框呢?实际上就是求两个矩形的IOU值;
采用Python的图形库——shapely
第一步:创建两个矩形框(不规则图形也可以)
from shapely.geometry import Polygon # convex_hull的作用是计算凸包 a = Polygon([(0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]).convex_hull b = Polygon([(0, 0), (2, 0), (2, 2), (0, 2)]).convex_hull第二步:计算重合部分面积
inter = a.intersection(b).area第三步:求IOU的值(也就是重合部分对目标的占比)
inter / a.area当然这是一种计算IOU的快捷方式,基本上就是调用库来实现(可能对效率有一定影响,而且引用库也添加了额外的操作),实际上可用numpy实现IOU的计算,具体实现可自行查找;
get_score_geo函数
作用:获取训练所需map数据;
首先要说明一些概念,也是对部分代码的一个图示;
shrink_poly函数起到缩小文本框的作用,主要是实现所需数据展示部分中缩小文本框的效果;
计算θ的map值:
find_min_rect_angle函数是为了找到角度,原理图如下:

实现步骤:
1、通过遍历0-180°,每次旋转后都将外接矩形的面积保存下来;
2、和原始文本框的面积作对比,取出差值最小的十个旋转框;
3、计算十个框的拟合误差,返回误差最小的弧度;
计算d的map值:
计算文本框中的点离文本框边界的距离,需要先将整个图片旋转,保证文本框处于水平方向,原理图如下:

实现步骤:
1、先将图像进行旋转,保证文本框处于水平方向;
2、计算每个像素点距离边界的距离,这里如果小于0的值置为0,也就是负数为0;
def get_score_geo(img, vertices, labels, scale, length):'''Input:img : PIL Image# quad 的8个顶点vertices: vertices of text regions <numpy.ndarray, (n,8)>labels : 1->valid, 0->ignore, <numpy.ndarray, (n,)>scale : feature map / image # 为0.25,根据网络结构理解length : image lengthOutput:score gt, geo gt, ignored'''# 产生零map,注意这里产生了5个mapscore_map = np.zeros((int(img.height * scale), int(img.width * scale), 1), np.float32)geo_map = np.zeros((int(img.height * scale), int(img.width * scale), 5), np.float32)# 忽略的map,训练中不需要用到ignored_map = np.zeros((int(img.height * scale), int(img.width * scale), 1), np.float32)#按照length和1/scale产生这个np.meshgrid是进行下采样缩小四倍# np.arange是按步长生成数组index = np.arange(0, length, int(1/scale)) # 间隔4个像素取一个点# np.meshgrid:从一个坐标向量中返回一个坐标矩阵index_x, index_y = np.meshgrid(index, index)ignored_polys = []polys = []# 遍历顶点,给geo_map赋值for i, vertice in enumerate(vertices):#记录需要忽略掉得四边形if labels[i] == 0:ignored_polys.append(np.around(scale * vertice.reshape((4,2))).astype(np.int32))continue # 产生一个缩小0.3倍的poly(选定的正样本标签) 也就是文本框向内缩小0.3# scale只为fillPoly使用,实际标签不缩小4倍# shrink_poly的作用就是向内缩小0.3倍poly = np.around(scale * shrink_poly(vertice).reshape((4,2))).astype(np.int32)polys.append(poly)# 单个文本框的掩码,用于限定d1_map,d2_map,d3_map,d4_map中哪些位置应该赋值temp_mask = np.zeros(score_map.shape[:-1], np.float32)# 将全为0的mask中指定区域设置为1,也就是目标区域cv2.fillPoly(temp_mask, [poly], 1)# 通过遍历的方法,找到最小外接矩形,然后找到矩形的角度theta = find_min_rect_angle(vertice)# 旋转文本框,并旋转所有像素坐标,旋转为theta=0的水平状态,方便计算d# 找到矩形的角度对应到的旋转角度# get_rotate_mat作用:返回一个旋转矩阵(每个点的θ都是一样的)rotate_mat = get_rotate_mat(theta)rotated_vertices = rotate_vertices(vertice, theta)x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max = get_boundary(rotated_vertices)# 得到旋转后的x,y的值,为[512, 512]rotated_x, rotated_y = rotate_all_pixels(rotate_mat, vertice[0], vertice[1], length)# 计算d,负数表示在文本框外侧,置零d1 = rotated_y - y_mind1[d1<0] = 0d2 = y_max - rotated_yd2[d2<0] = 0d3 = rotated_x - x_mind3[d3<0] = 0d4 = x_max - rotated_xd4[d4<0] = 0# 每隔4个像素采样(index_y, index_x),乘以文本框缩小0.3后的掩码# 这里的作用是:通过掩码将0.3外的部分的d值去掉geo_map[:,:,0] += d1[index_y, index_x] * temp_maskgeo_map[:,:,1] += d2[index_y, index_x] * temp_maskgeo_map[:,:,2] += d3[index_y, index_x] * temp_maskgeo_map[:,:,3] += d4[index_y, index_x] * temp_maskgeo_map[:,:,4] += theta * temp_mask# 忽略标签为###的文本框cv2.fillPoly(ignored_map, ignored_polys, 1)# 得到[score_map] 全部文本框的掩码,即得分标签cv2.fillPoly(score_map, polys, 1)return torch.Tensor(score_map).permute(2,0,1), torch.Tensor(geo_map).permute(2,0,1), torch.Tensor(ignored_map).permute(2,0,1)# 作用:缩小文本框
def shrink_poly(vertices, coef=0.3):'''Input:vertices: vertices of text region <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>coef : shrink ratio in paperOutput:v : vertices of shrinked text region <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>'''x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = vertices# 获取每个点的短边,后面缩小范围的时候使用# 使用欧式距离计算每个点相邻边中最小的那条边r1 = min(cal_distance(x1,y1,x2,y2), cal_distance(x1,y1,x4,y4))r2 = min(cal_distance(x2,y2,x1,y1), cal_distance(x2,y2,x3,y3))r3 = min(cal_distance(x3,y3,x2,y2), cal_distance(x3,y3,x4,y4))r4 = min(cal_distance(x4,y4,x1,y1), cal_distance(x4,y4,x3,y3))r = [r1, r2, r3, r4]# 判断哪两个对边较长,后续move_points先移动长边# obtain offset to perform move_points() automaticallyif cal_distance(x1,y1,x2,y2) + cal_distance(x3,y3,x4,y4) > \cal_distance(x2,y2,x3,y3) + cal_distance(x1,y1,x4,y4):offset = 0 # two longer edges are (x1y1-x2y2) & (x3y3-x4y4)else:offset = 1 # two longer edges are (x2y2-x3y3) & (x4y4-x1y1)v = vertices.copy()# 先移动长边,再移动短边,这个先后有关系么?# 先移动短边上得两个点得话,得到得缩小后的四边形面积更小一些v = move_points(v, 0 + offset, 1 + offset, r, coef)v = move_points(v, 2 + offset, 3 + offset, r, coef)v = move_points(v, 1 + offset, 2 + offset, r, coef)v = move_points(v, 3 + offset, 4 + offset, r, coef)return v# 作用:找到最佳弧度
def find_min_rect_angle(vertices):'''Input:vertices: vertices of text region <numpy.ndarray, (8,)>Output:the best angle <radian measure>'''# 每隔1度遍历所有角度angle_interval = 1angle_list = list(range(-90, 90, angle_interval))area_list = []for theta in angle_list: rotated = rotate_vertices(vertices, theta / 180 * math.pi)x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 = rotated# 直接计算平行于x轴和y轴的包围框temp_area = (max(x1, x2, x3, x4) - min(x1, x2, x3, x4)) * \(max(y1, y2, y3, y4) - min(y1, y2, y3, y4))area_list.append(temp_area)# 相当于argsort,获取从小到大的排序索引sorted_area_index = sorted(list(range(len(area_list))), key=lambda k : area_list[k])min_error = float('inf')best_index = -1rank_num = 10# 遍历前10个最小面积的矩形,计算拟合误差,并返回拟合误差最小的弧度# find the best angle with correct orientationfor index in sorted_area_index[:rank_num]:rotated = rotate_vertices(vertices, angle_list[index] / 180 * math.pi)# 计算拟合误差temp_error = cal_error(rotated)if temp_error < min_error:min_error = temp_errorbest_index = indexreturn angle_list[best_index] / 180 * math.pi # 返回弧度
拓展:
-
np.meshgrid的作用是什么?
在这里np.meshgrid的作用是表示间隔像素点的位置,具体案例如下:
a = np.arange(0, 16, 4) # array([ 0, 4, 8, 12]) x, y = np.meshgrid(index, index) print(x) """ array([[ 0, 4, 8, 12],[ 0, 4, 8, 12],[ 0, 4, 8, 12],[ 0, 4, 8, 12]]) """ print(y) """ array([[ 0, 0, 0, 0],[ 4, 4, 4, 4],[ 8, 8, 8, 8],[12, 12, 12, 12]]) """可以看出,(x,y)对应的矩阵就是对应每个像素点的索引,根据该索引得到的图像相当于是原图进行了1/4的下采样操作,可能会造成一定的信息损失;
-
cv2.fillPoly的作用?
用于对图像中的掩码部分进行处理,修改为指定的值,下图为原理图:

总结
到这里ICDAR_2015的数据终于处理好了,本次数据处理是为了EAST模型使用,如果使用其他文本检测的模型,数据则需要做其他的处理;从整个代码可以看出,数据处理的工作量挺大的,并且还会遇到很多细节问题,出问题就会导致标签错误,整个任务都等于白做了!(在AI领域有一句话:数据是AI的基石,也是AI的上限)
其实在日常工作中,数据处理往往占了算法工程师一大部分时间,如何根据业务场景处理数据是最关键的一步;至于模型的选型,往往改动并不大,最繁琐也最费时间的步骤就是在数据处理这步!
所以作为算法工程师来说,对数据和业务场景的理解,对图像的基本处理,都是必备的技能。