hashCode
文章目录
- hashCode
- hashCode 的生成逻辑
- 第 0 种算法
- 第 1 种算法
- 第 2 种算法
- 第 3 种算法
- 第 4 种算法
- 第 5 种算法
根据一定的规则将与对象相关的信息(比如对象的存储地址,对象的字段等)映射成一个数值,这个数值称作为散列值。
public static void main(String[] args) {Object o = new Object();System.out.println(o);int hashCode = o.hashCode();//hashCode 16进制System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(hashCode));System.out.println(hashCode);//获取hashCodeSystem.out.println(System.identityHashCode(o));}
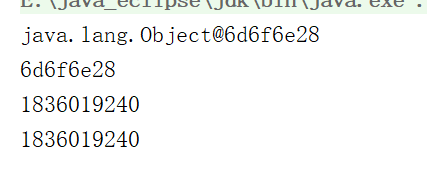
@后面的为16进制的hashCode
hashCode 的生成逻辑
openjdk 源码里生成 hashCode 的核心方法
static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread * Self, oop obj) { intptr_t value = 0 ; if (hashCode == 0) { // This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG, // so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG. // On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the // mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic. value = os::random() ; } else if (hashCode == 1) { // This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent) // between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0 // synchronization schemes. intptr_t addrBits = intptr_t(obj) >> 3 ; value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ; } else if (hashCode == 2) { value = 1 ; // for sensitivity testing } else if (hashCode == 3) { value = ++GVars.hcSequence ; } else if (hashCode == 4) { value = intptr_t(obj) ; } else { // Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state // This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll // likely make this the default in future releases. unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ; t ^= (t << 11) ; Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ; Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ; Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ; unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ; v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ; Self->_hashStateW = v ; value = v ; } value &= markOopDesc::hash_mask; if (value == 0) value = 0xBAD ; assert (value != markOopDesc::no_hash, "invariant") ; TEVENT (hashCode: GENERATE) ; return value;
}
从源码里可以发现,生成策略是由一个 hashCode 的全局变量控制的,默认为5;而这个变量的定义在另一个头文件里:
product(intx, hashCode, 5, "(Unstable) select hashCode generation algorithm" )

第 0 种算法
if (hashCode == 0) { // This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG, // so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG. // On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the // mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic. value = os::random(); }
这种生成算法,使用的一种Park-Miller RNG的随机数生成策略。不过需要注意的是……这个随机算法在高并发的时候会出现自旋等待
第 1 种算法
if (hashCode == 1) { // This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent) // between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0 // synchronization schemes. intptr_t addrBits = intptr_t(obj) >> 3 ; value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;
}
这个算法,真的是对象的内存地址了,直接获取对象的 intptr_t 类型指针只不过封装了一下数字。
第 2 种算法
if (hashCode == 2) { value = 1 ; // for sensitivity testing
}
value = 1
第 3 种算法
if (hashCode == 3) { value = ++GVars.hcSequence ;
}
递增
第 4 种算法
{value = intptr_t(obj) ;
}
真实的指针地址
第 5 种算法
// Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state // This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll // likely make this the default in future releases. unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ; t ^= (t << 11) ; Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ; Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ; Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ; unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ; v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ; Self->_hashStateW = v ; value = v ; }












![[carla入门教程]-5 使用ROS与carla通信](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7f16d89b49704a998518792966cbe775.png)



