新年第一篇。
最近在做蓝牙开锁的小项目,手机去连接单片机总是出现问题,和手机的连接也不稳定,看了不少蓝牙方面的文档,做了个关于蓝牙连接的小结。
在做android蓝牙串口连接的时候一般会使用
BluetoothSocket tmp = null;
// Get a BluetoothSocket for a connection with the
// given BluetoothDevice
try {tmp = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);
} catch (IOException e) {Log.e(TAG, "create() failed", e);
}
然后是tmp赋给BluetoothSocket,接着调用connect方法进行蓝牙设备的连接。
可是 BluetoothSocket 的connect方法本身就会报很多异常错误。
以下根据对蓝牙开发的一点研究可通过以下方法解决:
方法1.先进行蓝牙自动配对,配对成功,通过UUID获得BluetoothSocket,然后执行connect()方法。
方法2.通过UUID获得BluetoothSocket,然后先根据mDevice.getBondState()进行判断是否需要配对,最后执行connnect()方法。
private class ConnectThread extends Thread {String macAddress = "";public ConnectThread(String mac) {macAddress = mac;}public void run() {connecting = true;connected = false;if(mBluetoothAdapter == null){mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();}mBluetoothDevice = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(macAddress);mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();try {socket = mBluetoothDevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(uuid);} catch (IOException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch block//e.printStackTrace();Log.e(TAG, "Socket", e);} //adapter.cancelDiscovery();while (!connected && connetTime <= 10) { connectDevice();}// 重置ConnectThread //synchronized (BluetoothService.this) {//ConnectThread = null;//}}public void cancel() {try {socket.close();socket = null;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {connecting = false;}}}接下来是调用的连接设备方法connectDevice():
protected void connectDevice() { try { // 连接建立之前的先配对 if (mBluetoothDevice.getBondState() == BluetoothDevice.BOND_NONE) { Method creMethod = BluetoothDevice.class .getMethod("createBond"); Log.e("TAG", "开始配对"); creMethod.invoke(mBluetoothDevice); } else { } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception //DisplayMessage("无法配对!"); e.printStackTrace(); } mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery(); try { socket.connect(); //DisplayMessage("连接成功!"); //connetTime++;connected = true;} catch (IOException e) { // TODO: handle exception //DisplayMessage("连接失败!");connetTime++;connected = false;try { socket.close();socket = null;} catch (IOException e2) { // TODO: handle exception Log.e(TAG, "Cannot close connection when connection failed"); } } finally {connecting = false;} }
方法3.利用反射通过端口获得BluetoothSocket,然后执行connect()方法。
private class ConnectThread extends Thread {String macAddress = "";public ConnectThread(String mac) {macAddress = mac;}public void run() {connecting = true;connected = false;if(mBluetoothAdapter == null){mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();}mBluetoothDevice = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(macAddress);mBluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();initSocket(); //adapter.cancelDiscovery();while (!connected && connetTime <= 10) {try {socket.connect();connected = true;} catch (IOException e1) {connetTime++;connected = false;// 关闭 sockettry {socket.close();socket = null;} catch (IOException e2) {//TODO: handle exception Log.e(TAG, "Socket", e2);}} finally {connecting = false;}//connectDevice();}// 重置ConnectThread //synchronized (BluetoothService.this) {//ConnectThread = null;//}}public void cancel() {try {socket.close();socket = null;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {connecting = false;}}}接下来是初始化并得到BluetoothSocket的方法
/*** 取得BluetoothSocket*/private void initSocket() {BluetoothSocket temp = null;try { Method m = mBluetoothDevice.getClass().getMethod("createRfcommSocket", new Class[] { int.class });temp = (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(mBluetoothDevice, 1);//这里端口为1 } catch (SecurityException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {e.printStackTrace();}socket = temp;}
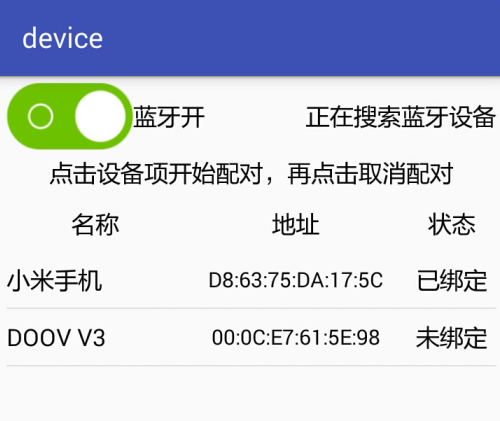
要点:1.蓝牙配对和连接是两回事,不可混为一谈。
2.蓝牙串口连接可通过端口 (1-30)和UUID两种方法进行操作。
3.通过UUID进行蓝牙连接最好先进行配对操作。
作者:jason0539
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/jason0539(转载请说明出处)
扫码关注我微信公众号