2020/06/10: first version, 主要介绍smmu驱动的初始化流程
在前一篇博文ARM SMMU学习笔记中, 介绍了SMMU的一些基本概念以及SMMU地址转换的基本流程,本文主要分析linux kernel中SMMUv3的代码(drivers/iommu/arm-smmu-v3.c)
linux kernel版本是linux 5.7, 体系结构是aarch64
smmu的位置

SMMU的作用是把CPU提交给设备的VA地址,直接作为设备发出的地址,变成正确的物理地址,访问到物理内存上。
和mmu不同的是,一个smmu可以有多个设备连着,他们的页表不可能复用,SMMU 用stream id作区分。
一个设备有多个进程,所以smmu单元也要支持多页表,smmu使用substream id区分多进程的页表。
smmu的设备节点定义
在讨论smmu的代码前,先看下smmu的设备节点是怎么定义的:
Example:
smmu@2b400000 {compatible = "arm,smmu-v3";reg = <0x0 0x2b400000 0x0 0x20000>;interrupts = <GIC_SPI 74 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 75 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 77 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>,<GIC_SPI 79 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING>;interrupt-names = "eventq", "priq", "cmdq-sync", "gerror";dma-coherent;#iommu-cells = <1>;msi-parent = <&its 0xff0000>;};compatible: 用于匹配smmu驱动。
reg:smmu设备的物理基地址。
interrupts: 描述与中断名称对应的smmu中断源,上述分别对应中断类型,中断号以及中断触发方式。
interrupt-names: 中断名称。
eventq,当event queue从空变为非空状态时上报中断。
priq, 当pri queue从空变为非空状态时上报中断。
cmdq-sync, command queue中CMDQ_SYNC命令完成时产生中断。
gerror,event记录到event queue过程中产生的错误会记录在SMMU_GERROR寄存器中,并产生中断。
combined,组合中断,需要硬件支持,如果提供了组合中断,则将优先使用组合中断。
dma-coherent:表示设备通过smmu进行的DMA访问是否cache coherent的,假设DMA把外设的数据搬运到内存的某个位置,cpu去读那段地址,因为cache命中了,读到的还是旧的值,这就是cache的不coherent。
#iommu-cells: 一个cell代表一个streamid, smmu-v3必须定义为1。
msi-parent:指定msi中断控制器。
SMMU结构体
struct arm_smmu_domain {struct arm_smmu_device *smmu;struct mutex init_mutex; /* Protects smmu pointer */struct io_pgtable_ops *pgtbl_ops;bool non_strict;atomic_t nr_ats_masters;enum arm_smmu_domain_stage stage;union {struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg s1_cfg;struct arm_smmu_s2_cfg s2_cfg;};struct iommu_domain domain;struct list_head devices;spinlock_t devices_lock;
};
arm_smmu_device: 指定smmu设备
io_pgtable_ops: io页表映射定义的一系列操作
non_strict: smmu non-strict模式,在该补丁集中引入 add non-strict mode support for arm-smmu-v3,
主要是为了解决开启smmu后,频繁的unmap,需要频繁的invalid tlb带来的性能损失, 所以不在每一次unmap后都进行tlb invalidate操作,而是累计一定次数或者时间后执行invalid all操作,但这样是有一定的安全风险(页表虽然释放了但是还是在tlb中有残留,可能被利用到)。可以通过启动参数控制。
nr_ats_masters: ats的设备数量,enable_ats时数量+1, disable ats时数量减1
arm_smmu_domain_stage: 代表smmu支持的方式,支持stage1的转换,stage2的转换,stage1 + stage2的转换,以及bypass模式。
arm_smmu_s1_cfg: stage1转换需要的数据结构
arm_smmu_s2_cfg: stage2转换需要的数据结构
smmu驱动初始化
从smmu驱动的probe函数开始分析
+->arm_smmu_device_probe() //smmu设备驱动probe入口函数+-> arm_smmu_device_dt_probe() //smmu设备树解析+-> platform_get_irq_byname() // smmu设备中断解析+-> arm_smmu_device_hw_probe() // smmu硬件规格探测+-> arm_smmu_init_structures() //smmu 数据结构初始化+-> arm_smmu_device_reset() // smmu设备复位, 硬件初始化配置+-> iommu_device_register() // iommu设备注册+-> arm_smmu_set_bus_ops() // 给支持的总线设置bus->iommu_ops
对probe中调用的这些函数进行详细分析
(1)arm_smmu_device_dt_probe
static int arm_smmu_device_dt_probe(struct platform_device *pdev,struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret = -EINVAL;if (of_property_read_u32(dev->of_node, "#iommu-cells", &cells)) ---- (a)dev_err(dev, "missing #iommu-cells property\n");else if (cells != 1)dev_err(dev, "invalid #iommu-cells value (%d)\n", cells);elseret = 0;parse_driver_options(smmu); ----- (b)if (of_dma_is_coherent(dev->of_node)) ---- (c)smmu->features |= ARM_SMMU_FEAT_COHERENCY;return ret;
}
a. 读取设备树,看smmu的设备节点定义中#iommu-cells是否为1, 如果不为1则直接bypass 掉smmu
b. parse_driver_options, 主要解析smmu是否有需要规避的硬件bug
c. 解析smmu设备中的dma-coherent属性
(2) platform_get_irq_byname
/* Interrupt lines */irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "combined"); if (irq > 0)smmu->combined_irq = irq;else {irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "eventq"); if (irq > 0)smmu->evtq.q.irq = irq;irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "priq");if (irq > 0)smmu->priq.q.irq = irq;irq = platform_get_irq_byname_optional(pdev, "gerror");if (irq > 0)smmu->gerr_irq = irq;}
分别获取dts节点中定义的"combined", “eventq”, “priq”, "gerror"中断号
(3) arm_smmu_device_hw_probe
该函数主要探测smmu设备的硬件规格,主要是通过读SMMU的IDR0,IDR1,IDR5寄存器确认
SMMU_IDR0:
| 域段 | offset | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| ST_LEVEL | 28: 27 | 确认stream table格式是线性table还是2-level table |
| TERM_MODEL | 26 | fault的处理方式, |
| STALL_MODEL | 25: 24 | 确认是否是stall mode。 该模式下smmu会暂停引发stall的transaction, 然后stall,之后根据软件的commad是resume还是stall_term来决定stall命令是retry还是terminate。当前只允许4种fault类型被stall: F_TRANSLATION, F_ACCESS, F_ADDR_SIZE. F_PERMISSION.【spec 5.5 Fault configuration (A,R,S bits)】 |
| TTENDIAN | 22: 21 | 确认traslation table支持的大小端模式 |
| CD2L | 19 | 确认是否支持2-level 的CD table |
| VMW | 17 | 用于控制vmid wildcards的功能和范围。 vmid wildcard, vmid的模糊匹配,是为了方便tlb无效化, 两种tlb无效化的方式:command和广播tlb无效都会使用到vmid wildcards |
| VMID16 | 18 | 确认是否支持16bit VMID。 每一个虚拟机都被分配一个ID号,这个ID号用于标记某个特定的TLB项属于哪一个VM。每一个VM有它自己的ASID空间。例如两个不同的VMs同时使用ASID 5,但指的是不同的东西。对于虚拟机而言,通常VMID会结合ASID同时使用。 |
| PRI | 16 | 确认是否支持page request interface。 属于pcie 硬件特性,PCIe设备可以发出缺页请求,SMMU硬件在解析到缺页请求后可以直接将缺页请求写入PRI queueu, 软件在建立好页表后,可以通过CMD queue发送PRI response给PCIe设备。 [Linux SVA特性分析] |
| SEV | 14 | 确认是否支持WFE wake-up事件的产生。 当SEV == 1时,command queue从满到非满状态会触发WFE wake-up event。 此外,当CMD_SYNC完成且要求SIG_SEV时也会产生WFE wake-up event |
| MSI | 13 | 确认是否支持MSI消息中断 |
| ASID16 | 12 | 确认是否支持16bit ASID.。 在TLB的表项中,每个项都有一个ASID,当切换进程的时候,TLB中可以存在多个进程的页表项, 不再需要清空TLB,因为B进程用不了里面A进程的页表项,可以带来性能提升。[TLB flush操作] |
| ATS | 10 | Address Translation Service, 也是pcie的硬件特性,有ATS能力的PCIE,自带地址翻译功能,如果它要发出一个地址,进入PCIE总线的时候,一定程度上可以认为就是物理地址。ats会在设备中缓存va对应的pa, 设备随后使用pa做内存访问时无需经过SMMU页表转换,可以提高性能。 【PCIe/SMMU ATS analysis note】 |
| HTTU | 7:6 | Hardware Translation Table Update,在访问或写入相关页面后,硬件自动更新相关页面的Access flag、Dirty state。该特性和armv8.1的tthm特性一样,在没有tthm 特性之前,软件去更新页表的young和dirty page, 会有一定的开销。 |
| S1P | 1 | 确认是否支持stage1转换,va->pa |
| S2P | 0 | 确认是否支持stage2转换,ipa->pa |
SMMU_IDR1:
| 域段 | offset | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| TABLES_PRESET | 30 | 确认smmu_strtab_base和smmu_strtab_base_cfg的基地址是否固定, smmu_strtab_base是stream table的物理基地址,smmu_strtab_base_cfg是stream table的配置寄存器 |
| QUEUES_PRESET | 29 | 确认smmu queue的基地址是否固定,queue指的是smmu event queue, smmu cmd queue, smmu pri queue |
| CMDQS | 25:21 | cmd queue 最大entry数目, 等于log2(entries), 最大是19 |
| EVENTQS | 20:16 | event queue的最大entry数目,等于log2(entries), 最大是19 |
| PRIQS | 15:11 | pri queue 最大entry数目,等于log2(entries), 最大是19 |
| SSIDSIZE | 10:6 | 确认硬件支持substreamID的bit数,范围为【0,20】, 0表示不支持substreamid |
| SIDSIZE | 5:0 | 确认硬件支持streamID的bit数,范围为【0,32】, 0表示支持一个stream |
IDR1主要用来设置smmu 各个queue的entry数量, 设置ssid和sid的size.
SMMU_IDR5:
| 域段 | offset | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| STALL_MAX | 31:16 | smmu支持的最大未完成stall 事务数 |
| VAX | 11:10 | 表示smmu支持的va地址是48bit还是52bit |
| GRAN64K | 6 | 支持64KB翻译粒度, Translation Granule表示translation table的size大小, 页表粒度是smmu管理的最小地址空间 |
| GRAN16K | 5 | 支持16KB翻译粒度 |
| GRAN4K | 4 | 支持4KB翻译粒度 |
| OAS | 2:0 | 表示output address size, 32bit ~ 52bit |
IDR5主要设置smmu ias(input address size) 和 oas (output address size), ias代表IPA,oas代表PA。
(4)arm_smmu_init_structures()
smmu相关的数据结构的内存申请和初始化
static int arm_smmu_init_structures(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{int ret;ret = arm_smmu_init_queues(smmu); ----------------- (a)if (ret)return ret;return arm_smmu_init_strtab(smmu); ----------------- (b)
}
(a) arm_smmu_init_queues() 会初始化三个queue, 分别为cmd queue, event queue, pri queue.
SMMU使用这3个队列做基本的事件管理。
event queue用于记录软件配置错误的状态信息,smmu将配置错误信息记录到event queue中,软件会通过从event queue读取配置错误信息,然后进行相应的配置错误处理。
软件使用command queue和smmu 硬件进行交互,软件写命令发送到command queue中,smmu会从command queue中读取命令进行处理。
pri queue需要硬件支持pri 特性,和event queue类似,当有相应硬件事件发生时,硬件把相应的描述符写入pri queue, 然后上报中断。
(b) arm_smmu_init_strtab
static int arm_smmu_init_strtab(struct arm_smmu_device *smmu)
{u64 reg;int ret;if (smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_STRTAB) ret = arm_smmu_init_strtab_2lvl(smmu);elseret = arm_smmu_init_strtab_linear(smmu);if (ret)return ret;/* Set the strtab base address */reg = smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_dma & STRTAB_BASE_ADDR_MASK; reg |= STRTAB_BASE_RA;smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base = reg;/* Allocate the first VMID for stage-2 bypass STEs */set_bit(0, smmu->vmid_map);return 0;
}
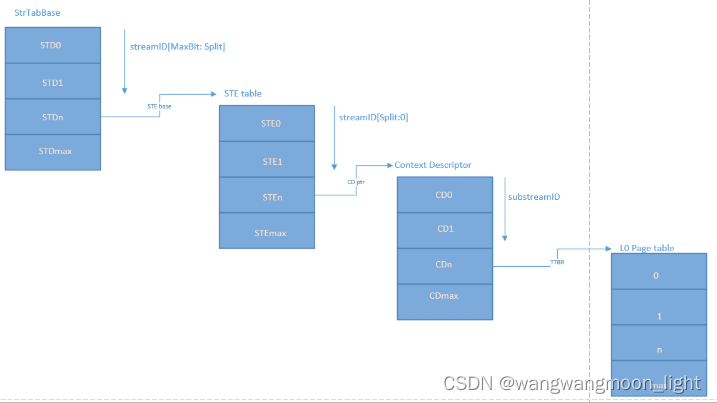
首先确认SMMU的stream table的组织方式是线性table还是2-level table.
如果是linear table:

使用STRTAB_BASE + sid * 64(一个STE的大小为64B)找到STE
+-> arm_smmu_init_strtab_linear// 计算stream table的size, 如果使用linear 查找,stream table的size = sid * 64(sid表示有多少个ste, 一个STE的大小为64B)+-> size = (1 << smmu->sid_bits) * (STRTAB_STE_DWORDS << 3); // 申请Stream table的内存+-> strtab = dmam_alloc_coherent()// 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的format, 决定stream table的格式是linear+-> reg = FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT, STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT_LINEAR);// 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的log2size, ste的entry数目是2 ^ log2size+-> reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_LOG2SIZE, smmu->sid_bits); // cfg->num_l1_ents对应的是sid, 对SMMU下的所有sid逐一调用arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent+-> arm_smmu_init_bypass_stes(strtab, cfg->num_l1_ents) +-> arm_smmu_write_strtab_ent()// 发送CMDQ_OP_PREFETCH_CFG+-> arm_smmu_cmdq_issue_cmd()
如果是2-level table:
先通过sid的高位找到L1_STD(STRTAB_BASE + sid[9:8] * 8, 一个L1_STD的大小为8B), L1_STD定义了下一级查找的基地址,然后通过sid 找到具体的STE(l2ptr + sid[7:0] * 64).
结合代码分析:
+-> arm_smmu_init_strtab_2lvl()/* 计算l1的大小, 一个l1 std的大小为8byte, 对应的l1_std = sid[maxbit:split], maxbit是log2Size - 1, 所以l1的大小等于2 ^ (log2Size - split) * 8 */+-> l1size = cfg->num_l1_ents * (STRTAB_L1_DESC_DWORDS << 3);// 申请L1 stream table的空间+-> strtab = dmam_alloc_coherent()// 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的format, 决定stream table的格式是2-level+-> reg = FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT, STRTAB_BASE_CFG_FMT_2LVL);/* 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的log2size,2级ste的entry是2 ^ log2size, l1 std的entry大小为2 ^ (log2size - split) */+-> reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_LOG2SIZE, size);/* 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的split, split的值可以被配置为6/8/10, 分别对应l1 std能够指向的最大二级ste的空间为4k/16k/64k*/+-> reg |= FIELD_PREP(STRTAB_BASE_CFG_SPLIT, STRTAB_SPLIT);/* 分配L1STD的内存, 并配置L1 descriptor的SPAN,SPAN表示L2 table包含多少个STE */+-> arm_smmu_init_l1_strtab()
- 申请l1 Stream table的内存,内存大小为2 ^ (log2Size - split) * 8
- 申请L1 STD的内存, L1 STD在stream table的索引是streamID[maxbit: split]
配置完stream table的结构和各级大小后,再配置stream table的基地址:
/* 配置stream table(STRTAB_BASE_CFG)的RA和addr, addr对应的是stream table的物理地址ra为read allocate hint */+-> reg = smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_dma & STRTAB_BASE_ADDR_MASK;+-> reg |= STRTAB_BASE_RA;
至此stream table的初始化流程结束
(5) arm_smmu_device_reset
该函数主要是进行smmu的硬件配置
主要流程如下:
+-> arm_smmu_device_reset()// 写SMMU_CR0来disable smmu,并通过SMMU_CR0ACK检查CR0是否被clear+-> arm_smmu_device_disable()// 配置读取ste和command queue的属性+-> writel_relaxed(ARM_SMMU_CR1);// random crap+-> writel_relaxed(ARM_SMMU_CR2);/* 配置ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE和ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE寄存器,分别对应stream table的物理基地址以及格式,大小等*/+->writeq_relaxed(smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base, ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE);+->writel_relaxed(smmu->strtab_cfg.strtab_base_cfg, ARM_SMMU_STRTAB_BASE);/* 配置cmd queue相关寄存器* ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_BASE是配置command queue的基地址* ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_PROD, 可以表示取出命令的位置* ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_CONS, 可以表示输入命令的位置* ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_PROD和ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_CONS初始化时配置为相同的值,都为0* 通过CMDQ_PROD和CMDQ_CONS, 可以判断command queue是否还有空间*/+-> writeq_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.q_base, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_BASE);+-> writel_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.llq.prod, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_PROD);+-> writel_relaxed(smmu->cmdq.q.llq.cons, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_CMDQ_CONS);// 最后配置command queue的en,对command queue进行使能+-> enables = CR0_CMDQEN;// 配置event queue相关寄存器, 流程和command queue类似+-> config event queue// 如果支持pri, 则配置pri queue相关寄存器, 流程和上面一致+-> config pri queue// 申请并使能smmu支持的相关中断(eventq irq, priq irq, gerror irq)+-> arm_smmu_setup_irqs()// enable smmu, 写SMMU_CR0,并通过SMMU_CR0ACK检查CR0是否被enable+-> arm_smmu_write_reg_sync(smmu, enables, ARM_SMMU_CR0, ARM_SMMU_CR0ACK);
再着重讲下smmu的中断注册:arm_smmu_setup_irqs()
+-> arm_smmu_setup_irqs()+-> arm_smmu_setup_unique_irqs()+-> arm_smmu_setup_msis(smmu);+-> arm_smmu_write_msi_msg()+-> devm_request_irq(smmu->dev, irq, arm_smmu_gerror_handler,0, "arm-smmu-v3-gerror", smmu);
arm_smmu_write_msi_msg()函数里会去:
- 配置MSI中断的目的地址
- 配置MSI的中断数据
- 配置MSI中断的写地址的属性
配置完成后,当中断产生时,最终会进入中断注册的处理函数, 以gerror的中断处理为例:
arm_smmu_gerror_handler()// 读gerror和gerrorrn寄存器,确认gerror中断发生的错误类型+-> gerror = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_GERROR);+-> gerrorn = readl_relaxed(smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_GERRORN);// 完成中断处理后,写gerror和gerrorn对应的的位一致,global中断处理完成+-> writel(gerror, smmu->base + ARM_SMMU_GERRORN);
(6) iommu_device_register
注册iommu设备,主要设计一个操作,就是将smmu设备添加到iommu_device_list中
int iommu_device_register(struct iommu_device *iommu)
{spin_lock(&iommu_device_lock);list_add_tail(&iommu->list, &iommu_device_list);spin_unlock(&iommu_device_lock);return 0;
}
着重讲下和iommu_device相关的两个重要数据结构iommu_group 和 iommu_domain
看下iommu_device结构体的定义
struct iommu_device {struct list_head list;const struct iommu_ops *ops;struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;struct device *dev;
};
iommu_device中定义了iommu_ops以及struct device,
在struct device中,有iommu_group的成员,iommu_group 又包含了iommu_domain。
iommu_device->device->iommu_group->iommu_domain
iommu_domain的具体定义:
struct iommu_domain {unsigned type;const struct iommu_ops *ops;unsigned long pgsize_bitmap; /* Bitmap of page sizes in use */iommu_fault_handler_t handler;void *handler_token;struct iommu_domain_geometry geometry;void *iova_cookie;
};
每一个domain 代表一个具体的设备使用iommu的详细spec
在arm_smmu_domain结构体中,又将arm_smmu_domain和iommu_domain关联, 所以iommu_ops指向SMMU驱动。所以最终ARM是用arm_smmu_domain来管理驱动和设备之间的关联的。
iommu_group的具体定义:[drivers/iommu/iommu.c: iommu_group]
struct iommu_group {struct kobject kobj;struct kobject *devices_kobj;struct list_head devices;struct mutex mutex;struct blocking_notifier_head notifier;void *iommu_data;void (*iommu_data_release)(void *iommu_data);char *name;int id;struct iommu_domain *default_domain;struct iommu_domain *domain;
};为什么会有一个iommu_group的概念,直接将device和iommu_domain关联不香吗?
假设我们通过iommu提供设备的DMA能力,当发起dma_map的时候,设备设置了streamid, 但是多个设备的streamid有可能是一样的。 那么这时候修改其中一个设备的页表体系,也就相当于修改了另一个设备的页表体系。所以,修改页表的最小单位不是设备,而是streamid。
因此,为了避免这种情况,增加了一个iommu_group的概念,iommu_group代表共享同一个streamid的一组device(表述在/sys/kernel/iommu_group中)。
有了iommu_group, 设备发起dma_map操作时,会定位streamid和iommu_group, group定位了iommu_device和iommu_domain,iommu_domain定位了asid,这样,硬件要求的全部信息都齐了。
(Linux iommu和vfio概念空间解构)
(7) arm_smmu_set_bus_ops
给smmu支持的总线设置bus->iommu_ops, 让总线具有了iommu attach的能力。
arm_smmu_set_bus_ops(&arm_smmu_ops)+-> bus_set_iommu(&pci_bus_type, ops);+-> bus_set_iommu(&amba_bustype, ops);+-> bus_set_iommu(&platform_bus_type, ops);
arm_smmu_ops结构体定义如下:
static struct iommu_ops arm_smmu_ops = {.capable = arm_smmu_capable,.domain_alloc = arm_smmu_domain_alloc,.domain_free = arm_smmu_domain_free,.attach_dev = arm_smmu_attach_dev, ----- .map = arm_smmu_map,.unmap = arm_smmu_unmap,.flush_iotlb_all = arm_smmu_flush_iotlb_all,.iotlb_sync = arm_smmu_iotlb_sync,.iova_to_phys = arm_smmu_iova_to_phys,.add_device = arm_smmu_add_device,.remove_device = arm_smmu_remove_device,.device_group = arm_smmu_device_group,.domain_get_attr = arm_smmu_domain_get_attr,.domain_set_attr = arm_smmu_domain_set_attr,.of_xlate = arm_smmu_of_xlate,.get_resv_regions = arm_smmu_get_resv_regions,.put_resv_regions = generic_iommu_put_resv_regions,.pgsize_bitmap = -1UL, /* Restricted during device attach */
};
主要分析smmu的两个关键操作:arm_smmu_attach_dev和arm_smmu_add_device
arm_smmu_add_device: 将smmu设备添加到总线
arm_smmu_add_device()+-> smmu = arm_smmu_get_by_fwnode(fwspec->iommu_fwnode);/* for each sid, 如果是2-level ste, 为l2 ste分配内存*在之前的init_l1_strtab, 已经初始化了L1_std, L1_STD定义了下一级查找的基地址,* 现在可以通过sid 找到具体的STE(l2ptr + sid[7:0] * 64)* 这个函数先为每一个sid分配L2_STE的内存, 分配完成后在为每一个SID进行cfg配置*/+-> arm_smmu_init_l2_strtab()// 将device和group关联起来+-> iommu_device_link()总线扫描发现了设备,总线的发现流程负责调用iommu_ops(arm_smmu_ops )给这个设备加上iommu_group,然后让iommu_group指向对应的iommu控制器
arm_smmu_attach_dev, 尝试为设备寻找到驱动
arm_smmu_attach_dev()// 从iommu_domain 中得到arm_smmu_domain+-> smmu_domain = to_smmu_domain(iommu_domain );// 一般情况下smmu_domain->smmu = NULL// 在arm_smmu_add_device中,我们已经为STE项分配了内存+-> arm_smmu_domain_finalise(domain, master);// 分配asid+-> asids = arm_smmu_bitmap_alloc()// 根据smmu stage是stage1还是stage2, 如果smmu domain是stage1+-> arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s1()// 分配CD table的空间+-> arm_smmu_alloc_cd_tables(smmu_domain);// 配置CD descriptor的cfg+-> cfg->cd.tcr = FIELD_PREP(CTXDESC_CD_0_XXX)...// 如果smmu domain是stage2, STE已经包含了页表的s2ttb基地址和vmid,结束+-> arm_smmu_domain_finalise_s2()+-> finalise_stage_fn(smmu_domain, master, &pgtbl_cfg);支持了2-leveli的CD或linear格式的CD, 方式和SID查找ste类似。

结合代码分析:
static int arm_smmu_alloc_cd_tables(struct arm_smmu_domain *smmu_domain)
{int ret;size_t l1size;size_t max_contexts;struct arm_smmu_device *smmu = smmu_domain->smmu;struct arm_smmu_s1_cfg *cfg = &smmu_domain->s1_cfg;struct arm_smmu_ctx_desc_cfg *cdcfg = &cfg->cdcfg;max_contexts = 1 << cfg->s1cdmax; -------------- (a) if (!(smmu->features & ARM_SMMU_FEAT_2_LVL_CDTAB) ||max_contexts <= CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES) {cfg->s1fmt = STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT_LINEAR; -------- (b)cdcfg->num_l1_ents = max_contexts; l1size = max_contexts * (CTXDESC_CD_DWORDS << 3); ------- (c)} else {cfg->s1fmt = STRTAB_STE_0_S1FMT_64K_L2; cdcfg->num_l1_ents = DIV_ROUND_UP(max_contexts,CTXDESC_L2_ENTRIES);cdcfg->l1_desc = devm_kcalloc(smmu->dev, cdcfg->num_l1_ents,sizeof(*cdcfg->l1_desc),GFP_KERNEL);if (!cdcfg->l1_desc)return -ENOMEM;l1size = cdcfg->num_l1_ents * (CTXDESC_L1_DESC_DWORDS << 3);}cdcfg->cdtab = dmam_alloc_coherent(smmu->dev, l1size, &cdcfg->cdtab_dma,GFP_KERNEL);if (!cdcfg->cdtab) {dev_warn(smmu->dev, "failed to allocate context descriptor\n");ret = -ENOMEM;goto err_free_l1;}return 0;err_free_l1:if (cdcfg->l1_desc) {devm_kfree(smmu->dev, cdcfg->l1_desc);cdcfg->l1_desc = NULL;}return ret;
}
在CD的建立过程中,主要涉及到以下几点:
ste.S1Contextptr中定义了CD的基地址,CD的大小为64byte
a. 需要配置ste.S1CDMax, cdmax为0表示这个ste只有一个CD, 不需要使用到substreamid, 如果cdmax不为0, 那么CD的数目是2 ^ S1CDMax;
b. 需要配置ste.S1Fmt, 如果是linear结构的CD,CD的获取方法为S1ContextPTR + 64 * ssid; 如果是2-level结构的CD, L1CD的索引为ssid[s1cdmax - 1: 6], L2CD的索引为ssid[5:0]
attach_dev完成后,如果是stage1相关,CD的结构,大小和基地址已经成功建立,成功获取STE后,可以通过substreamid找到CD(S1ContextPTR + 64 * ssid)。找到的CD中包含页表PTW需要的TTBR寄存器,所以每一个CD对应一个页表, 这样一个SMMU单元,就可以有多张页表。
总结:
smmu驱动的初始化流程就是一个探测硬件规格,初始化硬件配置,分配STD/STE/CD等空间的过程。

参考资料
Linux iommu和vfio概念空间解构
IHI0070_System_Memory_Management_Unit_Arm_Architecture_Specification