文章目录
- Overview
- Concept
- Hardware
- 1. Node
- 2. Cluster
- 3. Persistent Volumes
- Software
- 1. Container
- 2. Pod
- 3. Deployment
- 4. Ingress
- Kaniko
- using docker
- using k8s
- Helm
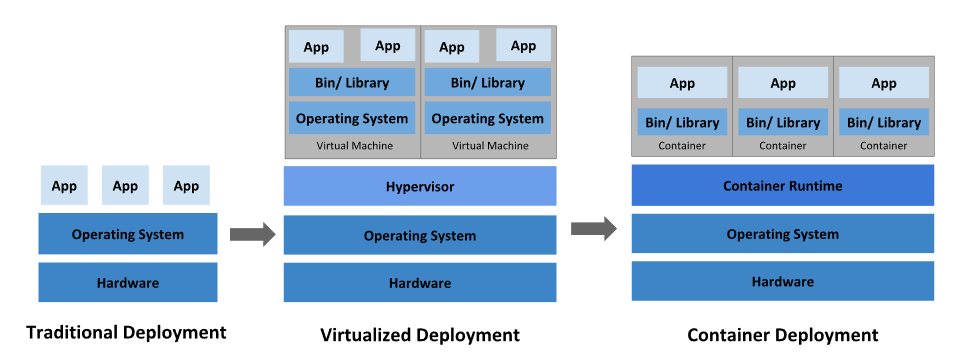
Overview
**kubelet: **An agent that runs on each node in the cluster. It makes sure that containers are running in a Pod.
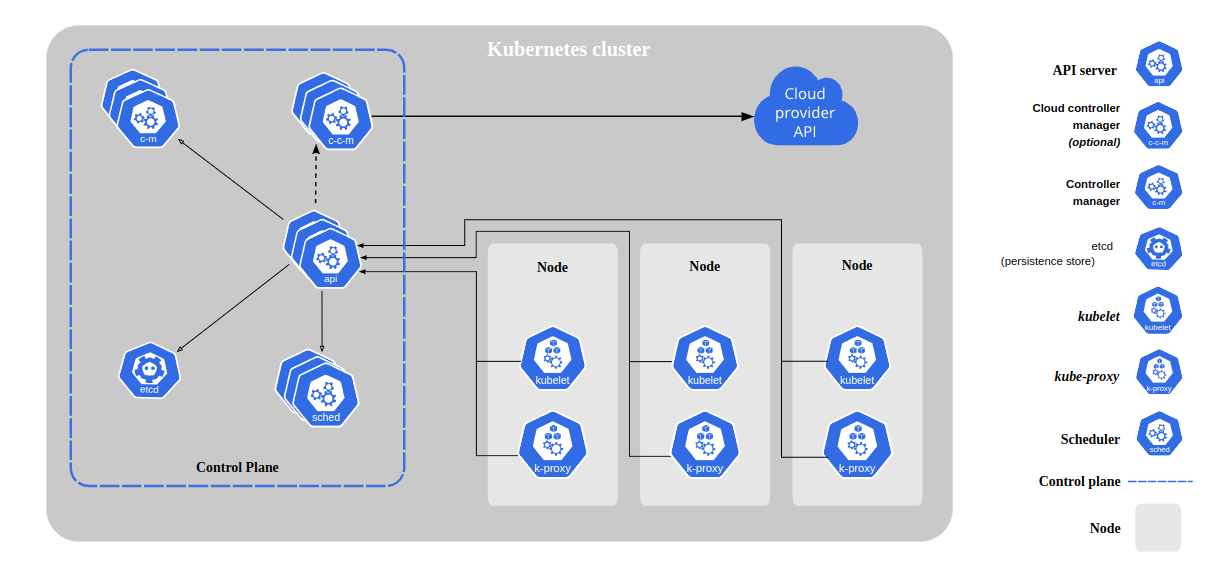
Concept
https://medium.com/google-cloud/kubernetes-101-pods-nodes-containers-and-clusters-c1509e409e16
Hardware
1. Node
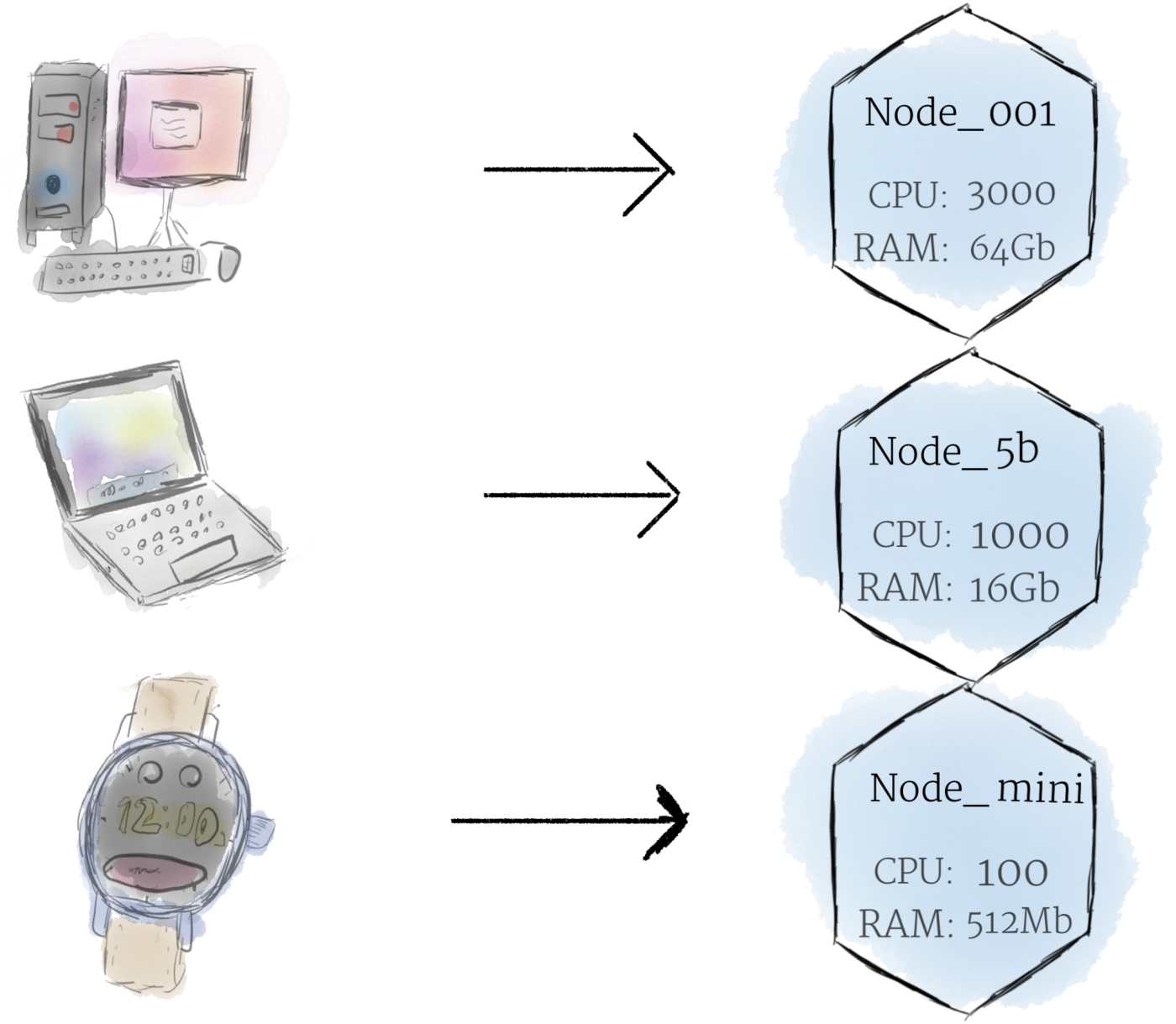
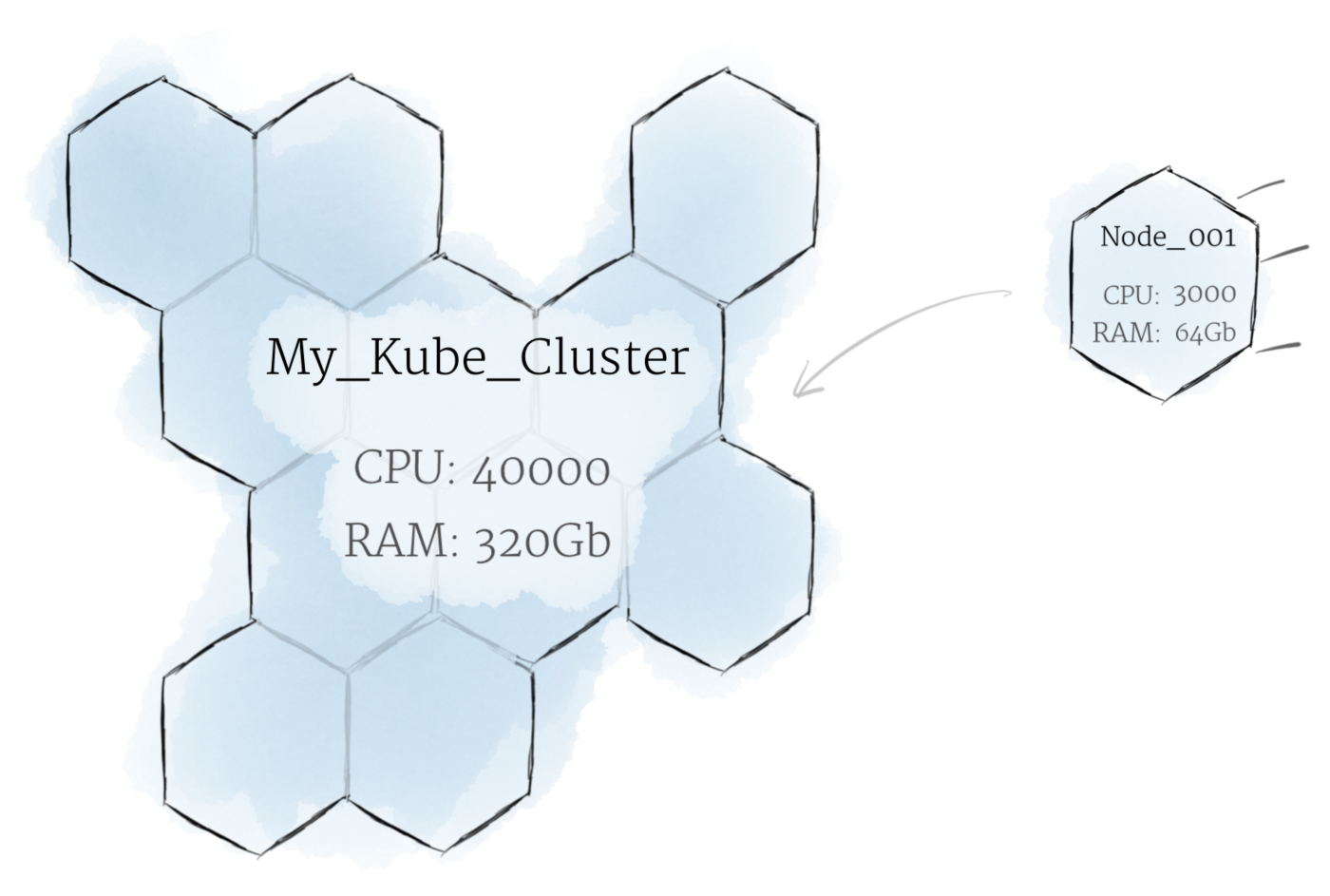
2. Cluster
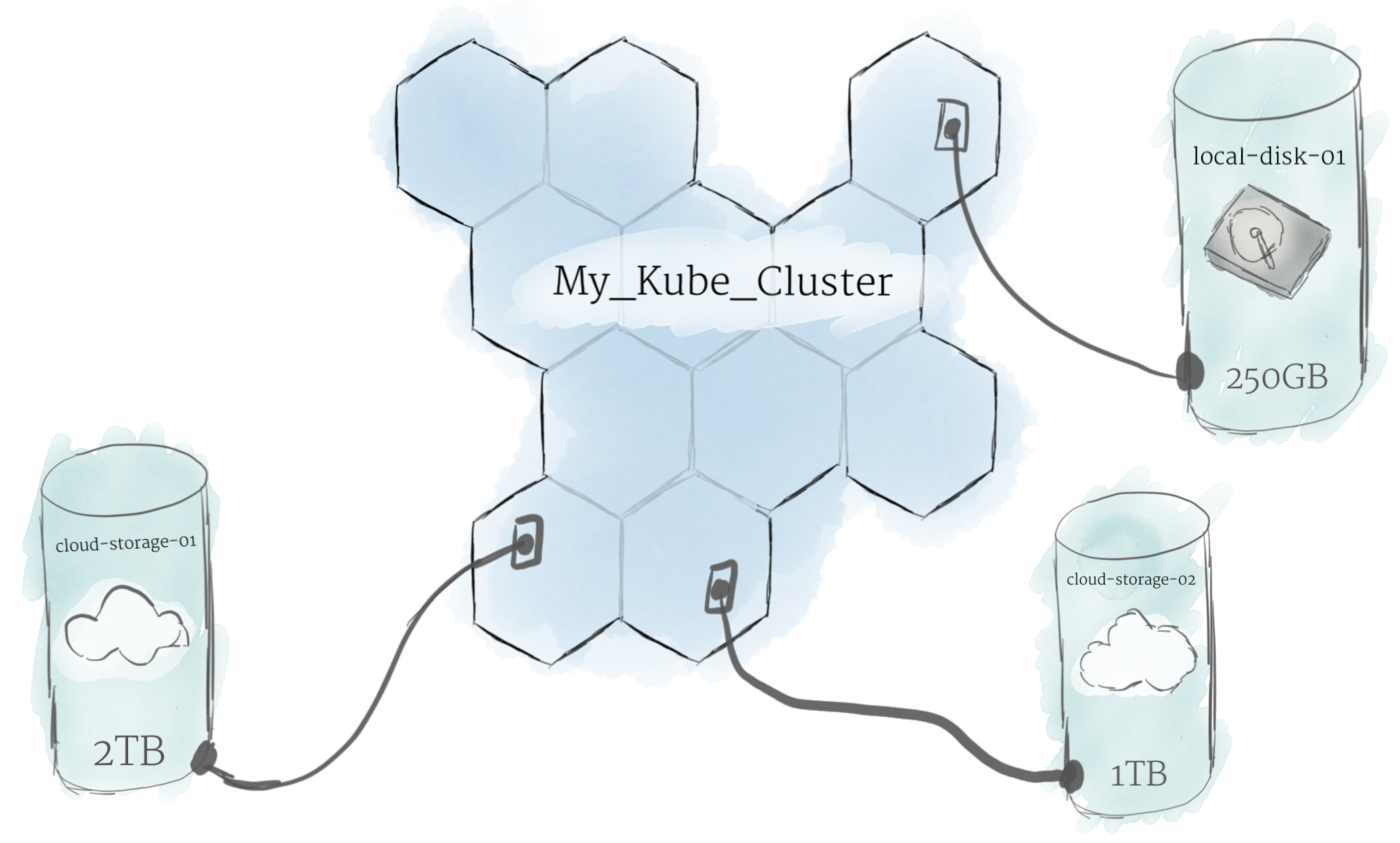
3. Persistent Volumes
Software
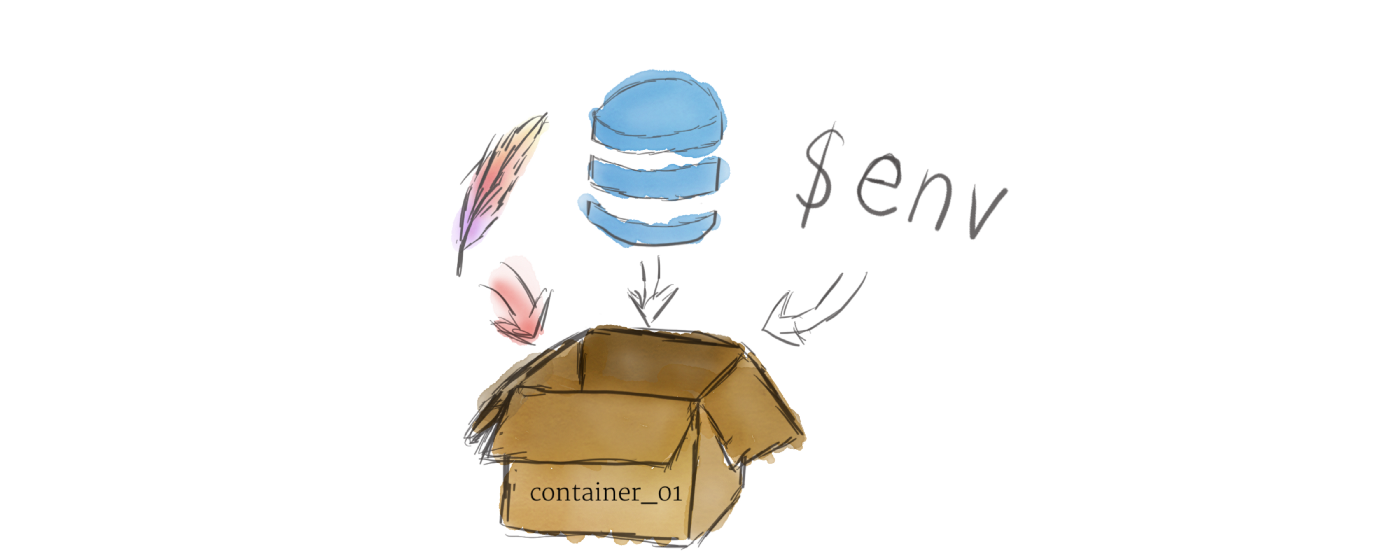
1. Container
2. Pod
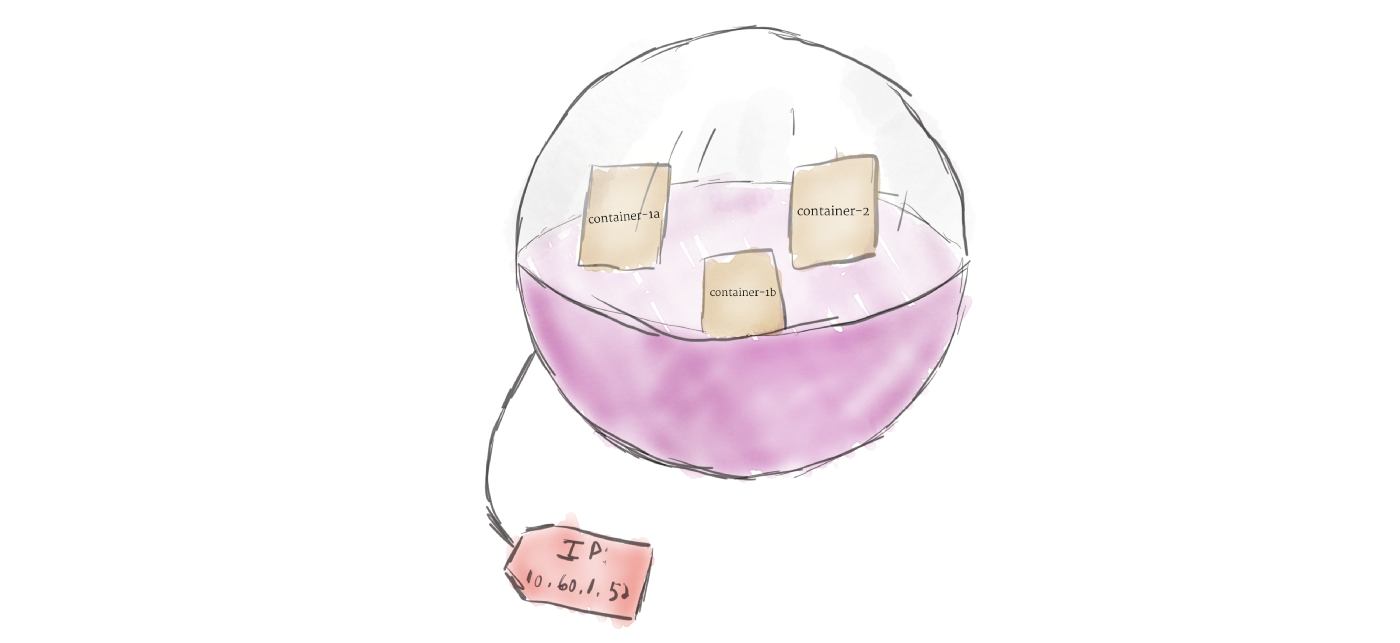
Unlike other systems you may have used in the past, Kubernetes doesn’t run containers directly; instead it wraps one or more containers into a higher-level structure called a pod. Any containers in the same pod will share the same resources and local network. Containers can easily communicate with other containers in the same pod as though they were on the same machine while maintaining a degree of isolation from others.
3. Deployment
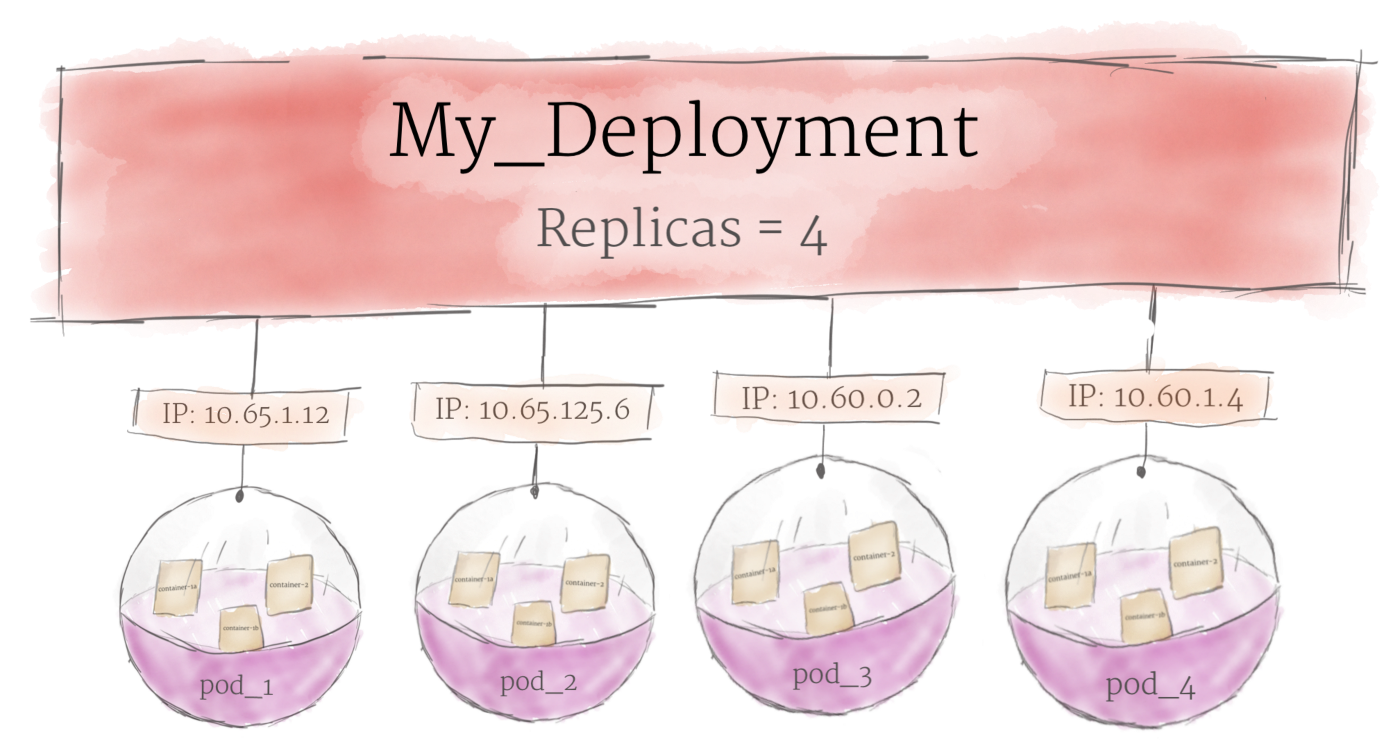
A deployment’s primary purpose is to declare how many replicas of a pod should be running at a time. When a deployment is added to the cluster, it will automatically spin up the requested number of pods, and then monitor them. If a pod dies, the deployment will automatically re-create it.
4. Ingress
There are multiple ways to add ingress to your cluster. The most common ways are by adding either an Ingress controller, or a LoadBalancer.
Kaniko
Since docker is not the only tool to use container, we have many other choices.
As a container engine, docker can be the best choice.
While there are tools that can build image without daemon thread: Buildah & Kaniko.
While Podman is a container engine without daemon thread and root, and podman build == buildah.
While Kaniko is widely used to build image in K8S.
Since is difficult for docker to build image in container:
- mount socket to access the docker daemon, root needed.
- use dind container with –privileged.
Kaniko totally run in user space, do not need daemon or root:
- in k8s
- in docker
It has three parameters:
- dockerfile: the container dockerfile need to be build
- context
- destination: the cloud image base need to upload
using docker
docker run --name kaniko \-v $HOME/.docker/:/kaniko/.docker \-v /data/kaniko:/workspace \gcr.azk8s.cn/kaniko-project/executor:latest \--dockerfile /workspace/Dockerfile \--destination willdockerhub/ubuntu:test \--context dir:///workspace/
using k8s
cat > kaniko-pod.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:name: kaniko
spec:containers:- name: kanikoimage: gcr.azk8s.cn/kaniko-project/executor:latestargs: ["--dockerfile=/workspace/Dockerfile","--context=dir://workspace","--destination=willdockerhub/ubuntu:test"] # replace with your dockerhub accountvolumeMounts:- name: kaniko-secretmountPath: /kaniko/.docker- name: dockerfile-storagemountPath: /workspacerestartPolicy: Nevervolumes:- name: kaniko-secretsecret:secretName: regcreditems:- key: .dockerconfigjsonpath: config.json- name: dockerfile-storagehostPath:path: /data/kaniko/type: Directory
EOF
Helm
对于应用发布者而言,可以通过Helm打包应用,管理应用依赖关系,管理应用版本并发布应用到软件仓库。
对于使用者而言,使用Helm后不用需要了解Kubernetes的Yaml语法并编写应用部署文件,可以通过Helm下载并在kubernetes上安装需要的应用。
**A Chart **is a Helm package. It contains all of the resource definitions necessary to run an application, tool, or service inside of a Kubernetes cluster. Think of it like the Kubernetes equivalent of a Homebrew formula, an Apt dpkg, or a Yum RPM file.
**A Repository **is the place where charts can be collected and shared. It’s like Perl’s CPAN archive or the Fedora Package Database, but for Kubernetes packages.
**A Release **is an instance of a chart running in a Kubernetes cluster. One chart can often be installed many times into the same cluster. And each time it is installed, a new release is created. Consider a MySQL chart. If you want two databases running in your cluster, you can install that chart twice. Each one will have its own release, which will in turn have its own release name.