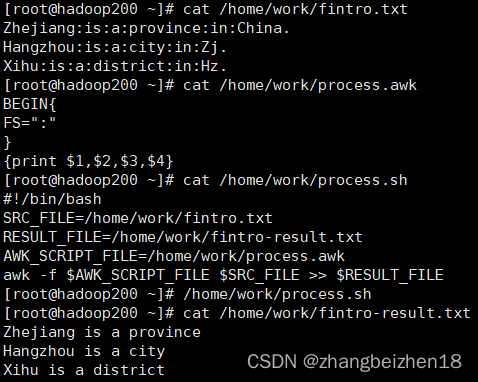
这里从云游戏的触控操作看起,
PC端的客户端支持按键和鼠标滑动操作,手机上的云游戏客户端则是和手机游戏一样的touch触控,客户端的touch操作是怎样处理给服务端的呢,猜测是把touch操作“实时”的传送给了服务器,Android服务器上把这些数据转换为相应的MotionEvent事件。
MotionEvent主要包含触控点的信息,由于其实现了Parcelable接口,所以可以使用Parcel来进行序列化保存和传输。
public final class MotionEvent extends InputEvent implements Parcelable
这里再进一步考虑一下,在Input事件分发的时候,InputDispatcher把input事件通过InputChannel发送给对应的应用进程的时候,是怎样传送input事件数据的呢,
在frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp中有
1999void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
2000 const sp<Connection>& connection) {
2001#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
2002 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ startDispatchCycle",
2003 connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());
2004#endif
2005
2006 while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL
2007 && !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
2008 DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.head;
2009 dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;
2010
2011 // Publish the event.
2012 status_t status;
2013 EventEntry* eventEntry = dispatchEntry->eventEntry;
2014 switch (eventEntry->type) {
2015 case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
2016 KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
2017
2018 // Publish the key event.
2019 status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
2020 keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
2021 dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
2022 keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
2023 keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
2024 keyEntry->eventTime);
2025 break;
2026 }
2027
2028 case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
2029 MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(eventEntry);
2030
2031 PointerCoords scaledCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
2032 const PointerCoords* usingCoords = motionEntry->pointerCoords;
2033
2034 // Set the X and Y offset depending on the input source.
2035 float xOffset, yOffset;
2036 if ((motionEntry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER)
2037 && !(dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_ZERO_COORDS)) {
2038 float scaleFactor = dispatchEntry->scaleFactor;
2039 xOffset = dispatchEntry->xOffset * scaleFactor;
2040 yOffset = dispatchEntry->yOffset * scaleFactor;
2041 if (scaleFactor != 1.0f) {
2042 for (uint32_t i = 0; i < motionEntry->pointerCount; i++) {
2043 scaledCoords[i] = motionEntry->pointerCoords[i];
2044 scaledCoords[i].scale(scaleFactor);
2045 }
2046 usingCoords = scaledCoords;
2047 }
2048 } else {
2049 xOffset = 0.0f;
2050 yOffset = 0.0f;
2051
2052 // We don't want the dispatch target to know.
2053 if (dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_ZERO_COORDS) {
2054 for (uint32_t i = 0; i < motionEntry->pointerCount; i++) {
2055 scaledCoords[i].clear();
2056 }
2057 usingCoords = scaledCoords;
2058 }
2059 }
2060
2061 // Publish the motion event.
2062 status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
2063 motionEntry->deviceId, motionEntry->source, motionEntry->displayId,
2064 dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, motionEntry->actionButton,
2065 dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags, motionEntry->edgeFlags,
2066 motionEntry->metaState, motionEntry->buttonState,
2067 xOffset, yOffset, motionEntry->xPrecision, motionEntry->yPrecision,
2068 motionEntry->downTime, motionEntry->eventTime,
2069 motionEntry->pointerCount, motionEntry->pointerProperties,
2070 usingCoords);
2071 break;
2072 }调用到inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent
284status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(
285 uint32_t seq,
286 int32_t deviceId,
287 int32_t source,
288 int32_t displayId,
289 int32_t action,
290 int32_t actionButton,
291 int32_t flags,
292 int32_t edgeFlags,
293 int32_t metaState,
294 int32_t buttonState,
295 float xOffset,
296 float yOffset,
297 float xPrecision,
298 float yPrecision,
299 nsecs_t downTime,
300 nsecs_t eventTime,
301 uint32_t pointerCount,
302 const PointerProperties* pointerProperties,
303 const PointerCoords* pointerCoords) {
304#if DEBUG_TRANSPORT_ACTIONS
305 ALOGD("channel '%s' publisher ~ publishMotionEvent: seq=%u, deviceId=%d, source=0x%x, "
306 "action=0x%x, actionButton=0x%08x, flags=0x%x, edgeFlags=0x%x, "
307 "metaState=0x%x, buttonState=0x%x, xOffset=%f, yOffset=%f, "
308 "xPrecision=%f, yPrecision=%f, downTime=%" PRId64 ", eventTime=%" PRId64 ", "
309 "pointerCount=%" PRIu32,
310 mChannel->getName().c_str(), seq,
311 deviceId, source, action, actionButton, flags, edgeFlags, metaState, buttonState,
312 xOffset, yOffset, xPrecision, yPrecision, downTime, eventTime, pointerCount);
313#endif
314
315 if (!seq) {
316 ALOGE("Attempted to publish a motion event with sequence number 0.");
317 return BAD_VALUE;
318 }
319
320 if (pointerCount > MAX_POINTERS || pointerCount < 1) {
321 ALOGE("channel '%s' publisher ~ Invalid number of pointers provided: %" PRIu32 ".",
322 mChannel->getName().c_str(), pointerCount);
323 return BAD_VALUE;
324 }
325
326 InputMessage msg;
327 msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_MOTION;
328 msg.body.motion.seq = seq;
329 msg.body.motion.deviceId = deviceId;
330 msg.body.motion.source = source;
331 msg.body.motion.displayId = displayId;
332 msg.body.motion.action = action;
333 msg.body.motion.actionButton = actionButton;
334 msg.body.motion.flags = flags;
335 msg.body.motion.edgeFlags = edgeFlags;
336 msg.body.motion.metaState = metaState;
337 msg.body.motion.buttonState = buttonState;
338 msg.body.motion.xOffset = xOffset;
339 msg.body.motion.yOffset = yOffset;
340 msg.body.motion.xPrecision = xPrecision;
341 msg.body.motion.yPrecision = yPrecision;
342 msg.body.motion.downTime = downTime;
343 msg.body.motion.eventTime = eventTime;
344 msg.body.motion.pointerCount = pointerCount;
345 for (uint32_t i = 0; i < pointerCount; i++) {
346 msg.body.motion.pointers[i].properties.copyFrom(pointerProperties[i]);
347 msg.body.motion.pointers[i].coords.copyFrom(pointerCoords[i]);
348 }
349 return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
350}input事件被转换成InputMessage来进行传送
151status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
152 size_t msgLength = msg->size();
153 ssize_t nWrite;
154 do {
155 nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
156 } while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
157
158 if (nWrite < 0) {
159 int error = errno;
160#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
161 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ error sending message of type %d, errno=%d", mName.c_str(),
162 msg->header.type, error);
163#endif
164 if (error == EAGAIN || error == EWOULDBLOCK) {
165 return WOULD_BLOCK;
166 }
167 if (error == EPIPE || error == ENOTCONN || error == ECONNREFUSED || error == ECONNRESET) {
168 return DEAD_OBJECT;
169 }
170 return -error;
171 }
172
173 if (size_t(nWrite) != msgLength) {
174#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
175 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ error sending message type %d, send was incomplete",
176 mName.c_str(), msg->header.type);
177#endif
178 return DEAD_OBJECT;
179 }
180
181#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
182 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ sent message of type %d", mName.c_str(), msg->header.type);
183#endif
184 return OK;
185}接收InputMessage数据的socket处理如下:
187status_t InputChannel::receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg) {
188 ssize_t nRead;
189 do {
190 nRead = ::recv(mFd, msg, sizeof(InputMessage), MSG_DONTWAIT);
191 } while (nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR);
192
193 if (nRead < 0) {
194 int error = errno;
195#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
196 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ receive message failed, errno=%d", mName.c_str(), errno);
197#endif
198 if (error == EAGAIN || error == EWOULDBLOCK) {
199 return WOULD_BLOCK;
200 }
201 if (error == EPIPE || error == ENOTCONN || error == ECONNREFUSED) {
202 return DEAD_OBJECT;
203 }
204 return -error;
205 }
206
207 if (nRead == 0) { // check for EOF
208#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
209 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ receive message failed because peer was closed", mName.c_str());
210#endif
211 return DEAD_OBJECT;
212 }
213
214 if (!msg->isValid(nRead)) {
215#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
216 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ received invalid message", mName.c_str());
217#endif
218 return BAD_VALUE;
219 }
220
221#if DEBUG_CHANNEL_MESSAGES
222 ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ received message of type %d", mName.c_str(), msg->header.type);
223#endif
224 return OK;
225}
226
227sp<InputChannel> InputChannel::dup() const {
228 int fd = ::dup(getFd());
229 return fd >= 0 ? new InputChannel(getName(), fd) : NULL;
230}
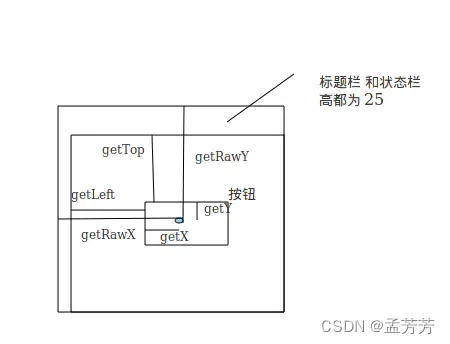
![[Android]视图的控触操作-MotionEvent](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7fd8fd978751449383a4485f8d52d5ba.gif)