目录
1、栈
(1)栈的概念及结构
(2)栈的实现
2、队列
(1)队列的概念及结构
(2)队列的实现
前言:栈和队列是在顺序表和链表的延伸,如果前面的顺序表和链表你已经掌握了的话,栈和队列对你来说应该就是小菜一碟了。
1、栈
(1)栈的概念及结构
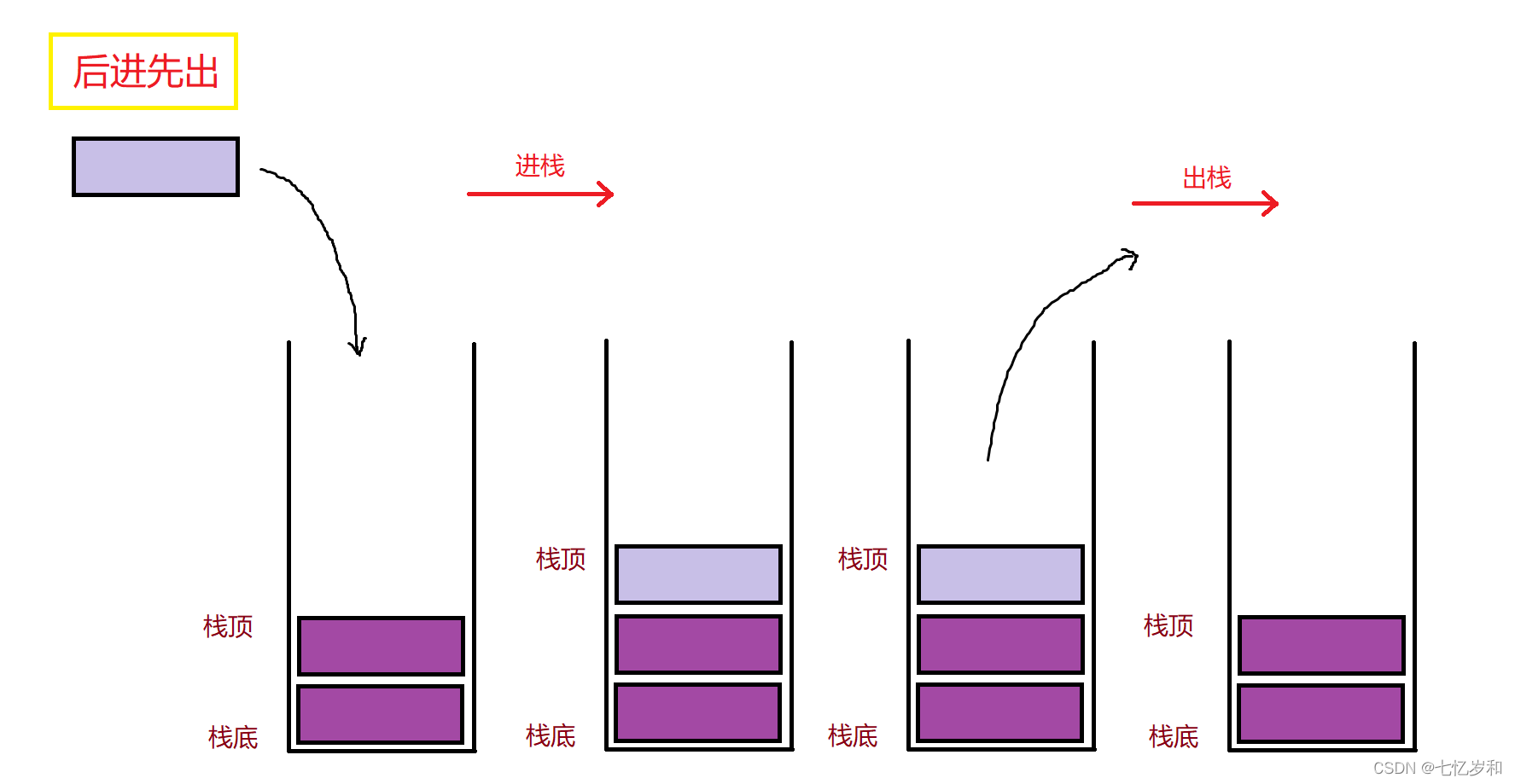
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
(2)栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
Stack.h
#pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stdbool.h>typedef char STDataType;typedef struct Stack {STDataType* a;int top;int capacity; }SL;//初始化 void StackInit(SL* ps);//使用后销毁 void StackDestroy(SL* ps);//入栈 void StackPush(SL* ps, STDataType x);//出栈 void StackPop(SL* ps);//判断栈空 bool StackEmpty(SL* ps);//栈的大小 int StackSize(SL* ps);//栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(SL* ps);Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Stack.h"//初始化 void StackInit(SL* ps) {assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0; }//使用后销毁 void StackDestroy(SL* ps) {assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0; }//入栈 void StackPush(SL* ps, STDataType x) {assert(ps);//如果栈满增容if (ps->top == ps->capacity){STDataType newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);}else{ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++; }//出栈 void StackPop(SL* ps) {assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);ps->top--; }//判断栈空 bool StackEmpty(SL* ps) {assert(ps);return (ps->top == 0); }//栈的大小 int StackSize(SL* ps) {assert(ps);return ps->top; }//栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(SL* ps) {assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top-1]; }test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Stack.h"//void test() //{ // SL st; // // StackInit(&st); // StackPush(&st, 1); // StackPush(&st, 2); // //StackPush(&st, 3); // //StackPush(&st, 4); // // printf("%d\n", StackTop(&st)); // // StackPop(&st); // // StackPush(&st, 3); // StackPush(&st, 4); // // while (!StackEmpty(&st)) // { // printf("%d ", StackTop(&st)); // StackPop(&st); // } // printf("\n"); // // StackDestroy(&st); // //}bool isValid(char* s) {SL st;StackInit(&st);while (*s){if (*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '['){StackPush(&st, *s);s++;}else{if (StackEmpty(&st))return false;char top = StackTop(&st);StackPop(&st);if ((*s == ')' && top != '(')|| (*s == ']' && top != '[')|| (*s == '}' && top != '{')){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}else{s++;}}}//栈为空,说明左括号都匹配完了bool ret = StackEmpty(&st);StackDestroy(&st);return ret; }int main() {//test();char a[] = { "{()}" };bool ret = isValid(a);printf("%d", ret);return 0; }
2、队列
(1)队列的概念及结构
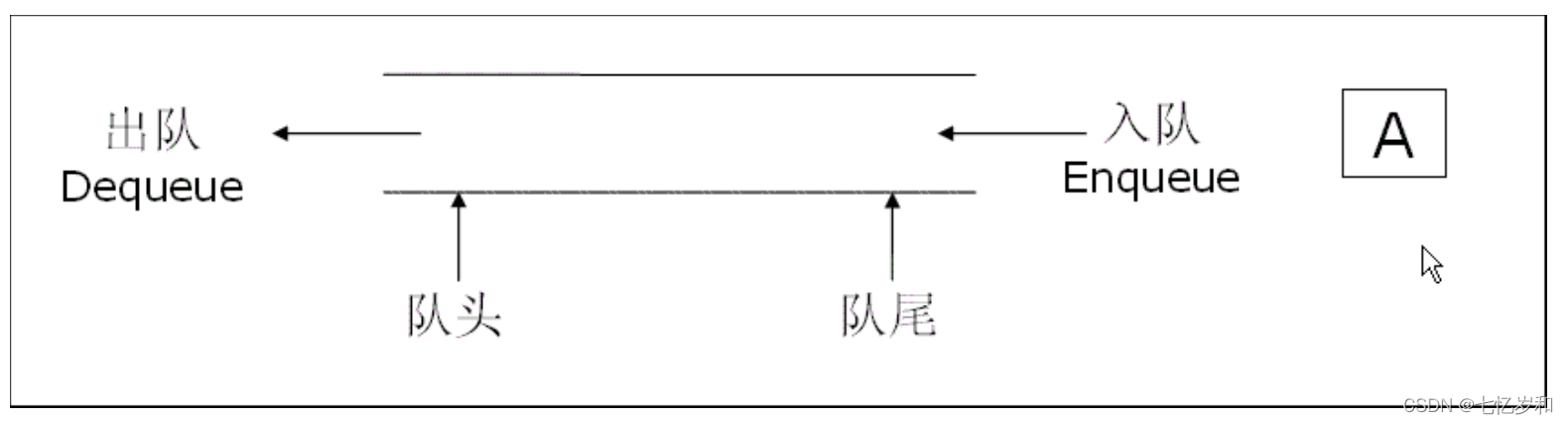
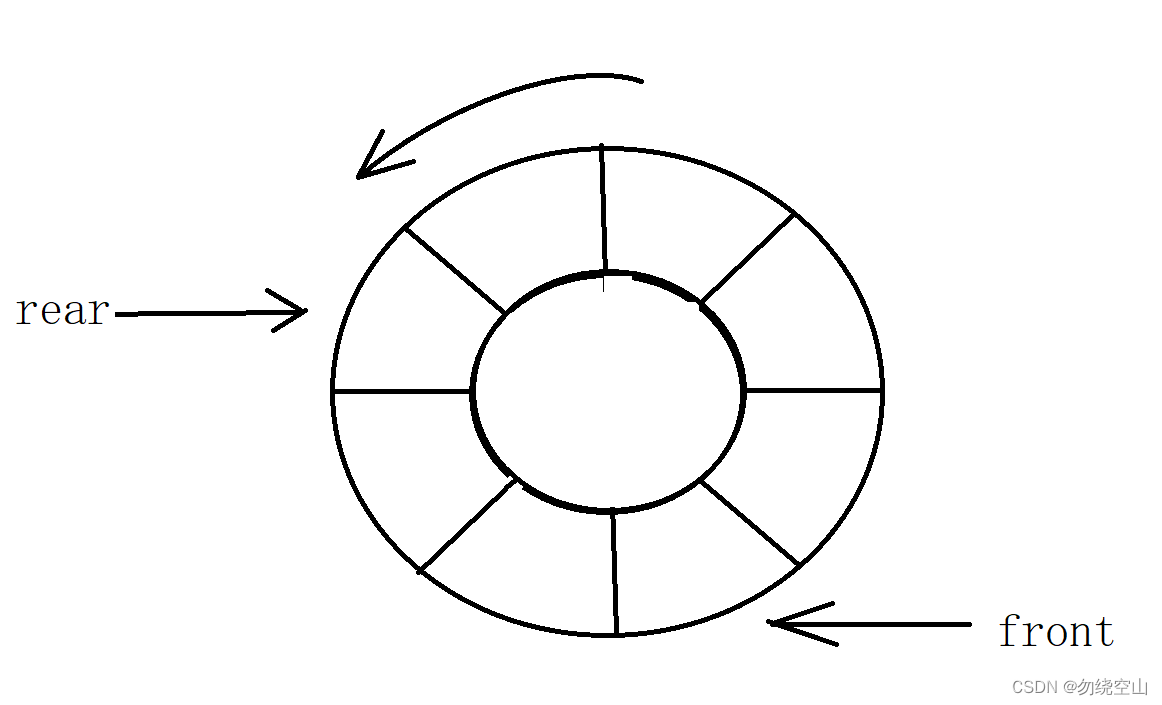
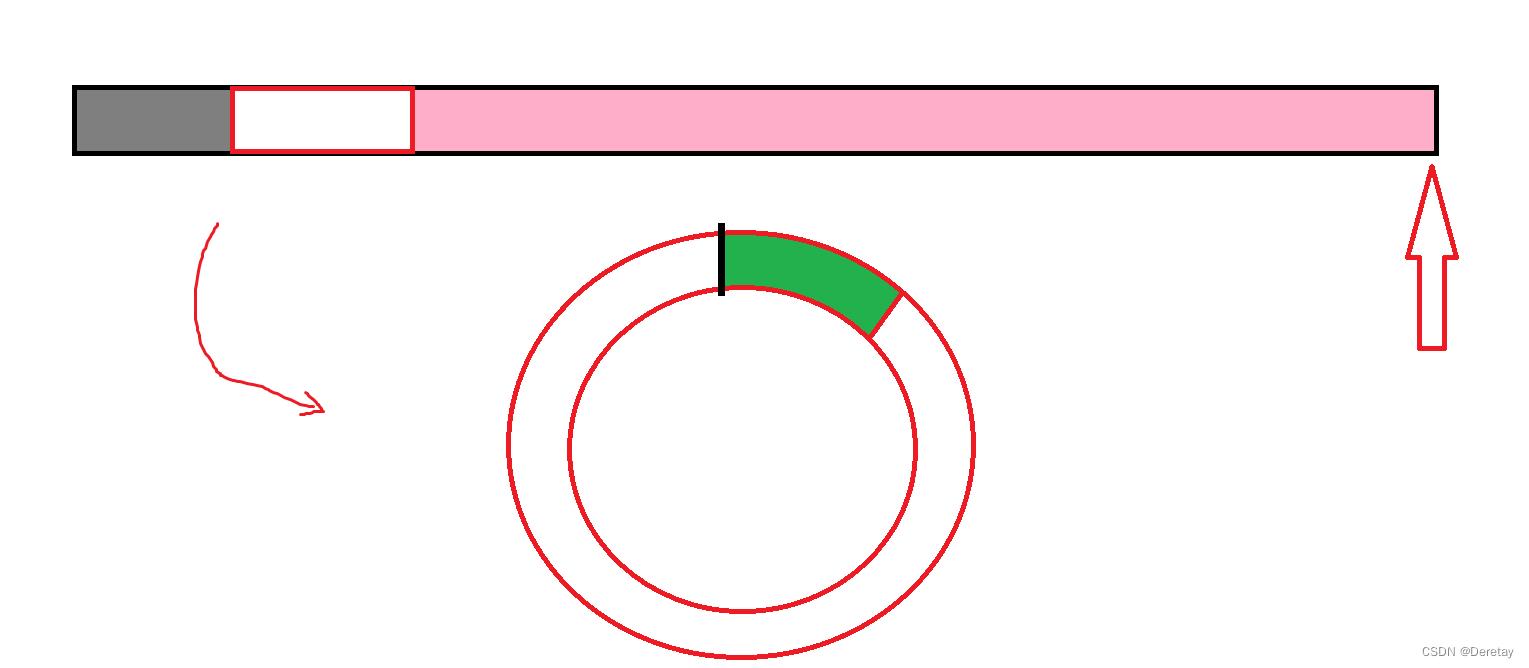
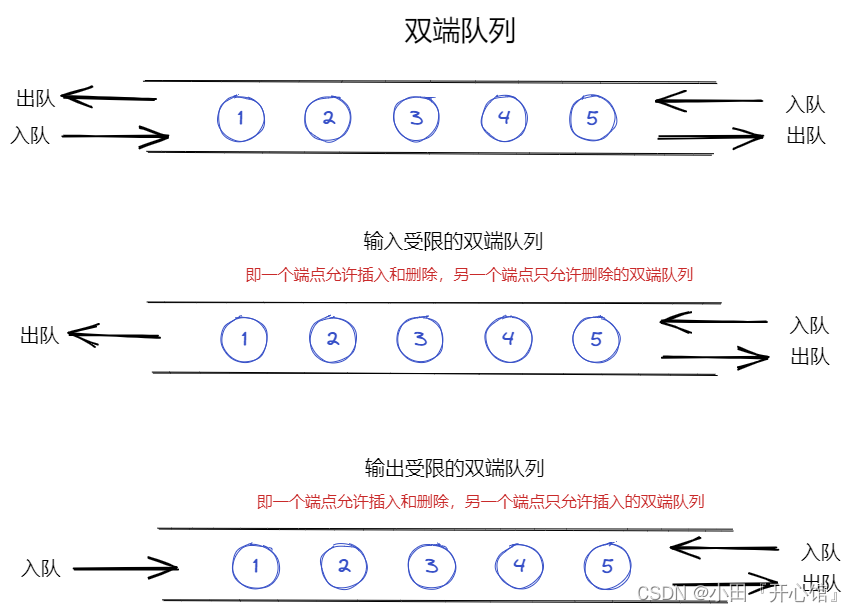
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
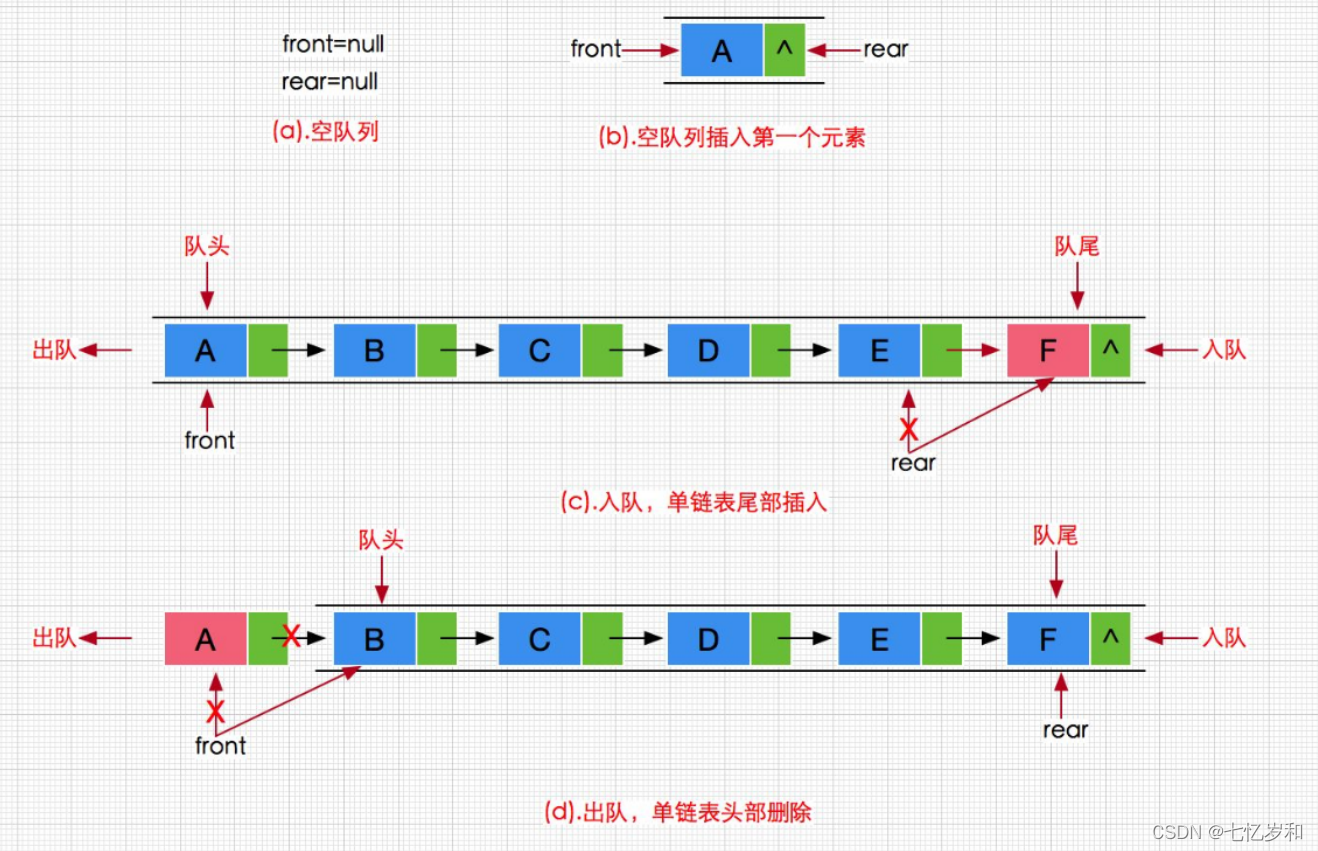
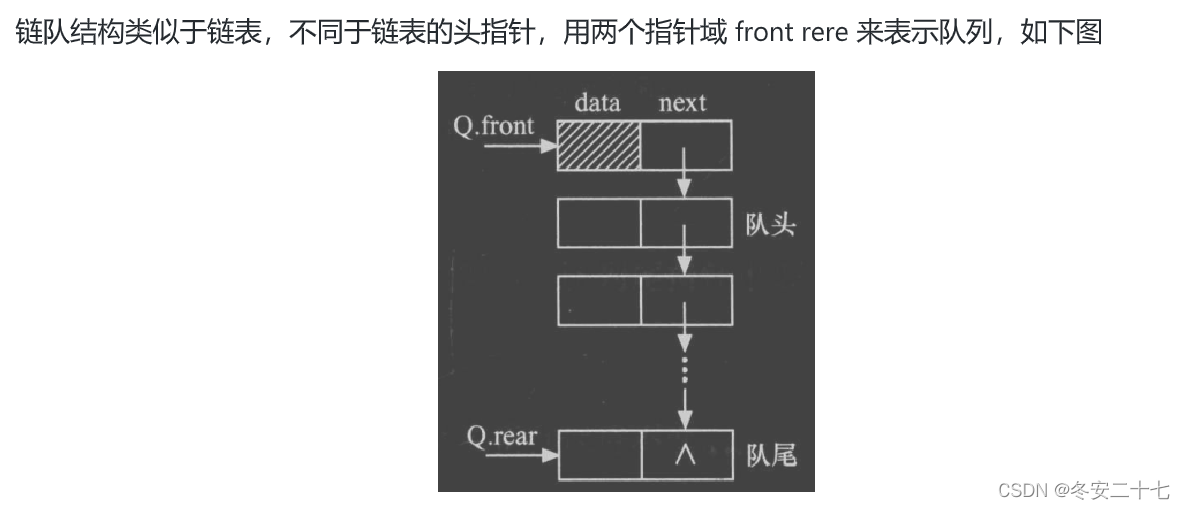
(2)队列的实现
Queue.h
#pragma once#include<stdio.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdbool.h> #include<stdlib.h>typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode {QDataType data;struct QueueNode* next; }QNode;typedef struct Queue {QNode* head;QNode* tail; }Queue;//初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//入队 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//出队 void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//判断队空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//队的大小 size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//队长 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//队尾 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Queue.h"//初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; }//销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; }//入队 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) {assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));assert(newnode);newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;} }//出队 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);assert(pq->head && pq->tail);if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;} }//判断队空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);//return (pq->head == NULL) && (pq->tail == NULL);return pq->head == NULL; }//队的大小 size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);QDataType size = 0;QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){size++;cur = cur->next;}return size; }//队长 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);assert(pq->head);return pq->head->data; }//队尾 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) {assert(pq);assert(pq->tail);return pq->tail->data; }Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Queue.h"void test() {Queue q;QueueInit(&q);QueuePush(&q, 1);QueuePush(&q, 2);QueuePush(&q, 3);QueuePush(&q, 4);printf("%d\n", QueueFront(&q));printf("%d\n", QueueBack(&q));/*while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));QueuePop(&q);}printf("\n");*/QueuePop(&q);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));QueuePop(&q);}printf("\n");QueueDestroy(&q); }int main() {test();return 0; }
栈和队列到此结束,若想再进一步,请关注下章讲解!