KEIL编译器C语言编译选项优化等级说明
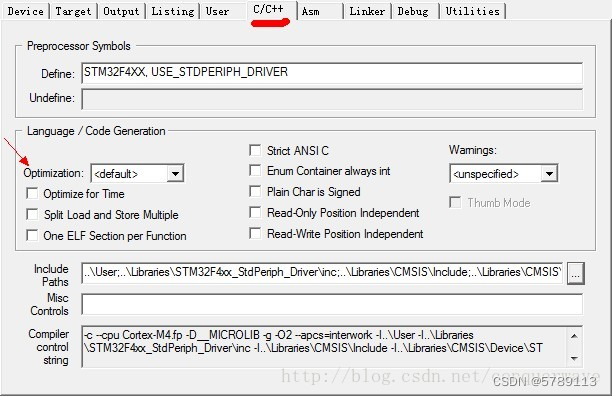
-Onum
Specifies the level of optimization to be used when compiling source files.
Syntax
-Onum
Where num is one of the following:
0
Minimum optimization. Turns off most optimizations. When debugging is enabled, this option gives the best possible debug view because the structure of the generated code directly corresponds to the source code. All optimization that interferes with the debug view is disabled.
最小的优化。关闭大多数优化。当启用调试时,该选项将提供最佳的调试视图,因为生成的代码的结构直接对应于源代码。所有干扰调试视图的优化都被禁用。
In particular:
• Breakpoints can be set on any reachable point, including dead code.
断点可以设置在任何可达点上,包括死代码。
• The value of a variable is available everywhere within its scope, except where it is uninitialized.
变量的值在其作用域内的任何地方都是可用的,除非它是未初始化的。
• Backtrace gives the stack of open function activations that is expected from reading the source.
Note
Backtrace给出了从读取源代码中预期的打开函数激活的堆栈。
Although the debug view produced by -O0 corresponds most closely to the source code, users might prefer the debug view produced by -O1 because this improves the quality of the code without changing the fundamental structure.
尽管由-O0生成的调试视图最接近源代码,但用户可能更喜欢由-O1生成的调试视图,因为这在不改变基本结构的情况下提高了代码的质量。
Note
Dead code includes reachable code that has no effect on the result of the program, for example an assignment to a local variable that is never used. Unreachable code is specifically code that cannot be reached via any control flow path, for example code that immediately follows a return statement.
死代码包括对程序结果没有影响的可访问代码,例如对从未使用过的局部变量的赋值。无法到达的代码是指不能通过任何控制流路径到达的代码,例如紧跟在返回语句后面的代码。
1
Restricted optimization. The compiler only performs optimizations that can be described by debug information. Removes unused inline functions and unused static functions. Turns off optimizations that seriously degrade the debug view. If used with --debug, this option gives a generally satisfactory debug view with good code density.
受限制的优化。编译器只执行可以通过调试信息描述的优化。删除未使用的内联函数和未使用的静态函数。关闭会严重降低调试视图的优化。如果与 --debug 一起使用,该选项将提供一个令人满意的调试视图,具有良好的代码密度。
The differences in the debug view from –O0 are:
调试视图与-O0的区别是:
• Breakpoints cannot be set on dead code.
•不能在死代码上设置断点。
• Values of variables might not be available within their scope after they have been initialized.
•变量的值在初始化后可能在其作用域内不可用。
For example if their assigned location has been reused.
例如,如果它们指定的位置已被重用。
• Functions with no side-effects might be called out of sequence, or might be omitted if the result is not needed.
•没有副作用的函数可能会被打乱顺序调用,或者如果结果不需要,可能会被省略。
• Backtrace might not give the stack of open function activations that is expected from reading the source because of the presence of tailcalls.
•由于尾部调用的存在,Backtrace可能不会给出读源代码所期望的打开函数激活堆栈。
The optimization level –O1 produces good correspondence between source code and object code, especially when the source code contains no dead code. The generated code can be significantly smaller than the code at –O0, which can simplify analysis of the object code.
优化级别-O1在源代码和目标代码之间产生良好的对应关系,特别是当源代码不包含死代码时。生成的代码可以明显小于-O0处的代码,这可以简化目标代码的分析。
2
High optimization. If used with --debug, the debug view might be less satisfactory because the mapping of object code to source code is not always clear. The compiler might perform optimizations that cannot be described by debug information.
高优化。如果与 --debug 一起使用,调试视图可能不太令人满意,因为目标代码到源代码的映射并不总是清楚的。编译器可能执行调试信息无法描述的优化。
This is the default optimization level.
这是默认的优化级别
The differences in the debug view from –O1 are:
调试视图与-O1的区别是:
• The source code to object code mapping might be many to one, because of the possibility of multiple source code locations mapping to one point of the file, and more aggressive instruction scheduling.
•源代码到目标代码的映射可能是多对一,因为多个源代码位置映射到文件的一个点的可能性,以及更激进的指令调度。
• Instruction scheduling is allowed to cross sequence points. This can lead to mismatches between the reported value of a variable at a particular point, and the value you might expect from reading the source code.
•允许指令调度跨序列点。这可能导致在特定点报告的变量值与您从阅读源代码中可能期望的值之间的不匹配。
• The compiler automatically inlines functions.
编译器自动内联函数。
3
Maximum optimization. When debugging is enabled, this option typically gives a poor debug view. ARM recommends debugging at lower optimization levels.
最大的优化。当启用调试时,该选项通常给出一个糟糕的调试视图。ARM建议在较低的优化级别进行调试。
If you use -O3 and -Otime together, the compiler performs extra optimizations that are more aggressive, such as:
如果你同时使用-O3和-Otime,编译器会执行更激进的额外优化,例如:
• High-level scalar optimizations, including loop unrolling. This can give significant performance benefits at a small code size cost, but at the risk of a longer build time.
•高级标量优化,包括循环展开。这可以以较小的代码规模成本获得显著的性能优势,但有可能需要更长的构建时间。
• More aggressive inlining and automatic inlining.
•更积极的内联和自动内联。
These optimizations effectively rewrite the input source code, resulting in object code with the lowest correspondence to source code and the worst debug view. The --loop_optimization_level=option controls the amount of loop optimization performed at –O3 –Otime. The higher the amount of loop optimization the worse the correspondence between source and object code.
这些优化有效地重写了输入源代码,导致目标代码与源代码的对应程度最低,调试视图最差。选项 --loop_optimization_level=控制在-O3 -Otime执行的循环优化量。循环优化的数量越高,源代码和目标代码之间的对应关系就越差。
Use of the --vectorize option also lowers the correspondence between source and object code.
使用–vectorize选项还降低了源代码和目标代码之间的通信。
For extra information about the high level transformations performed on the source code at –O3 –Otime use the --remarks command-line option.
有关在-O3 -Otime对源代码执行的高级转换的额外信息,请使用–remarks命令行选项。
Note
The performance of floating-point code can be influenced by selecting an appropriate numerical model using the --fpmode option.
通过使用–fpmode选项选择合适的数值模型,可以影响浮点代码的性能。
Note
Do not rely on the implementation details of these optimizations, because they might change in future releases.
不要依赖于这些优化的实现细节,因为它们可能在未来的版本中发生更改。
Note
By default, the compiler optimizes to reduce image size at the expense of a possible increase in execution time. That is, -Ospace is the default, rather than -Otime. Note that -Ospace is not affected by the optimization level -Onum. That is, -O3 -Ospace enables more optimizations than -O2 -Ospace, but does not perform more aggressive size reduction.
默认情况下,编译器优化以减少映像大小,代价是可能增加执行时间。也就是说,-Ospace是默认值,而不是-Otime。注意-Ospace不受优化级别-Onum的影响。也就是说,-O3 -Ospace比-O2 -Ospace支持更多的优化,但不会执行更积极的大小缩减。
Default
If you do not specify -Onum, the compiler assumes -O2.
如果不指定-Onum,编译器假定为-O2。
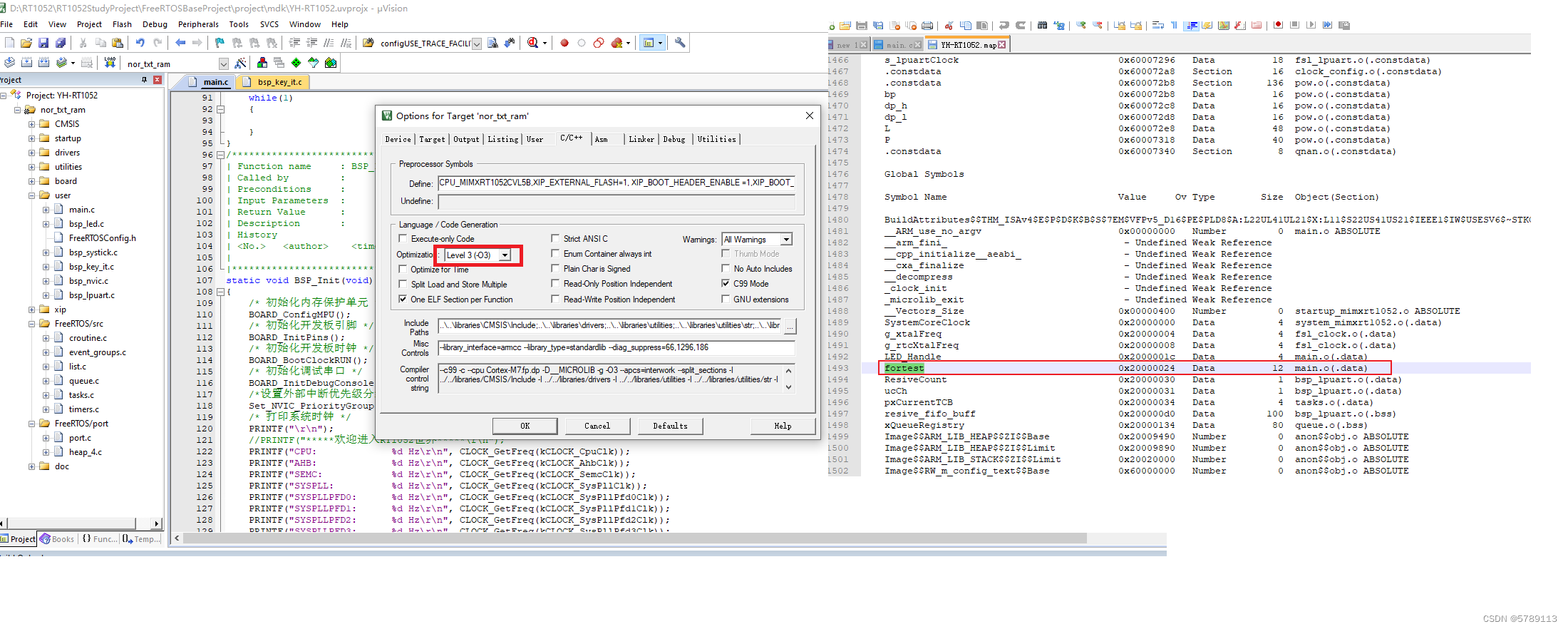
例:在main.c文件中定义一个全局变量fortest,optimization选择-O0,编译后分析map文件时查找不到变量fortest的信息
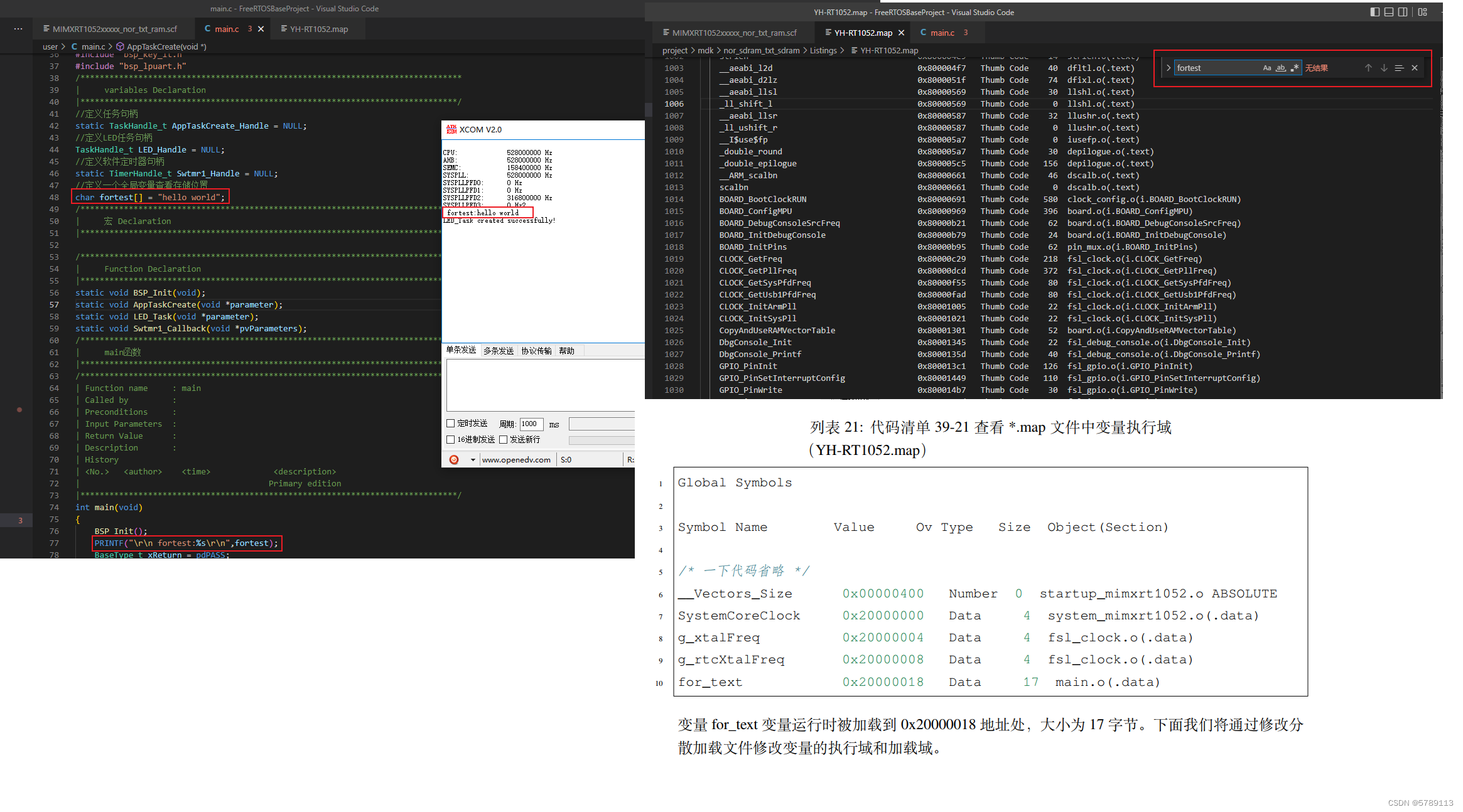
将optimization选择-O3后,重新编译后,在map文件中可查找到fortest的详细信息,而不是像-O0一样无法体现出各个变量的具体信息