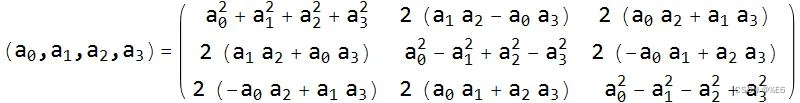| 原文: http://www.linuxgraphics.cn/graphics/opengl_quaternion.html Quaternion(四元数)和旋转 本文介绍了四元数以及如何在OpenGL中使用四元数表示旋转。 |
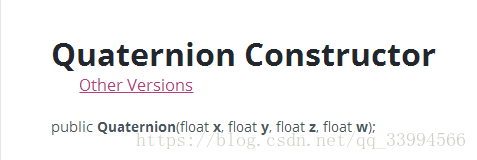
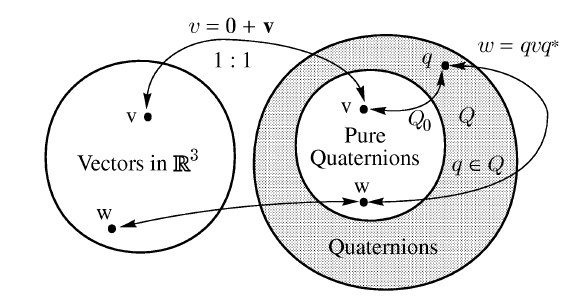
Quaternion 的定义四元数一般定义如下: q=w+xi+yj+zk 其中 w,x,y,z是实数。同时,有: i*i=-1j*j=-1k*k=-1 四元数也可以表示为: q=[w,v] 其中v=(x,y,z)是矢量,w是标量,虽然v是矢量,但不能简单的理解为3D空间的矢量,它是4维空间中的的矢量,也是非常不容易想像的。 通俗的讲,一个四元数(Quaternion)描述了一个旋转轴和一个旋转角度。这个旋转轴和这个角度可以通过 Quaternion::ToAngleAxis转换得到。当然也可以随意指定一个角度一个旋转轴来构造一个Quaternion。这个角度是相对于单位四元数而言的,也可以说是相对于物体的初始方向而言的。 当用一个四元数乘以一个向量时,实际上就是让该向量围绕着这个四元数所描述的旋转轴,转动这个四元数所描述的角度而得到的向量。 四元组的优点1有多种方式可表示旋转,如 axis/angle、欧拉角(Euler angles)、矩阵(matrix)、四元组等。 相对于其它方法,四元组有其本身的优点:
Quaternion 的基本运算1Normalizing a quaternion// normalising a quaternion works similar to a vector. This method will not do anything
// if the quaternion is close enough to being unit-length. define TOLERANCE as something
// small like 0.00001f to get accurate results
void Quaternion::normalise()
{// Don't normalize if we don't have tofloat mag2 = w * w + x * x + y * y + z * z;if ( mag2!=0.f && (fabs(mag2 - 1.0f) > TOLERANCE)) {float mag = sqrt(mag2);w /= mag;x /= mag;y /= mag;z /= mag;}
} The complex conjugate of a quaternion// We need to get the inverse of a quaternion to properly apply a quaternion-rotation to a vector
// The conjugate of a quaternion is the same as the inverse, as long as the quaternion is unit-length
Quaternion Quaternion::getConjugate()
{return Quaternion(-x, -y, -z, w);
} Multiplying quaternions// Multiplying q1 with q2 applies the rotation q2 to q1
Quaternion Quaternion::operator* (const Quaternion &rq) const
{// the constructor takes its arguments as (x, y, z, w)return Quaternion(w * rq.x + x * rq.w + y * rq.z - z * rq.y,w * rq.y + y * rq.w + z * rq.x - x * rq.z,w * rq.z + z * rq.w + x * rq.y - y * rq.x,w * rq.w - x * rq.x - y * rq.y - z * rq.z);
} Rotating vectors// Multiplying a quaternion q with a vector v applies the q-rotation to v
Vector3 Quaternion::operator* (const Vector3 &vec) const
{Vector3 vn(vec);vn.normalise();Quaternion vecQuat, resQuat;vecQuat.x = vn.x;vecQuat.y = vn.y;vecQuat.z = vn.z;vecQuat.w = 0.0f;resQuat = vecQuat * getConjugate();resQuat = *this * resQuat;return (Vector3(resQuat.x, resQuat.y, resQuat.z));
} How to convert to/from quaternions1Quaternion from axis-angle// Convert from Axis Angle
void Quaternion::FromAxis(const Vector3 &v, float angle)
{float sinAngle;angle *= 0.5f;Vector3 vn(v);vn.normalise();sinAngle = sin(angle);x = (vn.x * sinAngle);y = (vn.y * sinAngle);z = (vn.z * sinAngle);w = cos(angle);
} Quaternion from Euler angles// Convert from Euler Angles
void Quaternion::FromEuler(float pitch, float yaw, float roll)
{// Basically we create 3 Quaternions, one for pitch, one for yaw, one for roll// and multiply those together.// the calculation below does the same, just shorterfloat p = pitch * PIOVER180 / 2.0;float y = yaw * PIOVER180 / 2.0;float r = roll * PIOVER180 / 2.0;float sinp = sin(p);float siny = sin(y);float sinr = sin(r);float cosp = cos(p);float cosy = cos(y);float cosr = cos(r);this->x = sinr * cosp * cosy - cosr * sinp * siny;this->y = cosr * sinp * cosy + sinr * cosp * siny;this->z = cosr * cosp * siny - sinr * sinp * cosy;this->w = cosr * cosp * cosy + sinr * sinp * siny;normalise();
} Quaternion to Matrix// Convert to Matrix
Matrix4 Quaternion::getMatrix() const
{float x2 = x * x;float y2 = y * y;float z2 = z * z;float xy = x * y;float xz = x * z;float yz = y * z;float wx = w * x;float wy = w * y;float wz = w * z;// This calculation would be a lot more complicated for non-unit length quaternions// Note: The constructor of Matrix4 expects the Matrix in column-major format like expected by// OpenGLreturn Matrix4( 1.0f - 2.0f * (y2 + z2), 2.0f * (xy - wz), 2.0f * (xz + wy), 0.0f,2.0f * (xy + wz), 1.0f - 2.0f * (x2 + z2), 2.0f * (yz - wx), 0.0f,2.0f * (xz - wy), 2.0f * (yz + wx), 1.0f - 2.0f * (x2 + y2), 0.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)
} Quaternion to axis-angle// Convert to Axis/Angles
void Quaternion::getAxisAngle(Vector3 *axis, float *angle)
{float scale = sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);axis->x = x / scale;axis->y = y / scale;axis->z = z / scale;*angle = acos(w) * 2.0f;
} Quaternion 插值2线性插值最简单的插值算法就是线性插值,公式如: q(t)=(1-t)q1 + t q2 但这个结果是需要规格化的,否则q(t)的单位长度会发生变化,所以 q(t)=(1-t)q1+t q2 / || (1-t)q1+t q2 || 球形线性插值尽管线性插值很有效,但不能以恒定的速率描述q1到q2之间的曲线,这也是其弊端,我们需要找到一种插值方法使得q1->q(t)之间的夹角θ是线性的,即θ(t)=(1-t)θ1+t*θ2,这样我们得到了球形线性插值函数q(t),如下: q(t)=q1 * sinθ(1-t)/sinθ + q2 * sinθt/sineθ 如果使用D3D,可以直接使用 D3DXQuaternionSlerp 函数就可以完成这个插值过程。 用 Quaternion 实现 Camera 旋转总体来讲,Camera 的操作可分为如下几类:
下面是一个使用了 Quaternion 的 Camera 类: class Camera {private:Quaternion m_orientation;public:void rotate (const Quaternion& q);void rotate(const Vector3& axis, const Radian& angle);void roll (const GLfloat angle);void yaw (const GLfloat angle);void pitch (const GLfloat angle);};void Camera::rotate(const Quaternion& q){// Note the order of the mult, i.e. q comes afterm_Orientation = q * m_Orientation;}void Camera::rotate(const Vector3& axis, const Radian& angle){Quaternion q;q.FromAngleAxis(angle,axis);rotate(q);}void Camera::roll (const GLfloat angle) //in radian{Vector3 zAxis = m_Orientation * Vector3::UNIT_Z;rotate(zAxis, angleInRadian);}void Camera::yaw (const GLfloat angle) //in degree{Vector3 yAxis;{// Rotate around local Y axisyAxis = m_Orientation * Vector3::UNIT_Y;}rotate(yAxis, angleInRadian);}void Camera::pitch (const GLfloat angle) //in radian{Vector3 xAxis = m_Orientation * Vector3::UNIT_X;rotate(xAxis, angleInRadian);}void Camera::gluLookAt() {GLfloat m[4][4];identf(&m[0][0]);m_Orientation.createMatrix (&m[0][0]);glMultMatrixf(&m[0][0]);glTranslatef(-m_eyex, -m_eyey, -m_eyez);} 用 Quaternion 实现 trackball用鼠标拖动物体在三维空间里旋转,一般设计一个 trackball,其内部实现也常用四元数。 class TrackBall
{
public:TrackBall();void push(const QPointF& p);void move(const QPointF& p);void release(const QPointF& p);QQuaternion rotation() const;private:QQuaternion m_rotation;QVector3D m_axis;float m_angularVelocity;QPointF m_lastPos;};void TrackBall::move(const QPointF& p)
{if (!m_pressed)return;QVector3D lastPos3D = QVector3D(m_lastPos.x(), m_lastPos.y(), 0.0f);float sqrZ = 1 - QVector3D::dotProduct(lastPos3D, lastPos3D);if (sqrZ > 0)lastPos3D.setZ(sqrt(sqrZ));elselastPos3D.normalize();QVector3D currentPos3D = QVector3D(p.x(), p.y(), 0.0f);sqrZ = 1 - QVector3D::dotProduct(currentPos3D, currentPos3D);if (sqrZ > 0)currentPos3D.setZ(sqrt(sqrZ));elsecurrentPos3D.normalize();m_axis = QVector3D::crossProduct(lastPos3D, currentPos3D);float angle = 180 / PI * asin(sqrt(QVector3D::dotProduct(m_axis, m_axis)));m_axis.normalize();m_rotation = QQuaternion::fromAxisAndAngle(m_axis, angle) * m_rotation;m_lastPos = p;} Yaw, pitch, roll 的含义3Yaw – Vertical axis:
Pitch – Lateral axis
Roll – Longitudinal axis
The Position of All three axes
|







![Unity3D - 详解Quaternion类[转载]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c483c41d74754e688620c250ec1ef653.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3N1bmhhbzUyMTExMQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70#pic_center)