序言
@JsonProperty
当一个Java对象转换成Json字符串后,如果不是正确的实际名称有可能会出现异常。比如数据库中的坐标名称是x_axis,而定义Java对象是是xAxis,那么这时就需要使用到@JsonProperty注解,并且配合ObjectMapper.writeValueAsString方法使用去序列化对象成字符串。如下示例demo,
@JsonProperty(value = "", index = 1, access = JsonProperty.Access.xxx)
其中value为成员变量真实名称,index为序列化之后所展示的顺序,access为该对象的访问控制权限。
@Slf4j
public class JsonPropertyDemo {@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@Builder@ToStringprivate static class Coordinate {@JsonProperty(value = "x_axis", index = 1, access = JsonProperty.Access.WRITE_ONLY)private String xAxis;@JsonProperty(value = "y_axis", index = 2, access = JsonProperty.Access.READ_WRITE)private String yAxis;@JsonProperty(value = "z_axis", index = 3, access = JsonProperty.Access.READ_WRITE)private String zAxis;}public static void main(String[] args) {Coordinate coordinate = Coordinate.builder().xAxis("113.58").yAxis("37.86").zAxis("40.05").build();String jsonStr = JSON.toJSONString(coordinate);log.info("serializes the specified object into its equivalent Json representation :" + jsonStr);ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();try {String str = mapper.writeValueAsString(coordinate);log.info("serialize any Java value as a String : " + str);Object bean = mapper.readerFor(Coordinate.class).readValue(str);log.info("read or update instances of specified type : " + bean);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.error("error message : " + e);}}
}
注解一般都是通过反射拿到对映的成员变量然后再进行增强,@JsonProperty把成员变量序列化成另外一个名称,并且它在序列化和反序列化的过程中都是使用的实际名称。
@JsonAlias
com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation中的@JsonProperty是可以在序列化和反序列化中使用,而@JsonAlias只在反序列化中起作用,指定Java属性可以接受的更多名称。文末链接也有JsonAlias的实例源码,下面就简单举一个例子,
@Slf4j
public class JsonAliasDemo {@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@Builder@ToStringprivate static class Coordinate {@JsonAlias(value = "x_location")@JsonProperty(value = "x_axis")private String xAxis;@JsonProperty(value = "y_axis")@JsonAlias(value = "y_location")private String yAxis;@JsonProperty(value = "z_axis")@JsonAlias(value = "z_location")private String zAxis;}public static void main(String[] args) {String location = "{\"x_location\":\"113.58\",\"y_location\":\"37.86\",\"z_location\":\"40.05\"}";ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();try {Object bean = mapper.readValue(location, Coordinate.class);log.info("read or update instances of specified type : " + bean);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.error("error message : " + e);}}
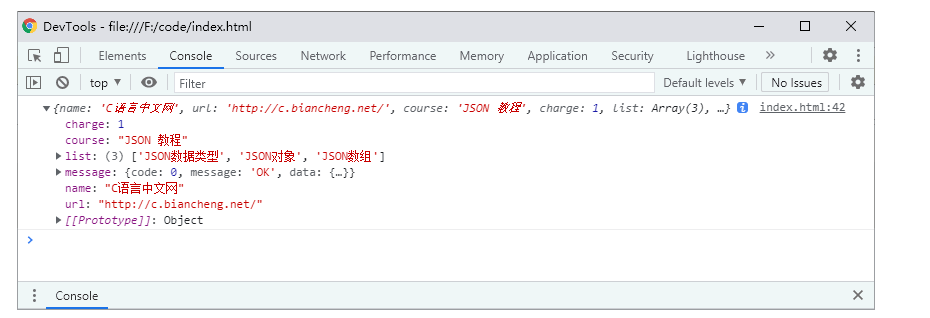
}@JsonAlias里的别名的json字符串,在反序列化时可以识别出来,不会反序列化失败,结果如下图,

@JsonProperty源码
JsonProperty的源码是一个注解类,注解类上的几个元注解就不解释了,可以参考文末链接7,该注解的主要作用就是在pojo属性上执行自定义处理器流程。
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@JacksonAnnotation
public @interface JsonProperty {String USE_DEFAULT_NAME = "";int INDEX_UNKNOWN = -1;String value() default "";boolean required() default false;int index() default -1;String defaultValue() default "";JsonProperty.Access access() default JsonProperty.Access.AUTO;public static enum Access {AUTO,READ_ONLY,WRITE_ONLY,READ_WRITE;private Access() {}}
}那么下面就看一下处理器流程做了一些什么事,找到JacksonAnnotationIntrospector类,
先看在jackson 2.6版本之后找到添加了@JsonProperty注解的pojo属性做了什么事,注意这里是一个过期的旧方法,保留是为了兼容使用老版本jackson的方法(@Deprecated注解)。首先该方法通过反射拿到成员变量,然后再获取注解中的属性值(eg:@JsonProperty(value = "x_axis")),如果找到则返回value值,否则就返回原成员变量的name。
/*** Since 2.6, we have supported use of {@link JsonProperty} for specifying* explicit serialized name*/@Override@Deprecated // since 2.8public String findEnumValue(Enum<?> value){// 11-Jun-2015, tatu: As per [databind#677], need to allow explicit naming.// Unfortunately cannot quite use standard AnnotatedClass here (due to various// reasons, including odd representation JVM uses); has to do for nowtry {// We know that values are actually static fields with matching name so:Field f = value.getClass().getField(value.name());if (f != null) {JsonProperty prop = f.getAnnotation(JsonProperty.class);if (prop != null) {String n = prop.value();if (n != null && !n.isEmpty()) {return n;}}}} catch (SecurityException e) {// 17-Sep-2015, tatu: Anything we could/should do here?} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {// 17-Sep-2015, tatu: should not really happen. But... can we do anything?}return value.name();}下面再看一下jackson2.7之后是怎么做的,首先该方法不是根据成员变量的name获取类的属性,而是直接遍历类中所有的属性,然后用哈希表expl存属性的name和注解中的value映射关系,然后一次性遍历一遍把所有的属性的真实值集合返回出来(如果没有配置@JsonProperty的value则是属性原值,如果配有@JsonProperty的value则返回value值),这么做的好处在于不用一次一次的解析真实属性值而是一起解析真实属性值。
@Override // since 2.7public String[] findEnumValues(Class<?> enumType, Enum<?>[] enumValues, String[] names) {HashMap<String,String> expl = null;for (Field f : ClassUtil.getDeclaredFields(enumType)) {if (!f.isEnumConstant()) {continue;}JsonProperty prop = f.getAnnotation(JsonProperty.class);if (prop == null) {continue;}String n = prop.value();if (n.isEmpty()) {continue;}if (expl == null) {expl = new HashMap<String,String>();}expl.put(f.getName(), n);}// and then stitch them together if and as necessaryif (expl != null) {for (int i = 0, end = enumValues.length; i < end; ++i) {String defName = enumValues[i].name();String explValue = expl.get(defName);if (explValue != null) {names[i] = explValue;}}}return names;}其他属性的解析也基本上如出一辙,代码如下,
@Overridepublic Boolean hasRequiredMarker(AnnotatedMember m){JsonProperty ann = _findAnnotation(m, JsonProperty.class);if (ann != null) {return ann.required();}return null;}@Overridepublic JsonProperty.Access findPropertyAccess(Annotated m) {JsonProperty ann = _findAnnotation(m, JsonProperty.class);if (ann != null) {return ann.access();}return null;}@Overridepublic Integer findPropertyIndex(Annotated ann) {JsonProperty prop = _findAnnotation(ann, JsonProperty.class);if (prop != null) {int ix = prop.index();if (ix != JsonProperty.INDEX_UNKNOWN) {return Integer.valueOf(ix);}}return null;}@Overridepublic String findPropertyDefaultValue(Annotated ann) {JsonProperty prop = _findAnnotation(ann, JsonProperty.class);if (prop == null) {return null;}String str = prop.defaultValue();// Since annotations do not allow nulls, need to assume empty means "none"return str.isEmpty() ? null : str;}
序列化和反序列化配置
另外,序列化和反序列化中会有些常见配置,比如常见的如下,
DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES
在反序列化json字符串成Java对象时,遇到未知属性是否抛出异常信息。
@Slf4j
public class DeserializationFeatureDemo {/*** 注意上面的实例对象必须要有无参构造函数,否则在反序列化时创建实例对象* 会抛出异常com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException*/@Data@Builder@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorprivate static class Person {private String name;private Long age;}public static void main(String[] args) {String jsonStr = "{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":18,\"sex\":\"男\"}";System.out.println("serialize java object to json : " + jsonStr);Person A = parse(jsonStr, Person.class, false);System.out.println("after deserialize to object :" + JSON.toJSONString(A));Person B = parse(jsonStr, Person.class, true);System.out.println("after deserialize to object :" + JSON.toJSONString(B));}private static <T> T parse(String json, Class<T> tClass, boolean failOnUnknownProperties) {ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, failOnUnknownProperties);T result = null;try {result = objectMapper.readValue(json, tClass);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.error("Failed to deserialize JSON content, json value : " + json);}return result;}
}可以看到输出结果,配置设为true时在反序列化未知属性直接抛出异常信息,

JsonReadFeature.ALLOW_UNESCAPED_CONTROL_CHARS
是否允许JSON字符串包含非引号控制字符(值小于32的ASCII字符,包含制表符和换行符)。 由于JSON规范要求对所有控制字符使用引号,这是一个非标准的特性,因此默认禁用。
更多配置参考文末链接6。
参考链接:
1、JSON在线 | JSON解析格式化—SO JSON在线工具
2、JsonProperty (Jackson JSON Processor)
3、Java类com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty的实例源码 - 编程字典
4、Java类com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAlias的实例源码 - 编程字典
5、Jackson data binding - 知乎
6、4. JSON字符串是如何被解析的?JsonParser了解一下(中)-阿里云开发者社区
7、注解的使用_四问四不知的博客-CSDN博客