文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Canny的实现步骤
- 二、具体实现
- 1.高斯平滑滤波
- 2.计算梯度大小和方向
- 3.非极大抑制
- 4.双阈值(Double Thresholding)和滞后边界跟踪
- 总结
前言
Canny边缘检测是一种非常流行的边缘检测算法,是John Canny在1986年提出的。它是一个多阶段的算法,即由多个步骤构成。本文主要讲解了Canny算子的原理及实现过程。一、Canny的实现步骤
通常情况下边缘检测的目的是在保留原有图像属性的情况下,显著减少图像的数据规模。有多种算法可以进行边缘检测,虽然Canny算法年代久远,但可以说它是边缘检测的一种标准算法,而且仍在研究中广泛使用。
- 应用高斯滤波来平滑图像,目的是去除噪声
- 找寻图像的强度梯度(intensity gradients)
- 应用非最大抑制(non-maximum suppression)技术来消除边误检(本来不是但检测出来是)
- 应用双阈值的方法来决定可能的(潜在的)边界
- 利用滞后技术来跟踪边界
二、具体实现
1.高斯平滑滤波
滤波是为了去除噪声,选用高斯滤波也是因为在众多噪声滤波器中,高斯表现最好(表现怎么定义的?最好好到什么程度?),你也可以试试其他滤波器如均值滤波、中值滤波等等。一个大小为(2k+1)x(2k+1)的高斯滤波器核(核一般都是奇数尺寸的)的生成方程式由下式给出:
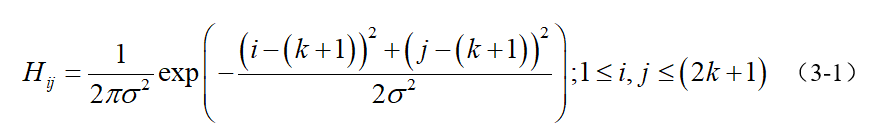
下面是手动创建一个高斯滤波核的函数:
def gaussian_kernel(size, sigma):""" Implementation of Gaussian Kernel.This function follows the gaussian kernel formula,and creates a kernel matrix.Hints:- Use np.pi and np.exp to compute pi and exp.Args:size: int of the size of output matrix.sigma: float of sigma to calculate kernel.Returns:kernel: numpy array of shape (size, size)."""kernel = np.zeros((size, size))### YOUR CODE HEREfor x in range(size):for y in range(size):kernel[x, y] = 1 / (2*np.pi*sigma*sigma) * np.exp(-(x*x+y*y)/(2*sigma*sigma))### END YOUR CODEreturn kernel
这是定义卷积计算过程的函数:
def conv(image, kernel):""" An implementation of convolution filter.This function uses element-wise multiplication and np.sum()to efficiently compute weighted sum of neighborhood at eachpixel.Args:image: numpy array of shape (Hi, Wi).kernel: numpy array of shape (Hk, Wk).Returns:out: numpy array of shape (Hi, Wi)."""Hi, Wi = image.shapeHk, Wk = kernel.shapeout = np.zeros((Hi, Wi))# For this assignment, we will use edge values to pad the images.# Zero padding will make derivatives at the image boundary very big,# whereas we want to ignore the edges at the boundary.pad_width0 = Hk // 2pad_width1 = Wk // 2pad_width = ((pad_width0,pad_width0),(pad_width1,pad_width1))padded = np.pad(image, pad_width, mode='edge')### YOUR CODE HEREx = Hk // 2y = Wk // 2# 横向遍历卷积后的图像for i in range(pad_width0, Hi-pad_width0): # 纵向遍历卷积后的图像for j in range(pad_width1, Wi-pad_width1): split_img = image[i-pad_width0:i+pad_width0+1, j-pad_width1:j+pad_width1+1]# 对应元素相乘out[i, j] = np.sum(np.multiply(split_img, kernel))# out = (out-out.min()) * (1/(out.max()-out.min()) * 255).astype('uint8')### END YOUR CODEreturn out
接下来就是用自己写的高斯滤波卷积核去卷原来的图片:
# Test with different kernel_size and sigma
kernel_size = 5
sigma = 1.4# Load image
img = io.imread('iguana.png', as_gray=True)# Define 5x5 Gaussian kernel with std = sigma
kernel = gaussian_kernel(kernel_size, sigma)# Convolve image with kernel to achieve smoothed effect
smoothed = conv(img, kernel)plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title('Original image')
plt.axis('off')plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.imshow(smoothed)
plt.title('Smoothed image')
plt.axis('off')plt.show()
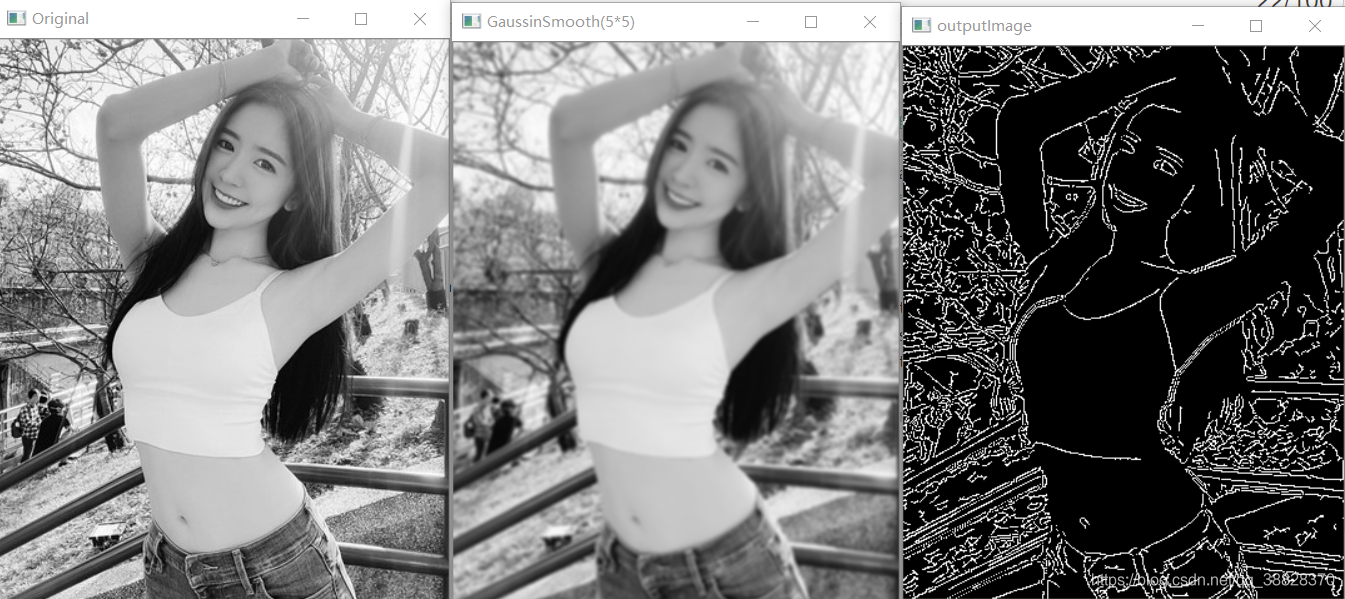
结果是下面两张图片,可以看到图像的边缘被明显地模糊了,图像的抗噪能力变强了。

总结一下这一步:高斯滤波其实就是将所指像素用周围的像素的某种均值代替(即卷积核),卷积核尺寸越大,去噪能力越强,因此噪声越少,但图片越模糊,canny检测算法抗噪声能力越强,但模糊的副作用也会导致定位精度不高。
高斯的卷积核大小推荐:一般情况下,尺寸5 * 5,3 * 3也行。
2.计算梯度大小和方向
对于一张图片来说,梯度能很好地反映其像素的变化情况,而梯度变化越大,说明相邻像素之间存在着较大差异,放大到整张图片来说,就是在某一块区域存在边缘,从视觉上来说就是用黑到白(灰度图片读入)。
梯度的计算分为大小和方向,首先需要求出各个方向上的梯度,然后求平方根和切线。
以下是x、y方向上梯度的计算方式:
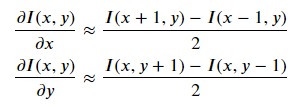
代码实现:
def partial_x(img):""" Computes partial x-derivative of input img.Hints:- You may use the conv function in defined in this file.Args:img: numpy array of shape (H, W).Returns:out: x-derivative image."""out = None### YOUR CODE HERE# 对x求偏导kernel = np.array(([-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1]))# np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 3))out = conv(img, kernel) / 2### END YOUR CODEreturn outdef partial_y(img):""" Computes partial y-derivative of input img.Hints:- You may use the conv function in defined in this file.Args:img: numpy array of shape (H, W).Returns:out: y-derivative image."""out = None### YOUR CODE HERE# 对y求偏导kernel = np.array(([1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]))# np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 3))out = conv(img, kernel) / 2### END YOUR CODEreturn outdef gradient(img):""" Returns gradient magnitude and direction of input img.Args:img: Grayscale image. Numpy array of shape (H, W).Returns:G: Magnitude of gradient at each pixel in img.Numpy array of shape (H, W).theta: Direction(in degrees, 0 <= theta < 360) of gradientat each pixel in img. Numpy array of shape (H, W).Hints:- Use np.sqrt and np.arctan2 to calculate square root and arctan"""G = np.zeros(img.shape)theta = np.zeros(img.shape)### YOUR CODE HEREGx = partial_x(img)Gy = partial_y(img)# 求梯度的大小(平方和的根号)G = np.sqrt(np.power(Gx, 2) + np.power(Gy, 2))theta = np.arctan2(Gy, Gx) * 180 / np.pi # 转换成角度制### END YOUR CODEreturn G, theta
可以拿一张图片来测试一下:
# Compute partial derivatives of smoothed image
Gx = partial_x(smoothed)
Gy = partial_y(smoothed)plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.imshow(Gx)
plt.title('Derivative in x direction')
plt.axis('off')plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.imshow(Gy)
plt.title('Derivative in y direction')
plt.axis('off')plt.show()
可以看到,[-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1]对应了x方向上的边缘检测(在碰到x方向垂直的边界的时候计算出来的数值更大,所以像素更亮),[1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]同理对应了y方向上的边缘检测。
另外有45°和135°的边缘检测,我这里没有着手去实现,如果有兴趣可以去尝试一下,就是会出现不同方向上的边缘。
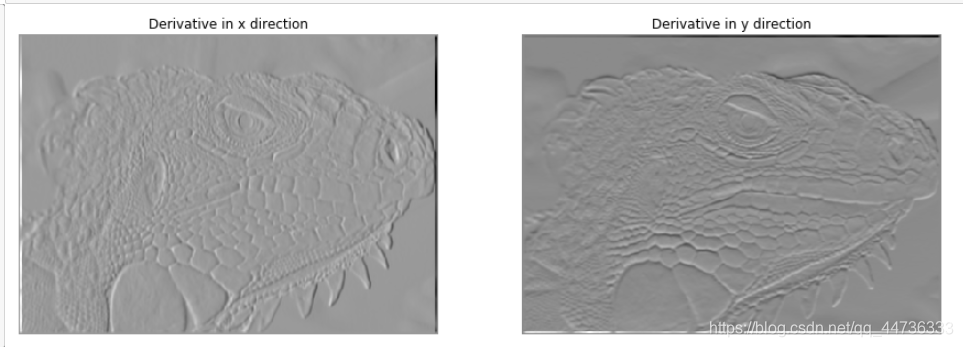
3.非极大抑制
用sobel算子或者是其他简单的边缘检测方法,计算出来的边缘太粗了,就是说原本的一条边用几条几乎重叠的边所代替了,导致视觉上看起来边界很粗。非极大抑制是一种瘦边经典算法。它抑制那些梯度不够大的像素点,只保留最大的梯度,从而达到瘦边的目的。
a) 将其梯度方向近似为以下值中的一个[0,45,90,135,180,225,270,315](即上下左右和45度方向)这一步是为了方便使用梯度;
b) 比较该像素点,和其梯度方向正负方向的像素点的梯度强度,这里比较的范围一般为像素点的八邻域;
c) 如果该像素点梯度强度最大则保留,否则抑制(删除,即置为0);
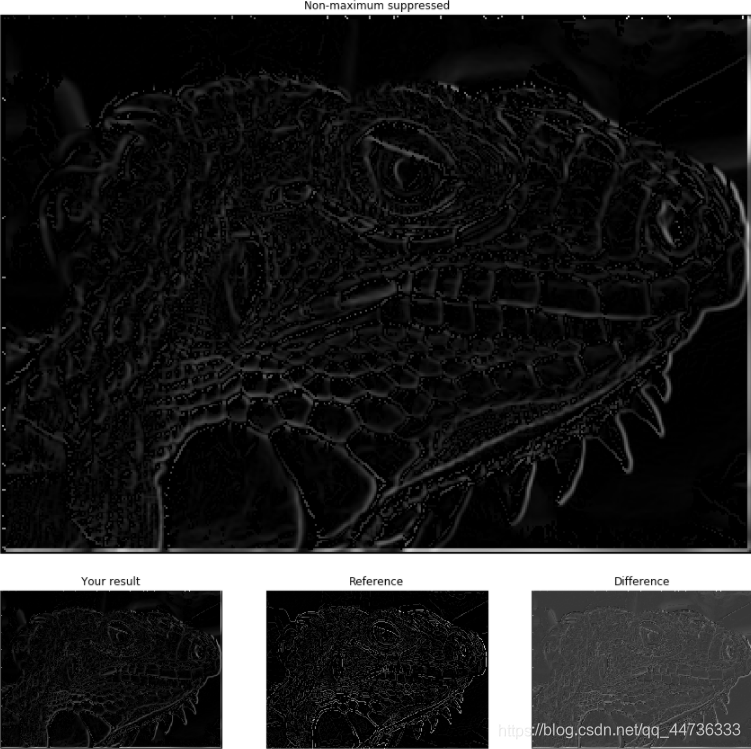
可以看到经过非极大抑制后,图像的边缘明显变细了,边界显得更加清晰了。
代码附上:
def non_maximum_suppression(G, theta):""" Performs non-maximum suppression.This function performs non-maximum suppression along the directionof gradient (theta) on the gradient magnitude image (G).Args:G: gradient magnitude image with shape of (H, W).theta: direction of gradients with shape of (H, W).Returns:out: non-maxima suppressed image."""H, W = G.shapeout = np.zeros((H, W))# 将角度近似到45°的对角线, 正负无所谓, 只看对角线跟水平垂直# Round the gradient direction to the nearest 45 degreestheta = np.floor((theta + 22.5) / 45) * 45### BEGIN YOUR CODEanchor = np.stack(np.where(G!=0)).T # 获取非零梯度的位置 for x, y in anchor:center_point = G[x, y]current_theta = theta[x, y]dTmp1 = 0dTmp2 = 0W = 0if current_theta >= 0 and current_theta < 45:g1, g2, g3, g4 = G[x + 1, y - 1], G[x + 1, y], G[x - 1, y + 1], G[x - 1, y]W = abs(np.tan(current_theta*np.pi/180)) # tan0-45范围为0-1dTmp1 = W * g1 + (1-W) * g2dTmp2 = W * g3 + (1-W) * g4elif current_theta >= 45 and current_theta < 90:g1, g2, g3, g4 = G[x+1, y-1], G[x, y-1], G[x-1, y+1], G[x, y+1]W = abs(np.tan((current_theta-90)*np.pi/180))dTmp1 = W * g1 + (1-W) * g2dTmp2 = W * g3 + (1-W) * g4elif current_theta >= -90 and current_theta < -45:g1, g2, g3, g4 = G[x-1, y-1], G[x, y-1], G[x+1, y+1], G[x, y+1]W = abs(np.tan((current_theta-90)*np.pi/180))dTmp1 = W * g1 + (1-W) * g2dTmp2 = W * g3 + (1-W) * g4elif current_theta>=-45 and current_theta<0:g1, g2, g3, g4 = G[x+1, y+1], G[x+1, y], G[x-1, y-1], G[x-1, y]W = abs(np.tan(current_theta * np.pi / 180))dTmp1 = W * g1 + (1-W) * g2dTmp2 = W * g3 + (1-W) * g4if dTmp1 < center_point and dTmp2 < center_point: out[x,y]=center_pointreturn out
4.双阈值(Double Thresholding)和滞后边界跟踪
经过非极大抑制后图像中仍然有很多噪声点。Canny算法中应用了一种叫双阈值的技术。
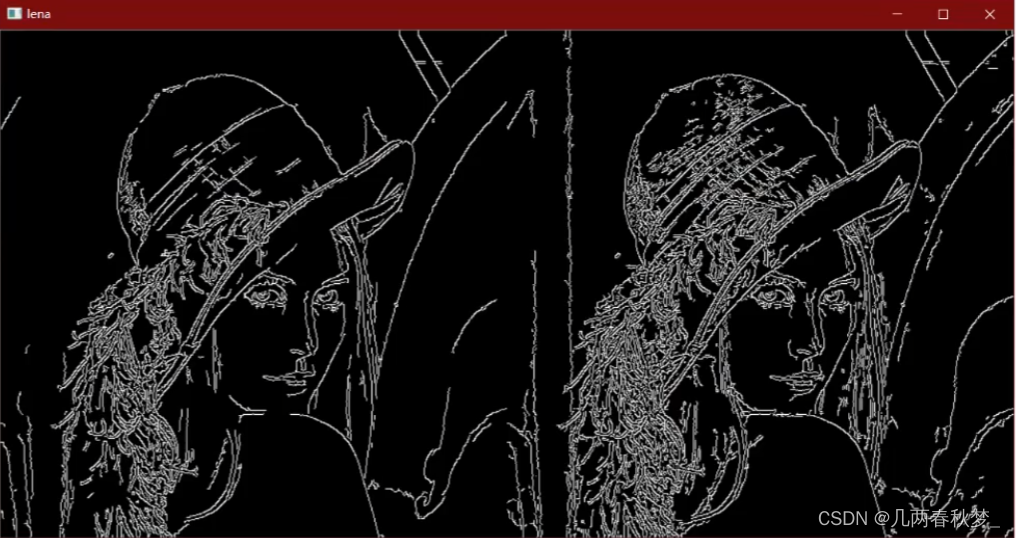
即设定一个阈值上界和阈值下界(opencv中通常由人为指定的),图像中的像素点如果大于阈值上界则认为必然是边界(称为强边界,strong edge),小于阈值下界则认为必然不是边界,两者之间的则认为是候选项(称为弱边界,weak edge),需进行进一步处理。我查阅资料,了解到上界一般是下界的2-3倍,实现出来的效果比较好。

上图中,左边的是经过上界筛选的强边界,即肯定是边界;右边的是结果是强边界加上0.5权重的弱边界所呈现的效果(展示弱边界没有啥意义)。可以看到相较于之前的非极大抑制,双阈值的算法很大程度上提取到了真正的边界(但是对于不同的图片有不同的阈值参数)。
代码附上:
def double_thresholding(img, high, low):"""Args:img: numpy array of shape (H, W) representing NMS edge response.high: high threshold(float) for strong edges.low: low threshold(float) for weak edges.Returns:strong_edges: Boolean array representing strong edges.Strong edeges are the pixels with the values greater thanthe higher threshold.weak_edges: Boolean array representing weak edges.Weak edges are the pixels with the values smaller or equal to thehigher threshold and greater than the lower threshold."""strong_edges = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype=np.bool)weak_edges = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype=np.bool)### YOUR CODE HEREH, W = img.shapefor i in range(0, H):for j in range(0, W):if img[i, j] > high:strong_edges[i, j] = Trueelif img[i, j] >= low:weak_edges[i, j] = True### END YOUR CODEreturn strong_edges, weak_edges
可以肯定的是,强边缘必然是边缘点,因此必须将T1设置的足够高,以要求像素点的梯度值足够大(变化足够剧烈),而弱边缘可能是边缘,也可能是噪声,如何判断呢?当弱边缘的周围8邻域有强边缘点存在时,就将该弱边缘点变成强边缘点,以此来实现对强边缘的补充。
滞后边界跟踪(对弱边缘的二次判断),代码如下:
def get_neighbors(y, x, H, W):""" Return indices of valid neighbors of (y, x).Return indices of all the valid neighbors of (y, x) in an array ofshape (H, W). An index (i, j) of a valid neighbor should satisfythe following:1. i >= 0 and i < H2. j >= 0 and j < W3. (i, j) != (y, x)Args:y, x: location of the pixel.H, W: size of the image.Returns:neighbors: list of indices of neighboring pixels [(i, j)]."""neighbors = []for i in (y-1, y, y+1):for j in (x-1, x, x+1):if i >= 0 and i < H and j >= 0 and j < W:if (i == y and j == x):continueneighbors.append((i, j))return neighborsdef link_edges(strong_edges, weak_edges):""" Find weak edges connected to strong edges and link them.Iterate over each pixel in strong_edges and perform breadth firstsearch across the connected pixels in weak_edges to link them.Here we consider a pixel (a, b) is connected to a pixel (c, d)if (a, b) is one of the eight neighboring pixels of (c, d).Args:strong_edges: binary image of shape (H, W).weak_edges: binary image of shape (H, W).Returns:edges: numpy boolean array of shape(H, W)."""H, W = strong_edges.shape# 获取强边界的非零元素坐标,一行为一组坐标indices = np.stack(np.nonzero(strong_edges)).Tprint(indices)edges = np.zeros((H, W), dtype=np.bool)# Make new instances of arguments to leave the original# references intactweak_edges = np.copy(weak_edges)edges = np.copy(strong_edges)### YOUR CODE HEREfor (x, y) in indices:neighbors = get_neighbors(x, y, H, W)edges[x, y] = Truefor neighbor in neighbors:if weak_edges[neighbor]:edges[neighbor] = True### END YOUR CODEreturn edges
可以拿一个简单的例子来测试一下算法的正确性:
'''
我们假设两类边缘:经过非极大值抑制之后的边缘点中,梯度值超过T1的称为强边缘,梯度值小于T1大于T2的称为弱边缘,梯度小于T2的不是边缘。
可以肯定的是,强边缘必然是边缘点,因此必须将T1设置的足够高,以要求像素点的梯度值足够大(变化足够剧烈),而弱边缘可能是边缘,也可能是噪声,如何判断呢?
当弱边缘的周围8邻域有强边缘点存在时,就将该弱边缘点变成强边缘点,以此来实现对强边缘的补充。
实际中人们发现T1:T2=2:1的比例效果比较好,其中T1可以人为指定,也可以设计算法来自适应的指定,比如定义梯度直方图的前30%的分界线为T1,我实现的是人为指定阈值。
检查8邻域的方法叫边缘滞后跟踪,连接边缘的办法还有区域生长法等等。
'''
from edge import get_neighbors, link_edgestest_strong = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]],dtype=np.bool
)test_weak = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1],[0, 1, 0, 0],[1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0]],dtype=np.bool
)test_linked = link_edges(test_strong, test_weak)plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(test_strong)
plt.title('Strong edges')plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(test_weak)
plt.title('Weak edges')plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(test_linked)
plt.title('Linked edges')
plt.show()
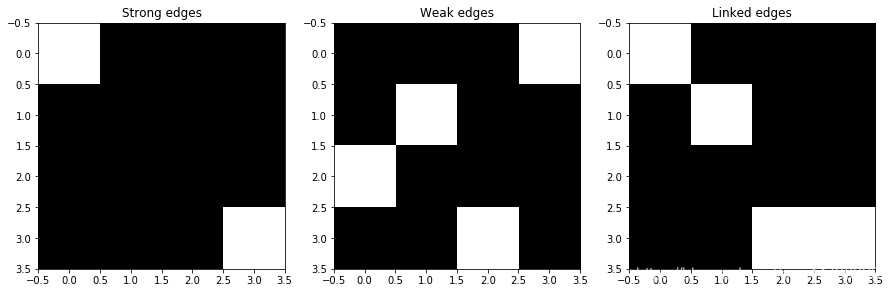
在上图中,白色方块代表存在边缘(包括强弱边缘),遍历弱边缘中的每个像素,如果像素的八邻域存在强边缘对应的像素,则将这个弱边缘像素归为真正的边缘(从视觉上来理解,就是存在一条不确定的边缘,如果这条不确定的边缘旁存在真正的边缘,则将这条边归为真边,非则就将其删除)
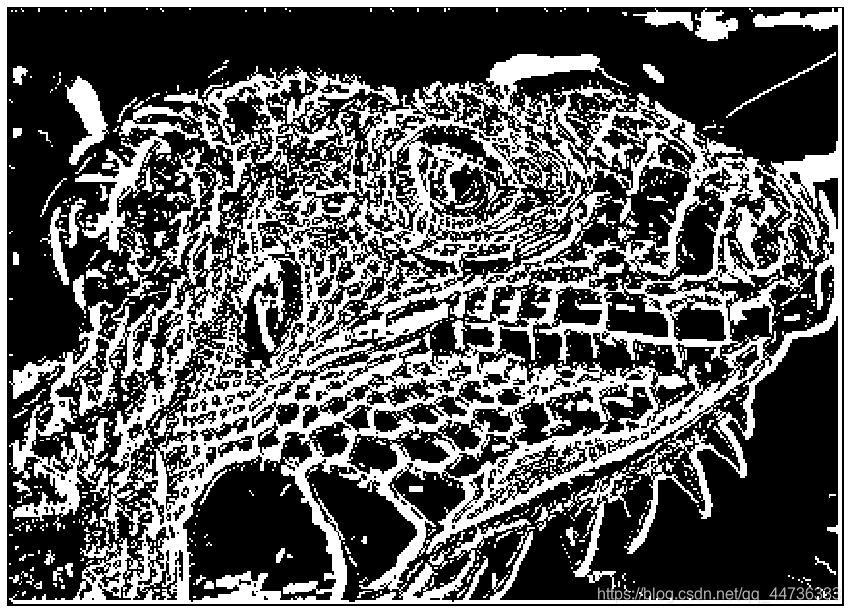


可以看到相较于只保留弱边缘的效果图,滞后边界跟踪算法保留了更多的边缘细节。
整理一下整个算法,我们将Canny算子归纳到一个函数,调用一下看一下效果:
def canny(img, kernel_size=5, sigma=1.4, high=20, low=15):""" Implement canny edge detector by calling functions above.Args:img: binary image of shape (H, W).kernel_size: int of size for kernel matrix.sigma: float for calculating kernel.high: high threshold for strong edges.low: low threashold for weak edges.Returns:edge: numpy array of shape(H, W)."""### YOUR CODE HERE# 高斯模糊kernel = gaussian_kernel(kernel_size, sigma)img = conv(img, kernel)#io.imshow(color.gray2rgb(img))# 计算梯度Prewitt算子G, theta = gradient(img)#io.imshow(color.gray2rgb(G))# 非极大值抑制G = non_maximum_suppression(G, theta)#io.imshow(color.gray2rgb(G))# 双阈值抑制strong_edges, weak_edges = double_thresholding(G, high, low)# 连通边edge = link_edges(strong_edges, weak_edges)### END YOUR CODEreturn edge
from edge import canny# Load image
img = io.imread('iguana.png', as_gray=True)# Run Canny edge detector
edges = canny(img, kernel_size=5, sigma=1.4, high=0.03, low=0.02)
print (edges.shape)plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(edges)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Your result')plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
reference = np.load('references/iguana_canny.npy')
plt.imshow(reference)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Reference')plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(edges ^ reference)
plt.title('Difference')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

总结
这次写整个Canny算法其实遇到了很多坑,比如角度弧度换算那里,课件上写得很模糊,后来查阅资料才理清楚的。其次就是弱边界判断那里,我一开始对应每一个像素都要遍历整张图片的梯度方向,然后时间复杂度太大了,其实只要遍历八邻域就可以了。最后就是写代码一定要一定要细心,虽然python相较于c有很多东西都已经帮你写好了,但是还是要注意类似list下标之类的问题。
差不多就这样啦~