1、Spring AOP
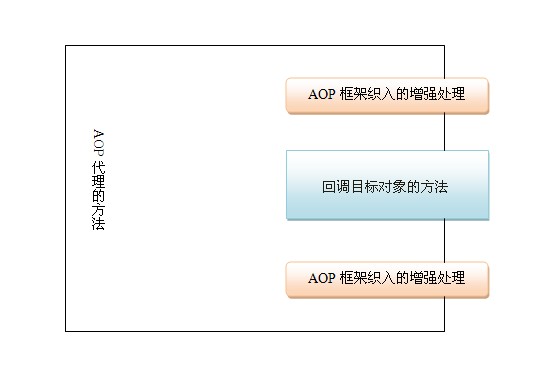
Spring AOP的面向切面编程,是面向对象编程的一种补充,用于处理系统中分布的各个模块的横切关注点,比如说事务管理、日志、缓存等。它是使用动态代理实现的,在内存中临时为方法生成一个AOP对象,这个对象包含目标对象的所有方法,在特定的切点做了增强处理,并回调原来的方法。
Spring AOP的动态代理主要有两种方式实现,JDK动态代理和cglib动态代理。JDK动态代理通过反射来接收被代理的类,但是被代理的类必须实现接口,核心是InvocationHandler和Proxy类。cglib动态代理的类一般是没有实现接口的类,cglib是一个代码生成的类库,可以在运行时动态生成某个类的子类,所以,CGLIB是通过继承的方式做的动态代理,因此如果某个类被标记为final,那么它是无法使用CGLIB做动态代理的。
Spring AOP使用哪种方式实现代理的逻辑在org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory中实现的。
package org.springframework.aop.framework;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy;@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}//判断如果是接口,或者是被代理的类,则使用JDK动态代理if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}//否则用cglib动态代理,(没有实现接口的类)return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {//默认使用jdk动态代理return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}/*** 确定提供的{@link AdvisedSupport}是否仅有* 指定了{@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy}接口*(或者根本没有指定的代理接口)。*/private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));}}
2、Spring AOP类结构图
最核心的处理是InvocationHandler接口中的invoke()方法
3、JdkDynamicAopProxy动态代理
JdkDynamicAopProxy源码:
package org.springframework.aop.framework;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.List;import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;import org.springframework.aop.AopInvocationException;
import org.springframework.aop.RawTargetAccess;
import org.springframework.aop.TargetSource;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 5531744639992436476L;/**注意:我们可以避免这个类和CGLIB之间的代码重复*代理通过重构“调用”到模板方法中。 但是,这种方法*与复制粘贴解决方案相比,至少增加了10%的性能开销,所以我们牺牲了*优雅的表现。 (我们有一个很好的测试套件来确保不同的*代理行为相同:-)*这样,我们也可以更轻松地利用每个班级中的次要优化。*// **我们使用静态日志来避免序列化问题* /private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(JdkDynamicAopProxy.class);/** Config used to configure this proxy */private final AdvisedSupport advised; //代理接口上是否定义了{@link #hashCode}方法?private boolean equalsDefined;
* @param将AOP配置配置为AdvisedSupport对象
*如果配置无效,则引发AopConfigException。 我们试图提供信息
*在这种情况下是例外情况,而不是在稍后发生神秘故障。 */public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");}this.advised = config;}@Overridepublic Object getProxy() {return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());}@Overridepublic Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised);findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);}private void findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces) {for (Class<?> proxiedInterface : proxiedInterfaces) {Method[] methods = proxiedInterface.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method method : methods) {if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {this.equalsDefined = true;}if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {this.hashCodeDefined = true;}if (this.equalsDefined && this.hashCodeDefined) {return;}}}}/** * Implementation of {@code InvocationHandler.invoke}. * <p>Callers will see exactly the exception thrown by the target, * unless a hook method throws an exception. */@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {MethodInvocation invocation;Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Class<?> targetClass = null;Object target = null;try {if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.return equals(args[0]);}if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.return hashCode();}if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);}Object retVal;if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,// in case it comes from a pool.target = targetSource.getTarget();if (target != null) {targetClass = target.getClass();}// Get the interception chain for this method.List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.if (chain.isEmpty()) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);}else {// We need to create a method invocation...invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.retVal = invocation.proceed();}// Massage return value if necessary.Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets// a reference to itself in another returned object.retVal = proxy;}else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {throw new AopInvocationException("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);}return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {// Must have come from TargetSource.targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object other) {if (other == this) {return true;}if (other == null) {return false;}JdkDynamicAopProxy otherProxy;if (other instanceof JdkDynamicAopProxy) {otherProxy = (JdkDynamicAopProxy) other;}else if (Proxy.isProxyClass(other.getClass())) {InvocationHandler ih = Proxy.getInvocationHandler(other);if (!(ih instanceof JdkDynamicAopProxy)) {return false;}otherProxy = (JdkDynamicAopProxy) ih;}else {// Not a valid comparison...return false;}// 如果我们到达这里,otherProxy是另一个AopProxy。return AopProxyUtils.equalsInProxy(this.advised, otherProxy.advised);}/** * 代理使用TargetSource的哈希码。. */@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return JdkDynamicAopProxy.class.hashCode() * 13 + this.advised.getTargetSource().hashCode();}}从源码可以看到,JdkDynamicAopProxy同时实现了AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable三个接口,其中InvocationHandler是动态代理的核心接口。所有的动态代理都是通过InvocationHandler.invoke()方法实现的。
4、cgLibAopProxy动态代理
CglibAopProxy使用getProxy()方法来实现代理,getProxy中使生成的代理对象的方法都委托到了getCallbacks()方法,然后是调用createProxyClassAndInstance()方法来执行代理。createProxyClassAndInstance()又在ObjenesisCglibAopProxy类中重写。具体看下源码:
CglibAopProxy源码,只保留了几个核心的方法:
package org.springframework.aop.framework;@SuppressWarnings("serial")
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {// Constants for CGLIB callback array indicesprivate static final int AOP_PROXY = 0;private static final int INVOKE_TARGET = 1;private static final int NO_OVERRIDE = 2;private static final int DISPATCH_TARGET = 3;private static final int DISPATCH_ADVISED = 4;private static final int INVOKE_EQUALS = 5;private static final int INVOKE_HASHCODE = 6;/** Logger available to subclasses; static to optimize serialization */protected static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(CglibAopProxy.class);/** Keeps track of the Classes that we have validated for final methods */private static final Map<Class<?>, Boolean> validatedClasses = new WeakHashMap<Class<?>, Boolean>();/** The configuration used to configure this proxy */protected final AdvisedSupport advised;protected Object[] constructorArgs;protected Class<?>[] constructorArgTypes;/** Dispatcher used for methods on Advised */private final transient AdvisedDispatcher advisedDispatcher;private transient Map<String, Integer> fixedInterceptorMap;private transient int fixedInterceptorOffset;/*** Create a new CglibAopProxy for the given AOP configuration.* @param config the AOP configuration as AdvisedSupport object* @throws AopConfigException if the config is invalid. We try to throw an informative* exception in this case, rather than let a mysterious failure happen later.*/public CglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");}this.advised = config;this.advisedDispatcher = new AdvisedDispatcher(this.advised);}/*** Set constructor arguments to use for creating the proxy.* @param constructorArgs the constructor argument values* @param constructorArgTypes the constructor argument types*/public void setConstructorArguments(Object[] constructorArgs, Class<?>[] constructorArgTypes) {if (constructorArgs == null || constructorArgTypes == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Both 'constructorArgs' and 'constructorArgTypes' need to be specified");}if (constructorArgs.length != constructorArgTypes.length) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of 'constructorArgs' (" + constructorArgs.length +") must match number of 'constructorArgTypes' (" + constructorArgTypes.length + ")");}this.constructorArgs = constructorArgs;this.constructorArgTypes = constructorArgTypes;}@Overridepublic Object getProxy() {return getProxy(null);}@Overridepublic Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Creating CGLIB proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}try {Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call aboveenhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);}catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (Exception ex) {// TargetSource.getTarget() failedthrow new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);}}protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false);enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);return (this.constructorArgs != null ?enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs) :enhancer.create());}private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {// Parameters used for optimisation choices...boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.Callback targetInterceptor;if (exposeProxy) {targetInterceptor = isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());}else {targetInterceptor = isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());}// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).Callback targetDispatcher = isStatic ?new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp();Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {aopInterceptor, // for normal advicetargetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimizednew SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to thistargetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)};Callback[] callbacks;// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,// then we can make some optimisations by sending the AOP calls// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.if (isStatic && isFrozen) {Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(methods.length);// TODO: small memory optimisation here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(methods[x], rootClass);fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(methods[x].toString(), x);}// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;}else {callbacks = mainCallbacks;}return callbacks;}
}
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy的源码,其中重写了createProxyClassAndInstance()方法,该方法中使用了SpringObjenesis来生成代理实例对象。
package org.springframework.aop.framework;import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import org.springframework.objenesis.SpringObjenesis;@SuppressWarnings("serial")
class ObjenesisCglibAopProxy extends CglibAopProxy {private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ObjenesisCglibAopProxy.class);private static final SpringObjenesis objenesis = new SpringObjenesis();/*** Create a new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy for the given AOP configuration.* @param config the AOP configuration as AdvisedSupport object*/public ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) {super(config);}@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {Class<?> proxyClass = enhancer.createClass();Object proxyInstance = null;if (objenesis.isWorthTrying()) {try {proxyInstance = objenesis.newInstance(proxyClass, enhancer.getUseCache());}catch (Throwable ex) {logger.debug("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, " +"falling back to regular proxy construction", ex);}}if (proxyInstance == null) {// Regular instantiation via default constructor...try {proxyInstance = (this.constructorArgs != null ?proxyClass.getConstructor(this.constructorArgTypes).newInstance(this.constructorArgs) :proxyClass.newInstance());}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, " +"and regular proxy instantiation via default constructor fails as well", ex);}}((Factory) proxyInstance).setCallbacks(callbacks);return proxyInstance;}}