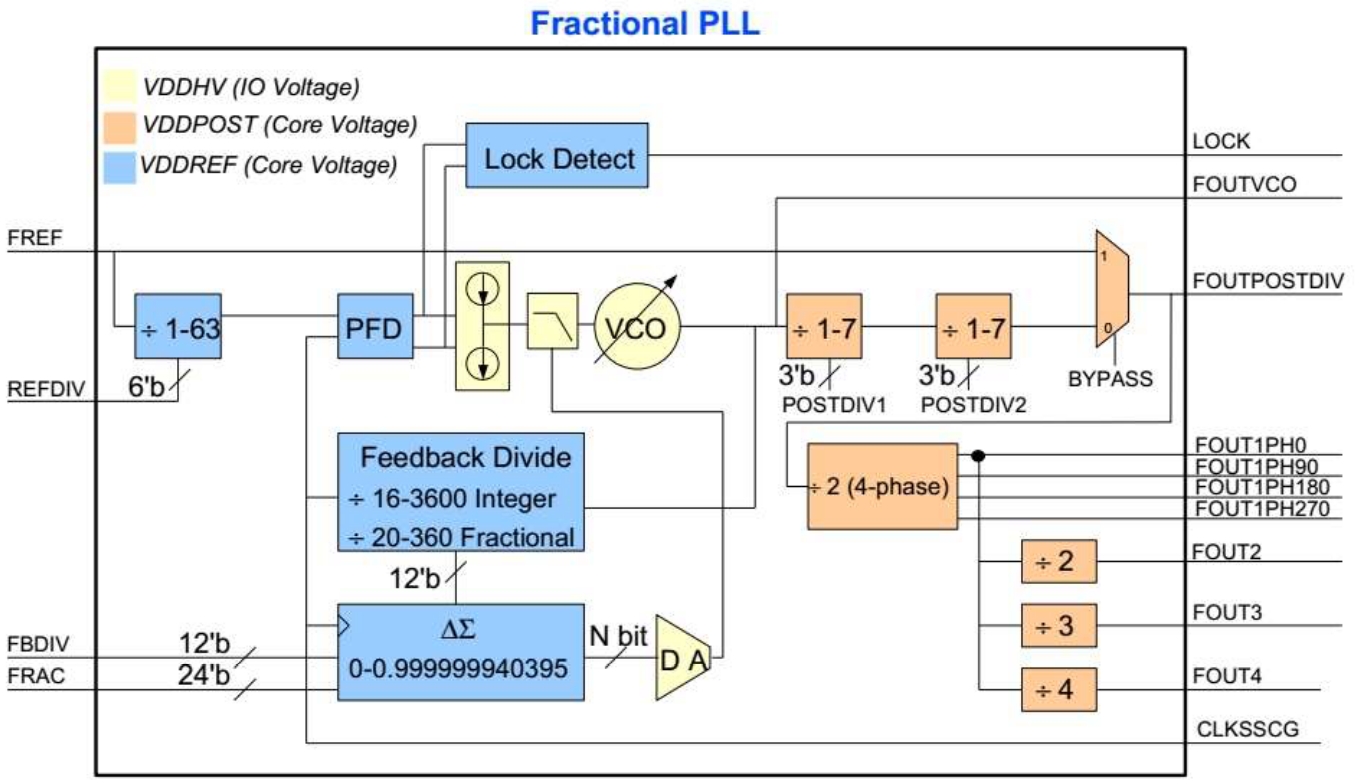
VGG16-keras 优化
- 优化结果对比
- VGG16网络结构
- VGG16网络结构优化
- 自定义loss
- 训练
- 预测
优化结果对比
原始VGG16

普通调优

使用预训练权重

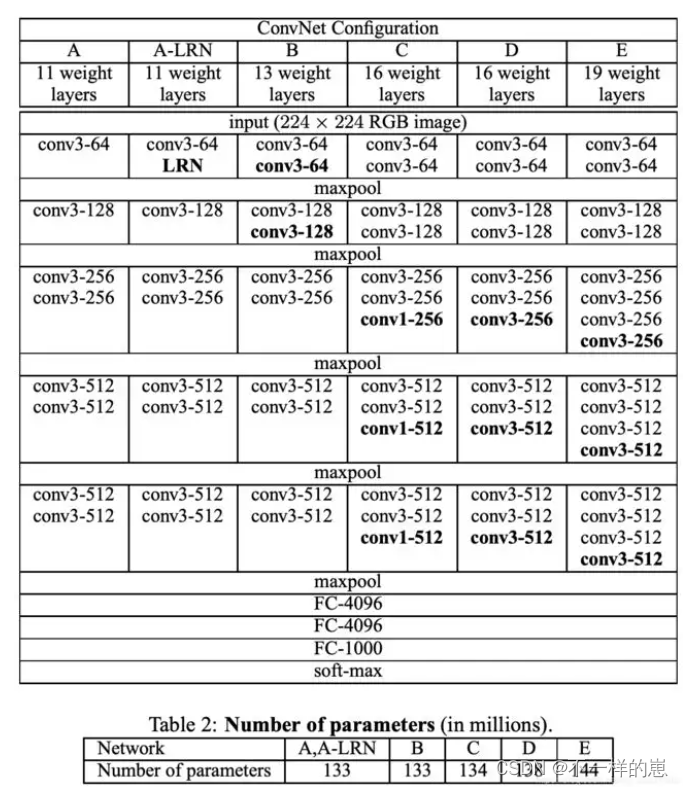
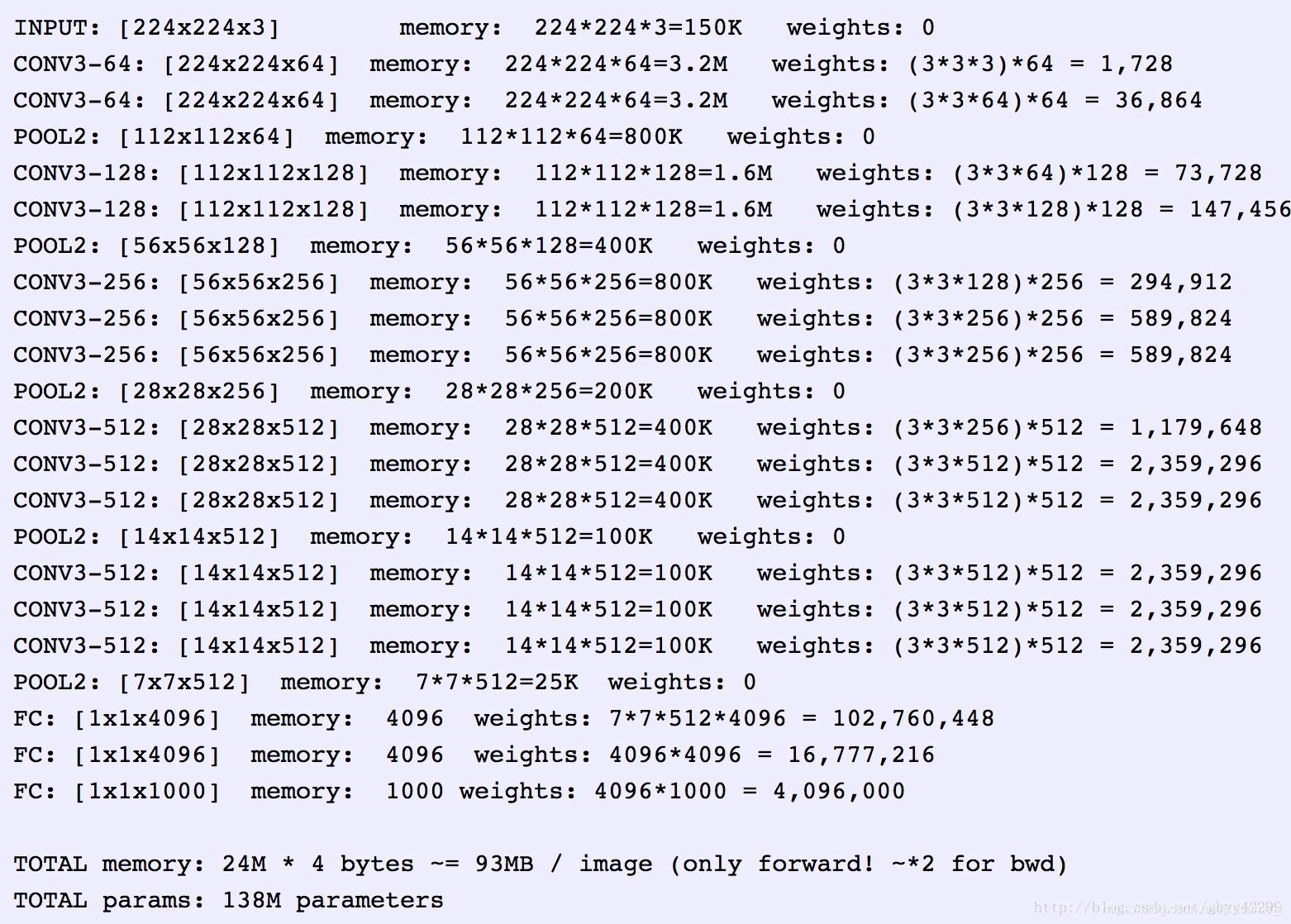
VGG16网络结构

VGG16网络结构优化
1.增加正则化
2.使用BN/GN层(中间层数据的标准化)
3.使用dropout
Net.py
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.utils import get_file
from keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, MaxPool2D , Flatten,BatchNormalization,Dropout
import numpy as np# 原始VGG16
def VGG16(num_classes = 2,input_shape = (224, 224, 3)):# 使用序贯式模型model = Sequential()# 两个3*3*64卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(input_shape=input_shape,filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3),padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3),padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 两个3*3*128卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*56卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,即把多维的输入一维化,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。Flatten不影响batch的大小。# 连接三个全连接层Dense,最后一层用于预测分类。model.add(Flatten())model.add(Dense(units=4096,activation="relu"))model.add(Dense(units=4096,activation="relu"))model.add(Dense(units=num_classes, activation="softmax"))# 打印模型结构model.summary()return model#优化VGG16
def OVGG16(num_classes = 2,input_shape = (224, 224, 3)):weight_decay = 0.0005# 使用序贯式模型model = Sequential()# 两个3*3*64卷积核 + 一个最大池化层# 优化 增加L2正则化model.add(Conv2D(input_shape=input_shape,filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3), padding='same', kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.3))model.add(Conv2D(filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3),padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 两个3*3*128卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*56卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay), activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.4))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu"))# 优化 添加BN层和Dropoutmodel.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))model.add(Dropout(0.5))# Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,即把多维的输入一维化,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。Flatten不影响batch的大小。# 连接三个全连接层Dense,最后一层用于预测分类。model.add(Flatten())model.add(Dense(units=512, kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu")) # VGG16为4096model.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dense(units=512, kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l2(weight_decay),activation="relu")) # VGG16为4096model.add(BatchNormalization())model.add(Dropout(0.5))model.add(Dense(units=num_classes, activation="softmax")) # VGG16为1000# 打印模型结构model.summary()return model#迁移训练VGG16
def MVGG16(num_classes = 2,input_shape = (224, 224, 3)):#预训练模型WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP = ('https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/''releases/download/v0.1/''vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5')# 使用序贯式模型model = Sequential()# 两个3*3*64卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(input_shape=input_shape,filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3),padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=64,kernel_size=(3,3),padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 两个3*3*128卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*56卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 三个3*3*512卷积核 + 一个最大池化层model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size=(3,3), padding="same", activation="relu"))model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(2,2)))# 加载预训练模型weights_path = get_file('vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5',WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP,cache_subdir='models',file_hash='6d6bbae143d832006294945121d1f1fc')# 加载模型参数model.load_weights(weights_path)# 冻结前13层网络参数 保证加载的预训练参数不被改变for layer in model.layers[:13]:layer.trainable = False# Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,即把多维的输入一维化,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。Flatten不影响batch的大小。# 连接三个全连接层Dense,最后一层用于预测分类。model.add(Flatten())model.add(Dense(units=256,activation="relu")) # VGG16为4096model.add(Dense(units=128,activation="relu")) # VGG16为4096model.add(Dense(units=num_classes, activation="softmax")) # VGG16为1000# 打印模型结构model.summary()return model自定义loss
Loss.py
import keras.backend as K
import tensorflow as tf# focal loss
def binary_focal_loss(gamma=2, alpha=0.25):"""Binary form of focal loss.适用于二分类问题的focal lossfocal_loss(p_t) = -alpha_t * (1 - p_t)**gamma * log(p_t)where p = sigmoid(x), p_t = p or 1 - p depending on if the label is 1 or 0, respectively.References:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdfUsage:model.compile(loss=[binary_focal_loss(alpha=.25, gamma=2)], metrics=["accuracy"], optimizer=adam)"""alpha = tf.constant(alpha, dtype=tf.float32)gamma = tf.constant(gamma, dtype=tf.float32)def binary_focal_loss_fixed(y_true, y_pred):"""y_true shape need be (None,1)y_pred need be compute after sigmoid"""y_true = tf.cast(y_true, tf.float32)alpha_t = y_true*alpha + (K.ones_like(y_true)-y_true)*(1-alpha)p_t = y_true*y_pred + (K.ones_like(y_true)-y_true)*(K.ones_like(y_true)-y_pred) + K.epsilon()focal_loss = - alpha_t * K.pow((K.ones_like(y_true)-p_t),gamma) * K.log(p_t)return K.mean(focal_loss)return binary_focal_loss_fixeddef multi_category_focal_loss2(gamma=2., alpha=.25):"""focal loss for multi category of multi label problem适用于多分类或多标签问题的focal lossalpha控制真值y_true为1/0时的权重1的权重为alpha, 0的权重为1-alpha当你的模型欠拟合,学习存在困难时,可以尝试适用本函数作为loss当模型过于激进(无论何时总是倾向于预测出1),尝试将alpha调小当模型过于惰性(无论何时总是倾向于预测出0,或是某一个固定的常数,说明没有学到有效特征)尝试将alpha调大,鼓励模型进行预测出1。Usage:model.compile(loss=[multi_category_focal_loss2(alpha=0.25, gamma=2)], metrics=["accuracy"], optimizer=adam)"""epsilon = 1.e-7gamma = float(gamma)alpha = tf.constant(alpha, dtype=tf.float32)def multi_category_focal_loss2_fixed(y_true, y_pred):y_true = tf.cast(y_true, tf.float32)y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred, epsilon, 1. - epsilon)alpha_t = y_true*alpha + (tf.ones_like(y_true)-y_true)*(1-alpha)y_t = tf.multiply(y_true, y_pred) + tf.multiply(1-y_true, 1-y_pred)ce = -tf.log(y_t)weight = tf.pow(tf.subtract(1., y_t), gamma)fl = tf.multiply(tf.multiply(weight, ce), alpha_t)loss = tf.reduce_mean(fl)return lossreturn multi_category_focal_loss2_fixed训练
import os
from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint,EarlyStopping
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras import optimizers
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from Net import VGG16,OVGG16,MVGG16
from Loss import binary_focal_loss,multi_category_focal_loss2files_train = 0
files_validation = 0cwd = os.getcwd()
folder = 'train_data/train'
for sub_folder in os.listdir(folder):path, dirs, files = next(os.walk(os.path.join(folder,sub_folder)))files_train += len(files)folder = 'train_data/test'
for sub_folder in os.listdir(folder):path, dirs, files = next(os.walk(os.path.join(folder,sub_folder)))files_validation += len(files)print(files_train,files_validation)img_width, img_height = 48, 48
train_data_dir = "train_data/train"
validation_data_dir = "train_data/test"
nb_train_samples = files_train
nb_validation_samples = files_validation
batch_size = 32
epochs = 1000
num_classes = 2type = 1
# 加载原始VGG16
if type==0:model_name="ori.h5"img_name = "ori_epoch_loss.png"model = VGG16(num_classes=2, input_shape = (img_width, img_height, 3))
# 加载调优VGG16
elif type==1:model_name="opt.h5"img_name = "opt_epoch_loss.png"model = OVGG16(num_classes=2, input_shape = (img_width, img_height, 3))
# 加载迁移学习VGG16
elif type==2:model_name="Mopt.h5"img_name = "Mopt_epoch_loss.png"model = MVGG16(num_classes=2, input_shape = (img_width, img_height, 3))# 定义模型优化器, 使用分类交叉熵损失
# 随机梯度下降 lr是学习率 decay衰变参数 momentum和NAG 都是在更新梯度时顺应 loss function 的梯度来调整速度,并且对 SGD 进行加速。
opt = optimizers.SGD(lr=0.001, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9,nesterov=True)
# focal loss
model.compile(loss = [binary_focal_loss(alpha=.5, gamma=1)], optimizer = opt, metrics=["accuracy"])
# 自带loss
# mean_squared_error
# mean_absolute_error
# mean_absolute_percentage_error
# mean_squared_logarithmic_error
# hinge
# logcosh
# squared_hinge
# categorical_crossentropy
# sparse_categorical_crossentropy
# binary_crossentropy
# kullback_leibler_divergence
# poisson
# cosine_proximity
# model.compile(loss = "categorical_crossentropy", optimizer = opt, metrics=["accuracy"]) train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale = 1./255,
horizontal_flip = True,
fill_mode = "nearest",
zoom_range = 0.1,
width_shift_range = 0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1,
rotation_range=5)test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale = 1./255,
horizontal_flip = True,
fill_mode = "nearest",
zoom_range = 0.1,
width_shift_range = 0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1,
rotation_range=5)train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_data_dir,
target_size = (img_height, img_width),
batch_size = batch_size,
class_mode = "categorical")validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_data_dir,
target_size = (img_height, img_width),
class_mode = "categorical")# 定义模型和精度计算方式
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(model_name, monitor='val_acc', verbose=1, save_best_only=True, save_weights_only=False, mode='auto', period=1)
early = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_acc', min_delta=0, patience=100, verbose=1, mode='auto')# 训练模型并计算精度
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
samples_per_epoch = nb_train_samples,
epochs = epochs,
validation_data = validation_generator,
nb_val_samples = nb_validation_samples,
callbacks = [checkpoint, early])plt.plot(history.history["acc"])
plt.plot(history.history['val_acc'])
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title("model accuracy")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.legend(["Accuracy","Validation Accuracy","loss","Validation Loss"])
plt.savefig(img_name)
plt.show()
预测
import cv2
from keras.models import load_model
from Loss import binary_focal_loss,multi_category_focal_loss2type = 1
# 加载原始VGG16
if type ==0:weights_path="ori.h5"
# 加载调优VGG16
elif type==1:weights_path="opt.h5"
# 加载迁移学习VGG16
elif type==2:weights_path="Mopt.h5"image = cv2.imread(path)
class_dictionary = {}
class_dictionary[0] = 'empty'
class_dictionary[1] = 'occupied'model=load_model(weights_path,custom_objects={'binary_focal_loss_fixed':binary_focal_loss(alpha=.5, gamma=1)})
#预处理
img = image/255.
#转换成4D tensor
image = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
# 用训练好的模型进行训练
class_predicted = model.predict(image)
inID = np.argmax(class_predicted[0])
label = class_dictionary[inID]
if label == 'empty':print(0)
else:print(1)