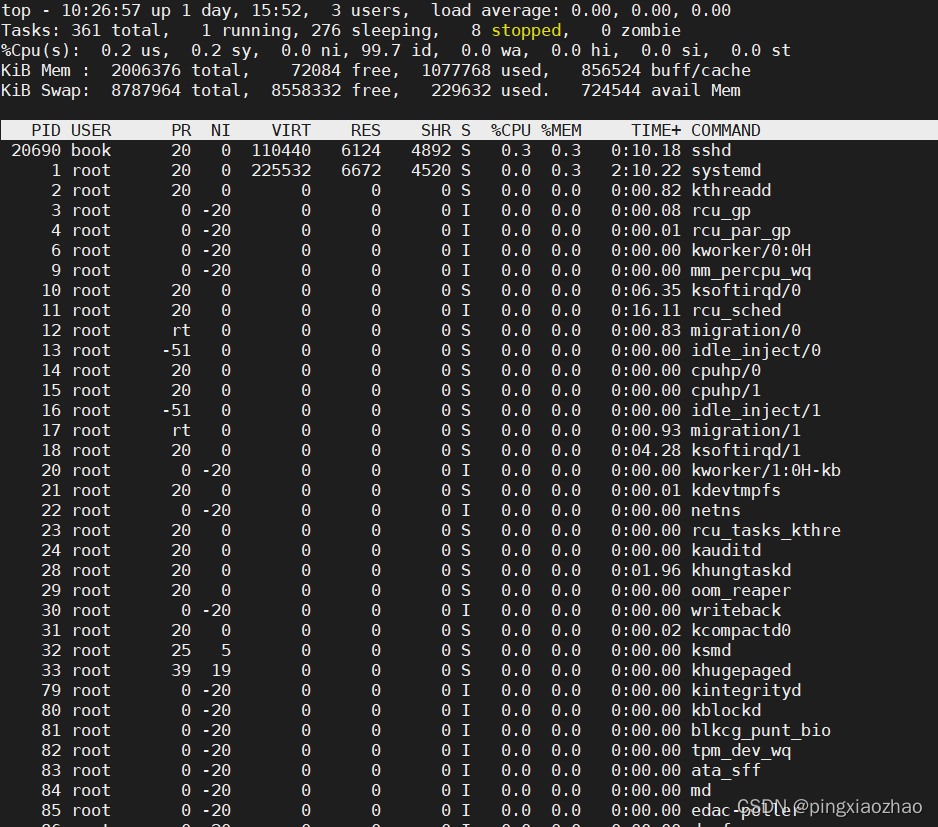
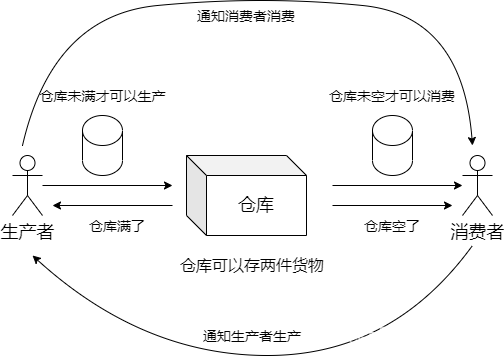
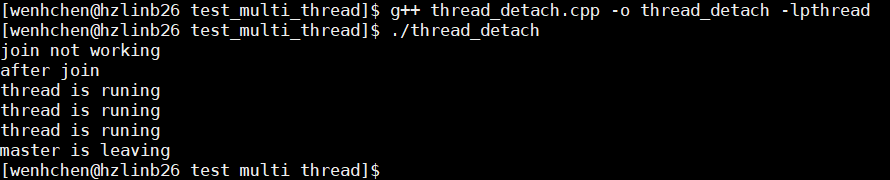
后面会尝试使用冰搜和goole搜索来学习技术,互联网上知识的学习也是符合二八定律的,既然如此,我们何不去选择最好的文章呢。
文章参考:
https://randu.org/tutorials/threads/
http://www.yolinux.com/TUTORIALS/LinuxTutorialPosixThreads.html
https://blog.csdn.net/stpeace/article/details/79575493
一、多线程相关API学习
线程的学习主要包括三方面:线程管理(创建、分离、joinable以及设置线程属性等);互斥锁(创建、销毁、lock 和unlock等);条件变量(conditon variable)。
这里记录一些重要的API作为记录学习吧。
线程创建
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
参数:
pthread_t *thread: the actual thread object that contains pthread id
pthread_attr_t *attr: attributes to apply to this thread
void *(*start_routine)(void *): the function this thread executes
void *arg: arguments to pass to thread function above
线程创建时应保证线程ID thread被成功创建(检查返回值);线程属性attr默认值为NULL,可设置为其他属性;start_routine是创建线程后所执行的函数体;arg是传入的参数。
线程等待和终止
void pthread_exit(void *value_ptr);
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **value_ptr);
pthread_exit() 终止线程,并且提供指针变量*value_ptr给pthread_join()调用
pthread_join() 阻塞调用线程调用,并等待线程结束,得到可选返回值*value_ptr。
//1. 确保检查重要函数返回值
//2. pthread_create()的第二个参数为NULL,属性为默认属性(比如joinable)
//3. 参数传递
//4. pthread_join()是阻塞的,可接收pthread_exit()返回的线程结果信息
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>#define NUM_THREADS 2//thread argument struct
typedef struct _thread_data {int tid;double studff;
} thread_data;//thread function
void *thr_func(void *arg) {thread_data *data = (thread_data *)arg;printf("from thr_func, thread id:%d\n",data->tid);pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main() {pthread_t thr[NUM_THREADS];int i,rc;//thread_data argument arraythread_data thr_data[NUM_THREADS];//create threadsfor(i=0; i<NUM_THREADS; ++i) {thr_data[i].tid = i;if((rc = pthread_create(&thr[i],NULL,thr_func,&thr_data[i]))) {fprintf(stderr,"error:pthread_create,rc: %d\n",rc);return EXIT_FAILURE;}}//block untill all threads completefor(i=0; i<NUM_THREADS; ++i) {pthread_join(thr[i],NULL);}return 0;
}
线程属性
属性的初始化、属性的设置set、属性的获取get
int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr);
int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate);
int pthread_attr_setguardsize(pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t guardsize);
int pthread_attr_setinheritsched(pthread_attr_t *attr, int inheritsched);
int pthread_attr_setschedparam(pthread_attr_t *attr, const struct sched_param *param);
int pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(pthread_attr_t *attr, int policy);
int pthread_attr_setscope(pthread_attr_t *attr, int contentionscope);
int pthread_attr_setstackaddr(pthread_attr_t *attr, void *stackaddr);
int pthread_attr_setstacksize(pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t stacksize);
示例:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 2//thread argument struct
typedef struct _thread_data {int tid;double studff;
} thread_data;//thread function
void *thr_func(void *arg) {thread_data *data = (thread_data *)arg;printf("from thr_func, thread id:%d\n",data->tid);pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main() {pthread_t thr[NUM_THREADS];int i,rc;//thread_data argument arraythread_data thr_data[NUM_THREADS];//initialize and set thread datachedpthread_attr_t attr;pthread_attr_init(&attr);pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);//create threadsfor(i=0; i<NUM_THREADS; ++i) {thr_data[i].tid = i;if((rc = pthread_create(&thr[i],&attr,thr_func,&thr_data[i]))) {fprintf(stderr,"error:pthread_create,rc: %d\n",rc);return EXIT_FAILURE;}}pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);sleep(5);return 0;
}
其实,这个代码和上一个代码是类似的:
线程一得等到pthread_join来释放系统资源,线程一的线程函数一结束就自动释放资源
总之为了在使用 pthread 时避免线程的资源在线程结束时不能得到正确释放,从而避免产生潜在的内存泄漏问题,在对待线程结束时,要确保该线程处于 detached 状态,否着就需要调用 pthread_join() 函数来对其进行资源回收。
线程互斥锁
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *mutexattr);//动态初始化
pthread_mutex_t lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; //静态初始化//acquire a lock on the specified mutex variable. If the mutex is already locked by another thread,
//this call will block the calling thread until the mutex is unlocked.
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
// attempt to lock a mutex or will return error code if busy. Useful for preventing deadlock conditions.
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
//unlock a mutex variable. An error is returned if mutex is already unlocked or owned by another thread.
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>void * updateCounter(void*);pthread_mutex_t mutex1 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int counter =0;int main(){int rc1,rc2;pthread_t thread1,thread2;if( (rc1=pthread_create( &thread1, NULL, &updateCounter, NULL)) ){printf("Thread creation failed: %d\n", rc1);}if( (rc2=pthread_create( &thread2, NULL, &updateCounter, NULL)) ){printf("Thread creation failed: %d\n", rc2);}/* Wait till threads are complete before main continues.*/pthread_join( thread1, NULL);pthread_join( thread2, NULL);return 0;}void * updateCounter(void*){pthread_mutex_lock( &mutex1 );counter++;printf("Counter value: %d\n",counter);pthread_mutex_unlock( &mutex1 );
}
线程条件变量
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>pthread_mutex_t count_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t condition_var = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;void *functionCount1(void*);
void *functionCount2(void*);
int count = 0;
#define COUNT_DONE 10
#define COUNT_HALT1 3
#define COUNT_HALT2 6int main()
{pthread_t thread1, thread2;pthread_create( &thread1, NULL, &functionCount1, NULL);pthread_create( &thread2, NULL, &functionCount2, NULL);pthread_join( thread1, NULL);pthread_join( thread2, NULL);printf("Final count: %d\n",count);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}// Write numbers 1-3 and 8-10 as permitted by functionCount2()
void *functionCount1(void*)
{for(;;){// Lock mutex and then wait for signal to relase mutexpthread_mutex_lock( &count_mutex );// Wait while functionCount2() operates on count// mutex unlocked if condition varialbe in functionCount2() signaled.pthread_cond_wait( &condition_var, &count_mutex );count++;printf("Counter value functionCount1: %d\n",count);pthread_mutex_unlock( &count_mutex );if(count >= COUNT_DONE) return(NULL);}
}// Write numbers 4-7
void *functionCount2(void*)
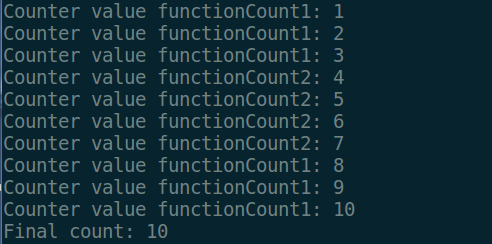
{for(;;){pthread_mutex_lock( &count_mutex );if( count < COUNT_HALT1 || count > COUNT_HALT2 ){// Condition of if statement has been met. // Signal to free waiting thread by freeing the mutex.// Note: functionCount1() is now permitted to modify "count".pthread_cond_signal( &condition_var );}else{count++;printf("Counter value functionCount2: %d\n",count);}pthread_mutex_unlock( &count_mutex );if(count >= COUNT_DONE) return(NULL);}}
标准模板以及解释:
void *thr_func1(void *arg) {/* thread code blocks here until MAX_COUNT is reached */pthread_mutex_lock(&count_lock);while (count < MAX_COUNT) {pthread_cond_wait(&count_cond, &count_lock);}pthread_mutex_unlock(&count_lock);/* proceed with thread execution */pthread_exit(NULL);
}/* some other thread code that signals a waiting thread that MAX_COUNT has been reached */
void *thr_func2(void *arg) {pthread_mutex_lock(&count_lock);/* some code here that does interesting stuff and modifies count */if (count == MAX_COUNT) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&count_lock);pthread_cond_signal(&count_cond);} else {pthread_mutex_unlock(&count_lock);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
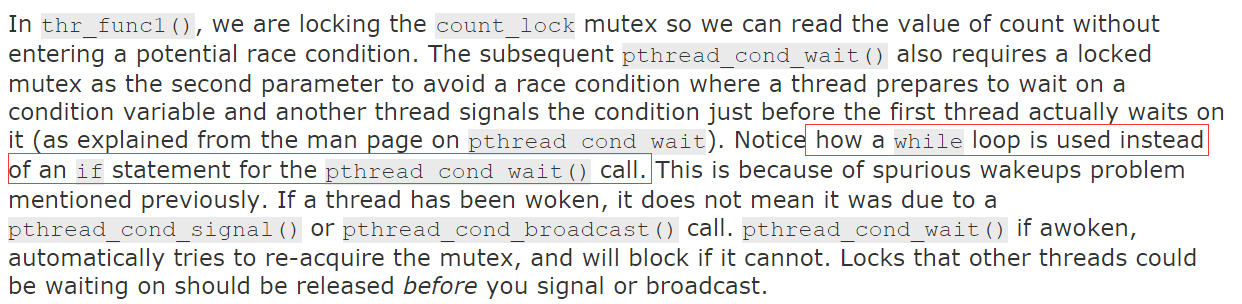
为什么这里要记录一些呢?pthread_cond_wait要使用while而不是if,解释如下:
pthread Barrier及其它
int pthread_barrier_init(pthread_barrier_t *barrier, pthread_barrierattr_t *barrier_attr, unsigned int count);pthread_barrier_t barrier = PTHREAD_BARRIER_INITIALIZER(count);
int pthread_barrier_wait(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);pthread_kill() can be used to deliver signals to specific threads.
pthread_self() returns a handle on the calling thread.
pthread_equal() compares for equality between two pthread ids
pthread_once() can be used to ensure that an initializing function within a thread is only run once.
二、Pthread创建线程后必须使用join或detach释放线程资源
When a joinable thread terminates, its memory resources (thread descriptor and stack) are
not deallocated until another thread performs pthread_join on it.
Therefore, pthread_join must be called once for each joinable thread created to avoid memory leaks.
有问题的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>void* threadFunc(void* p)
{ char szTest[1024 * 32] = {0};return NULL;
} int main(void)
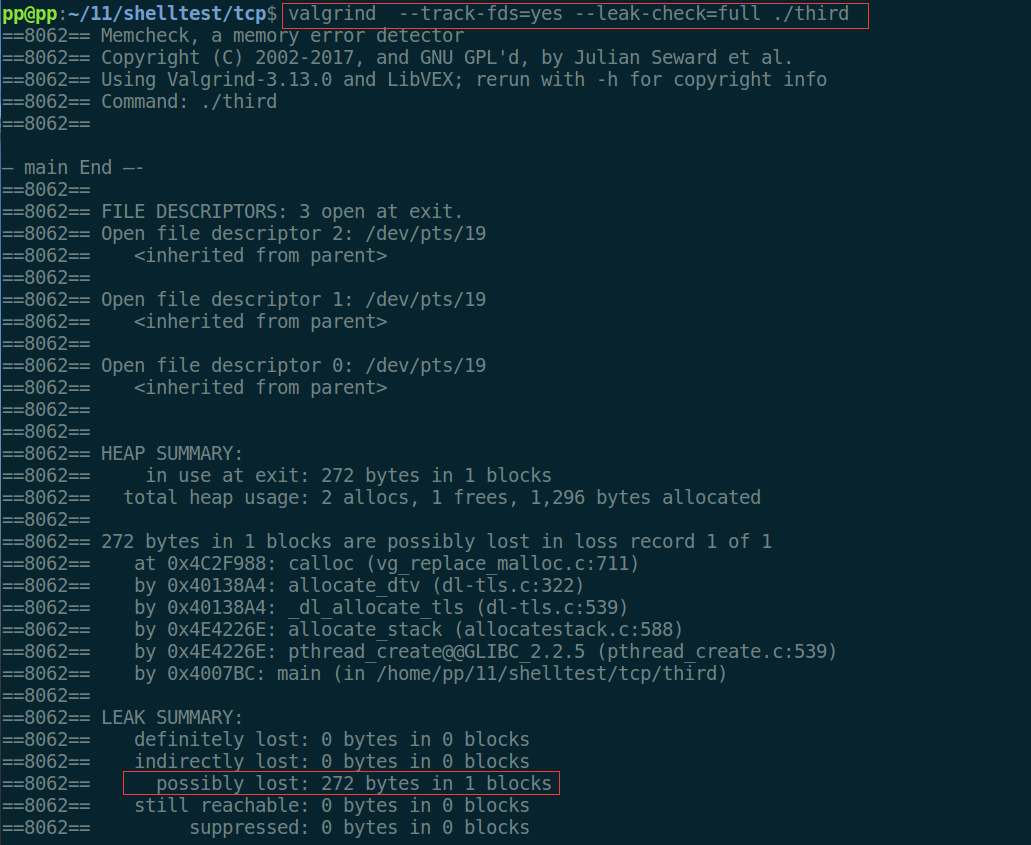
{pthread_t id; pthread_create (&id, NULL, threadFunc, NULL); sleep(1);printf("\n— main End —- \n");return 0;
}
解决方法有三个:
- 线程里面调用 pthread_detach(pthread_self()) 这个方法最简单
- 在创建线程的设置PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED属性
- 创建线程后用 pthread_join() 一直等待子线程结束。
方法一:
void* threadFunc(void* p)
{ //注意1:pthread_detach(pthread_self());char szTest[1024 * 32] = {0};return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{pthread_t id; //注意2:参数2为NULLpthread_create (&id, NULL, threadFunc, NULL); sleep(1);printf("\n— main End —- \n");return 0;
}方法二:
void* threadFunc(void* p)
{ char szTest[1024 * 32] = {0};return NULL;
} int main(void)
{ //注意1:pthread_attr_t attr; pthread_attr_init(&attr);pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);pthread_t id; //注意2:参数2为attrpthread_create (&id, &attr, threadFunc, NULL); sleep(1);printf("\n— main End —- \n");return 0;
}方法三:
void* threadFunc(void* p)
{ char szTest[1024 * 32] = {0};return NULL;
} int main(void)
{pthread_t id; //注意1:参数2为NULLpthread_create (&id, NULL, threadFunc, NULL); //注意2:blockpthread_join(id, NULL);sleep(1);printf("\n— main End —- \n");return 0;
}
再次检测:
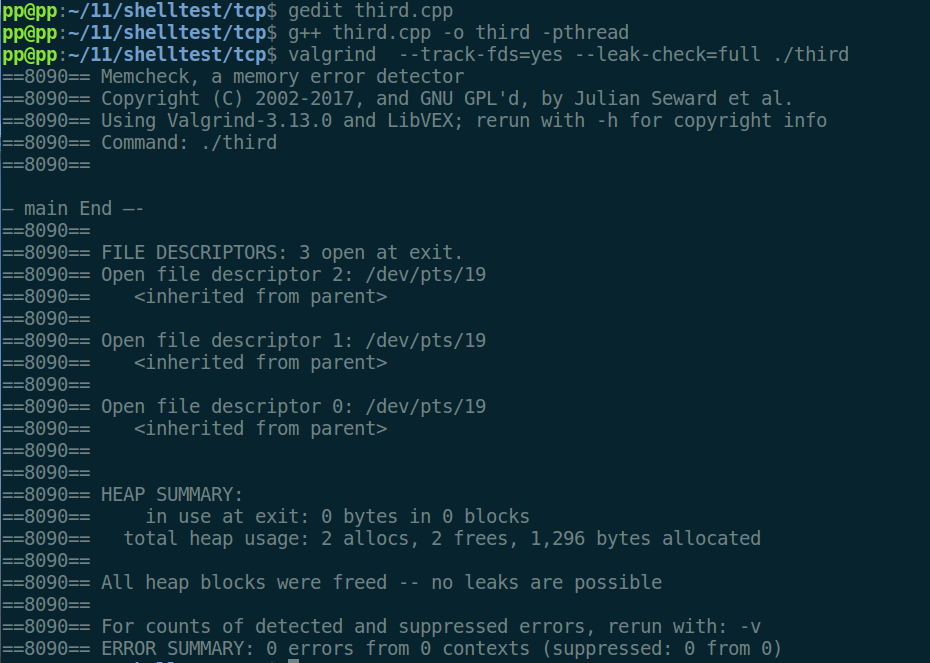
综上,无论是pthread线程库,还是最近我在使用C++11线程,对于joinable线程,如果最后没有添加t.join(),就会coredump。本质就是要考虑内存泄漏问题,我们可以使用valgrind检测查看。