1.1代码
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>static int my_thread_func (void *data)
{while(1){sleep(1);}
}main()
{pthread_t tid;int ret;// 1.创建接收线程ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL,my_thread_func, NULL);if(ret){printf("pthread_create error!\n");}//2.主线程读取标准输入,发给“接收线程”while(1){sleep(1);}return 0;
}1.2执行命令:gcc -o pthread1 pthread1.c -lpthread
1.3运行代码:./pthread1
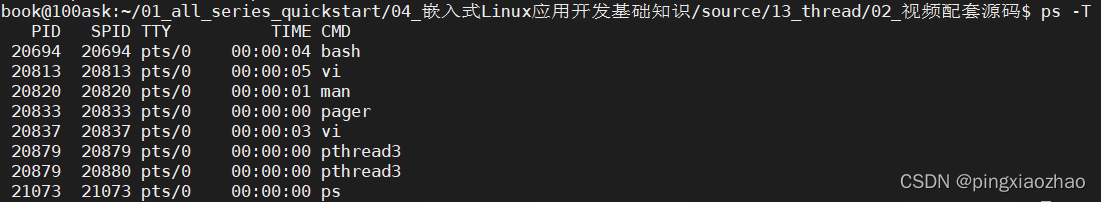
1.4.查看进程: ps
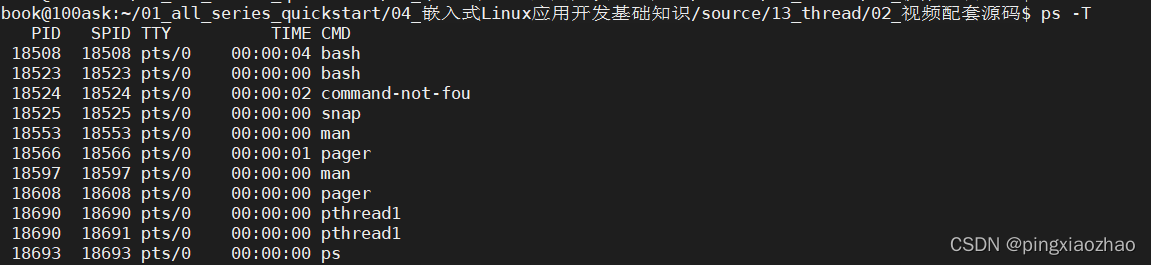
1.5.查看线程:ps -T
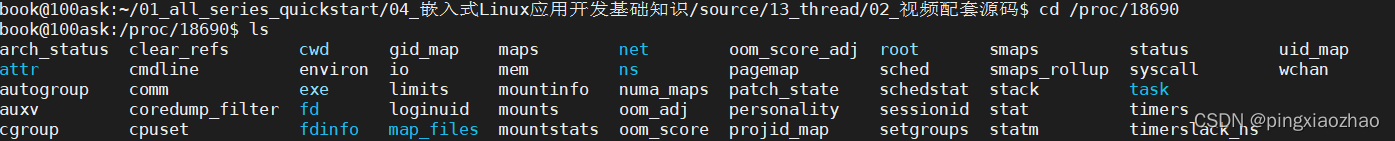
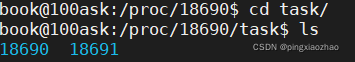
1.6.查看task
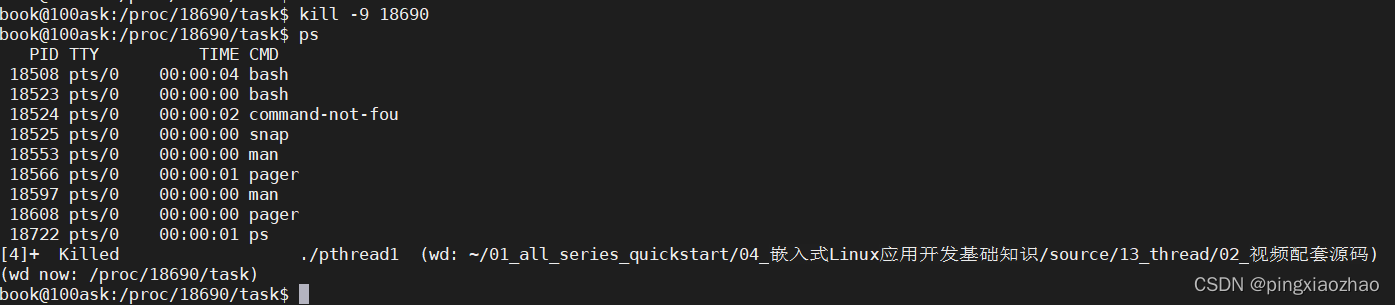
2.1 删除之前的线程 :kill -9 18690
2.2. 代码
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>static char g_buf[1000];
static int g_hasData = 0;static int my_thread_func (void *data)
{while(1){//sleep(1);// 等待通知while(g_hasData == 0); //一直死等,非常消耗CPU资源//打印printf("recv:%s\n",g_buf);g_hasData = 0;}
}main()
{pthread_t tid;int ret;// 1.创建接收线程ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL,my_thread_func, NULL);if(ret){printf("pthread_create error!\n");}//2.主线程读取标准输入,发给“接收线程”while(1){fget(g_buf,1000,stdin);//通知接收线程g_hasData = 1;}return 0;
}2.3 执行命令:gcc -o pthread2 pthread2.c -lpthread
2.4运行代码:./pthread2 注意:程序中使用了fget函数,所以不能使用后台执行./pthread2 &
2.5 查看进程:ps
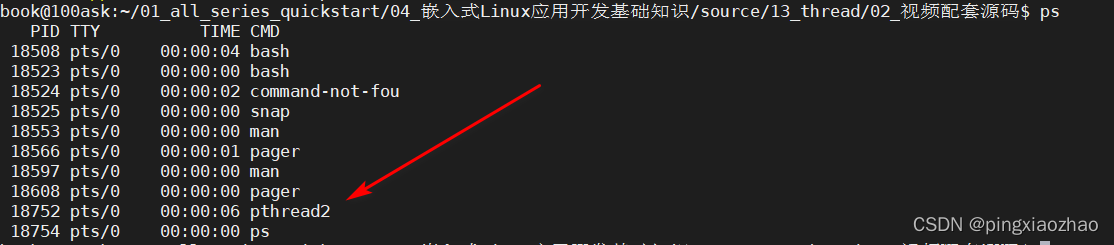
2.5查看线程:ps -T

2.6 再次执行程序并发送123456,接收到123456

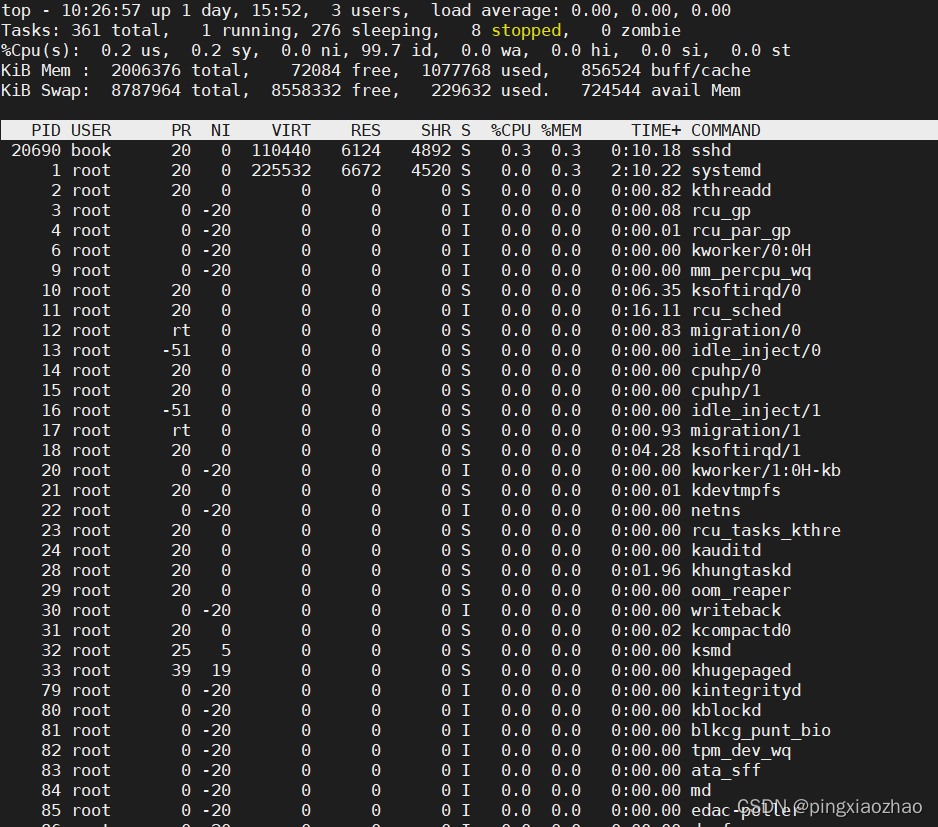
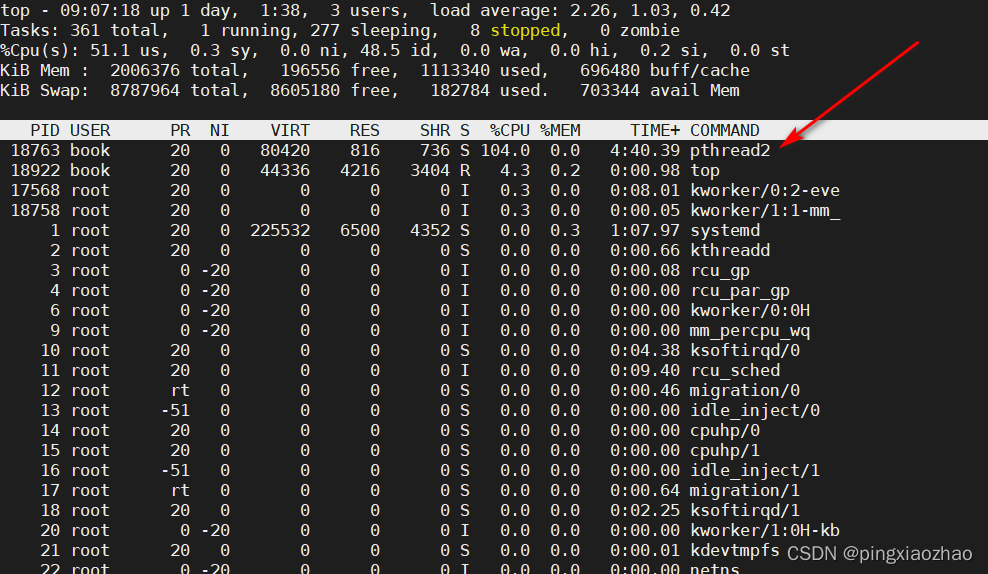
2.7 用另一个终端执行命令:top , 发现如此简单的程序尽然消耗CPU资源如此之高
3.1 代码(使用信号量优化上边代码)
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>static char g_buf[1000];
static sem_t g_sem;
static void *my_thread_func (void *data)
{while (1){//sleep(1);// 等待通知 //while (g_hasData == 0);sem_wait(&g_sem);// 打印 printf("recv: %s\n", g_buf);}return NULL;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t tid;int ret;sem_init(&g_sem, 0, 0);// 1. 创建"接收线程" ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, my_thread_func, NULL);if (ret){printf("pthread_create err!\n");return -1;}// 2. 主线程读取标准输入, 发给"接收线程" while (1){fgets(g_buf, 1000, stdin);// 通知接收线程 sem_post(&g_sem);}return 0;
}
3.2 执行命令:gcc -o pthread3 pthread3.c -lpthread
3.3运行代码:./pthread
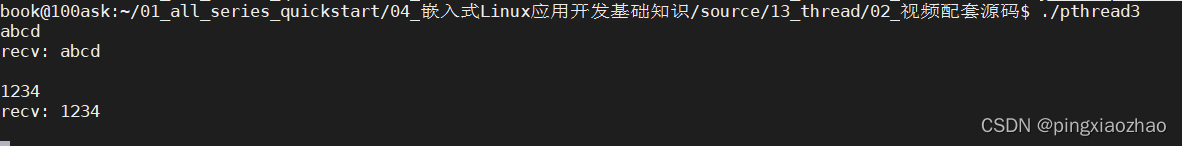
3.4查看进程 :ps
 3.5 查看线程:ps -T
3.5 查看线程:ps -T
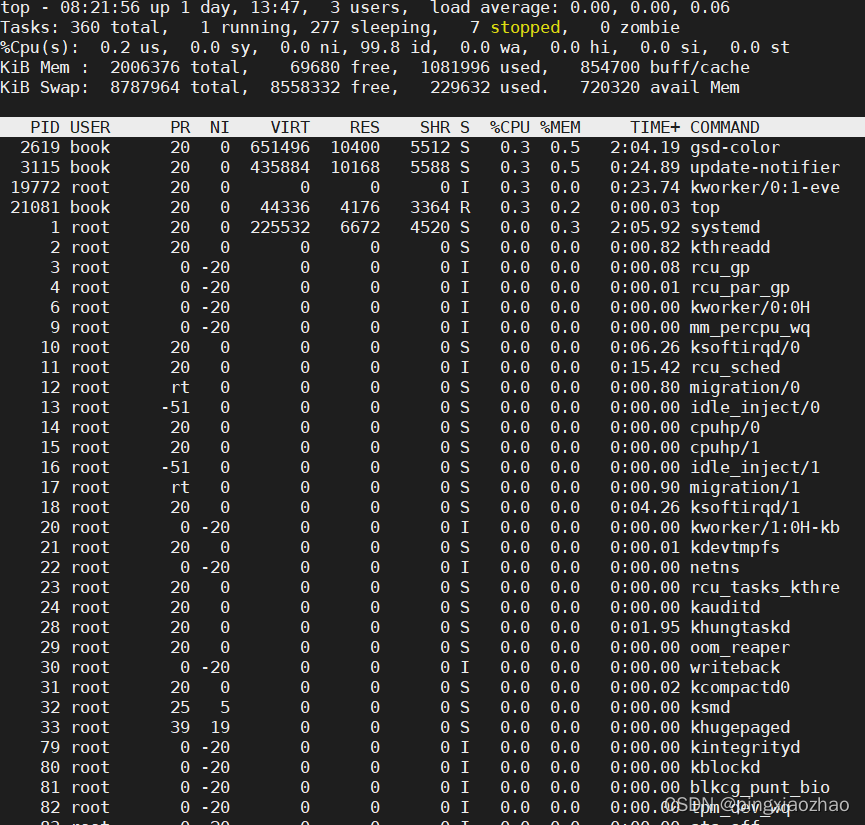
3.6 用另一个终端执行命令:top ,发现在前根本看不到pthread3,说明优化后基本不占CPU资源
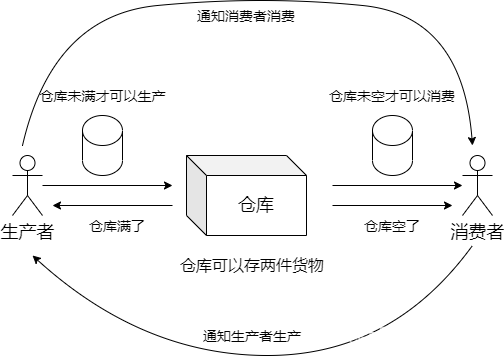
由于g_buf在主线程里正在写入时,子线程也去读取,数据就会乱,所以需要再次优化,加入互斥进行同步数据
4.1.代码(使用信号量加互斥优化上边代码)
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <string.h>static char g_buf[1000];
static sem_t g_sem;
static pthread_mutex_t g_tMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;static void *my_thread_func (void *data)
{while (1){//sleep(1);//等待通知 //while (g_hasData == 0);sem_wait(&g_sem);//打印 pthread_mutex_lock(&g_tMutex);printf("recv: %s\n", g_buf);pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_tMutex);}return NULL;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t tid;int ret;char buf[1000];sem_init(&g_sem, 0, 0);//1. 创建"接收线程" ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, my_thread_func, NULL);if (ret){printf("pthread_create err!\n");return -1;}//2. 主线程读取标准输入, 发给"接收线程" while (1){fgets(buf, 1000, stdin);pthread_mutex_lock(&g_tMutex);memcpy(g_buf, buf, 1000);pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_tMutex);// 通知接收线程 sem_post(&g_sem);}return 0;
}
4.2.执行命令:gcc -o pthread4 pthread4.c -lpthread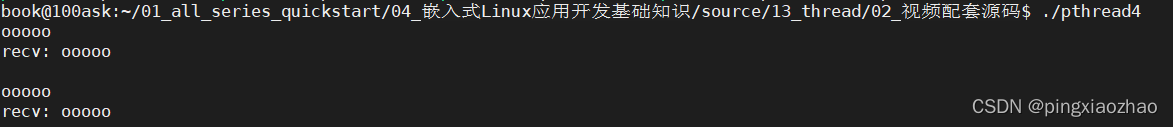
4.3.如果按如下所示增加互斥,主线程输入占用时间较多,就会一直互斥在主线里,接收线程接收不到数据
//2. 主线程读取标准输入, 发给"接收线程" while (1){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_tMutex);fgets(g_buf, 1000, stdin);pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_tMutex);// 通知接收线程 sem_post(&g_sem);}5.1.代码(使用条件变量加互斥优化上边代码)
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <string.h>static char g_buf[1000];
static pthread_mutex_t g_tMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t g_tConVar = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;static void *my_thread_func (void *data)
{while (1){//sleep(1);// 等待通知 //while (g_hasData == 0);pthread_mutex_lock(&g_tMutex);pthread_cond_wait(&g_tConVar, &g_tMutex);//等待接受主线程发来信号 //打印printf("recv: %s\n", g_buf);pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_tMutex);}return NULL;
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t tid;int ret;char buf[1000];//1. 创建"接收线程" ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, my_thread_func, NULL);if (ret){printf("pthread_create err!\n");return -1;}//2. 主线程读取标准输入, 发给"接收线程" while (1){fgets(buf, 1000, stdin);pthread_mutex_lock(&g_tMutex);memcpy(g_buf, buf, 1000);pthread_cond_signal(&g_tConVar); //通知接收线程 pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_tMutex);}return 0;
}5.2 执行命令:gcc -o pthread5 pthread5.c -lpthread
5.3运行代码:./pthread5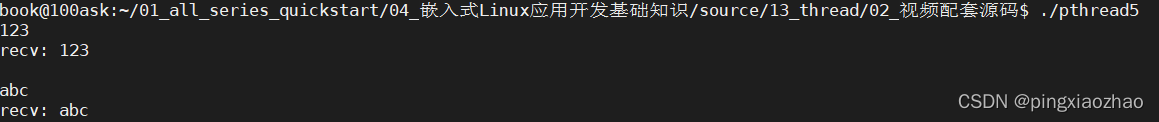
5.4查看进程:ps
5.5查看线程:ps -T
 5.6查看CPU占用率:top,发现pthread5几乎不占用CPU资源
5.6查看CPU占用率:top,发现pthread5几乎不占用CPU资源