0. 参考
c++文件读写(很全)
1. 简要
C++ 文件读写很重要,我们经常要面临数据的读写以及读写之后的类型转换,接下来我们就详细的讲解C++中的文件读写。
2. 读写步骤
2.1 包含头文件
#include <fstream>
2.2 创建流对象
- ofstream:写文件
- ifstream:读文件
- fstream:读写文件
ofstream fout;
ifstream fin;
fstream finout;
2.3 打开文件
流对象.open("文件路径",打开方式)
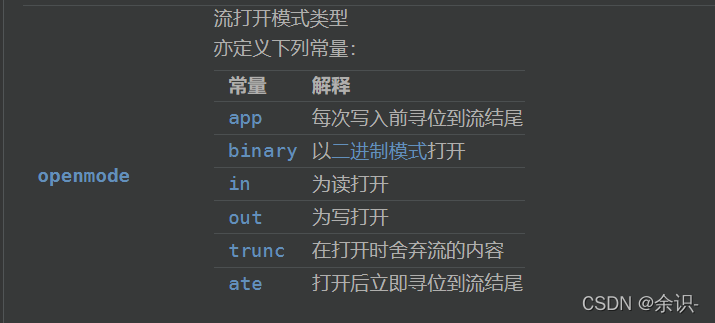
打开方式(可以不填)包括:
- ios::in 读文件
- ios::out 写文件(覆盖写)
- ios::binary 二进制方式
- ios::app 追加写(要配合out使用)
- ios::trunc 覆盖写(要配合out使用)
- ios::out | ios::binary 二进制写
2.4 读写数据
2.4.1 写入数据
fout << x << " " << y << endl;
fout.close(); //手动关闭流
2.4.2 读取数据
首先判断文件是否被正常打开:
if (!fin.is_open()) {cout << "Could not open " << path << endl;return;
}
有四种读的方式,下面我们来逐一介绍。
第一种读的方式——按元素(字符串)读
char buf[1024] = { 0 };
while (fin >> buf) {cout << buf << endl; //每一次的buf是空格或回车键(即白色字符)分开的元素(字符串)
}/*
文件:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
读取结果:
1
2
3
a
b
c
112
geya
*/
第二种读的方式——使用getline按行读
使用getline(char* s, streamsize n)函数,作用是从istream中读取至多n个字符保存在s对应的数组中,即使没有读够n个字符,如果遇到换行符则终止本次读取,跳到下一行。
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); //清空数组
while (fin.getline(buf, sizeof(buf))) {cout << buf << endl;
}/*
文件:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
读取结果:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
*/
第三种读的方式——使用get按字符读
char c;
while ((c = fin.get()) != EOF) {cout << c;
}/*
文件:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
读取结果:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
*/
第四种读的方式——按变量读
若已知文件中数据的顺序,则直接定义字符变量或字符串变量存储单个元素,以空格为分割。
char a, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5;
string s6;
fin >> a >> s1 >> s2 >> s3 >> s4 >> s5 >> s6;
cout << a << " " << s1 << " " << s2 << " " << s3 << " " << s4 << " " << s5 << " " << s6;/*
文件:
1 2 3
a b c
112
geya
读取结果:
1 2 3 a b c 112
*/
2.5 数据类型转换
一般从文件中读取的是字符或字符串格式的数据,如果是数字要转化为float等格式应该怎么做呢?
这里给出一种方法:
直接定义负责接受的变量数据类型,按行分后再按元素分
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <typeinfo>using namespace std;struct people {string name; //人名float height; //身高int age; //年龄
};void readFile(const string& filename)
{ifstream fin;fin.open(filename);if (!fin.is_open()) {cerr << "cannot open the file" << endl;}char line[1024] = { 0 };vector<people> peoples;//从文件中提取行while (fin.getline(line, sizeof(line))) {//定义局部变量,存储一行中的数据people p;//从一行中提取元素stringstream word(line);//提取人名word >> p.name; //提取身高float height;word >> p.height;//提取年龄int age;word >> p.age;//保存peoplepeoples.push_back(p);}for (auto& p : peoples) {cout << p.name << " " << p.height << " " << p.age << endl;//用typeid(变量名).name()来输出变量数据类型,要添加头文件#include <typeinfo>cout << typeid(p.name).name() << " " << typeid(p.height).name() << " " << typeid(p.age).name() << endl;}
}int main()
{string filename = "people.txt";readFile(filename);/*文件:Peter 176.49 25John 176.49 25Michael 176.49 25读取结果:Peter 176.49 25class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > float intJohn 176.49 25class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > float intMichael 176.49 25class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> > float int*/return 0;
}
下面给出一个例子,读取存储点云数据的txt文件,然后可视化点云。
void txt2point_cloud(const string& path) {ifstream fin;fin.open(path);if (!fin.is_open()) {cout << "Could not open " << path << endl;return;}//定义点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>());//定义点pcl::PointXYZRGB p;//读取数据char line[1024] = { 0 };while (fin.getline(line, sizeof(line))) {stringstream word(line);word >> p.x;word >> p.y;word >> p.z;int num; //因为p.b g r都是uchar类型的数据,字符型,若直接word>>p.b,则只能提取一个字符,因此要定义一个int来提取一个整数word >> num;p.b = num;word >> num;p.g = num;word >> num;p.r = num;cloud->push_back(p);}//打印点云中的点/*for (auto& point : *cloud) {cout << point.x << " " << point.y << " " << point.z << " " << (int)point.b << " " << (int)point.g << " " << (int)point.r << endl;}*/pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("cloud viewer");viewer.showCloud(cloud);while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {}
}int main() {string path = "point_cloud-left.txt";txt2point_cloud(path);return 0;
}
点云数据:
-1162.63 -999.604 3949.78 49 49 181
-1159.85 -1000.62 3953.79 46 44 182
-1155.9 -1000.62 3953.79 43 44 178
-1150.77 -999.604 3949.78 40 47 169
-1146.82 -999.604 3949.78 40 42 162
-1142.98 -999.701 3950.16 54 56 143
-1129.7 -991.516 3917.82 67 109 105
...