1 RPC 框架原理
RPC 框架的目标就是让远程服务调用更加简单、透明,RPC 框架负责屏蔽底层的传输方式(TCP 或者 UDP)、序列化方式(XML/Json/ 二进制)和通信细节。服务调用者可以像调用本地接口一样调用远程的服务提供者,而不需要关心底层通信细节和调用过程。RPC 框架的调用原理图如下所示:
2 业界主流的 RPC 框架
业界主流的 RPC 框架整体上分为三类:1. 支持多语言的 RPC 框架,比较成熟的有 Google 的 gRPC、Apache(Facebook)的 Thrift;
2. 只支持特定语言的 RPC 框架,例如新浪微博的 Motan;
3. 支持服务治理等服务化特性的分布式服务框架,其底层内核仍然是 RPC 框架, 例如阿里的 Dubbo。
随着微服务的发展,基于语言中立性原则构建微服务,逐渐成为一种主流模式,例如对于后端并发处理要求高的微服务,比较适合采用 Go 语言构建,而对于前端的 Web 界面,则更适合 Java 和 JavaScript。因此,基于多语言的 RPC 框架来构建微服务,是一种比较好的技术选择。例如 Netflix,API 服务编排层和后端的微服务之间就采用 gRPC 进行通信。
3 gRPC 简介
gRPC 是一个高性能、开源和通用的 RPC 框架,面向服务端和移动端,基于 HTTP/2 设计。
4 gRPC 特点
1. 语言中立,支持多种语言;2. 基于 IDL 文件定义服务,通过 proto3 工具生成指定语言的数据结构、服务端接口以及客户端 Stub;
3. 通信协议基于标准的 HTTP/2 设计,支持双向流、消息头压缩、单 TCP 的多路复用、服务端推送等特性,这些特性使得 gRPC 在移动端设备上更加省电和节省网络流量;
4. 序列化支持 PB(Protocol Buffer)和 JSON,PB 是一种语言无关的高性能序列化框架,基于 HTTP/2 + PB, 保障了 RPC 调用的高性能。
5 简单样例
本文的demo使用的项目构建工具是gradle,版本是4.6,配置如下:
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'com.google.protobuf'repositories {jcenter()
}buildscript {repositories {mavenCentral()}dependencies {classpath 'com.google.protobuf:protobuf-gradle-plugin:0.8.3'}
}sourceSets {main {java{srcDir 'gen/main/java'srcDir 'gen/main/grpc'}proto {srcDir 'src/main/proto'}}
}jar {from {configurations.runtime.collect {it.isDirectory() ? it : zipTree(it)}configurations.compile.collect {it.isDirectory() ? it : zipTree(it)}}manifest {attributes 'Main-Class': 'com.ylifegroup.protobuf.server.GRpcServer'}
}protobuf {protoc {artifact = "com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.5.1-1"}plugins {grpc {artifact = 'io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.11.0'}}generatedFilesBaseDir = "$projectDir/gen/"generateProtoTasks {all()*.plugins {grpc {}}}
}dependencies {//jsoncompile group: 'com.alibaba', name: 'fastjson', version: '1.2.8'//logbackcompile 'ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.1.8'//logstash-logback-encodercompile 'net.logstash.logback:logstash-logback-encoder:4.8'//grpccompile 'io.grpc:grpc-netty:1.11.0'compile 'io.grpc:grpc-protobuf:1.11.0'compile 'io.grpc:grpc-stub:1.11.0'//sslcompile 'io.netty:netty-tcnative-boringssl-static:2.0.8.Final'//nettycompile 'io.netty:netty-all:4.1.22.Final'// The production code uses the SLF4J logging API at compile timecompile 'org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.21'testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
}tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {options.encoding = "UTF-8"options.fork = true
}eclipse {classpath {defaultOutputDir = file('build/eclipse/bin')}
}clean {delete protobuf.generatedFilesBaseDir
}简单说明一下,apply plugin: 'com.google.protobuf' ,这个是生成protobuf的强大工具,能够把proto文件生成protobuf对应的基础文件跟rpc文件;sourceSets定义了protobuf生成的规范,srcDir 'src/main/proto'表示存放proto原始文件目录, srcDir 'gen/main/java'表示存放proto基础文件的目录,srcDir 'gen/main/grpc'表示基础文件对应的rpc调用目录。整体项目结构图如下:
其中,grpc的基本依赖如下(no android):
//grpccompile 'io.grpc:grpc-netty:1.11.0'compile 'io.grpc:grpc-protobuf:1.11.0'compile 'io.grpc:grpc-stub:1.11.0'按照之前概念说的,基于 IDL 文件定义服务,通过 proto3 工具生成指定语言的数据结构、服务端接口以及客户端 Stub,本demo 的 phonebook.proto 定义如下
syntax = "proto3";option go_package = "user";
option java_package = "com.ylifegroup.protobuf";enum PhoneType {HOME = 0;WORK = 1;OTHER = 2;
}message ProtobufUser {int32 id = 1;string name = 2;message Phone{PhoneType phoneType = 1;string phoneNumber = 2;}repeated Phone phones = 3;
}message AddPhoneToUserRequest{int32 uid = 1;PhoneType phoneType = 2;string phoneNumber = 3;
}message AddPhoneToUserResponse{bool result = 1;
}service PhoneService {rpc addPhoneToUser(AddPhoneToUserRequest) returns (AddPhoneToUserResponse);
}其中rpc的配置是:
service PhoneService {rpc addPhoneToUser(AddPhoneToUserRequest) returns (AddPhoneToUserResponse);
}其它部分都是基本数据的定义。
那么接下来怎么 通过 proto3 工具生成指定语言的数据结构、服务端接口以及客户端 Stub 呢?
运行gradle指令: gradle build
我们看到生成了grpc对应的PhoneServiceGrpc文件,以及其基础类Phonebook。
到此基础工作已经准备好了,接下来我们构建server服务,构建server服务之前我们需要重新实现PhoneServiceGrpc,
/*** @describe PhoneService Imp* @author zhikai.chen* @date 2018年5月7日 下午3:56:54*/
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.PhoneServiceGrpc;
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.Phonebook.AddPhoneToUserRequest;
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.Phonebook.AddPhoneToUserResponse;import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;public class PhoneServiceImp extends PhoneServiceGrpc.PhoneServiceImplBase{@Overridepublic void addPhoneToUser(AddPhoneToUserRequest request, StreamObserver<AddPhoneToUserResponse> responseObserver) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubAddPhoneToUserResponse response = null;if(request.getPhoneNumber().length() == 11 ){System.out.printf("uid = %s , phone type is %s, nubmer is %s\n", request.getUid(), request.getPhoneType(), request.getPhoneNumber());response = AddPhoneToUserResponse.newBuilder().setResult(true).build();}else{System.out.printf("The phone nubmer %s is wrong!\n",request.getPhoneNumber());response = AddPhoneToUserResponse.newBuilder().setResult(false).build();}responseObserver.onNext(response);responseObserver.onCompleted();}}为了项目的简单易懂,这里我们使用默认的Block配置
import java.io.IOException;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import com.kenhome.protobuf.service.PhoneServiceImp;import io.grpc.Server;
import io.grpc.ServerBuilder;/*** @describe GRpcServer demo* @author zhikai.chen* @date 2018年5月7日 下午3:55:10*/
public class GRpcServerDefault {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GRpcServerDefault.class);private Server server;private void start() throws IOException {/* The port on which the server should run */int port = 50051;server = ServerBuilder .forPort(port).addService(new PhoneServiceImp()).build().start();logger.info("Server started, listening on " + port);Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.err.println("*** shutting down gRPC server since JVM is shutting down");GRpcServerDefault.this.stop();System.err.println("*** server shut down");}});}private void stop() {if (server != null) {server.shutdown();}}/*** Await termination on the main thread since the grpc library uses daemon* threads.*/private void blockUntilShutdown() throws InterruptedException {if (server != null) {server.awaitTermination();}}/*** Main launches the server from the command line.*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {final GRpcServerDefault server = new GRpcServerDefault();server.start();server.blockUntilShutdown();}}ServerBuilder 底层默认使用netty4.1的nio非阻塞模型。服务提供的内容通过addService添加 ,这里对应的是我们刚刚重写的PhoneServiceImp类。
最后我们来构建client类,一样的为了项目的易懂,这里也使用默认的Block配置:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.PhoneServiceGrpc;
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.Phonebook.AddPhoneToUserRequest;
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.Phonebook.AddPhoneToUserResponse;
import com.ylifegroup.protobuf.Phonebook.PhoneType;import io.grpc.ManagedChannel;
import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder;
import io.grpc.StatusRuntimeException;/*** @describe GRpcClient Block demo* @author zhikai.chen* @date 2018年5月7日 下午4:00:58*/
public class GRpcClientBlock {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GRpcClientBlock.class);private final ManagedChannel channel;private final PhoneServiceGrpc.PhoneServiceBlockingStub blockingStub;/** Construct client connecting to gRPC server at {@code host:port}. */public GRpcClientBlock(String host, int port) {ManagedChannelBuilder<?> channelBuilder = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress(host, port).usePlaintext();channel = channelBuilder.build();blockingStub = PhoneServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);}public void shutdown() throws InterruptedException {channel.shutdown().awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}/** add phone to user. */public void addPhoneToUser(int uid, PhoneType phoneType, String phoneNubmer) {logger.info("Will try to add phone to user " + uid);AddPhoneToUserRequest request = AddPhoneToUserRequest.newBuilder().setUid(uid).setPhoneType(phoneType).setPhoneNumber(phoneNubmer).build();AddPhoneToUserResponse response;try {response = blockingStub.addPhoneToUser(request);} catch (StatusRuntimeException e) {logger.warn("RPC failed: {0} --> "+e.getLocalizedMessage(), e.getStatus());return;}logger.info("Result: " + response.getResult());}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {GRpcClientBlock client = new GRpcClientBlock("localhost", 50051);try {client.addPhoneToUser(1, PhoneType.WORK, "13888888888");} finally {client.shutdown();}}}
ManagedChannel 将处理后的请求和响应传递给与之相关联的 ClientCall 进行上层处理,同时,ManagedChannel 提供了对 Channel 的生命周期管理(链路创建、空闲、关闭等)。
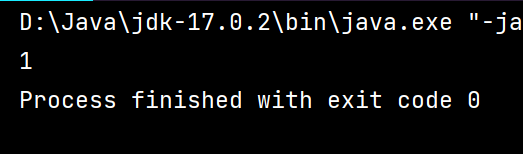
运行效果:
好了,本教程就到这里了,下一章我会为大家讲解grpc有哪些io通信模型,以及他们各个部分简单的使用。