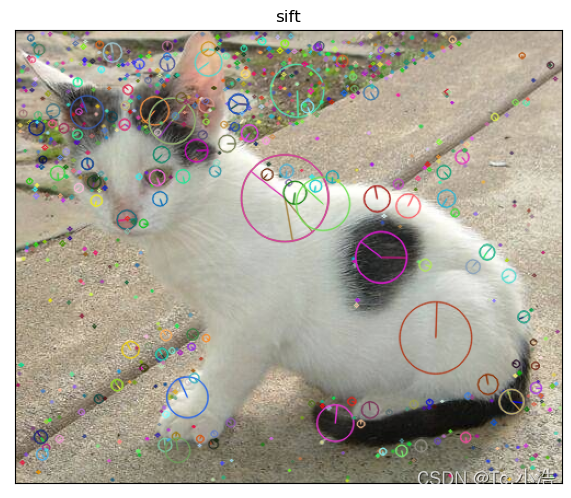
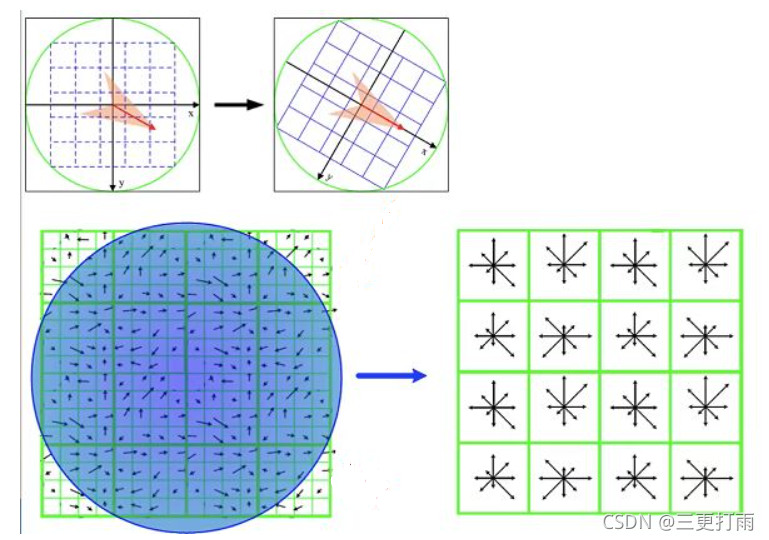
0. 算法原理细节可参考:
- https://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7639681
- https://blog.csdn.net/zddblog/article/details/7521424?depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-1&utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-1
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Qb411W7cK?p=1
本文参考了up主的代码,并在匹配阶段、金字塔输出方式等部分进行了重新设计,同时使代码实现完全对像素操作。
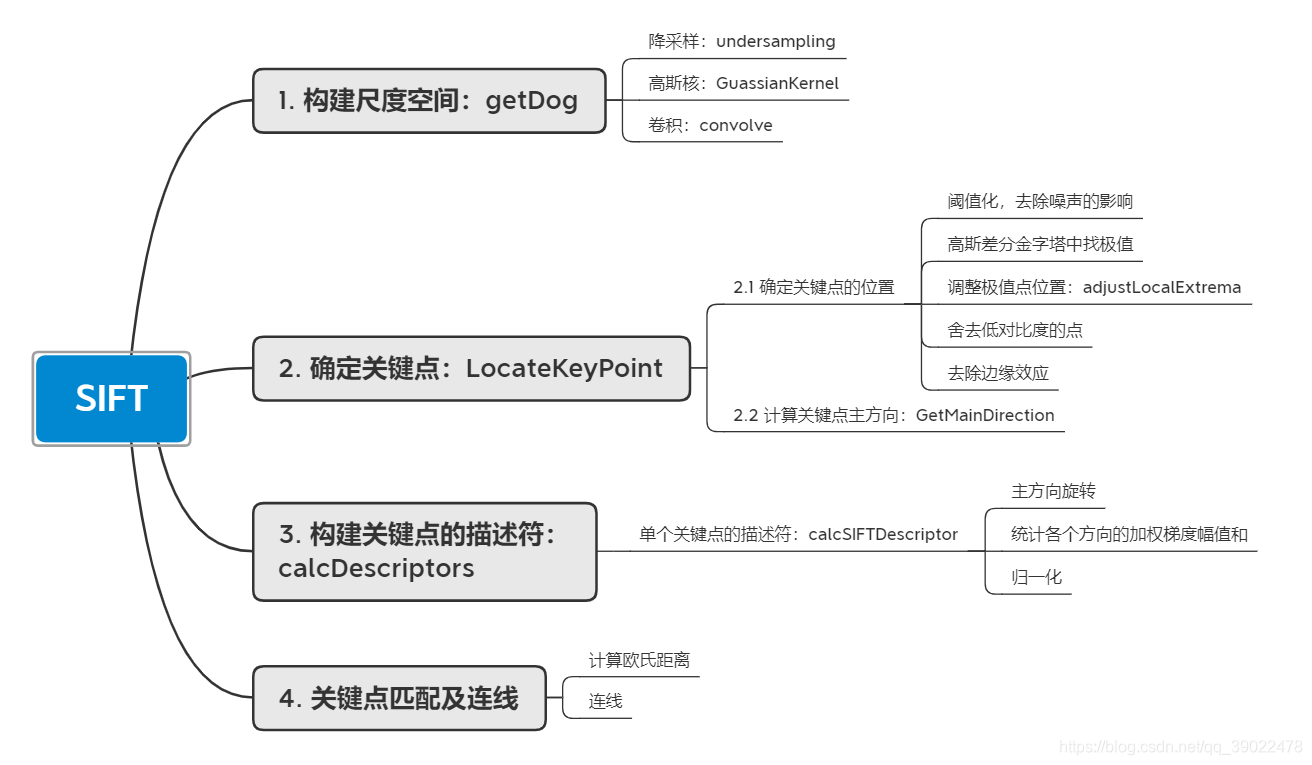
1. 算法流程
SIFT(Scale-invariant feature transform),即尺度不变特征变换,是一种检测图像局部特征并进行特征点匹配的算法。
算法流程如下:
2. python实现
OPENCV库中有SIFT函数,调用此函数很容易实现。下面的是直接对像素操作实现SIFT的源代码。
# coding: utf-8
import warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # 忽略警告
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Imagedef convolve(kernel, img, padding, strides):''':param kernel: 输入的核函数:param img: 输入的图片:param padding: 需要填充的位置:param strides: 高斯核移动的步长:return: 返回卷积的结果'''result = Nonekernel_size = kernel.shapeimg_size = img.shapeif len(img_size) == 3: # 三通道图片就对每通道分别卷积 dstack和并channel = []for i in range(img_size[-1]):pad_img = np.pad(img[:, :, i], ((padding[0], padding[1]), (padding[2], padding[3])), 'constant')temp = []for j in range(0, img_size[0], strides[1]):temp.append([])for k in range(0, img_size[1], strides[0]):val = (kernel * pad_img[j * strides[1]:j * strides[1] + kernel_size[0],k * strides[0]:k * strides[0] + kernel_size[1]]).sum()temp[-1].append(val)channel.append(np.array(temp))channel = tuple(channel)result = np.dstack(channel)elif len(img_size) == 2:channel = []pad_img = np.pad(img, ((padding[0], padding[1]), (padding[2], padding[3])),'constant') # pad是填充函数 边界处卷积需要对边界外根据高斯核大小填0for j in range(0, img_size[0], strides[1]): # 第j列 strides 是步长 本例步长为1 相当于遍历channel.append([])for k in range(0, img_size[1], strides[0]): # 第i行val = (kernel * pad_img[j * strides[1]:j * strides[1] + kernel_size[0],k * strides[0]:k * strides[0] + kernel_size[1]]).sum() # 卷积的定义 相当于用高斯核做加权和channel[-1].append(val)result = np.array(channel)return result# 函数1.1.1 undersampling
# 降采样,隔点取点
def undersampling(img, step=2):'''临近降采样:param img: 输入图片:param step: 降采样步长 默认为2(缩小两倍):return: 返回降采样结果'''return img[::step, ::step]# 函数1.1.2 GuassianKernel
# 产生高斯核
def GuassianKernel(sigma, dim):''':param sigma: 标准差:param dim: 高斯核的纬度(必须是个奇数):return: 返回高斯核'''temp = [t - (dim // 2) for t in range(dim)] # 生成二维高斯的x与yassistant = []for i in range(dim):assistant.append(temp)assistant = np.array(assistant)temp = 2 * sigma * sigmaresult = (1.0 / (temp * np.pi)) * np.exp(-(assistant ** 2 + (assistant.T) ** 2) / temp) # 二维高斯公式return result# 函数1.1,getDoG
# 得到高斯金字塔和高斯差分金字塔
def getDoG(img, n, sigma0, S=None, O=None):''':param img: 输入的图像:param sigma0: 输入的sigma:param n: 有几层用于提取特征:param S: 金字塔每层有几张gauss滤波后的图像:param O: 金字塔有几层:return: 返回差分高斯金字塔和高斯金字塔'''if S == None:S = n + 3 # 至少有4张 (第一张和最后一张高斯金字塔无法提取特征,差分以后的第一张和最后一张也无法提取特征)if O == None:O = int(np.log2(min(img.shape[0], img.shape[1]))) - 3 # 计算最大可以计算多少层 O=log2(min(img长,img宽))-3k = 2 ** (1.0 / n)sigma = [[(k ** s) * sigma0 * (1 << o) for s in range(S)] for o in range(O)] # 每一层 sigma按照 k^1/s * sigama0 排列 下一层的sigma都要比上一层sigma大两倍sample = [undersampling(img, 1 << o) for o in range(O)] # 降采样取图片作为该层的输入Guass_Pyramid = []for i in range(O):Guass_Pyramid.append([]) # 申明二维空数组for j in range(S):dim = int(6*sigma[i][j] + 1) # 上网查找相关信息 高斯核大小随sigma变化的效果更好#dim = int(9)if dim % 2 == 0: # 防止输入的高斯核不是奇数dim += 1Guass_Pyramid[-1].append(convolve(GuassianKernel(sigma[i][j], dim), sample[i], [dim // 2, dim // 2, dim // 2, dim // 2], [1, 1])) # 在第i层添加第j张 经过高斯卷积的 该图片四周扩展 5//2=2 用于高斯卷积DoG_Pyramid = [[Guass_Pyramid[o][s + 1] - Guass_Pyramid[o][s] for s in range(S - 1)] for o in range(O)] #每一层中 上一张减去下一张得到高斯核return DoG_Pyramid, Guass_Pyramid, O # 返回高斯金字塔和高斯差分金字塔# 函数2.1.1 adjustLocalExtrema
# 功能:通过泰勒展开精调位置精调位置
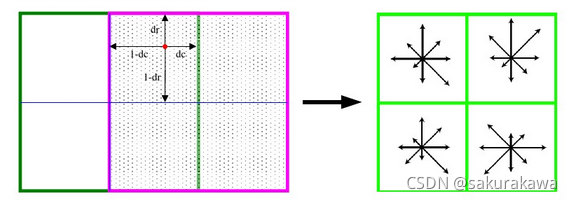
def adjustLocalExtrema(DoG, o, s, x, y, contrastThreshold, edgeThreshold, sigma, n, SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE):SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS = 5SIFT_IMG_BORDER = 5point = []img_scale = 1.0 / (255 * SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.5second_deriv_scale = img_scalecross_deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.25img = DoG[o][s]i = 0while i < SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS:if s < 1 or s > n or y < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or y >= img.shape[1] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x >= \img.shape[0] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER:return None, None, None, Noneimg = DoG[o][s]prev = DoG[o][s - 1]next = DoG[o][s + 1]dD = [(img[x, y + 1] - img[x, y - 1]) * deriv_scale,(img[x + 1, y] - img[x - 1, y]) * deriv_scale,(next[x, y] - prev[x, y]) * deriv_scale]v2 = img[x, y] * 2dxx = (img[x, y + 1] + img[x, y - 1] - v2) * second_deriv_scaledyy = (img[x + 1, y] + img[x - 1, y] - v2) * second_deriv_scaledss = (next[x, y] + prev[x, y] - v2) * second_deriv_scaledxy = (img[x + 1, y + 1] - img[x + 1, y - 1] - img[x - 1, y + 1] + img[x - 1, y - 1]) * cross_deriv_scaledxs = (next[x, y + 1] - next[x, y - 1] - prev[x, y + 1] + prev[x, y - 1]) * cross_deriv_scaledys = (next[x + 1, y] - next[x - 1, y] - prev[x + 1, y] + prev[x - 1, y]) * cross_deriv_scaleH = [[dxx, dxy, dxs],[dxy, dyy, dys],[dxs, dys, dss]]X = np.matmul(np.linalg.pinv(np.array(H)), np.array(dD))xi = -X[2]xr = -X[1]xc = -X[0]if np.abs(xi) < 0.5 and np.abs(xr) < 0.5 and np.abs(xc) < 0.5:breaky += int(np.round(xc))x += int(np.round(xr))s += int(np.round(xi))i += 1if i >= SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS:return None, x, y, sif s < 1 or s > n or y < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or y >= img.shape[1] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x >= \img.shape[0] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER:return None, None, None, Nonet = (np.array(dD)).dot(np.array([xc, xr, xi]))contr = img[x, y] * img_scale + t * 0.5# 确定极值点位置第四步:舍去低对比度的点if np.abs(contr) * n < contrastThreshold:return None, x, y, s# 确定极值点位置第五步:边缘效应的去除。 利用Hessian矩阵的迹和行列式计算主曲率的比值tr = dxx + dyydet = dxx * dyy - dxy * dxyif det <= 0 or tr * tr * edgeThreshold >= (edgeThreshold + 1) * (edgeThreshold + 1) * det:return None, x, y, spoint.append((x + xr) * (1 << o))point.append((y + xc) * (1 << o))point.append(o + (s << 8) + (int(np.round((xi + 0.5)) * 255) << 16))point.append(sigma * np.power(2.0, (s + xi) / n) * (1 << o) * 2)return point, x, y, sdef GetMainDirection(img, r, c, radius, sigma, BinNum):expf_scale = -1.0 / (2.0 * sigma * sigma)X = []Y = []W = []temphist = []for i in range(BinNum):temphist.append(0.0)# 图像梯度直方图统计的像素范围k = 0for i in range(-radius, radius + 1):y = r + iif y <= 0 or y >= img.shape[0] - 1:continuefor j in range(-radius, radius + 1):x = c + jif x <= 0 or x >= img.shape[1] - 1:continuedx = (img[y, x + 1] - img[y, x - 1])dy = (img[y - 1, x] - img[y + 1, x])X.append(dx)Y.append(dy)W.append((i * i + j * j) * expf_scale)k += 1length = kW = np.exp(np.array(W))Y = np.array(Y)X = np.array(X)Ori = np.arctan2(Y, X) * 180 / np.piMag = (X ** 2 + Y ** 2) ** 0.5# 计算直方图的每个binfor k in range(length):bin = int(np.round((BinNum / 360.0) * Ori[k]))if bin >= BinNum:bin -= BinNumif bin < 0:bin += BinNumtemphist[bin] += W[k] * Mag[k]# smooth the histogram# 高斯平滑temp = [temphist[BinNum - 1], temphist[BinNum - 2], temphist[0], temphist[1]]temphist.insert(0, temp[0])temphist.insert(0, temp[1])temphist.insert(len(temphist), temp[2])temphist.insert(len(temphist), temp[3]) # paddinghist = []for i in range(BinNum):hist.append((temphist[i] + temphist[i + 4]) * (1.0 / 16.0) + (temphist[i + 1] + temphist[i + 3]) * (4.0 / 16.0) +temphist[i + 2] * (6.0 / 16.0))# 得到主方向maxval = max(hist)return maxval, hist# 函数2.1 LocateKeyPoint
# 功能:关键点定位,共分为5步
def LocateKeyPoint(DoG, sigma, GuassianPyramid, n, BinNum=36, contrastThreshold=0.04, edgeThreshold=10.0):SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR = 1.52SIFT_ORI_RADIUS = 3 * SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTRSIFT_ORI_PEAK_RATIO = 0.8SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR = 512.0# SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE = 48SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE = 1KeyPoints = []O = len(DoG)S = len(DoG[0])for o in range(O):for s in range(1, S - 1):# 第一步:设定阈值threshold = 0.5 * contrastThreshold / (n * 255 * SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)# 用于阈值化,去噪img_prev = DoG[o][s - 1]img = DoG[o][s]img_next = DoG[o][s + 1]for i in range(img.shape[0]):for j in range(img.shape[1]):val = img[i, j]eight_neiborhood_prev = img_prev[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img_prev.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img_prev.shape[1])]eight_neiborhood = img[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img.shape[1])]eight_neiborhood_next = img_next[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img_next.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img_next.shape[1])]# 第二步:阈值化,在高斯差分金字塔中找极值if np.abs(val) > threshold and \((val > 0 and (val >= eight_neiborhood_prev).all() and (val >= eight_neiborhood).all() and (val >= eight_neiborhood_next).all())or (val < 0 and (val <= eight_neiborhood_prev).all() and (val <= eight_neiborhood).all() and (val <= eight_neiborhood_next).all())): # 如果某点大于阈值,并且 比周围8个点、上下2*9个点共26个点都大或都小,则认为是关键点# 第三步:精调位置,通过函数2.1.1 adjustLocalExtrema:实现point, x, y, layer = adjustLocalExtrema(DoG, o, s, i, j, contrastThreshold, edgeThreshold,sigma, n, SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)if point == None:continuescl_octv = point[-1] * 0.5 / (1 << o)# GetMainDirection:(确定极值点的位置以后就)求主方向omax, hist = GetMainDirection(GuassianPyramid[o][layer], x, y,int(np.round(SIFT_ORI_RADIUS * scl_octv)),SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR * scl_octv, BinNum)mag_thr = omax * SIFT_ORI_PEAK_RATIOfor k in range(BinNum):if k > 0:l = k - 1else:l = BinNum - 1if k < BinNum - 1:r2 = k + 1else:r2 = 0if hist[k] > hist[l] and hist[k] > hist[r2] and hist[k] >= mag_thr:bin = k + 0.5 * (hist[l] - hist[r2]) / (hist[l] - 2 * hist[k] + hist[r2])if bin < 0:bin = BinNum + binelse:if bin >= BinNum:bin = bin - BinNumtemp = point[:]temp.append((360.0 / BinNum) * bin)KeyPoints.append(temp)return KeyPoints# calcSIFTDescriptor:更小的计算描述符函数
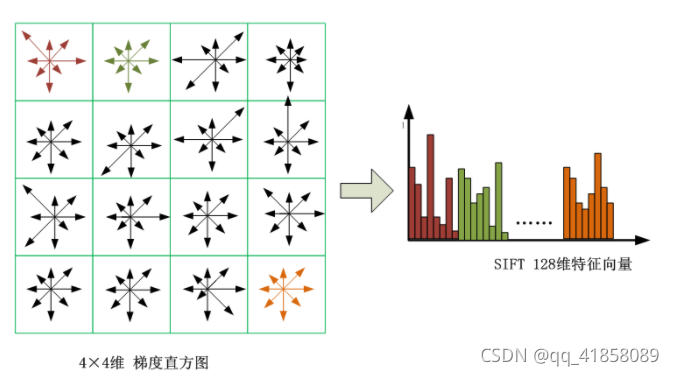
def calcSIFTDescriptor(img, ptf, ori, scl, d, n, SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR=3.0, SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THR=0.2,SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR=512.0, FLT_EPSILON=1.19209290E-07):dst = []pt = [int(np.round(ptf[0])), int(np.round(ptf[1]))] # 坐标点取整# 旋转到主方向cos_t = np.cos(ori * (np.pi / 180)) # 余弦值sin_t = np.sin(ori * (np.pi / 180)) # 正弦值bins_per_rad = n / 360.0exp_scale = -1.0 / (d * d * 0.5)hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl# radius: 统计区域边长的一半radius = int(np.round(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951 * (d + 1) * 0.5))cos_t /= hist_widthsin_t /= hist_widthrows = img.shape[0]cols = img.shape[1]hist = [0.0] * ((d + 2) * (d + 2) * (n + 2))X = []Y = []RBin = []CBin = []W = []k = 0for i in range(-radius, radius + 1):for j in range(-radius, radius + 1):c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_tr_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_trbin = r_rot + d // 2 - 0.5cbin = c_rot + d // 2 - 0.5r = pt[1] + ic = pt[0] + jif rbin > -1 and rbin < d and cbin > -1 and cbin < d and r > 0 and r < rows - 1 and c > 0 and c < cols - 1:dx = (img[r, c + 1] - img[r, c - 1])dy = (img[r - 1, c] - img[r + 1, c])X.append(dx)Y.append(dy)RBin.append(rbin)CBin.append(cbin)W.append((c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale)k += 1length = kY = np.array(Y)X = np.array(X)Ori = np.arctan2(Y, X) * 180 / np.piMag = (X ** 2 + Y ** 2) ** 0.5W = np.exp(np.array(W))for k in range(length):rbin = RBin[k]cbin = CBin[k]obin = (Ori[k] - ori) * bins_per_radmag = Mag[k] * W[k]r0 = int(rbin)c0 = int(cbin)o0 = int(obin)rbin -= r0cbin -= c0obin -= o0if o0 < 0:o0 += nif o0 >= n:o0 -= n# histogram update using tri-linear interpolationv_r1 = mag * rbinv_r0 = mag - v_r1v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbinv_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbinv_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obinv_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obinv_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obinv_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obinv_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n + 2) + o0hist[idx] += v_rco000hist[idx + 1] += v_rco001hist[idx + (n + 2)] += v_rco010hist[idx + (n + 3)] += v_rco011hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n + 2)] += v_rco100hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n + 2) + 1] += v_rco101hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n + 2)] += v_rco110hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n + 2) + 1] += v_rco111# finalize histogram, since the orientation histograms are circularfor i in range(d):for j in range(d):idx = ((i + 1) * (d + 2) + (j + 1)) * (n + 2)hist[idx] += hist[idx + n]hist[idx + 1] += hist[idx + n + 1]for k in range(n):dst.append(hist[idx + k])# copy histogram to the descriptor,# apply hysteresis thresholding# and scale the result, so that it can be easily converted# to byte arraynrm2 = 0length = d * d * nfor k in range(length):nrm2 += dst[k] * dst[k]thr = np.sqrt(nrm2) * SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THRnrm2 = 0for i in range(length):val = min(dst[i], thr)dst[i] = valnrm2 += val * valnrm2 = SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR / max(np.sqrt(nrm2), FLT_EPSILON) # 归一化for k in range(length):dst[k] = min(max(dst[k] * nrm2, 0), 255)return dst# calcDescriptors:计算描述符
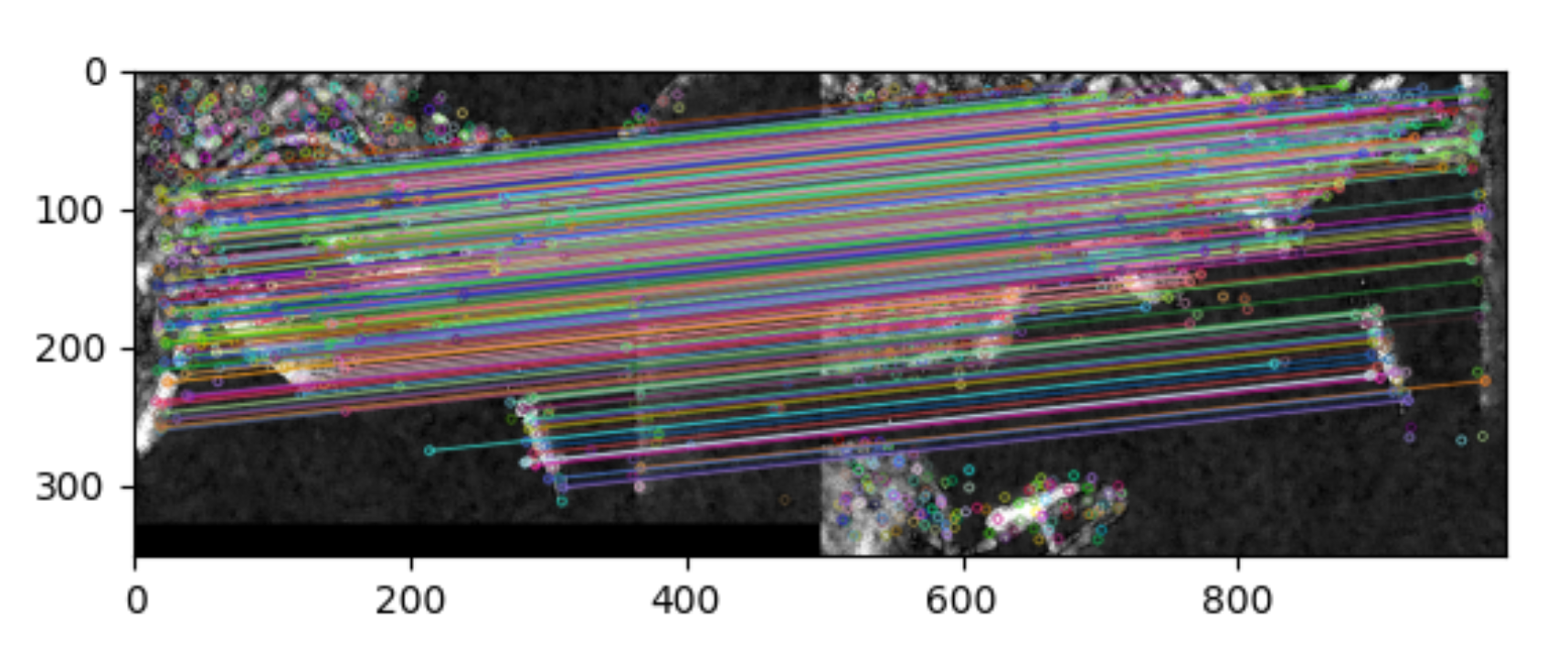
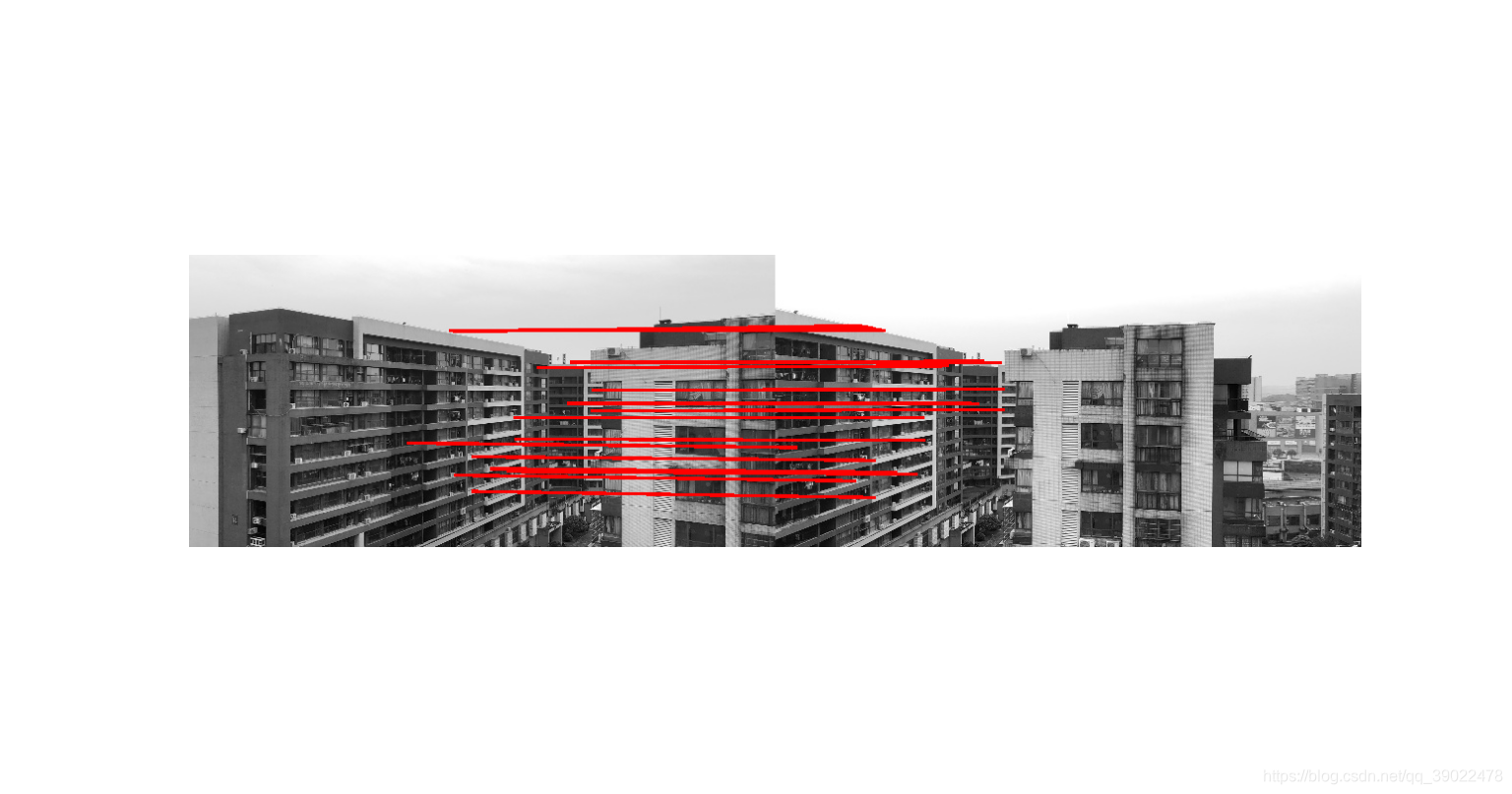
def calcDescriptors(gpyr, keypoints, SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH=4, SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS=8):# SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH = 4,描述直方图的宽度# SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS = 8d = SIFT_DESCR_WIDTHn = SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINSdescriptors = []# keypoints(x,y,低8位组数次8位层数,尺度,主方向)for i in range(len(keypoints)):kpt = keypoints[i]o = kpt[2] & 255 # 组序号s = (kpt[2] >> 8) & 255 # 该特征点所在的层序号scale = 1.0 / (1 << o) # 缩放倍数size = kpt[3] * scale # 该特征点所在组的图像尺寸ptf = [kpt[1] * scale, kpt[0] * scale] # 该特征点在金字塔组中的坐标img = gpyr[o][s] # 该点所在的金字塔图像descriptors.append(calcSIFTDescriptor(img, ptf, kpt[-1], size * 0.5, d, n)) # calcSIFTDescriptor:更小的计算描述符函数return descriptorsdef SIFT(img, showDoGimgs=False):# 1. 建立高斯差分金字塔,SIFT_SIGMA = 1.6SIFT_INIT_SIGMA = 0.5 # 假设的摄像头的尺度sigma0 = np.sqrt(SIFT_SIGMA ** 2 - SIFT_INIT_SIGMA ** 2) #初始sigma0n = 2######DoG, GuassianPyramid,octaves = getDoG(img, n, sigma0) # 函数1.1,getDoG:得到高斯金字塔和高斯差分金字塔if showDoGimgs:plt.figure(1)for i in range(octaves):for j in range(n + 3):array = np.array(GuassianPyramid[i][j], dtype=np.float32)plt.subplot(octaves, n + 3, j + (i) * octaves + 1)plt.imshow(array.astype(np.uint8), cmap='gray')plt.axis('off')plt.show()plt.figure(2)for i in range(octaves):for j in range(n + 2):array = np.array(DoG[i][j], dtype=np.float32)plt.subplot(octaves, n + 3, j + (i) * octaves + 1)plt.imshow(array.astype(np.uint8), cmap='gray')plt.axis('off')plt.show()#2. 确定关键点位置,为关键点赋予方向KeyPoints = LocateKeyPoint(DoG, SIFT_SIGMA, GuassianPyramid, n) # 函数2.1,LocateKeyPoint:关键点定位#3. 计算关键点的描述符discriptors = calcDescriptors(GuassianPyramid, KeyPoints) # 函数3.1,calcDescriptors:计算描述符return KeyPoints, discriptorsdef Lines(img, info, color=(255, 0, 0), err=700):if len(img.shape) == 2:result = np.dstack((img, img, img))else:result = imgk = 0for i in range(result.shape[0]):for j in range(result.shape[1]):temp = (info[:, 1] - info[:, 0])A = (j - info[:, 0]) * (info[:, 3] - info[:, 2])B = (i - info[:, 2]) * (info[:, 1] - info[:, 0])temp[temp == 0] = 1e-9t = (j - info[:, 0]) / tempe = np.abs(A - B)temp = e < errif (temp * (t >= 0) * (t <= 1)).any():result[i, j] = colork += 1#print(k)return resultdef drawLines(X1, X2, Y1, Y2, dis, img, num=10):info = list(np.dstack((X1, X2, Y1, Y2, dis))[0])info = sorted(info, key=lambda x: x[-1])info = np.array(info)info = info[:min(num, info.shape[0]), :]img = Lines(img, info)# plt.imsave('./sift/3.jpg', img)if len(img.shape) == 2:plt.imshow(img.astype(np.uint8), cmap='gray')else:plt.imshow(img.astype(np.uint8))plt.axis('off')# plt.plot([info[:,0], info[:,1]], [info[:,2], info[:,3]], 'c')# fig = plt.gcf()# fig.set_size_inches(int(img.shape[0]/100.0),int(img.shape[1]/100.0))plt.savefig('result.jpg')plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':origimg = plt.imread(r'01.jpg') # 读第一张图片if len(origimg.shape) == 3:#如果是彩色图,就按照三通道取均值的方式转成灰度图img = origimg.mean(axis=-1)else:img = origimgkeyPoints, discriptors = SIFT(img) # 用SIFT算法计算关键点(x坐标,y坐标,sigma,主方向,梯度幅值)和描述符(128维的向量)origimg2 = plt.imread(r'02.jpg') # 读第二张图片if len(origimg.shape) == 3:img2 = origimg2.mean(axis=-1)else:img2 = origimg2ScaleRatio = img.shape[0] * 1.0 / img2.shape[0]img2 = np.array(Image.fromarray(img2).resize((int(round(ScaleRatio * img2.shape[1])), img.shape[0]), Image.BICUBIC))keyPoints2, discriptors2 = SIFT(img2) # 用SIFT算关键点和描述符indexs = []deltas = []for i in range(len(keyPoints2)):ds = discriptors2[i]mindetal = 10000000index = -1detal = 0for j in range(len(keyPoints)):ds0 = discriptors[j]d = np.array(ds)-np.array(ds0)detal = d.dot(d)if( detal <= mindetal):mindetal = detalindex = jindexs.append(index)deltas.append(mindetal)keyPoints = np.array(keyPoints)[:,:2]keyPoints2 = np.array(keyPoints2)[:,:2]keyPoints2[:, 1] = img.shape[1] + keyPoints2[:, 1]origimg2 = np.array(Image.fromarray(origimg2).resize((img2.shape[1],img2.shape[0]), Image.BICUBIC))result = np.hstack((origimg,origimg2))keyPoints = keyPoints[indexs[:]]X1 = keyPoints[:, 1]X2 = keyPoints2[:, 1]Y1 = keyPoints[:, 0]Y2 = keyPoints2[:, 0]drawLines(X1,X2,Y1,Y2,deltas,result)#把匹配的结果放到这里画线3. 算法结果
20点匹配结果如下:

最终展示ppt:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Y1Os2imDhRvNptHwWShdBw
提取码:2n0s