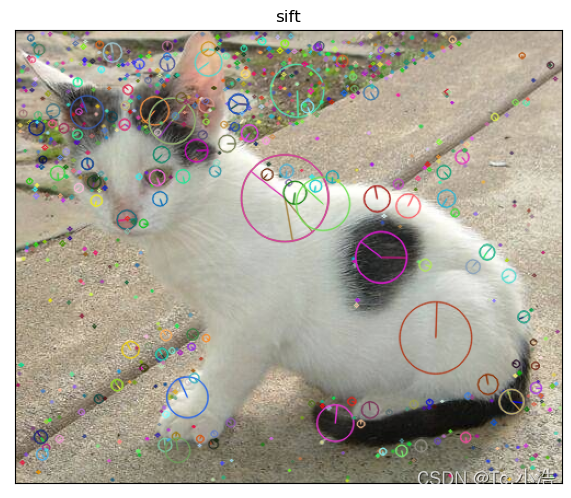
说明:本文旨在给出 SIFT 算法的具体实现,而在 SIFT 详解上只是做出简单介绍,在这里可以给大家推荐一篇好文:https://blog.csdn.net/zddblog/article/details/7521424;结合这篇文章和下文的具体代码实现,我相信你能很快掌握并运用 SIFT 算法,加油哦!!!如有疑问大家可以一起讨论学习!!!
一、SIFT算法简介
SIFT,即尺度不变特征变换(Scale-invariant feature transform,SIFT),是用于图像处理领域的一种描述。这种描述具有尺度不变性,可在图像中检测出关键点,是一种局部特征描述子。该方法于1999年由David Lowe 首先发表于计算机视觉国际会议(International Conference on Computer Vision,ICCV),2004年再次经David Lowe整理完善后发表于International journal of computer vision(IJCV)。截止2014年8月,该论文单篇被引次数达25000余次。
1、SIFT算法的特点
(1) SIFT特征是图像的局部特征,其对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化保持不变性,对视角变化、仿射变换、噪声也保持一定程度的稳定性;
(2)独特性(Distinctiveness)好,信息量丰富,适用于在海量特征数据库中进行快速、准确的匹配;
(3)多量性,即使少数的几个物体也可以产生大量的SIFT特征向量;
(4)高速性,经优化的SIFT匹配算法甚至可以达到实时的要求;
(5)可扩展性,可以很方便的与其他形式的特征向量进行联合。
2、SIFT算法可以解决的问题
目标的自身状态、场景所处的环境和成像器材的成像特性等因素影响图像配准/目标识别跟踪的性能。而SIFT算法在一定程度上可解决:
(1)目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
(2)图像仿射/投影变换(视点viewpoint)
(3)光照影响(illumination)
(4)目标遮挡(occlusion)
(5)杂物场景(clutter)
(6)噪声
SIFT算法的实质是在不同的尺度空间上查找关键点(特征点),并计算出关键点的方向。SIFT所查找到的关键点是一些十分突出,不会因光照,仿射变换和噪音等因素而变化的点,如角点、边缘点、暗区的亮点及亮区的暗点等。
二、SIFT算法分为如下四步
1. 尺度空间极值检测
搜索所有尺度上的图像位置。通过高斯微分函数来识别潜在的对于尺度和旋转不变的兴趣点。
2. 关键点定位
在每个候选的位置上,通过一个拟合精细的模型来确定位置和尺度。关键点的选择依据于它们的稳定程度。
3. 方向确定
基于图像局部的梯度方向,分配给每个关键点位置一个或多个方向。所有后面的对图像数据的操作都相对于关键点的方向、尺度和位置进行变换,从而提供对于这些变换的不变性。
4. 关键点描述
在每个关键点周围的邻域内,在选定的尺度上测量图像局部的梯度。这些梯度被变换成一种表示,这种表示允许比较大的局部形状的变形和光照变化。
三、SIFT具体实现
说明:代码实现主要有七个源文件,我和大家一样有时候下载了好几个资源然而没有一个能用的,导致最后都不知道要下载哪一个、是否要下载;所以这里直接把代码贴出来了!
1、mySift.h
#pragma once //防止头文件重复包含和下面作用一样#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include<opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace cv;/*************************定义常量*****************************///高斯核大小和标准差关系,size=2*(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO*sigma)+1,经常设置GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO=2-3之间
const double GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO = 3;const int MAX_OCTAVES = 8; //金字塔最大组数const float CONTR_THR = 0.04f; //默认是的对比度阈值(D(x))const float CURV_THR = 10.0f; //关键点主曲率阈值const float INIT_SIGMA = 0.5f; //输入图像的初始尺度const int IMG_BORDER = 2; //图像边界忽略的宽度,也可以改为 1 const int MAX_INTERP_STEPS = 5; //关键点精确插值次数const int ORI_HIST_BINS = 36; //计算特征点方向直方图的BINS个数const float ORI_SIG_FCTR = 1.5f; //计算特征点主方向时候,高斯窗口的标准差因子const float ORI_RADIUS = 3 * ORI_SIG_FCTR; //计算特征点主方向时,窗口半径因子const float ORI_PEAK_RATIO = 0.8f; //计算特征点主方向时,直方图的峰值比const int DESCR_WIDTH = 4; //描述子直方图的网格大小(4x4)const int DESCR_HIST_BINS = 8; //每个网格中直方图角度方向的维度const float DESCR_MAG_THR = 0.2f; //描述子幅度阈值const float DESCR_SCL_FCTR = 3.0f; //计算描述子时,每个网格的大小因子const int SAR_SIFT_GLOH_ANG_GRID = 8; //GLOH网格沿角度方向等分区间个数const int SAR_SIFT_DES_ANG_BINS = 8; //像素梯度方向在0-360度内等分区间个数const float SAR_SIFT_RADIUS_DES = 12.0f; //描述子邻域半径 const int Mmax = 8; //像素梯度方向在0-360度内等分区间个数const double T = 100.0; //sobel算子去除冗余特征点的阈值const float SAR_SIFT_GLOH_RATIO_R1_R2 = 0.73f;//GLOH网格中间圆半径和外圆半径之比const float SAR_SIFT_GLOH_RATIO_R1_R3 = 0.25f;//GLOH网格最内层圆半径和外圆半径之比#define Feature_Point_Minimum 1500 //输入图像特征点最小个数#define We 0.2#define Wn 0.5#define Row_num 3#define Col_num 3#define SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE 48 //不理解,后面可查原论文/************************sift类*******************************/
class mySift
{public://默认构造函数mySift(int nfeatures = 0, int nOctaveLayers = 3, double contrastThreshold = 0.03,double edgeThreshold = 10, double sigma = 1.6, bool double_size = true) :nfeatures(nfeatures),nOctaveLayers(nOctaveLayers), contrastThreshold(contrastThreshold),edgeThreshold(edgeThreshold), sigma(sigma), double_size(double_size) {}//获得尺度空间每组中间层数int get_nOctave_layers() { return nOctaveLayers; }//获得图像尺度是否扩大一倍bool get_double_size() { return double_size; }//计算金字塔组数int num_octaves(const Mat& image);//生成高斯金字塔第一组,第一层图像void create_initial_image(const Mat& image, Mat& init_image);//使用 sobel 算子创建高斯金字塔第一层图像,以减少冗余特征点void sobel_create_initial_image(const Mat& image, Mat& init_image);//创建高斯金字塔void build_gaussian_pyramid(const Mat& init_image, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyramid, int nOctaves);//创建高斯差分金字塔void build_dog_pyramid(vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyramid, const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyramid);//该函数生成高斯差分金字塔void amplit_orient(const Mat& image, vector<Mat>& amplit, vector<Mat>& orient, float scale, int nums);//DOG金字塔特征点检测void find_scale_space_extrema(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints);//DOG金字塔特征点检测,特征点方向细化版void find_scale_space_extrema1(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints);//计算特征点的描述子void calc_sift_descriptors(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,Mat& descriptors, const vector<Mat>& amplit, const vector<Mat>& orient);//构建空间尺度—主要是为了获取 amplit 和 orient 在使用 GLOH 描述子的时候使用void build_sar_sift_space(const Mat& image, vector<Mat>& sar_harris_fun, vector<Mat>& amplit, vector<Mat>& orient);//GLOH 计算一个特征描述子void calc_gloh_descriptors(const vector<Mat>& amplit, const vector<Mat>& orient, const vector<KeyPoint>& keys, Mat& descriptors);//特征点检测void detect(const Mat& image, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,vector<vector<vector<float>>>& all_cell_contrasts,vector<vector<float>>& average_contrast, vector<vector<int>>& n_cells, vector<int>& num_cell, vector<vector<int>>& available_n,vector<int>& available_num, vector<KeyPoint>& final_keypoints,vector<KeyPoint>& Final_keypoints, vector<KeyPoint>& Final_Keypoints);//特征点描述void comput_des(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& final_keypoints, const vector<Mat>& amplit,const vector<Mat>& orient, Mat& descriptors);private:int nfeatures; //设定检测的特征点的个数值,如果此值设置为0,则不影响结果int nOctaveLayers; //每组金字塔中间层数double contrastThreshold; //对比度阈值(D(x))double edgeThreshold; //特征点边缘曲率阈值double sigma; //高斯尺度空间初始层的尺度bool double_size; //是否上采样原始图像};//注意类结束的分号
2、mySift.cpp
#include"mySift.h"#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream> //输入输出
#include<vector> //vector
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric> //用于容器元素求和#include<opencv2\core\hal\hal.hpp>
#include<opencv2\core\hal\intrin.hpp>#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2\core\core.hpp> //opencv基本数据结构
#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp> //图像界面
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp> //基本图像处理函数
#include<opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp> //特征提取
#include<opencv2\imgproc\types_c.h>
#include<opencv2\videoio.hpp>
#include <highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include <imgproc\imgproc.hpp>/******************根据输入图像大小计算高斯金字塔的组数****************************/
/*image表示原始输入灰度图像,inline函数必须在声明处定义
double_size_image表示是否在构建金字塔之前上采样原始图像
*/
int mySift::num_octaves(const Mat& image)
{int temp;float size_temp = (float)min(image.rows, image.cols);temp = cvRound(log(size_temp) / log((float)2) - 2);if (double_size)temp += 1;if (temp > MAX_OCTAVES) //尺度空间最大组数设置为MAX_OCTAVEStemp = MAX_OCTAVES;return temp;
}/************************sobel滤波器计算高斯尺度空间图像梯度大小*****************************/
void sobelfilter(Mat& image, Mat& G)
{// image 是经过归一化后的数据 (0,1)int rows = image.rows;int cols = image.cols;float dx = 0.0, dy = 0.0;//cv::Mat Gx = cv::Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_32FC1); //包含了图像像素在水平方向上的导数的近似值的图像//cv::Mat Gy = cv::Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_32FC1); //包含了图像像素在垂直方向上的导数的近似值的图像G = Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_32FC1); //在每个像素点处的灰度大小由Gx和Gy共同决定double v = 0.0, vx, vy;//利用 sobel 算子求梯度幅度图像for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){v = 0.0;if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == rows - 1 || j == cols - 1){G.at<float>(i, j) = 0.0;}else{float dx = image.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(i, j + 1) - 2 * image.at<float>(i, j - 1)+ image.at<float>(i + 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1);float dy = image.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(i + 1, j) - 2 * image.at<float>(i - 1, j) +image.at<float>(i + 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1);v = abs(dx) + abs(dy); //简化后 G = |Gx| + |Gy|//保证像素值在有效范围内v = fmax(v, 0); //返回浮点数中较大的一个v = fmin(v, 255); //返回浮点数中较小的一个if (v > T) //T为阈值等于50G.at<float>(i, j) = (float)v;elseG.at<float>(i, j) = 0.0;}}}//水平方向上的导数的近似值的图像/*for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){vx = 0;if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == rows - 1 || j == cols - 1)Gx.at<float>(i, j) = 0;else{dx = image.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(i, j + 1) - 2 * image.at<float>(i, j - 1)+ image.at<float>(i + 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1);vx = abs(dx);vx = fmax(vx, 0); vx = fmin(vx, 255);Gx.at<float>(i, j) = (float)vx;}}}*///垂直方向上的导数的近似值的图像/*for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){vy = 0;if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == rows - 1 || j == cols - 1)Gy.at<float>(i, j) = 0;else{dy = image.at<float>(i + 1, j - 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(i + 1, j) - 2 * image.at<float>(i - 1, j) +image.at<float>(i + 1, j + 1) - image.at<float>(i - 1, j + 1);vy = abs(dy);vy = fmax(vy, 0); vx = fmin(vy, 255);Gy.at<float>(i, j) = (float)vy;}}}*///cv::imshow("Gx", Gx); // horizontal//cv::imshow("Gy", Gy); // vertical//cv::imshow("G", G); // gradient
}/*********该函数根据尺度和窗口半径生成ROEWA滤波模板************/
/*size表示核半径,因此核宽度是2*size+1scale表示指数权重参数kernel表示生成的滤波核*/
static void roewa_kernel(int size, float scale, Mat& kernel)
{kernel.create(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1, CV_32FC1);for (int i = -size; i <= size; ++i){float* ptr_k = kernel.ptr<float>(i + size);for (int j = -size; j <= size; ++j){ptr_k[j + size] = exp(-1.f * (abs(i) + abs(j)) / scale);}}
}/************************创建高斯金字塔第一组,第一层图像************************************/
/*image表示输入原始图像init_image表示生成的高斯尺度空间的第一层图像*/
void mySift::create_initial_image(const Mat& image, Mat& init_image)
{Mat gray_image;if (image.channels() != 1)cvtColor(image, gray_image, CV_RGB2GRAY); //转换为灰度图像elsegray_image = image.clone();Mat floatImage; //转换到0-1之间的浮点类型数据归一化,方便接下来的处理//float_image=(float)gray_image*(1.0/255.0)gray_image.convertTo(floatImage, CV_32FC1, 1.0 / 255.0, 0);double sig_diff = 0;if (double_size){Mat temp_image;//通过插值的方法改变图像尺寸的大小resize(floatImage, temp_image, Size(2 * floatImage.cols, 2 * floatImage.rows), 0.0, 0.0, INTER_LINEAR);//高斯平滑的标准差,值较大时平滑效果比较明显sig_diff = sqrt(sigma * sigma - 4.0 * INIT_SIGMA * INIT_SIGMA);//高斯滤波窗口大小选择很重要,这里选择(4*sig_diff_1+1)-(6*sig_diff+1)之间,且四舍五入int kernel_width = 2 * cvRound(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO * sig_diff) + 1;Size kernel_size(kernel_width, kernel_width);//对图像进行平滑处理(高斯模糊),即降低图像的分辨率,高斯模糊是实现尺度变换的唯一变换核,并其实唯一的线性核GaussianBlur(temp_image, init_image, kernel_size, sig_diff, sig_diff);}else{sig_diff = sqrt(sigma * sigma - 1.0 * INIT_SIGMA * INIT_SIGMA);//高斯滤波窗口大小选择很重要,这里选择(4*sig_diff_1+1)-(6*sig_diff+1)之间int kernel_width = 2 * cvRound(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO * sig_diff) + 1;Size kernel_size(kernel_width, kernel_width);GaussianBlur(floatImage, init_image, kernel_size, sig_diff, sig_diff);}
}/************************使用 sobel 算子创建高斯金字塔第一组,第一层图像****************************/
//目的是为了减少冗余特征点
void mySift::sobel_create_initial_image(const Mat& image, Mat& init_image)
{Mat gray_image, gray_images; //gray_images用于存放经过sobel算子操作后的图像if (image.channels() != 1)cvtColor(image, gray_image, CV_RGB2GRAY); //转换为灰度图像elsegray_image = image.clone();sobelfilter(gray_image, gray_images);Mat floatImage; //转换到0-1之间的浮点类型数据归一化,方便接下来的处理//float_image=(float)gray_image*(1.0/255.0)gray_images.convertTo(floatImage, CV_32FC1, 1.0 / 255.0, 0);double sig_diff = 0;if (double_size){Mat temp_image;//通过插值的方法改变图像尺寸的大小resize(floatImage, temp_image, Size(2 * floatImage.cols, 2 * floatImage.rows), 0.0, 0.0, INTER_LINEAR);//高斯平滑的标准差,值较大时平滑效果比较明显sig_diff = sqrt(sigma * sigma - 4.0 * INIT_SIGMA * INIT_SIGMA);//高斯滤波窗口大小选择很重要,这里选择(4*sig_diff_1+1)-(6*sig_diff+1)之间,且四舍五入int kernel_width = 2 * cvRound(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO * sig_diff) + 1;Size kernel_size(kernel_width, kernel_width);//对图像进行平滑处理(高斯模糊),即降低图像的分辨率,高斯模糊是实现尺度变换的唯一变换核,并其实唯一的线性核GaussianBlur(temp_image, init_image, kernel_size, sig_diff, sig_diff);}else{sig_diff = sqrt(sigma * sigma - 1.0 * INIT_SIGMA * INIT_SIGMA);//高斯滤波窗口大小选择很重要,这里选择(4*sig_diff_1+1)-(6*sig_diff+1)之间int kernel_width = 2 * cvRound(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO * sig_diff) + 1;Size kernel_size(kernel_width, kernel_width);GaussianBlur(floatImage, init_image, kernel_size, sig_diff, sig_diff);}
}/**************************生成高斯金字塔*****************************************//*init_image表示已经生成的高斯金字塔第一层图像gauss_pyramid表示生成的高斯金字塔nOctaves表示高斯金字塔的组数*/
void mySift::build_gaussian_pyramid(const Mat& init_image, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyramid, int nOctaves)
{vector<double> sig;sig.push_back(sigma);double k = pow(2.0, 1.0 / nOctaveLayers); //高斯金字塔每一层的系数 kfor (int i = 1; i < nOctaveLayers + 3; ++i){double prev_sig = pow(k, i - 1) * sigma; //每一个尺度层的尺度double curr_sig = k * prev_sig;//组内每层的尺度坐标计算公式sig.push_back(sqrt(curr_sig * curr_sig - prev_sig * prev_sig));}gauss_pyramid.resize(nOctaves);for (int i = 0; i < nOctaves; ++i){gauss_pyramid[i].resize(nOctaveLayers + 3);}for (int i = 0; i < nOctaves; ++i) //对于每一组{for (int j = 0; j < nOctaveLayers + 3; ++j) //对于组内的每一层{if (i == 0 && j == 0) //第一组,第一层gauss_pyramid[0][0] = init_image;else if (j == 0){resize(gauss_pyramid[i - 1][3], gauss_pyramid[i][0],Size(gauss_pyramid[i - 1][3].cols / 2,gauss_pyramid[i - 1][3].rows / 2), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);}else{//高斯滤波窗口大小选择很重要,这里选择(4*sig_diff_1+1)-(6*sig_diff+1)之间int kernel_width = 2 * cvRound(GAUSS_KERNEL_RATIO * sig[j]) + 1;Size kernel_size(kernel_width, kernel_width);GaussianBlur(gauss_pyramid[i][j - 1], gauss_pyramid[i][j], kernel_size, sig[j], sig[j]);}}}
}/*******************生成高斯差分金字塔,即LOG金字塔*************************/
/*dog_pyramid表示DOG金字塔gauss_pyramin表示高斯金字塔*/
void mySift::build_dog_pyramid(vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyramid, const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyramid)
{vector<vector<Mat>>::size_type nOctaves = gauss_pyramid.size();for (vector<vector<Mat>>::size_type i = 0; i < nOctaves; ++i){//用于存放每一个梯度中的所有尺度层vector<Mat> temp_vec;for (auto j = 0; j < nOctaveLayers + 2; ++j){Mat temp_img = gauss_pyramid[i][j + 1] - gauss_pyramid[i][j];temp_vec.push_back(temp_img);}dog_pyramid.push_back(temp_vec);temp_vec.clear();}
}/***********生成高斯差分金字塔当前层对应的梯度幅度图像和梯度方向图像***********/
/*image为高斯差分金字塔当前层图像*amplit为当前层梯度幅度图像*orient为当前层梯度方向图像*scale当前层尺度*nums为相对底层的层数*/
void mySift::amplit_orient(const Mat& image, vector<Mat>& amplit, vector<Mat>& orient, float scale, int nums)
{//分配内存amplit.resize(Mmax * nOctaveLayers);orient.resize(Mmax * nOctaveLayers);int radius = cvRound(2 * scale);Mat kernel; //kernel(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1);roewa_kernel(radius, scale, kernel); //返回滤波核,也即指数部分,存放在矩阵的右下角//四个滤波模板生成Mat W34 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1); //把kernel矩阵下半部分复制到对应部分Mat W12 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1); //把kernel矩阵上半部分复制到对应部分Mat W14 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1); //把kernel矩阵右半部分复制到对应部分Mat W23 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1); //把kernel矩阵左半部分复制到对应部分kernel(Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1), Range::all()).copyTo(W34(Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1), Range::all()));kernel(Range(0, radius), Range::all()).copyTo(W12(Range(0, radius), Range::all()));kernel(Range::all(), Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1)).copyTo(W14(Range::all(), Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1)));kernel(Range::all(), Range(0, radius)).copyTo(W23(Range::all(), Range(0, radius)));//滤波Mat M34, M12, M14, M23;double eps = 0.00001;//float_image为图像归一化后的图像数据,做卷积运算filter2D(image, M34, CV_32FC1, W34, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(image, M12, CV_32FC1, W12, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(image, M14, CV_32FC1, W14, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(image, M23, CV_32FC1, W23, Point(-1, -1), eps);//计算水平梯度和竖直梯度Mat Gx, Gy;log((M14) / (M23), Gx);log((M34) / (M12), Gy);//计算梯度幅度和梯度方向magnitude(Gx, Gy, amplit[nums]); //梯度幅度图像,平方和开平方phase(Gx, Gy, orient[nums], true); //梯度方向图像}/***********************该函数计算尺度空间特征点的主方向,用于后面特征点的检测***************************/
/*image表示特征点所在位置的高斯图像,后面可对着源码进行修改pt表示特征点的位置坐标(x,y)scale特征点的尺度n表示直方图bin个数hist表示计算得到的直方图函数返回值是直方图hist中的最大数值*/
static float clac_orientation_hist(const Mat& image, Point pt, float scale, int n, float* hist)
{int radius = cvRound(ORI_RADIUS * scale); //特征点邻域半径(3*1.5*scale)int len = (2 * radius + 1) * (2 * radius + 1); //特征点邻域像素总个数(最大值)float sigma = ORI_SIG_FCTR * scale; //特征点邻域高斯权重标准差(1.5*scale)float exp_scale = -1.f / (2 * sigma * sigma); //权重的指数部分//使用AutoBuffer分配一段内存,这里多出4个空间的目的是为了方便后面平滑直方图的需要AutoBuffer<float> buffer((4 * len) + n + 4);//X保存水平差分,Y保存数值差分,Mag保存梯度幅度,Ori保存梯度角度,W保存高斯权重float* X = buffer, * Y = buffer + len, * Mag = Y, * Ori = Y + len, * W = Ori + len;float* temp_hist = W + len + 2; //临时保存直方图数据for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)temp_hist[i] = 0.f; //数据清零//计算邻域像素的水平差分和竖直差分int k = 0;for (int i = -radius; i < radius; ++i){int y = pt.y + i; //邻域点的纵坐标if (y <= 0 || y >= image.rows - 1)continue;for (int j = -radius; j < radius; ++j){int x = pt.x + j;if (x <= 0 || x >= image.cols - 1)continue;float dx = image.at<float>(y, x + 1) - image.at<float>(y, x - 1); //水平差分float dy = image.at<float>(y + 1, x) - image.at<float>(y - 1, x); //竖直差分//保存水平差分和竖直差分及其对应的权重X[k] = dx;Y[k] = dy;W[k] = (i * i + j * j) * exp_scale;++k;}}len = k; //邻域内特征点的个数cv::hal::exp(W, W, len); //计算邻域内所有像素的高斯权重cv::hal::fastAtan2(Y, X, Ori, len, true); //计算邻域内所有像素的梯度方向,角度范围0-360度cv::hal::magnitude32f(X, Y, Mag, len); //计算邻域内所有像素的梯度幅度,计算的是数学意义上的梯度//遍历邻域的像素for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){int bin = cvRound((n / 360.f) * Ori[i]); //利用像素的梯度方向,约束bin的范围在[0,(n-1)]//像素点梯度方向为360度时,和0°一样if (bin >= n)bin = bin - n;if (bin < 0)bin = bin + n;temp_hist[bin] = temp_hist[bin] + Mag[i] * W[i]; //统计邻域内像素各个方向在梯度直方图的幅值(加权后的幅值)}//平滑直方图temp_hist[-1] = temp_hist[n - 1];temp_hist[-2] = temp_hist[n - 2];temp_hist[n] = temp_hist[0];temp_hist[n + 1] = temp_hist[1];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){hist[i] = (temp_hist[i - 2] + temp_hist[i + 2]) * (1.f / 16.f) +(temp_hist[i - 1] + temp_hist[i + 1]) * (4.f / 16.f) +temp_hist[i] * (6.f / 16.f);}//获得直方图中最大值float max_value = hist[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){if (hist[i] > max_value)max_value = hist[i];}return max_value;
}/***********************使用 sobel 滤波器定义的新梯度计算尺度空间特征点的主方向**************************/
static float clac_orientation_hist_2(Mat& image, Point pt, float scale, int n, float* hist)
{Mat output_image; //使用 sobel 滤波器计算的图像的梯度幅度图像sobelfilter(image, output_image); //使用 sobel 滤波器求高斯差分图像的梯度幅度图像int radius = cvRound(ORI_RADIUS * scale); //特征点邻域半径(3*1.5*scale)int len = (2 * radius + 1) * (2 * radius + 1); //特征点邻域像素总个数(最大值)float sigma = ORI_SIG_FCTR * scale; //特征点邻域高斯权重标准差(1.5*scale)float exp_scale = -1.f / (2 * sigma * sigma); //权重的指数部分//使用AutoBuffer分配一段内存,这里多出4个空间的目的是为了方便后面平滑直方图的需要AutoBuffer<float> buffer((4 * len) + n + 4);//X保存水平差分,Y保存数值差分,Mag保存梯度幅度,Ori保存梯度角度,W保存高斯权重float* X = buffer, * Y = buffer + len, * Mag = Y, * Ori = Y + len, * W = Ori + len;float* temp_hist = W + len + 2; //临时保存直方图数据for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)temp_hist[i] = 0.f; //数据清零//计算邻域像素的水平差分和竖直差分int k = 0;for (int i = -radius; i < radius; ++i){int y = pt.y + i; //邻域点的纵坐标,行if (y <= 0 || y >= output_image.rows - 1)continue;for (int j = -radius; j < radius; ++j){int x = pt.x + j; //邻域点的纵坐标,列if (x <= 0 || x >= output_image.cols - 1)continue;//float dx = image.at<float>(y, x + 1) - image.at<float>(y, x - 1); //水平差分float dx = output_image.at<float>(y - 1, x + 1) - output_image.at<float>(y - 1, x - 1)+ 2 * output_image.at<float>(y, x + 1) - 2 * output_image.at<float>(y, x - 1)+ output_image.at<float>(y + 1, x + 1) - output_image.at<float>(y + 1, x - 1);float dy = output_image.at<float>(y + 1, x - 1) - output_image.at<float>(y - 1, x - 1)+ 2 * output_image.at<float>(y + 1, x) - 2 * output_image.at<float>(y - 1, x) +output_image.at<float>(y + 1, x + 1) - output_image.at<float>(y - 1, x + 1);/*float dx = image.at<float>(y - 1, x + 1) - image.at<float>(y - 1, x - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(y, x + 1) - 2 * image.at<float>(y, x - 1)+ image.at<float>(y + 1, x + 1) - image.at<float>(y + 1, x - 1);float dy = image.at<float>(y + 1, x - 1) - image.at<float>(y - 1, x - 1)+ 2 * image.at<float>(y + 1, x) - 2 * image.at<float>(y - 1, x) +image.at<float>(y + 1, x + 1) - image.at<float>(y - 1, x + 1);*///保存水平差分和竖直差分及其对应的权重X[k] = dx;Y[k] = dy;W[k] = (i * i + j * j) * exp_scale;++k;}}len = k; //邻域内特征点的个数cv::hal::exp(W, W, len); //计算邻域内所有像素的高斯权重cv::hal::fastAtan2(Y, X, Ori, len, true); //计算邻域内所有像素的梯度方向,角度范围0-360度cv::hal::magnitude32f(X, Y, Mag, len); //计算邻域内所有像素的梯度幅度,计算的是数学意义上的梯度//遍历邻域的像素for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){int bin = cvRound((n / 360.f) * Ori[i]); //利用像素的梯度方向,约束bin的范围在[0,(n-1)]//像素点梯度方向为360度时,和0°一样if (bin >= n)bin = bin - n;if (bin < 0)bin = bin + n;temp_hist[bin] = temp_hist[bin] + Mag[i] * W[i]; //统计邻域内像素各个方向在梯度直方图的幅值(加权后的幅值)}//平滑直方图temp_hist[-1] = temp_hist[n - 1];temp_hist[-2] = temp_hist[n - 2];temp_hist[n] = temp_hist[0];temp_hist[n + 1] = temp_hist[1];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){hist[i] = (temp_hist[i - 2] + temp_hist[i + 2]) * (1.f / 16.f) +(temp_hist[i - 1] + temp_hist[i + 1]) * (4.f / 16.f) +temp_hist[i] * (6.f / 16.f);}//获得直方图中最大值float max_value = hist[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){if (hist[i] > max_value)max_value = hist[i];}return max_value;
}/******************该函数计算特征点主方向,用于LOGH版本*********************/
/*amplit表示特征点所在层的梯度幅度,即输入图像对应像素点的梯度存在了对应位置orient表示特征点所在层的梯度方向,0-360度point表示特征点坐标scale表示特征点的所在层的尺度hist表示生成的直方图n表示主方向直方图bin个数*/
static float calc_orient_hist(const Mat& amplit, const Mat& orient, Point pt, float scale, float* hist, int n)
{//暂且认为是只进行了下采样,没有进行高斯模糊int num_row = amplit.rows;int num_col = amplit.cols;Point point(cvRound(pt.x), cvRound(pt.y));//int radius = cvRound(SAR_SIFT_FACT_RADIUS_ORI * scale);int radius = cvRound(6 * scale);radius = min(radius, min(num_row / 2, num_col / 2));float gauss_sig = 2 * scale; //高斯加权标准差float exp_temp = -1.f / (2 * gauss_sig * gauss_sig); //权重指数部分//邻域区域int radius_x_left = point.x - radius;int radius_x_right = point.x + radius;int radius_y_up = point.y - radius;int radius_y_down = point.y + radius;//防止越界if (radius_x_left < 0)radius_x_left = 0;if (radius_x_right > num_col - 1)radius_x_right = num_col - 1;if (radius_y_up < 0)radius_y_up = 0;if (radius_y_down > num_row - 1)radius_y_down = num_row - 1;//此时特征点周围矩形区域相对于本矩形区域的中心int center_x = point.x - radius_x_left;int center_y = point.y - radius_y_up;//矩形区域的边界,计算高斯权值Range x_rng(-(point.x - radius_x_left), radius_x_right - point.x);Range y_rng(-(point.y - radius_y_up), radius_y_down - point.y);Mat gauss_weight;gauss_weight.create(y_rng.end - y_rng.start + 1, x_rng.end - x_rng.start + 1, CV_32FC1);//求各个像素点的高斯权重for (int i = y_rng.start; i <= y_rng.end; ++i){float* ptr_gauss = gauss_weight.ptr<float>(i - y_rng.start);for (int j = x_rng.start; j <= x_rng.end; ++j)ptr_gauss[j - x_rng.start] = exp((i * i + j * j) * exp_temp);}//索引特征点周围的像素梯度幅度,梯度方向Mat sub_amplit = amplit(Range(radius_y_up, radius_y_down + 1), Range(radius_x_left, radius_x_right + 1));Mat sub_orient = orient(Range(radius_y_up, radius_y_down + 1), Range(radius_x_left, radius_x_right + 1));//Mat W = sub_amplit.mul(gauss_weight); //加入高斯权重,计算高斯权重时,正确匹配点对反而变少了Mat W = sub_amplit; //没加高斯权重,梯度幅值//计算直方图AutoBuffer<float> buffer(n + 4);float* temp_hist = buffer + 2;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)temp_hist[i] = 0.f;for (int i = 0; i < sub_orient.rows; i++){float* ptr_1 = W.ptr<float>(i);float* ptr_2 = sub_orient.ptr<float>(i);for (int j = 0; j < sub_orient.cols; j++){if (((i - center_y) * (i - center_y) + (j - center_x) * (j - center_x)) < radius * radius){int bin = cvRound(ptr_2[j] * n / 360.f);if (bin > n)bin = bin - n;if (bin < 0)bin = bin + n;temp_hist[bin] += ptr_1[j];}}}//平滑直方图,可以防止突变temp_hist[-1] = temp_hist[n - 1];temp_hist[-2] = temp_hist[n - 2];temp_hist[n] = temp_hist[0];temp_hist[n + 1] = temp_hist[1];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){hist[i] = (temp_hist[i - 2] + temp_hist[i + 2]) * (1.f / 16.f) +(temp_hist[i - 1] + temp_hist[i + 1]) * (4.f / 16.f) +temp_hist[i] * (6.f / 16.f);}//获得直方图中最大值float max_value = hist[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i){if (hist[i] > max_value)max_value = hist[i];}return max_value;
}/****************************该函数精确定位特征点位置(x,y,scale),用于后面特征点的检测*************************/
/*功能:确定特征点的位置,并通过主曲率消除边缘相应点,该版本是简化版dog_pry表示DOG金字塔kpt表示精确定位后该特征点的信息octave表示初始特征点所在的组layer表示初始特征点所在的层row表示初始特征点在图像中的行坐标col表示初始特征点在图像中的列坐标nOctaveLayers表示DOG金字塔每组中间层数,默认是3contrastThreshold表示对比度阈值,默认是0.04edgeThreshold表示边缘阈值,默认是10sigma表示高斯尺度空间最底层图像尺度,默认是1.6*/
static bool adjust_local_extrema_1(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, KeyPoint& kpt, int octave, int& layer, int& row,int& col, int nOctaveLayers, float contrastThreshold, float edgeThreshold, float sigma)
{float xi = 0, xr = 0, xc = 0;int i = 0;for (; i < MAX_INTERP_STEPS; ++i) //最大迭代次数{const Mat& img = dog_pyr[octave][layer]; //当前层图像索引const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[octave][layer - 1]; //之前层图像索引const Mat& next = dog_pyr[octave][layer + 1]; //下一层图像索引//特征点位置x方向,y方向,尺度方向的一阶偏导数float dx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) - img.at<float>(row, col - 1)) * (1.f / 2.f);float dy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col)) * (1.f / 2.f);float dz = (next.at<float>(row, col) - prev.at<float>(row, col)) * (1.f / 2.f);//计算特征点位置二阶偏导数float v2 = img.at<float>(row, col);float dxx = img.at<float>(row, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row, col - 1) - 2 * v2;float dyy = img.at<float>(row + 1, col) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col) - 2 * v2;float dzz = prev.at<float>(row, col) + next.at<float>(row, col) - 2 * v2;//计算特征点周围混合二阶偏导数float dxy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col - 1) -img.at<float>(row + 1, col - 1) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col + 1)) * (1.f / 4.f);float dxz = (next.at<float>(row, col + 1) + prev.at<float>(row, col - 1) -next.at<float>(row, col - 1) - prev.at<float>(row, col + 1)) * (1.f / 4.f);float dyz = (next.at<float>(row + 1, col) + prev.at<float>(row - 1, col) -next.at<float>(row - 1, col) - prev.at<float>(row + 1, col)) * (1.f / 4.f);Matx33f H(dxx, dxy, dxz, dxy, dyy, dyz, dxz, dyz, dzz);Vec3f dD(dx, dy, dz);Vec3f X = H.solve(dD, DECOMP_SVD);xc = -X[0]; //x方向偏移量xr = -X[1]; //y方向偏移量xi = -X[2]; //尺度方向偏移量//如果三个方向偏移量都小于0.5,说明已经找到特征点准确位置if (abs(xc) < 0.5f && abs(xr) < 0.5f && abs(xi) < 0.5f)break;//如果其中一个方向的偏移量过大,则删除该点if (abs(xc) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3) ||abs(xr) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3) ||abs(xi) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3))return false;col = col + cvRound(xc);row = row + cvRound(xr);layer = layer + cvRound(xi);//如果特征点定位在边界区域,同样也需要删除if (layer<1 || layer>nOctaveLayers ||col<IMG_BORDER || col>img.cols - IMG_BORDER ||row<IMG_BORDER || row>img.rows - IMG_BORDER)return false;}//如果i=MAX_INTERP_STEPS,说明循环结束也没有满足条件,即该特征点需要被删除if (i >= MAX_INTERP_STEPS)return false;/**************************再次删除低响应点(对比度较低的点)********************************///再次计算特征点位置x方向,y方向,尺度方向的一阶偏导数//高对比度的特征对图像的变形是稳定的{const Mat& img = dog_pyr[octave][layer];const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[octave][layer - 1];const Mat& next = dog_pyr[octave][layer + 1];float dx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) - img.at<float>(row, col - 1)) * (1.f / 2.f);float dy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col)) * (1.f / 2.f);float dz = (next.at<float>(row, col) - prev.at<float>(row, col)) * (1.f / 2.f);Matx31f dD(dx, dy, dz);float t = dD.dot(Matx31f(xc, xr, xi));float contr = img.at<float>(row, col) + t * 0.5f; //特征点响应 |D(x~)| 即对比度//Low建议contr阈值是0.03,但是RobHess等建议阈值为0.04/nOctaveLayersif (abs(contr) < contrastThreshold / nOctaveLayers) //阈值设为0.03时特征点数量过多return false;/******************************删除边缘响应比较强的点************************************///再次计算特征点位置二阶偏导数,获取特征点出的 Hessian 矩阵,主曲率通过 2X2 的 Hessian 矩阵求出//一个定义不好的高斯差分算子的极值在横跨边缘的地方有较大的主曲率而在垂直边缘的方向有较小的主曲率float v2 = img.at<float>(row, col);float dxx = img.at<float>(row, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row, col - 1) - 2 * v2;float dyy = img.at<float>(row + 1, col) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col) - 2 * v2;float dxy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col - 1) -img.at<float>(row + 1, col - 1) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col + 1)) * (1.f / 4.f);float det = dxx * dyy - dxy * dxy;float trace = dxx + dyy;//主曲率和阈值的对比判定if (det < 0 || (trace * trace * edgeThreshold >= det * (edgeThreshold + 1) * (edgeThreshold + 1)))return false;/*********到目前为止该特征的满足上面所有要求,保存该特征点信息***********/kpt.pt.x = ((float)col + xc) * (1 << octave); //相对于最底层的图像的x坐标kpt.pt.y = ((float)row + xr) * (1 << octave); //相对于最底层图像的y坐标kpt.octave = octave + (layer << 8); //组号保存在低字节,层号保存在高字节//相对于最底层图像的尺度kpt.size = sigma * powf(2.f, (layer + xi) / nOctaveLayers) * (1 << octave);kpt.response = abs(contr); //特征点响应值(对比度)return true;}}/****************************该函数精确定位特征点位置(x,y,scale),用于后面特征点的检测*************************/
//该版本是 SIFT 原版,检测得到的特征点数量更多
static bool adjust_local_extrema_2(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, KeyPoint& kpt, int octave, int& layer, int& row,int& col, int nOctaveLayers, float contrastThreshold, float edgeThreshold, float sigma)
{const float img_scale = 1.f / (255 * SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE); //SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE=48const float deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.5f;const float second_deriv_scale = img_scale;const float cross_deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.25f;float xi = 0, xr = 0, xc = 0;int i = 0;for (; i < MAX_INTERP_STEPS; ++i) //最大迭代次数{const Mat& img = dog_pyr[octave][layer]; //当前层图像索引const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[octave][layer - 1]; //之前层图像索引const Mat& next = dog_pyr[octave][layer + 1]; //下一层图像索引//计算一阶偏导数,通过临近点差分求得float dx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) - img.at<float>(row, col - 1)) * deriv_scale;float dy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col)) * deriv_scale;float dz = (next.at<float>(row, col) - prev.at<float>(row, col)) * deriv_scale;//计算特征点位置二阶偏导数//float v2 = img.at<float>(row, col);float v2 = (float)img.at<float>(row, col) * 2.f;float dxx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row, col - 1) - v2) * second_deriv_scale;float dyy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col) - v2) * second_deriv_scale;float dzz = (prev.at<float>(row, col) + next.at<float>(row, col) - v2) * second_deriv_scale;//计算特征点周围混合二阶偏导数float dxy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col - 1) -img.at<float>(row + 1, col - 1) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col + 1)) * cross_deriv_scale;float dxz = (next.at<float>(row, col + 1) + prev.at<float>(row, col - 1) -next.at<float>(row, col - 1) - prev.at<float>(row, col + 1)) * cross_deriv_scale;float dyz = (next.at<float>(row + 1, col) + prev.at<float>(row - 1, col) -next.at<float>(row - 1, col) - prev.at<float>(row + 1, col)) * cross_deriv_scale;Matx33f H(dxx, dxy, dxz, dxy, dyy, dyz, dxz, dyz, dzz);Vec3f dD(dx, dy, dz);Vec3f X = H.solve(dD, DECOMP_SVD);xc = -X[0]; //x方向偏移量xr = -X[1]; //y方向偏移量xi = -X[2]; //尺度方向偏移量//如果三个方向偏移量都小于0.5,说明已经找到特征点准确位置if (abs(xc) < 0.5f && abs(xr) < 0.5f && abs(xi) < 0.5f)break;//如果其中一个方向的偏移量过大,则删除该点if (abs(xc) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3) ||abs(xr) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3) ||abs(xi) > (float)(INT_MAX / 3))return false;col = col + cvRound(xc);row = row + cvRound(xr);layer = layer + cvRound(xi);//如果特征点定位在边界区域,同样也需要删除if (layer<1 || layer>nOctaveLayers ||col < IMG_BORDER || col >= img.cols - IMG_BORDER ||row < IMG_BORDER || row >= img.rows - IMG_BORDER)return false;}//如果i=MAX_INTERP_STEPS,说明循环结束也没有满足条件,即该特征点需要被删除if (i >= MAX_INTERP_STEPS)return false;/**************************再次删除低响应点(对比度较低的点)********************************///再次计算特征点位置x方向,y方向,尺度方向的一阶偏导数//高对比度的特征对图像的变形是稳定的const Mat& img = dog_pyr[octave][layer];const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[octave][layer - 1];const Mat& next = dog_pyr[octave][layer + 1];float dx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) - img.at<float>(row, col - 1)) * deriv_scale;float dy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col)) * deriv_scale;float dz = (next.at<float>(row, col) - prev.at<float>(row, col)) * deriv_scale;Matx31f dD(dx, dy, dz);float t = dD.dot(Matx31f(xc, xr, xi));float contr = img.at<float>(row, col) + t * 0.5f; //特征点响应 |D(x~)| 即对比度//Low建议contr阈值是0.03,但是RobHess等建议阈值为0.04/nOctaveLayersif (abs(contr) < contrastThreshold / nOctaveLayers) //阈值设为0.03时特征点数量过多return false;/******************************删除边缘响应比较强的点************************************///再次计算特征点位置二阶偏导数,获取特征点出的 Hessian 矩阵,主曲率通过 2X2 的 Hessian 矩阵求出//一个定义不好的高斯差分算子的极值在横跨边缘的地方有较大的主曲率而在垂直边缘的方向有较小的主曲率float v2 = (float)img.at<float>(row, col) * 2.f;float dxx = (img.at<float>(row, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row, col - 1) - v2) * second_deriv_scale;float dyy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col) - v2) * second_deriv_scale;float dxy = (img.at<float>(row + 1, col + 1) + img.at<float>(row - 1, col - 1) -img.at<float>(row + 1, col - 1) - img.at<float>(row - 1, col + 1)) * cross_deriv_scale;float det = dxx * dyy - dxy * dxy;float trace = dxx + dyy;//主曲率和阈值的对比判定if (det <= 0 || (trace * trace * edgeThreshold >= det * (edgeThreshold + 1) * (edgeThreshold + 1)))return false;/*********保存该特征点信息***********/kpt.pt.x = ((float)col + xc) * (1 << octave); //高斯金字塔坐标根据组数扩大相应的倍数kpt.pt.y = ((float)row + xr) * (1 << octave);// SIFT 描述子kpt.octave = octave + (layer << 8) + (cvRound((xi + 0.5) * 255) << 16); //特征点被检测出时所在的金字塔组kpt.size = sigma * powf(2.f, (layer + xi) / nOctaveLayers) * (1 << octave) * 2; //关键点邻域直径kpt.response = abs(contr); //特征点响应值(对比度)return true;}/************该函数在DOG金字塔上进行特征点检测,特征点精确定位,删除低对比度点,删除边缘响应较大点**********/
/*dog_pyr表示高斯金字塔 原始 SIFT 算子gauss_pyr表示高斯金字塔keypoints表示检测到的特征点*/
void mySift::find_scale_space_extrema(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints)
{int nOctaves = (int)dog_pyr.size(); //子八度个数//Low文章建议thresholdThreshold是0.03,Rob Hess等人使用0.04/nOctaveLayers作为阈值float threshold = (float)(contrastThreshold / nOctaveLayers);const int n = ORI_HIST_BINS; //n=36float hist[n];KeyPoint kpt;keypoints.clear(); //先清空keypointsfor (int i = 0; i < nOctaves; ++i) //对于每一组{for (int j = 1; j <= nOctaveLayers; ++j) //对于组内每一层{const Mat& curr_img = dog_pyr[i][j]; //当前层const Mat& prev_img = dog_pyr[i][j - 1]; //上一层const Mat& next_img = dog_pyr[i][j + 1]; //下一层int num_row = curr_img.rows;int num_col = curr_img.cols; //获得当前组图像的大小size_t step = curr_img.step1(); //一行元素所占字节数//遍历每一个尺度层中的有效像素,像素值for (int r = IMG_BORDER; r < num_row - IMG_BORDER; ++r){const float* curr_ptr = curr_img.ptr<float>(r); //指向的是第 r 行的起点,返回的是 float 类型的像素值const float* prev_ptr = prev_img.ptr<float>(r - 1);const float* next_ptr = next_img.ptr<float>(r + 1);for (int c = IMG_BORDER; c < num_col - IMG_BORDER; ++c){float val = curr_ptr[c]; //当前中心点响应值//开始检测特征点if (abs(val) > threshold &&((val > 0 && val >= curr_ptr[c - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= curr_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c - step] && val >= curr_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= curr_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c + step] && val >= curr_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c] && val >= prev_ptr[c - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c - step] && val >= prev_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c + step] && val >= prev_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c] && val >= next_ptr[c - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c - step] && val >= next_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c + step] && val >= next_ptr[c + step + 1]) ||(val < 0 && val <= curr_ptr[c - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= curr_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c - step] && val <= curr_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= curr_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c + step] && val <= curr_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c] && val <= prev_ptr[c - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c - step] && val <= prev_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c + step] && val <= prev_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c] && val <= next_ptr[c - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c - step] && val <= next_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c + step] && val <= next_ptr[c + step + 1]))){//++numKeys;//获得特征点初始行号,列号,组号,组内层号int octave = i, layer = j, r1 = r, c1 = c;if (!adjust_local_extrema_1(dog_pyr, kpt, octave, layer, r1, c1,nOctaveLayers, (float)contrastThreshold,(float)edgeThreshold, (float)sigma)){continue; //如果该初始点不满足条件,则不保存改点}float scale = kpt.size / float(1 << octave); //该特征点相对于本组的尺度//max_hist值对应的方向为主方向float max_hist = clac_orientation_hist(gauss_pyr[octave][layer], Point(c1, r1), scale, n, hist);//大于mag_thr值对应的方向为辅助方向float mag_thr = max_hist * ORI_PEAK_RATIO; //主峰值 80% 的方向作为辅助方向//遍历直方图中的 36 个binfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){int left = i > 0 ? i - 1 : n - 1;int right = i < n - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;//创建新的特征点,大于主峰值 80% 的方向,赋值给该特征点,作为一个新的特征点;即有多个特征点,位置、尺度相同,方向不同if (hist[i] > hist[left] && hist[i] > hist[right] && hist[i] >= mag_thr){float bin = i + 0.5f * (hist[left] - hist[right]) / (hist[left] + hist[right] - 2 * hist[i]);bin = bin < 0 ? n + bin : bin >= n ? bin - n : bin;kpt.angle = (360.f / n) * bin; //原始 SIFT 算子使用的特征点的主方向0-360度keypoints.push_back(kpt); //保存该特征点}}}}}}}//cout << "初始满足要求特征点个数是: " << numKeys << endl;
}/************该函数在DOG金字塔上进行特征点检测,特征点精确定位,删除低对比度点,删除边缘响应较大点**********/
//对特征点进行方向的细化 + 增加更多的主方向版本 ——此时细化是对最后要给关键点进行赋值时的细化
//还可以考虑直接对方向直方图进行细化
void mySift::find_scale_space_extrema1(const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr,vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints)
{int nOctaves = (int)dog_pyr.size(); //子八度个数//Low文章建议thresholdThreshold是0.03,Rob Hess等人使用0.04/nOctaveLayers作为阈值float threshold = (float)(contrastThreshold / nOctaveLayers);const int n = ORI_HIST_BINS; //n=36float hist[n];KeyPoint kpt;vector<Mat> amplit; //存放高斯差分金字塔每一层的梯度幅度图像vector<Mat> orient; //存放高斯差分金字塔每一层的梯度方向图像keypoints.clear(); //先清空keypointsfor (int i = 0; i < nOctaves; ++i) //对于每一组{for (int j = 1; j <= nOctaveLayers; ++j) //对于组内每一层{const Mat& curr_img = dog_pyr[i][j]; //当前层const Mat& prev_img = dog_pyr[i][j - 1]; //上一层const Mat& next_img = dog_pyr[i][j + 1]; //下一层int num_row = curr_img.rows;int num_col = curr_img.cols; //获得当前组图像的大小size_t step = curr_img.step1(); //一行元素所占字节数//遍历每一个尺度层中的有效像素,像素值for (int r = IMG_BORDER; r < num_row - IMG_BORDER; ++r){const float* curr_ptr = curr_img.ptr<float>(r); //指向的是第 r 行的起点,返回的是 float 类型的像素值const float* prev_ptr = prev_img.ptr<float>(r);const float* next_ptr = next_img.ptr<float>(r);for (int c = IMG_BORDER; c < num_col - IMG_BORDER; ++c){float val = curr_ptr[c]; //当前中心点响应值//开始检测特征点if (abs(val) > threshold &&((val > 0 && val >= curr_ptr[c - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= curr_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c - step] && val >= curr_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= curr_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= curr_ptr[c + step] && val >= curr_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c] && val >= prev_ptr[c - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c - step] && val >= prev_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= prev_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= prev_ptr[c + step] && val >= prev_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c] && val >= next_ptr[c - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c - step - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c - step] && val >= next_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val >= next_ptr[c + step - 1] && val >= next_ptr[c + step] && val >= next_ptr[c + step + 1]) ||(val < 0 && val <= curr_ptr[c - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= curr_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c - step] && val <= curr_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= curr_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= curr_ptr[c + step] && val <= curr_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c] && val <= prev_ptr[c - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c - step] && val <= prev_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= prev_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= prev_ptr[c + step] && val <= prev_ptr[c + step + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c] && val <= next_ptr[c - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c - step - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c - step] && val <= next_ptr[c - step + 1] &&val <= next_ptr[c + step - 1] && val <= next_ptr[c + step] && val <= next_ptr[c + step + 1]))){//++numKeys;//获得特征点初始行号,列号,组号,组内层号int octave = i, layer = j, r1 = r, c1 = c, nums = i * nOctaves + j;if (!adjust_local_extrema_2(dog_pyr, kpt, octave, layer, r1, c1,nOctaveLayers, (float)contrastThreshold,(float)edgeThreshold, (float)sigma)){continue; //如果该初始点不满足条件,则不保存改点}float scale = kpt.size / float(1 << octave); //该特征点相对于本组的尺度//计算梯度幅度和梯度方向//amplit_orient(curr_img, amplit, orient, scale, nums);//max_hist值对应的方向为主方向float max_hist = clac_orientation_hist(gauss_pyr[octave][layer], Point(c1, r1), scale, n, hist);//float max_hist = calc_orient_hist(amplit[nums], orient[nums], Point2f(c1, r1), scale, hist, n);大于mag_thr值对应的方向为辅助方向//float mag_thr = max_hist * ORI_PEAK_RATIO; //主峰值 80% 的方向作为辅助方向//增加更多的主方向,以增加特征点对梯度差异的鲁棒性float sum = 0.0; //直方图对应的幅值之和float mag_thr = 0.0; //判断是否为主方向的阈值for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){sum += hist[i];}mag_thr = 0.5 * (1.0 / 36) * sum;//遍历直方图中的 36 个binfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){int left = i > 0 ? i - 1 : n - 1;int right = i < n - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;//创建新的特征点,大于主峰值 80% 的方向,赋值给该特征点,作为一个新的特征点;即有多个特征点,位置、尺度相同,方向不同if (hist[i] > hist[left] && hist[i] > hist[right] && hist[i] >= mag_thr){float bin = i + 0.5f * (hist[left] - hist[right]) / (hist[left] + hist[right] - 2 * hist[i]);bin = bin < 0 ? n + bin : bin >= n ? bin - n : bin;//修改的地方,特征点的主方向修改为了0-180度,相当于对方向做了一个细化float angle = (360.f / n) * bin;if (angle >= 1 && angle <= 180){kpt.angle = angle;}else if (angle > 180 && angle < 360){kpt.angle = 360 - angle;}//kpt.angle = (360.f / n) * bin; //原始 SIFT 算子使用的特征点的主方向0-360度keypoints.push_back(kpt); //保存该特征点}}}}}}}//cout << "初始满足要求特征点个数是: " << numKeys << endl;
}/*该函数生成matlab中的meshgrid函数*/
/*x_range表示x方向的范围
y_range表示y方向的范围
X表示生成的沿x轴变化的网格
Y表示生成沿y轴变换的网格
*/
static void meshgrid(const Range& x_range, const Range& y_range, Mat& X, Mat& Y)
{int x_start = x_range.start, x_end = x_range.end;int y_start = y_range.start, y_end = y_range.end;int width = x_end - x_start + 1;int height = y_end - y_start + 1;X.create(height, width, CV_32FC1);Y.create(height, width, CV_32FC1);for (int i = y_start; i <= y_end; i++){float* ptr_1 = X.ptr<float>(i - y_start);for (int j = x_start; j <= x_end; ++j)ptr_1[j - x_start] = j * 1.0f;}for (int i = y_start; i <= y_end; i++){float* ptr_2 = Y.ptr<float>(i - y_start);for (int j = x_start; j <= x_end; ++j)ptr_2[j - x_start] = i * 1.0f;}
}/******************************计算一个特征点的描述子***********************************/
/*gauss_image表示特征点所在的高斯层main_angle表示特征点的主方向,角度范围是0-360度pt表示特征点在高斯图像上的坐标,相对与本组,不是相对于最底层scale表示特征点所在层的尺度,相对于本组,不是相对于最底层d表示特征点邻域网格宽度n表示每个网格内像素梯度角度等分个数descriptor表示生成的特征点的描述子*/
static void calc_sift_descriptor(const Mat& gauss_image, float main_angle, Point2f pt,float scale, int d, int n, float* descriptor)
{Point ptxy(cvRound(pt.x), cvRound(pt.y)); //坐标取整float cos_t = cosf(-main_angle * (float)(CV_PI / 180)); //把角度转化为弧度,计算主方向的余弦float sin_t = sinf(-main_angle * (float)(CV_PI / 180)); //把角度转化为弧度,计算主方向的正弦float bins_per_rad = n / 360.f; // n = 8 ,梯度直方图分为 8 个方向float exp_scale = -1.f / (d * d * 0.5f); //权重指数部分float hist_width = DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scale; //特征点邻域内子区域边长,子区域的边长int radius = cvRound(hist_width * (d + 1) * sqrt(2) * 0.5f);//特征点邻域半径(d+1)*(d+1),四舍五入int rows = gauss_image.rows, cols = gauss_image.cols; //当前高斯层行、列信息//特征点邻域半径radius = min(radius, (int)sqrt((double)rows * rows + cols * cols));cos_t = cos_t / hist_width;sin_t = sin_t / hist_width;int len = (2 * radius + 1) * (2 * radius + 1); //邻域内总像素数,为后面动态分配内存使用int histlen = (d + 2) * (d + 2) * (n + 2); //值为 360 AutoBuffer<float> buf(6 * len + histlen);//X保存水平差分,Y保存竖直差分,Mag保存梯度幅度,Angle保存特征点方向, W保存高斯权重float* X = buf, * Y = buf + len, * Mag = Y, * Angle = Y + len, * W = Angle + len;float* RBin = W + len, * CBin = RBin + len, * hist = CBin + len;//首先清空直方图数据for (int i = 0; i < d + 2; ++i) // i 对应 row{for (int j = 0; j < d + 2; ++j) // j 对应 col{for (int k = 0; k < n + 2; ++k)hist[(i * (d + 2) + j) * (n + 2) + k] = 0.f;}}//把邻域内的像素分配到相应子区域内,计算子区域内每个像素点的权重(子区域即 d*d 中每一个小方格)int k = 0;//实际上是在 4 x 4 的网格中找 16 个种子点,每个种子点都在子网格的正中心,//通过三线性插值对不同种子点间的像素点进行加权作用到不同的种子点上绘制方向直方图for (int i = -radius; i < radius; ++i) // i 对应 y 行坐标{for (int j = -radius; j < radius; ++j) // j 对应 x 列坐标{float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t; //旋转后邻域内采样点的 x 坐标float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t; //旋转后邻域内采样点的 y 坐标//旋转后 5 x 5 的网格中的所有像素点被分配到 4 x 4 的网格中float cbin = c_rot + d / 2 - 0.5f; //旋转后的采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标float rbin = r_rot + d / 2 - 0.5f; //旋转后的采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标int r = ptxy.y + i, c = ptxy.x + j; //ptxy是高斯金字塔中的坐标//这里rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)if (rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin>-1 && cbin < d && r>0 && r < rows - 1 && c>0 && c < cols - 1){float dx = gauss_image.at<float>(r, c + 1) - gauss_image.at<float>(r, c - 1);float dy = gauss_image.at<float>(r + 1, c) - gauss_image.at<float>(r - 1, c);X[k] = dx; //邻域内所有像素点的水平差分Y[k] = dy; //邻域内所有像素点的竖直差分CBin[k] = cbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标RBin[k] = rbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标W[k] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale; //高斯权值的指数部分++k;}}}//计算采样点落在子区域的像素梯度幅度,梯度角度,和高斯权值len = k;cv::hal::exp(W, W, len); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的高斯权值cv::hal::fastAtan2(Y, X, Angle, len, true); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的梯度方向,角度范围是0-360度cv::hal::magnitude(X, Y, Mag, len); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的梯度幅度//实际上是在 4 x 4 的网格中找 16 个种子点,每个种子点都在子网格的正中心,//通过三线性插值对不同种子点间的像素点进行加权作用到不同的种子点上绘制方向直方图//计算每个特征点的特征描述子for (k = 0; k < len; ++k){float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k]; //子区域内像素点坐标,rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)改进的地方,对方向进行了一个细化,也是为了增加对梯度差异的鲁棒性//if (Angle[k] > 180 && Angle[k] < 360)// Angle[k] = 360 - Angle[k];//子区域内像素点处理后的方向float temp = Angle[k] - main_angle;/*if (temp > 180 && temp < 360)temp = 360 - temp;*/float obin = temp * bins_per_rad; //指定方向的数量后,邻域内像素点对应的方向float mag = Mag[k] * W[k]; //子区域内像素点乘以权值后的梯度幅值int r0 = cvFloor(rbin); //ro取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3},没太懂为什么?int c0 = cvFloor(cbin); //c0取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3}int o0 = cvFloor(obin);rbin = rbin - r0; //子区域内像素点坐标的小数部分,用于线性插值,分配像素点的作用cbin = cbin - c0;obin = obin - o0; //子区域方向的小数部分//限制范围为梯度直方图横坐标[0,n),8 个方向直方图if (o0 < 0)o0 = o0 + n;if (o0 >= n)o0 = o0 - n;//三线性插值用于计算落在两个子区域之间的像素对两个子区域的作用,并把其分配到对应子区域的8个方向上//像素对应的信息通过加权分配给其周围的种子点,并把相应方向的梯度值进行累加 float v_r1 = mag * rbin; //第二行分配的值float v_r0 = mag - v_r1; //第一行分配的值float v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbin; //第二行第二列分配的值,右下角种子点float v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; //第二行第一列分配的值,左下角种子点float v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbin; //第一行第二列分配的值,右上角种子点float v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01; //第一行第一列分配的值,左上角种子点//一个像素点的方向为每个种子点的两个方向做出贡献float v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obin; //右下角种子点第二个方向上分配的值float v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; //右下角种子点第一个方向上分配的值float v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obin;float v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;float v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obin;float v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;float v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obin;float v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001;//该像素所在网格的索引int idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n + 2) + o0;hist[idx] += v_rco000;hist[idx + 1] += v_rco001;hist[idx + n + 2] += v_rco010;hist[idx + n + 3] += v_rco011;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n + 2)] += v_rco100;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n + 2) + 1] += v_rco101;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n + 2)] += v_rco110;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n + 2) + 1] += v_rco111;}//由于圆周循环的特性,对计算以后幅角小于 0 度或大于 360 度的值重新进行调整,使//其在 0~360 度之间for (int i = 0; i < d; ++i){for (int j = 0; j < d; ++j){//类似于 hist[0][2][3] 第 0 行,第 2 列,种子点直方图中的第 3 个 binint idx = ((i + 1) * (d + 2) + (j + 1)) * (n + 2);hist[idx] += hist[idx + n];//hist[idx + 1] += hist[idx + n + 1];//opencv源码中这句话是多余的,hist[idx + n + 1]永远是0.0for (k = 0; k < n; ++k)descriptor[(i * d + j) * n + k] = hist[idx + k];}}//对描述子进行归一化int lenght = d * d * n;float norm = 0;//计算特征描述向量的模值的平方for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){norm = norm + descriptor[i] * descriptor[i];}norm = sqrt(norm); //特征描述向量的模值//此次归一化能去除光照的影响for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = descriptor[i] / norm;}//阈值截断,去除特征描述向量中大于 0.2 的值,能消除非线性光照的影响(相机饱和度对某些放的梯度影响较大,对方向的影响较小)for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = min(descriptor[i], DESCR_MAG_THR);}//再次归一化,能够提高特征的独特性norm = 0;for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){norm = norm + descriptor[i] * descriptor[i];}norm = sqrt(norm);for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = descriptor[i] / norm;}
}/*************************该函数计算每个特征点的特征描述子*****************************/
/*amplit表示特征点所在层的梯度幅度图像orient表示特征点所在层的梯度角度图像pt表示特征点的位置scale表示特征点所在层的尺度main_ori表示特征点的主方向,0-360度d表示GLOH角度方向区间个数,默认是8,n表示每个网格内角度在0-360度之间等分个数,n默认是8*/
static void calc_gloh_descriptor(const Mat& amplit, const Mat& orient, Point2f pt, float scale, float main_ori, int d, int n, float* ptr_des)
{Point point(cvRound(pt.x), cvRound(pt.y));//特征点旋转方向余弦和正弦float cos_t = cosf(-main_ori / 180.f * (float)CV_PI);float sin_t = sinf(-main_ori / 180.f * (float)CV_PI);int num_rows = amplit.rows;int num_cols = amplit.cols;int radius = cvRound(SAR_SIFT_RADIUS_DES * scale);radius = min(radius, min(num_rows / 2, num_cols / 2));//特征点邻域半径int radius_x_left = point.x - radius;int radius_x_right = point.x + radius;int radius_y_up = point.y - radius;int radius_y_down = point.y + radius;//防止越界if (radius_x_left < 0)radius_x_left = 0;if (radius_x_right > num_cols - 1)radius_x_right = num_cols - 1;if (radius_y_up < 0)radius_y_up = 0;if (radius_y_down > num_rows - 1)radius_y_down = num_rows - 1;//此时特征点周围本矩形区域的中心,相对于该矩形int center_x = point.x - radius_x_left;int center_y = point.y - radius_y_up;//特征点周围区域内像素梯度幅度,梯度角度Mat sub_amplit = amplit(Range(radius_y_up, radius_y_down + 1), Range(radius_x_left, radius_x_right + 1));Mat sub_orient = orient(Range(radius_y_up, radius_y_down + 1), Range(radius_x_left, radius_x_right + 1));//以center_x和center_y位中心,对下面矩形区域进行旋转Range x_rng(-(point.x - radius_x_left), radius_x_right - point.x);Range y_rng(-(point.y - radius_y_up), radius_y_down - point.y);Mat X, Y;meshgrid(x_rng, y_rng, X, Y);Mat c_rot = X * cos_t - Y * sin_t;Mat r_rot = X * sin_t + Y * cos_t;Mat GLOH_angle, GLOH_amplit;phase(c_rot, r_rot, GLOH_angle, true);//角度在0-360度之间GLOH_amplit = c_rot.mul(c_rot) + r_rot.mul(r_rot);//为了加快速度,没有计算开方//三个圆半径平方float R1_pow = (float)radius * radius;//外圆半径平方float R2_pow = pow(radius * SAR_SIFT_GLOH_RATIO_R1_R2, 2.f);//中间圆半径平方float R3_pow = pow(radius * SAR_SIFT_GLOH_RATIO_R1_R3, 2.f);//内圆半径平方int sub_rows = sub_amplit.rows;int sub_cols = sub_amplit.cols;//开始构建描述子,在角度方向对描述子进行插值int len = (d * 2 + 1) * n;AutoBuffer<float> hist(len);for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)//清零hist[i] = 0;for (int i = 0; i < sub_rows; ++i){float* ptr_amplit = sub_amplit.ptr<float>(i);float* ptr_orient = sub_orient.ptr<float>(i);float* ptr_GLOH_amp = GLOH_amplit.ptr<float>(i);float* ptr_GLOH_ang = GLOH_angle.ptr<float>(i);for (int j = 0; j < sub_cols; ++j){if (((i - center_y) * (i - center_y) + (j - center_x) * (j - center_x)) < radius * radius){float pix_amplit = ptr_amplit[j];//该像素的梯度幅度float pix_orient = ptr_orient[j];//该像素的梯度方向float pix_GLOH_amp = ptr_GLOH_amp[j];//该像素在GLOH网格中的半径位置float pix_GLOH_ang = ptr_GLOH_ang[j];//该像素在GLOH网格中的位置方向int rbin, cbin, obin;rbin = pix_GLOH_amp < R3_pow ? 0 : (pix_GLOH_amp > R2_pow ? 2 : 1);//rbin={0,1,2}cbin = cvRound(pix_GLOH_ang * d / 360.f);cbin = cbin > d ? cbin - d : (cbin <= 0 ? cbin + d : cbin);//cbin=[1,d]obin = cvRound(pix_orient * n / 360.f);obin = obin > n ? obin - n : (obin <= 0 ? obin + n : obin);//obin=[1,n]if (rbin == 0)//内圆hist[obin - 1] += pix_amplit;else{int idx = ((rbin - 1) * d + cbin - 1) * n + n + obin - 1;hist[idx] += pix_amplit;}}}}//对描述子进行归一化float norm = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){norm = norm + hist[i] * hist[i];}norm = sqrt(norm);for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){hist[i] = hist[i] / norm;}//阈值截断for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){hist[i] = min(hist[i], DESCR_MAG_THR);}//再次归一化norm = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){norm = norm + hist[i] * hist[i];}norm = sqrt(norm);for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i){ptr_des[i] = hist[i] / norm;}}/******************************计算一个特征点的描述子—改进版***********************************/
static void improve_calc_sift_descriptor(const Mat& gauss_image, float main_angle, Point2f pt,float scale, int d, int n, float* descriptor)
{int n1 = 16, n2 = 6, n3 = 4;Point ptxy(cvRound(pt.x), cvRound(pt.y)); //坐标取整float cos_t = cosf(-main_angle * (float)(CV_PI / 180)); //计算主方向的余弦float sin_t = sinf(-main_angle * (float)(CV_PI / 180)); //计算主方向的正弦float bin_per_rad_1 = n1 / 360.f; //n=8float bin_per_rad_2 = n2 / 360.f; //原理特征点部分阈值float bin_per_rad_3 = n3 / 360.f; //原理特征点部分阈值float exp_scale = -1.f / (d * d * 0.5f); //权重指数部分float hist_width = DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scale; //子区域边长,子区域的面积也即采样像素点个数int radius = cvRound(hist_width * (d + 1) * sqrt(2) * 0.5f);//特征点邻域半径(d+1)*(d+1)int rows = gauss_image.rows, cols = gauss_image.cols;//特征点邻域半径radius = min(radius, (int)sqrt((double)rows * rows + cols * cols));cos_t = cos_t / hist_width;sin_t = sin_t / hist_width;int len = (2 * radius + 1) * (2 * radius + 1); //邻域内总像素数int histlen = (d + 2) * (d + 2) * (n1 + 2);AutoBuffer<float> buf(6 * len + histlen);//X保存水平差分,Y保存竖直差分,Mag保存梯度幅度,Angle保存特征点方向, W保存高斯权重float* X = buf, * Y = buf + len, * Mag = Y, * Angle = Y + len, * W = Angle + len;float* X2 = buf, * Y2 = buf + len, * Mag2 = Y, * Angle2 = Y + len, * W2 = Angle + len;float* X3 = buf, * Y3 = buf + len, * Mag3 = Y, * Angle3 = Y + len, * W3 = Angle + len;float* RBin = W + len, * CBin = RBin + len, * hist = CBin + len;float* RBin2 = W + len, * CBin2 = RBin + len;float* RBin3 = W + len, * CBin3 = RBin + len;//首先清空直方图数据for (int i = 0; i < d + 2; ++i){for (int j = 0; j < d + 2; ++j){for (int k = 0; k < n + 2; ++k)hist[(i * (d + 2) + j) * (n + 2) + k] = 0.f;}}//把邻域内的像素分配到相应子区域内,计算子区域内每个像素点的权重(子区域即 d*d 中每一个小方格)int k1 = 0, k2 = 0, k3 = 0;vector<int> v; //存放外邻域像素点对应的序号for (int i = -radius; i < radius; ++i){for (int j = -radius; j < radius; ++j){float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t; //旋转后邻域内采样点的 x 坐标float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t; //旋转后邻域内采样点的 y 坐标float rbin = r_rot + d / 2 - 0.5f; //旋转后的采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标float cbin = c_rot + d / 2 - 0.5f; //旋转后的采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标int r = ptxy.y + i, c = ptxy.x + j; //ptxy是高斯金字塔中的坐标//对离中心点近的部分进行操作if (abs(i) < (radius / 3) && abs(j) < (radius / 3)){//这里rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)if (rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin>-1 && cbin < d &&r>0 && r < rows - 1 && c>0 && c < cols - 1){float dx = gauss_image.at<float>(r, c + 1) - gauss_image.at<float>(r, c - 1);float dy = gauss_image.at<float>(r + 1, c) - gauss_image.at<float>(r - 1, c);X[k1] = dx; //邻域内所有像素点的水平差分Y[k1] = dy; //邻域内所有像素点的竖直差分RBin[k1] = rbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标CBin[k1] = cbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标//高斯权值的指数部分W[k1] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale;++k1;}}//对离中心点远的部分进行操作else if (abs(i) < (2 * radius / 3) && abs(i) > (radius / 3) && abs(j) < (2 * radius / 3) && abs(j) > (radius / 3)){//这里rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)if (rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin>-1 && cbin < d &&r>0 && r < rows - 1 && c>0 && c < cols - 1){float dx = gauss_image.at<float>(r, c + 1) - gauss_image.at<float>(r, c - 1);float dy = gauss_image.at<float>(r + 1, c) - gauss_image.at<float>(r - 1, c);X2[k2] = dx; //邻域内所有像素点的水平差分Y2[k2] = dy; //邻域内所有像素点的竖直差分RBin2[k2] = rbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标CBin2[k2] = cbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标//高斯权值的指数部分W2[k2] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale;++k2;}}else{//这里rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)if (rbin > -1 && rbin < d && cbin>-1 && cbin < d &&r>0 && r < rows - 1 && c>0 && c < cols - 1){float dx = gauss_image.at<float>(r, c + 1) - gauss_image.at<float>(r, c - 1);float dy = gauss_image.at<float>(r + 1, c) - gauss_image.at<float>(r - 1, c);X3[k3] = dx; //邻域内所有像素点的水平差分Y3[k3] = dy; //邻域内所有像素点的竖直差分RBin3[k3] = rbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 y 坐标CBin3[k3] = cbin; //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的 x 坐标//高斯权值的指数部分W3[k3] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale;++k3;}}}}//两个区域内数组的合并拼接for (int k = 0; k < k2; k++){X[k1 + k] = X2[k];Y[k1 + k] = Y2[k];RBin[k1 + k] = RBin2[k];CBin[k1 + k] = CBin2[k];W[k1 + k] = W2[k];}for (int k = 0; k < k3; k++){X[k1 + k2 + k] = X3[k];Y[k1 + k2 + k] = Y3[k];RBin[k1 + k2 + k] = RBin3[k];CBin[k1 + k2 + k] = CBin3[k];W[k1 + k2 + k] = W3[k];}//计算采样点落在子区域的像素梯度幅度,梯度角度,和高斯权值len = k1 + k2 + k3;cv::hal::exp(W, W, len); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的高斯权值cv::hal::fastAtan2(Y, X, Angle, len, true); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的梯度方向,角度范围是0-360度cv::hal::magnitude(X, Y, Mag, len); //邻域内所有采样点落在子区域的像素的梯度幅度//计算每个特征点的特征描述子for (int k = 0; k < len; ++k){float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k]; //子区域内像素点坐标,rbin,cbin范围是(-1,d)//离特征点进的邻域if (k < k1){//子区域内像素点处理后的方向float obin = (Angle[k] - main_angle) * bin_per_rad_1;float mag = Mag[k] * W[k]; //子区域内像素点乘以权值后的梯度幅值int r0 = cvFloor(rbin); //ro取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3},向下取整int c0 = cvFloor(cbin); //c0取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3}int o0 = cvFloor(obin);rbin = rbin - r0; //子区域内像素点坐标的小数部分,用于线性插值cbin = cbin - c0;obin = obin - o0;//限制范围为梯度直方图横坐标[0,n)if (o0 < 0)o0 = o0 + n1;if (o0 >= n1)o0 = o0 - n1;//三线性插值用于计算落在两个子区域之间的像素对两个子区域的作用,并把其分配到对应子区域的8个方向上//使用三线性插值(即三维)方法,计算直方图float v_r1 = mag * rbin; //第二行分配的值float v_r0 = mag - v_r1; //第一行分配的值float v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbin; //第二行第二列分配的值float v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; //第二行第一列分配的值float v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbin; //第一行第二列分配的值float v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01;float v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obin; //第二行第二列第二个方向上分配的值,每个采样点去邻近两个方向float v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; //第二行第二列第一个方向上分配的值float v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obin;float v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;float v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obin;float v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;float v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obin;float v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001;//该像素所在网格的索引int idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n1 + 2) + o0;hist[idx] += v_rco000;hist[idx + 1] += v_rco001;hist[idx + n1 + 2] += v_rco010;hist[idx + n1 + 3] += v_rco011;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n1 + 2)] += v_rco100;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n1 + 2) + 1] += v_rco101;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n1 + 2)] += v_rco110;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n1 + 2) + 1] += v_rco111;}//离特征点远的邻域else if (k >= k1 && k < k2){//子区域内像素点处理后的方向float obin = (Angle[k] - main_angle) * bin_per_rad_2;float mag = Mag[k] * W[k]; //子区域内像素点乘以权值后的梯度幅值int r0 = cvFloor(rbin); //ro取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3},向下取整int c0 = cvFloor(cbin); //c0取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3}int o0 = cvFloor(obin);rbin = rbin - r0; //子区域内像素点坐标的小数部分,用于线性插值cbin = cbin - c0;obin = obin - o0;//限制范围为梯度直方图横坐标[0,n)if (o0 < 0)o0 = o0 + n2;if (o0 >= n1)o0 = o0 - n2;//三线性插值用于计算落在两个子区域之间的像素对两个子区域的作用,并把其分配到对应子区域的8个方向上//使用三线性插值(即三维)方法,计算直方图float v_r1 = mag * rbin; //第二行分配的值float v_r0 = mag - v_r1; //第一行分配的值float v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbin; //第二行第二列分配的值float v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; //第二行第一列分配的值float v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbin; //第一行第二列分配的值float v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01;float v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obin; //第二行第二列第二个方向上分配的值,每个采样点去邻近两个方向float v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; //第二行第二列第一个方向上分配的值float v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obin;float v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;float v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obin;float v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;float v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obin;float v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001;//该像素所在网格的索引int idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n2 + 2) + o0;hist[idx] += v_rco000;hist[idx + 1] += v_rco001;hist[idx + n2 + 2] += v_rco010;hist[idx + n2 + 3] += v_rco011;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n2 + 2)] += v_rco100;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n2 + 2) + 1] += v_rco101;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n2 + 2)] += v_rco110;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n2 + 2) + 1] += v_rco111;}else{//子区域内像素点处理后的方向float obin = (Angle[k] - main_angle) * bin_per_rad_3;float mag = Mag[k] * W[k]; //子区域内像素点乘以权值后的梯度幅值int r0 = cvFloor(rbin); //ro取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3},向下取整int c0 = cvFloor(cbin); //c0取值集合是{-1,0,1,2,3}int o0 = cvFloor(obin);rbin = rbin - r0; //子区域内像素点坐标的小数部分,用于线性插值cbin = cbin - c0;obin = obin - o0;//限制范围为梯度直方图横坐标[0,n)if (o0 < 0)o0 = o0 + n3;if (o0 >= n1)o0 = o0 - n3;//三线性插值用于计算落在两个子区域之间的像素对两个子区域的作用,并把其分配到对应子区域的8个方向上//使用三线性插值(即三维)方法,计算直方图float v_r1 = mag * rbin; //第二行分配的值float v_r0 = mag - v_r1; //第一行分配的值float v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbin; //第二行第二列分配的值float v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11; //第二行第一列分配的值float v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbin; //第一行第二列分配的值float v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01;float v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obin; //第二行第二列第二个方向上分配的值,每个采样点去邻近两个方向float v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111; //第二行第二列第一个方向上分配的值float v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obin;float v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;float v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obin;float v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;float v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obin;float v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001;//该像素所在网格的索引int idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n3 + 2) + o0;hist[idx] += v_rco000;hist[idx + 1] += v_rco001;hist[idx + n3 + 2] += v_rco010;hist[idx + n3 + 3] += v_rco011;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n3 + 2)] += v_rco100;hist[idx + (d + 2) * (n3 + 2) + 1] += v_rco101;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n3 + 2)] += v_rco110;hist[idx + (d + 3) * (n3 + 2) + 1] += v_rco111;}}//由于圆周循环的特性,对计算以后幅角小于 0 度或大于 360 度的值重新进行调整,使//其在 0~360 度之间for (int i = 0; i < d; ++i){for (int j = 0; j < d; ++j){int idx = ((i + 1) * (d + 2) + (j + 1)) * (n + 2);hist[idx] += hist[idx + n];//hist[idx + 1] += hist[idx + n + 1];//opencv源码中这句话是多余的,hist[idx + n + 1]永远是0.0for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k)descriptor[(i * d + j) * n + k] = hist[idx + k];}}//对描述子进行归一化int lenght = d * d * n;float norm = 0;//计算特征描述向量的模值的平方for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){norm = norm + descriptor[i] * descriptor[i];}norm = sqrt(norm); //特征描述向量的模值//此次归一化能去除光照的影响for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = descriptor[i] / norm;}//阈值截断,去除特征描述向量中大于 0.2 的值,能消除非线性光照的影响(相机饱和度对某些放的梯度影响较大,对方向的影响较小)for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = min(descriptor[i], DESCR_MAG_THR);}//再次归一化,能够提高特征的独特性norm = 0;for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){norm = norm + descriptor[i] * descriptor[i];}norm = sqrt(norm);for (int i = 0; i < lenght; ++i){descriptor[i] = descriptor[i] / norm;}
}/********************************该函数计算所有特征点特征描述子***************************/
/*gauss_pyr表示高斯金字塔keypoints表示特征点、descriptors表示生成的特征点的描述子*/
void mySift::calc_sift_descriptors(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,Mat& descriptors, const vector<Mat>& amplit, const vector<Mat>& orient)
{int d = DESCR_WIDTH; //d=4,特征点邻域网格个数是d x dint n = DESCR_HIST_BINS; //n=8,每个网格特征点梯度角度等分为8个方向descriptors.create(keypoints.size(), d * d * n, CV_32FC1); //分配空间for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); ++i) //对于每一个特征点{int octaves, layer;//得到特征点所在的组号,层号octaves = keypoints[i].octave & 255;layer = (keypoints[i].octave >> 8) & 255;//得到特征点相对于本组的坐标,不是最底层Point2f pt(keypoints[i].pt.x / (1 << octaves), keypoints[i].pt.y / (1 << octaves));float scale = keypoints[i].size / (1 << octaves); //得到特征点相对于本组的尺度float main_angle = keypoints[i].angle; //特征点主方向//计算该点的描述子calc_sift_descriptor(gauss_pyr[octaves][layer], main_angle, pt, scale, d, n, descriptors.ptr<float>((int)i));//improve_calc_sift_descriptor(gauss_pyr[octaves][layer], main_angle, pt, scale, d, n, descriptors.ptr<float>((int)i));//calc_gloh_descriptor(amplit[octaves], orient[octaves], pt, scale, main_angle, d, n, descriptors.ptr<float>((int)i));if (double_size)//如果图像尺寸扩大一倍{keypoints[i].pt.x = keypoints[i].pt.x / 2.f;keypoints[i].pt.y = keypoints[i].pt.y / 2.f;}}}/*************该函数构建SAR_SIFT尺度空间*****************/
/*image表示输入的原始图像sar_harris_fun表示尺度空间的Sar_harris函数amplit表示尺度空间像素的梯度幅度orient表示尺度空间像素的梯度方向*/
void mySift::build_sar_sift_space(const Mat& image, vector<Mat>& sar_harris_fun, vector<Mat>& amplit, vector<Mat>& orient)
{//转换输入图像格式Mat gray_image;if (image.channels() != 1)cvtColor(image, gray_image, CV_RGB2GRAY);elsegray_image = image;//把图像转换为0-1之间的浮点数据Mat float_image;double ratio = pow(2, 1.0 / 3.0); //相邻两层的尺度比,默认是2^(1/3)//在这里转换为0-1之间的浮点数据和转换为0-255之间的浮点数据,效果是一样的//gray_image.convertTo(float_image, CV_32FC1, 1.f / 255.f, 0.f);//转换为0-1之间gray_image.convertTo(float_image, CV_32FC1, 1, 0.f); //转换为0-255之间的浮点数//分配内存sar_harris_fun.resize(Mmax);amplit.resize(Mmax);orient.resize(Mmax);for (int i = 0; i < Mmax; ++i){float scale = (float)sigma * (float)pow(ratio, i); //获得当前层的尺度int radius = cvRound(2 * scale);Mat kernel;roewa_kernel(radius, scale, kernel);//四个滤波模板生成Mat W34 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1);Mat W12 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1);Mat W14 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1);Mat W23 = Mat::zeros(2 * radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1, CV_32FC1);kernel(Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1), Range::all()).copyTo(W34(Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1), Range::all()));kernel(Range(0, radius), Range::all()).copyTo(W12(Range(0, radius), Range::all()));kernel(Range::all(), Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1)).copyTo(W14(Range::all(), Range(radius + 1, 2 * radius + 1)));kernel(Range::all(), Range(0, radius)).copyTo(W23(Range::all(), Range(0, radius)));//滤波Mat M34, M12, M14, M23;double eps = 0.00001;filter2D(float_image, M34, CV_32FC1, W34, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(float_image, M12, CV_32FC1, W12, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(float_image, M14, CV_32FC1, W14, Point(-1, -1), eps);filter2D(float_image, M23, CV_32FC1, W23, Point(-1, -1), eps);//计算水平梯度和竖直梯度Mat Gx, Gy;log((M14) / (M23), Gx);log((M34) / (M12), Gy);//计算梯度幅度和梯度方向magnitude(Gx, Gy, amplit[i]);phase(Gx, Gy, orient[i], true);//构建sar-Harris矩阵//Mat Csh_11 = log(scale)*log(scale)*Gx.mul(Gx);//Mat Csh_12 = log(scale)*log(scale)*Gx.mul(Gy);//Mat Csh_22 = log(scale)*log(scale)*Gy.mul(Gy);Mat Csh_11 = scale * scale * Gx.mul(Gx);Mat Csh_12 = scale * scale * Gx.mul(Gy);Mat Csh_22 = scale * scale * Gy.mul(Gy);//此时阈值为0.8//Mat Csh_11 = Gx.mul(Gx);//Mat Csh_12 = Gx.mul(Gy);//Mat Csh_22 = Gy.mul(Gy);//此时阈值为0.8/100//高斯权重float gauss_sigma = sqrt(2.f) * scale;int size = cvRound(3 * gauss_sigma);Size kern_size(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1);GaussianBlur(Csh_11, Csh_11, kern_size, gauss_sigma, gauss_sigma);GaussianBlur(Csh_12, Csh_12, kern_size, gauss_sigma, gauss_sigma);GaussianBlur(Csh_22, Csh_22, kern_size, gauss_sigma, gauss_sigma);/*Mat gauss_kernel;//自定义圆形高斯核gauss_circle(size, gauss_sigma, gauss_kernel);filter2D(Csh_11, Csh_11, CV_32FC1, gauss_kernel);filter2D(Csh_12, Csh_12, CV_32FC1, gauss_kernel);filter2D(Csh_22, Csh_22, CV_32FC1, gauss_kernel);*/Mat Csh_21 = Csh_12;//构建sar_harris函数Mat temp_add = Csh_11 + Csh_22;double d = 0.04; //sar_haiirs函数表达式中的任意参数,默认是0.04sar_harris_fun[i] = Csh_11.mul(Csh_22) - Csh_21.mul(Csh_12) - (float)d * temp_add.mul(temp_add);}
}/***************该函数计算所有特征点的特征向量*************/
/*amplit表示尺度空间像素幅度orient表示尺度空间像素梯度角度keys表示检测到的特征点descriptors表示特征点描述子向量,【M x N】,M表示描述子个数,N表示描述子维度*/
void mySift::calc_gloh_descriptors(const vector<Mat>& amplit, const vector<Mat>& orient, const vector<KeyPoint>& keys, Mat& descriptors)
{int d = SAR_SIFT_GLOH_ANG_GRID; //d=4或者d=8int n = SAR_SIFT_DES_ANG_BINS; //n=8默认int num_keys = (int)keys.size();int grids = 2 * d + 1;//descriptors.create(num_keys, grids * n, CV_32FC1);descriptors.create(num_keys, grids * n, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < num_keys; ++i){int octaves = keys[i].octave & 255; //特征点所在层float* ptr_des = descriptors.ptr<float>(i);float scale = keys[i].size / (1 << octaves); //得到特征点相对于本组的尺度; //特征点所在层的尺度float main_ori = keys[i].angle; //特征点主方向//得到特征点相对于本组的坐标,不是最底层Point2f point(keys[i].pt.x / (1 << octaves), keys[i].pt.y / (1 << octaves));cout << "layer=" << octaves << endl;cout << "scale=" << scale << endl;//计算该特征点的特征描述子calc_gloh_descriptor(amplit[octaves], orient[octaves], point, scale, main_ori, d, n, ptr_des);}
}//特征点检测和特征点描述把整个 SIFT 算子都涵盖在内了///******************************特征点检测*********************************/
/*image表示输入的图像gauss_pyr表示生成的高斯金字塔dog_pyr表示生成的高斯差分DOG金字塔keypoints表示检测到的特征点vector<float>& cell_contrast 用于存放一个单元格中所有特征点的对比度vector<float>& cell_contrasts用于存放一个尺度层中所有单元格中特征点的对比度vector<vector<vector<float>>>& all_cell_contrasts用于存放所有尺度层中所有单元格的对比度vector<vector<float>>& average_contrast用于存放所有尺度层中多有单元格的平均对比度*/
void mySift::detect(const Mat& image, vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,vector<vector<vector<float>>>& all_cell_contrasts,vector<vector<float>>& average_contrast, vector<vector<int>>& n_cells, vector<int>& num_cell, vector<vector<int>>& available_n,vector<int>& available_num, vector<KeyPoint>& final_keypoints,vector<KeyPoint>& Final_keypoints, vector<KeyPoint>& Final_Keypoints)
{if (image.empty() || image.depth() != CV_8U)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "输入图像为空,或者图像深度不是CV_8U");//计算高斯金字塔组数int nOctaves;nOctaves = num_octaves(image);//生成高斯金字塔第一层图像Mat init_gauss;create_initial_image(image, init_gauss);//生成高斯尺度空间图像build_gaussian_pyramid(init_gauss, gauss_pyr, nOctaves);//生成高斯差分金字塔(DOG金字塔,or LOG金字塔)build_dog_pyramid(dog_pyr, gauss_pyr);//在DOG金字塔上检测特征点find_scale_space_extrema1(dog_pyr, gauss_pyr, keypoints); //原始 SIFT 算子// UR_SIFT,仅仅是检测特征点,并未对不理想的点进行筛选/*UR_SIFT_find_scale_space_extrema(dog_pyr, gauss_pyr, keypoints, all_cell_contrasts,average_contrast, n_cells, num_cell, available_n, available_num, final_keypoints, Final_keypoints, Final_Keypoints, N);*///如果指定了特征点个数,并且设定的设置小于默认检测的特征点个数if (nfeatures != 0 && nfeatures < (int)keypoints.size()){//特征点响应值(即对比度,对比度越小越不稳定)从大到小排序sort(keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end(), [](const KeyPoint& a, const KeyPoint& b) {return a.response > b.response; });//删除点多余的特征点keypoints.erase(keypoints.begin() + nfeatures, keypoints.end());}
}/**********************特征点描述*******************/
/*gauss_pyr表示高斯金字塔keypoints表示特征点集合descriptors表示特征点的描述子*/
void mySift::comput_des(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& final_keypoints, const vector<Mat>& amplit,const vector<Mat>& orient, Mat& descriptors)
{calc_sift_descriptors(gauss_pyr, final_keypoints, descriptors, amplit, orient);
}3、 myMatch.h
#pragma once#include<opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include<opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp>#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>const double dis_ratio1 = 0.75; //最近邻和次近邻距离比阈值,就目前测试来看 dis_ratio = 0.75 时正确匹配的数量相对较多
const double dis_ratio2 = 0.8;
const double dis_ratio3 = 0.9;const float ransac_error = 1.5; //ransac算法误差阈值const double FSC_ratio_low = 0.8;const double FSC_ratio_up = 1;const int pointsCount = 9; // k均值聚类数据点个数
const int clusterCount = 3; // k均值聚类质心的个数enum DIS_CRIT { Euclidean = 0, COS }; //距离度量准则using namespace std;
using namespace cv;class myMatch
{
public:myMatch();~myMatch();//该函数根据正确的匹配点对,计算出图像之间的变换关系Mat LMS(const Mat& match1_xy, const Mat& match2_xy, string model, float& rmse);//改进版LMS超定方程Mat improve_LMS(const Mat& match1_xy, const Mat& match2_xy, string model, float& rmse);//该函数删除错误的匹配点对Mat ransac(const vector<Point2f>& points_1, const vector<Point2f>& points_2, string model, float threshold, vector<bool>& inliers, float& rmse);//绘制棋盘图像void mosaic_map(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, Mat& chessboard_1, Mat& chessboard_2, Mat& mosaic_image, int width);//该函数把两幅配准后的图像进行融合镶嵌void image_fusion(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, const Mat T, Mat& fusion_image, Mat& matched_image);//该函数进行描述子的最近邻和次近邻匹配void match_des(const Mat& des_1, const Mat& des_2, vector<vector<DMatch>>& dmatchs, DIS_CRIT dis_crite);//建立尺度直方图、ROM 直方图void scale_ROM_Histogram(const vector<DMatch>& matches, float* scale_hist, float* ROM_hist, int n);//该函数删除错误匹配点对,并进行配准Mat match(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, const vector<vector<DMatch>>& dmatchs, vector<KeyPoint> keys_1,vector<KeyPoint> keys_2, string model, vector<DMatch>& right_matchs, Mat& matched_line, vector<DMatch>& init_matchs);
};4、 myMatch.cpp
#include"myMatch.h"#include<opencv2\imgproc\types_c.h>
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp> //特征提取#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<opencv.hpp>#include <numeric> //用于容器元素求和using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//using namespace gpu;RNG rng(100);myMatch::myMatch()
{
}/********该函数根据正确的匹配点对,计算出图像之间的变换关系********/
/*注意:输入几个点都能计算对应的 x 矩阵,(2N,8)*(8,1)=(2N,1)match1_xy表示参考图像特征点坐标集合,[M x 2]矩阵,M表示特征的个数match2_xy表示待配准图像特征点集合,[M x 2]矩阵,M表示特征点集合model表示变换类型,“相似变换”,"仿射变换","透视变换"rmse表示均方根误差返回值为计算得到的3 x 3矩阵参数*/
Mat myMatch::LMS(const Mat& match1_xy, const Mat& match2_xy, string model, float& rmse)
{if (match1_xy.rows != match2_xy.rows)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "LMS模块输入特征点对个数不一致!");if (!(model == string("affine") || model == string("similarity") ||model == string("perspective") || model == string("projective")))CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "LMS模块图像变换类型输入错误!");const int N = match1_xy.rows; //特征点个数Mat match2_xy_trans, match1_xy_trans; //特征点坐标转置transpose(match1_xy, match1_xy_trans); //矩阵转置(2,M)transpose(match2_xy, match2_xy_trans);Mat change = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_32FC1); //变换矩阵//A*X=B,接下来部分仿射变换和透视变换一样,如果特征点个数是M,则A=[2*M,6]矩阵//A=[x1,y1,0,0,1,0;0,0,x1,y1,0,1;.....xn,yn,0,0,1,0;0,0,xn,yn,0,1],应该是改版过的Mat A = Mat::zeros(2 * N, 6, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);//xA.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);//yA.at<float>(2 * i, 4) = 1.f;A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 2) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 5) = 1.f;}//如果特征点个数是M,那个B=[2*M,1]矩阵//B=[u1,v1,u2,v2,.....,un,vn]Mat B;B.create(2 * N, 1, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){B.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0); //xB.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1);//y}//如果是仿射变换if (model == string("affine")){Vec6f values;solve(A, B, values, DECOMP_QR);change = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << values(0), values(1), values(4),values(2), values(3), values(5),+0.0f, +0.0f, 1.0f);Mat temp_1 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(0, 2)); //尺度和旋转量Mat temp_2 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(2, 3)); //平移量Mat match2_xy_change = temp_1 * match2_xy_trans + repeat(temp_2, 1, N);Mat diff = match2_xy_change - match1_xy_trans; //求差pow(diff, 2.f, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0) / N; //sum输出是各个通道的和, / N 初始实在括号里面}//如果是透视变换else if (model == string("perspective")){/*透视变换模型[u'*w,v'*w, w]'=[u,v,w]' = [a1, a2, a5;a3, a4, a6;a7, a8, 1] * [x, y, 1]'[u',v']'=[x,y,0,0,1,0,-u'x, -u'y;0, 0, x, y, 0, 1, -v'x,-v'y] * [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8]'即,Y = A*X *///构造 A 矩阵的后两列Mat A2;A2.create(2 * N, 2, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A2.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 1) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * (-1.f);}Mat A1; //完成的 A 矩阵,(8,8)A1.create(2 * N, 8, CV_32FC1);A.copyTo(A1(Range::all(), Range(0, 6)));A2.copyTo(A1(Range::all(), Range(6, 8)));Mat values; //values中存放的是待求的8个参数solve(A1, B, values, DECOMP_QR); //(2N,8)*(8,1)=(2N,1)好像本身就有点超定矩阵的意思change.at<float>(0, 0) = values.at<float>(0);change.at<float>(0, 1) = values.at<float>(1);change.at<float>(0, 2) = values.at<float>(4);change.at<float>(1, 0) = values.at<float>(2);change.at<float>(1, 1) = values.at<float>(3);change.at<float>(1, 2) = values.at<float>(5);change.at<float>(2, 0) = values.at<float>(6);change.at<float>(2, 1) = values.at<float>(7);change.at<float>(2, 2) = 1.f;Mat temp1 = Mat::ones(1, N, CV_32FC1);Mat temp2;temp2.create(3, N, CV_32FC1);match2_xy_trans.copyTo(temp2(Range(0, 2), Range::all()));temp1.copyTo(temp2(Range(2, 3), Range::all()));Mat match2_xy_change = change * temp2; //待配准图像中的特征点在参考图中的映射结果Mat match2_xy_change_12 = match2_xy_change(Range(0, 2), Range::all());//float* temp_ptr = match2_xy_change.ptr<float>(2);float* temp_ptr = match2_xy_change.ptr<float>(2);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){float div_temp = temp_ptr[i];match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) / div_temp;match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) / div_temp;}Mat diff = match2_xy_change_12 - match1_xy_trans;pow(diff, 2, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0) / N; //sum输出是各个通道的和,rmse为输入点的均方误差}//如果是相似变换else if (model == string("similarity")){/*[x, y, 1, 0;y, -x, 0, 1] * [a, b, c, d]'=[u,v]*/Mat A3;A3.create(2 * N, 4, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A3.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);A3.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A3.at<float>(2 * i, 2) = 1.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i, 3) = 0.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 2) = 0.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = 1.f;}Vec4f values;solve(A3, B, values, DECOMP_QR);change = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << values(0), values(1), values(2),values(1) * (-1.0f), values(0), values(3),+0.f, +0.f, 1.f);Mat temp_1 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(0, 2));//尺度和旋转量Mat temp_2 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(2, 3));//平移量Mat match2_xy_change = temp_1 * match2_xy_trans + repeat(temp_2, 1, N);Mat diff = match2_xy_change - match1_xy_trans;//求差pow(diff, 2, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0) / N;//sum输出是各个通道的和}return change;
}/********改进版LMS超定方程********/
Mat myMatch::improve_LMS(const Mat& match1_xy, const Mat& match2_xy, string model, float& rmse)
{if (match1_xy.rows != match2_xy.rows)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "LMS模块输入特征点对个数不一致!");if (!(model == string("affine") || model == string("similarity") ||model == string("perspective")))CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "LMS模块图像变换类型输入错误!");const int N = match1_xy.rows; //特征点个数Mat match2_xy_trans, match1_xy_trans; //特征点坐标转置transpose(match1_xy, match1_xy_trans); //矩阵转置(2,M)transpose(match2_xy, match2_xy_trans);Mat change = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_32FC1); //变换矩阵//A*X=B,接下来部分仿射变换和透视变换一样,如果特征点个数是M,则A=[2*M,6]矩阵//A=[x1,y1,0,0,1,0;0,0,x1,y1,0,1;.....xn,yn,0,0,1,0;0,0,xn,yn,0,1],应该是改版过的Mat A = Mat::zeros(2 * N, 6, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);//xA.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);//yA.at<float>(2 * i, 4) = 1.f;//A.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);//x//A.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);//y//A.at<float>(2 * i, 2) = 1.f;A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 2) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 5) = 1.f;/*A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 4) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 5) = 1.f;*/}//如果特征点个数是M,那个B=[2*M,1]矩阵//B=[u1,v1,u2,v2,.....,un,vn]Mat B;B.create(2 * N, 1, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){B.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0); //xB.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1);//y}//如果是仿射变换if (model == string("affine")){Vec6f values;solve(A, B, values, DECOMP_QR);change = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << values(0), values(1), values(4),values(2), values(3), values(5),+0.0f, +0.0f, 1.0f);Mat temp_1 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(0, 2));//尺度和旋转量Mat temp_2 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(2, 3));//平移量Mat match2_xy_change = temp_1 * match2_xy_trans + repeat(temp_2, 1, N);Mat diff = match2_xy_change - match1_xy_trans;//求差pow(diff, 2.f, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0 / N);//sum输出是各个通道的和}//如果是透视变换else if (model == string("perspective")){/*透视变换模型[u'*w,v'*w, w]'=[u,v,w]' = [a1, a2, a5;a3, a4, a6;a7, a8, 1] * [x, y, 1]'[u',v']'=[x,y,0,0,1,0,-u'x, -u'y;0, 0, x, y, 0, 1, -v'x,-v'y] * [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8]'即,Y = A*X *///构造 A 矩阵的后两列Mat A2;A2.create(2 * N, 2, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A2.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A2.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 1) = match1_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1) * (-1.f);}Mat A1; //完整的 A 矩阵,(8,8)A1.create(2 * N, 8, CV_32FC1);A.copyTo(A1(Range::all(), Range(0, 6)));A2.copyTo(A1(Range::all(), Range(6, 8)));Mat AA1, balance;Mat evects, evals;transpose(A1, AA1); //求矩阵 A1 的转置balance = AA1 * A1;double a[8][8];for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){a[i][j] = balance.at<float>(i, j);}}//构造输入矩阵CvMat SrcMatrix = cvMat(8, 8, CV_32FC1, a);double b[8][8] ={{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0},{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0}};// 构造输出特征向量矩阵,特征向量按行存储,且与特征值相对应CvMat ProVector = cvMat(8, 8, CV_32FC1, b);// 构造输出特征值矩阵,特征值按降序配列double c[8] = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 };CvMat ProValue = cvMat(8, 1, CV_32FC1, c);//求特征向量,最后一行特征向量即对应的 H 矩阵的参数cvEigenVV(&SrcMatrix, &ProVector, &ProValue, 1.0e-6F);输出特征向量矩阵//for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)//{// for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)// printf("%f\t", cvmGet(&ProVector, i, j));// printf("\n");//}//把计算得到的最小特征值对应的特征变量赋给 H 矩阵change.at<float>(0, 0) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 0);change.at<float>(0, 1) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 1);change.at<float>(0, 2) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 2);change.at<float>(1, 0) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 3);change.at<float>(1, 1) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 4);change.at<float>(1, 2) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 5);change.at<float>(2, 0) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 6);change.at<float>(2, 1) = cvmGet(&ProVector, 7, 7);change.at<float>(2, 2) = 1.f;Mat temp1 = Mat::ones(1, N, CV_32FC1);Mat temp2; //存放处理后的特征点(x,y,1)Ttemp2.create(3, N, CV_32FC1);match2_xy_trans.copyTo(temp2(Range(0, 2), Range::all()));temp1.copyTo(temp2(Range(2, 3), Range::all()));Mat match2_xy_change = change * temp2; //待配准图像中的特征点在参考图中的映射结果Mat match2_xy_change_12 = match2_xy_change(Range(0, 2), Range::all());//float* temp_ptr = match2_xy_change.ptr<float>(2);float* temp_ptr = match2_xy_change.ptr<float>(2);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){float div_temp = temp_ptr[i];match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) / div_temp;match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) / div_temp;}Mat diff = match2_xy_change_12 - match1_xy_trans;pow(diff, 2, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0 / N); //sum输出是各个通道的和,rmse为输入点的均方误差}//如果是相似变换else if (model == string("similarity")){/*[x, y, 1, 0;y, -x, 0, 1] * [a, b, c, d]'=[u,v]*/Mat A3;A3.create(2 * N, 4, CV_32FC1);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){A3.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0);A3.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A3.at<float>(2 * i, 2) = 1.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i, 3) = 0.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 1);A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 1) = match2_xy.at<float>(i, 0) * (-1.f);A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 2) = 0.f;A3.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = 1.f;}Vec4f values;solve(A3, B, values, DECOMP_QR);change = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << values(0), values(1), values(2),values(1) * (-1.0f), values(0), values(3),+0.f, +0.f, 1.f);Mat temp_1 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(0, 2));//尺度和旋转量Mat temp_2 = change(Range(0, 2), Range(2, 3));//平移量Mat match2_xy_change = temp_1 * match2_xy_trans + repeat(temp_2, 1, N);Mat diff = match2_xy_change - match1_xy_trans;//求差pow(diff, 2, diff);rmse = (float)sqrt(sum(diff)(0) * 1.0) / N;//sum输出是各个通道的和}return change;
}/*********************该函数删除错误的匹配点对****************************/
/*points_1表示参考图像上匹配的特征点位置points_2表示待配准图像上匹配的特征点位置model表示变换模型,“similarity”,"affine",“perspective”threshold表示内点阈值inliers表示points_1和points_2中对应的点对是否是正确匹配,如果是,对应元素值为1,否则为0rmse表示最后所有正确匹配点对计算出来的误差返回一个3 x 3矩阵,表示待配准图像到参考图像的变换矩阵*/
Mat myMatch::ransac(const vector<Point2f>& points_1, const vector<Point2f>& points_2, string model, float threshold, vector<bool>& inliers, float& rmse)
{if (points_1.size() != points_2.size())CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "ransac模块输入特征点数量不一致!");if (!(model == string("affine") || model == string("similarity") ||model == string("perspective") || model == string("projective")))CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "ransac模块图像变换类型输入错误!");const size_t N = points_1.size(); //特征点对数,size_t 类型常用来保存一个数据的大小,通常为整形,可移植性强int n; //相当于不同模型对应的标签size_t max_iteration, iterations;//确定最大迭代次数,就目前来看此法过于简单粗暴,可以使用自适应迭代次数法if (model == string("similarity")){n = 2;max_iteration = N * (N - 1) / 2;}else if (model == string("affine")){n = 3;max_iteration = N * (N - 1) * (N - 2) / (2 * 3);}else if (model == string("perspective")){n = 4;max_iteration = N * (N - 1) * (N - 2) / (2 * 3);}if (max_iteration > 800)iterations = 800;elseiterations = max_iteration;//取出保存在points_1和points_2中的点坐标,保存在Mat矩阵中,方便处理Mat arr_1, arr_2; //arr_1,和arr_2是一个[3 x N]的矩阵,每一列表示一个点坐标,第三行全是1arr_1.create(3, N, CV_32FC1);arr_2.create(3, N, CV_32FC1);//获取矩阵每一行的首地址float* p10 = arr_1.ptr<float>(0), * p11 = arr_1.ptr<float>(1), * p12 = arr_1.ptr<float>(2);float* p20 = arr_2.ptr<float>(0), * p21 = arr_2.ptr<float>(1), * p22 = arr_2.ptr<float>(2);//把特征点放到矩阵中for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){p10[i] = points_1[i].x;p11[i] = points_1[i].y;p12[i] = 1.f;p20[i] = points_2[i].x;p21[i] = points_2[i].y;p22[i] = 1.f;}Mat rand_mat; //特征点索引rand_mat.create(1, n, CV_32SC1);int* p = rand_mat.ptr<int>(0);Mat sub_arr1, sub_arr2; //存放随机挑选的特征点sub_arr1.create(n, 2, CV_32FC1);sub_arr2.create(n, 2, CV_32FC1);Mat T; //待配准图像到参考图像的变换矩阵int most_consensus_num = 0; //当前最优一致集个数初始化为0vector<bool> right;right.resize(N);inliers.resize(N);for (size_t i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) //迭代次数{//随机选择n个不同的点对,不同的模型每次随机选择的个数不同while (1){randu(rand_mat, 0, N - 1); //随机生成n个范围在[0,N-1]之间的数,作为获取特征点的索引//保证这n个点坐标不相同if (n == 2 && p[0] != p[1] &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[1]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[1]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[1]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[1]]))break;if (n == 3 && p[0] != p[1] && p[0] != p[2] && p[1] != p[2] &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[1]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[1]]) &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[2]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[2]]) &&(p10[p[1]] != p10[p[2]] || p11[p[1]] != p11[p[2]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[1]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[1]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[2]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[2]]) &&(p20[p[1]] != p20[p[2]] || p21[p[1]] != p21[p[2]]))break;if (n == 4 && p[0] != p[1] && p[0] != p[2] && p[0] != p[3] &&p[1] != p[2] && p[1] != p[3] && p[2] != p[3] &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[1]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[1]]) &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[2]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[2]]) &&(p10[p[0]] != p10[p[3]] || p11[p[0]] != p11[p[3]]) &&(p10[p[1]] != p10[p[2]] || p11[p[1]] != p11[p[2]]) &&(p10[p[1]] != p10[p[3]] || p11[p[1]] != p11[p[3]]) &&(p10[p[2]] != p10[p[3]] || p11[p[2]] != p11[p[3]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[1]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[1]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[2]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[2]]) &&(p20[p[0]] != p20[p[3]] || p21[p[0]] != p21[p[3]]) &&(p20[p[1]] != p20[p[2]] || p21[p[1]] != p21[p[2]]) &&(p20[p[1]] != p20[p[3]] || p21[p[1]] != p21[p[3]]) &&(p20[p[2]] != p20[p[3]] || p21[p[2]] != p21[p[3]]))break;}//提取出n个点对for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){sub_arr1.at<float>(i, 0) = p10[p[i]];sub_arr1.at<float>(i, 1) = p11[p[i]];sub_arr2.at<float>(i, 0) = p20[p[i]];sub_arr2.at<float>(i, 1) = p21[p[i]];}//根据这n个点对,计算初始变换矩阵 TT = LMS(sub_arr1, sub_arr2, model, rmse);int consensus_num = 0; //当前一致集(内点)个数if (model == string("perspective")){//变换矩阵计算待配准图像特征点在参考图像中的映射点Mat match2_xy_change = T * arr_2; //arr_2 中存放的是待配准图像的特征点 (3,N),//match2_xy_change(Range(0, 2), Range::all())意思是提取 match2_xy_change 的 0、1 行,所有的列Mat match2_xy_change_12 = match2_xy_change(Range(0, 2), Range::all());//获取 match2_xy_change 第二行首地址float* temp_ptr = match2_xy_change.ptr<float>(2);for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){float div_temp = temp_ptr[i]; //match2_xy_change 第二行第 i 列值,除以 div_temp ,是为了保证第三行为 1,和原始坐标相对应match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(0, i) / div_temp;match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) = match2_xy_change_12.at<float>(1, i) / div_temp;}//计算待配准图像特征点在参考图像中的映射点与参考图像中对应点的距离Mat diff = match2_xy_change_12 - arr_1(Range(0, 2), Range::all());pow(diff, 2, diff);//第一行和第二行求和,即两点间距离的平方Mat add = diff(Range(0, 1), Range::all()) + diff(Range(1, 2), Range::all());float* p_add = add.ptr<float>(0);//遍历所有距离,如果小于阈值,则认为是局内点for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){if (p_add[i] < threshold) //初始 p_add[i] {right[i] = true;++consensus_num;}elseright[i] = false;}}else if (model == string("affine") || model == string("similarity")){Mat match2_xy_change = T * arr_2; //计算在参考图像中的映射坐标Mat diff = match2_xy_change - arr_1;pow(diff, 2, diff);//第一行和第二行求和,计算特征点间的距离的平方Mat add = diff(Range(0, 1), Range::all()) + diff(Range(1, 2), Range::all());float* p_add = add.ptr<float>(0);for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){//如果小于阈值if (p_add[i] < threshold){right[i] = true;++consensus_num;}elseright[i] = false;}}//判断当前一致集是否是优于之前最优一致集,并更新当前最优一致集个数if (consensus_num > most_consensus_num){most_consensus_num = consensus_num;//把正确匹配的点赋予标签 1 for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)inliers[i] = right[i];}}//删除重复点对for (size_t i = 0; i < N - 1; ++i){for (size_t j = i + 1; j < N; ++j){if (inliers[i] && inliers[j]){if (p10[i] == p10[j] && p11[i] == p11[j] && p20[i] == p20[j] && p21[i] == p21[j]){inliers[j] = false;--most_consensus_num;}}}}//迭代结束,获得最优一致集合,根据这些最优一致集合计算出最终的变换关系 TMat consensus_arr1, consensus_arr2; //经过迭代后最终确认正确匹配的点consensus_arr1.create(most_consensus_num, 2, CV_32FC1);consensus_arr2.create(most_consensus_num, 2, CV_32FC1);int k = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){if (inliers[i]){consensus_arr1.at<float>(k, 0) = p10[i];consensus_arr1.at<float>(k, 1) = p11[i];consensus_arr2.at<float>(k, 0) = p20[i];consensus_arr2.at<float>(k, 1) = p21[i];++k;}}int num_ransac = (model == string("similarity") ? 2 : (model == string("affine") ? 3 : 4));if (k < num_ransac)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "ransac模块删除错误点对后剩下正确点对个数不足以计算出变换关系矩阵!");//利用迭代后正确匹配点计算变换矩阵,为什么不是挑选 n 个点计算变换矩阵T = LMS(consensus_arr1, consensus_arr2, model, rmse);return T;
}/********************该函数生成两幅图的棋盘网格图*************************/
/*image_1表示参考图像image_2表示配准后的待配准图像chessboard_1表示image_1的棋盘图像chessboard_2表示image_2的棋盘图像mosaic_image表示image_1和image_2的镶嵌图像width表示棋盘网格大小*/
void myMatch::mosaic_map(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, Mat& chessboard_1, Mat& chessboard_2, Mat& mosaic_image, int width)
{if (image_1.size != image_2.size)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "mosaic_map模块输入两幅图大小必须一致!");//生成image_1的棋盘网格图chessboard_1 = image_1.clone();int rows_1 = chessboard_1.rows;int cols_1 = chessboard_1.cols;int row_grids_1 = cvFloor((double)rows_1 / width); //行方向网格个数int col_grids_1 = cvFloor((double)cols_1 / width); //列方向网格个数//指定区域像素赋值为零,便形成了棋盘图//第一幅图,第一行 2、4、6 像素值赋值零;第一幅图与第二幅图零像素位置交叉,以便两幅图交叉显示for (int i = 0; i < row_grids_1; i = i + 2){for (int j = 1; j < col_grids_1; j = j + 2){Range range_x(j * width, (j + 1) * width);Range range_y(i * width, (i + 1) * width);chessboard_1(range_y, range_x) = 0;}}for (int i = 1; i < row_grids_1; i = i + 2){for (int j = 0; j < col_grids_1; j = j + 2){Range range_x(j * width, (j + 1) * width);Range range_y(i * width, (i + 1) * width);chessboard_1(range_y, range_x) = 0;}}//生成image_2的棋盘网格图chessboard_2 = image_2.clone();int rows_2 = chessboard_2.rows;int cols_2 = chessboard_2.cols;int row_grids_2 = cvFloor((double)rows_2 / width);//行方向网格个数int col_grids_2 = cvFloor((double)cols_2 / width);//列方向网格个数//第二幅图,第一行 1、3、5 像素值赋值零for (int i = 0; i < row_grids_2; i = i + 2){for (int j = 0; j < col_grids_2; j = j + 2){Range range_x(j * width, (j + 1) * width);Range range_y(i * width, (i + 1) * width);chessboard_2(range_y, range_x) = 0;}}for (int i = 1; i < row_grids_2; i = i + 2){for (int j = 1; j < col_grids_2; j = j + 2){Range range_x(j * width, (j + 1) * width);Range range_y(i * width, (i + 1) * width);chessboard_2(range_y, range_x) = 0;}}//两个棋盘图进行叠加,显示配准效果mosaic_image = chessboard_1 + chessboard_2;
}/*该函数对输入图像指定位置像素进行中值滤波,消除边缘拼接阴影*/
/*image表示输入的图像position表示需要进行中值滤波的位置*/
inline void median_filter(Mat& image, const vector<vector<int>>& pos)
{int channels = image.channels();switch (channels){case 1://单通道for (auto beg = pos.cbegin(); beg != pos.cend(); ++beg){int i = (*beg)[0];//yint j = (*beg)[1];//xuchar& pix_val = image.at<uchar>(i, j);vector<uchar> pixs;for (int row = -1; row <= 1; ++row){for (int col = -1; col <= 1; ++col){if (i + row >= 0 && i + row < image.rows && j + col >= 0 && j + col < image.cols){pixs.push_back(image.at<uchar>(i + row, j + col));}}}//排序std::sort(pixs.begin(), pixs.end());pix_val = pixs[pixs.size() / 2];}break;case 3://3通道for (auto beg = pos.cbegin(); beg != pos.cend(); ++beg){int i = (*beg)[0];//yint j = (*beg)[1];//xVec3b& pix_val = image.at<Vec3b>(i, j);vector<cv::Vec3b> pixs;for (int row = -1; row <= 1; ++row){for (int col = -1; col <= 1; ++col){if (i + row >= 0 && i + row < image.rows && j + col >= 0 && j + col < image.cols){pixs.push_back(image.at<Vec3b>(i + row, j + col));}}}//排序std::sort(pixs.begin(), pixs.end(),[pix_val](const Vec3b& a, const Vec3b& b)->bool {return sum((a).ddot(a))[0] < sum((b).ddot(b))[0];});pix_val = pixs[pixs.size() / 2];}break;default:break;}
}/***************该函数把配准后的图像进行融合*****************/
/*该函数功能主要是来对图像进行融合,以显示配准的效果*image_1表示参考图像*image_2表示待配准图像*T表示待配准图像到参考图像的转换矩阵*fusion_image表示参考图像和待配准图像融合后的图像*mosaic_image表示参考图像和待配准图像融合镶嵌后的图像,镶嵌图形是为了观察匹配效果*matched_image表示把待配准图像进行配准后的结果*/
void myMatch::image_fusion(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, const Mat T, Mat& fusion_image, Mat& matched_image)
{//有关depth()的理解,详解:https://blog.csdn.net/datouniao1/article/details/113524784if (!(image_1.depth() == CV_8U && image_2.depth() == CV_8U))CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "image_fusion模块仅支持uchar类型图像!");if (image_1.channels() == 4 || image_2.channels() == 4)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "image_fusion模块仅仅支持单通道或者3通道图像");int rows_1 = image_1.rows, cols_1 = image_1.cols;int rows_2 = image_2.rows, cols_2 = image_2.cols;int channel_1 = image_1.channels();int channel_2 = image_2.channels();//可以对:彩色-彩色、彩色-灰色、灰色-彩色、灰色-灰色的配准Mat image_1_temp, image_2_temp;if (channel_1 == 3 && channel_2 == 3){image_1_temp = image_1;image_2_temp = image_2;}else if (channel_1 == 1 && channel_2 == 3){image_1_temp = image_1;cvtColor(image_2, image_2_temp, CV_RGB2GRAY); //颜色空间转换,把彩色图转化为灰度图}else if (channel_1 == 3 && channel_2 == 1){cvtColor(image_1, image_1_temp, CV_RGB2GRAY);image_2_temp = image_2;}else if (channel_1 == 1 && channel_2 == 1){image_1_temp = image_1;image_2_temp = image_2;}//创建一个(3,3)float 矩阵 Mat_ 是一个模板类Mat T_temp = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, cols_1, 0, 1, rows_1, 0, 0, 1);Mat T_1 = T_temp * T;//对参考图像和待配准图像进行变换Mat trans_1, trans_2;//same type as image_2_temp trans_1 = Mat::zeros(3 * rows_1, 3 * cols_1, image_1_temp.type()); //创建扩大后的矩阵image_1_temp.copyTo(trans_1(Range(rows_1, 2 * rows_1), Range(cols_1, 2 * cols_1))); //把image_1_temp中的数据复制到扩大后矩阵的对应位置warpPerspective(image_2_temp, trans_2, T_1, Size(3 * cols_1, 3 * rows_1), INTER_LINEAR, 0, Scalar::all(0));/*功能:把image_2_temp投射到一个新的视平面,即变形*image_2_temp为输入矩阵*trans_2为输出矩阵,尺寸和输入矩阵大小一致*T_1为变换矩阵,(3, 3)矩阵用于透视变换, (2, 2)用于线性变换, (1, 1)用于平移*warpPerspective函数功能是进行透视变换,T_1是(3,3)的透视变换矩阵*int flags=INTER_LINEAR为输出图像的插值方法*int borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT,0 为图像边界的填充方式*const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar():边界的颜色设置,一般默认是0,Scalar::all(0)对影像边界外进行填充*///使用简单的均值法进行图像融合Mat trans = trans_2.clone(); //把经过透视变换的image_2复制给transint nRows = rows_1;int nCols = cols_1;int len = nCols;bool flag_1 = false;bool flag_2 = false;vector<vector<int>> positions; //保存边缘位置坐标switch (image_1_temp.channels()){case 1: //如果图像1是单通道的for (int i = 0; i < nRows; ++i){uchar* ptr_1 = trans_1.ptr<uchar>(i + rows_1); //访问trans_1中的指定行像素值uchar* ptr = trans.ptr<uchar>(i + rows_1); //访问trans 中的指定行像素值for (int j = 0; j < nCols; ++j){if (ptr[j + len] == 0 && ptr_1[j + len] != 0) //非重合区域{flag_1 = true;if (flag_2) //表明从重合区域过度到了非重合区域{for (int p = -1; p <= 1; ++p) //保存边界3x3区域像素{for (int q = -1; q <= 1; ++q){vector<int> pos;pos.push_back(i + rows_1 + p);pos.push_back(j + cols_1 + q);positions.push_back(pos);//保存边缘位置坐标}}flag_2 = false;}ptr[j + len] = ptr_1[j + len];}else//对于重合区域{flag_2 = true;if (flag_1)//表明从非重合区域过度到了重合区域{for (int p = -1; p <= 1; ++p)//保存边界3x3区域像素{for (int q = -1; q <= 1; ++q){vector<int> pos;pos.push_back(i + rows_1 + p);pos.push_back(j + cols_1 + q);positions.push_back(pos);//保存边缘位置坐标}}flag_1 = false;}ptr[j + len] = saturate_cast<uchar>(((float)ptr[j + len] + (float)ptr_1[j + len]) / 2);}}}break;case 3: //如果图像是三通道的len = len * image_1_temp.channels(); //3倍的列数for (int i = 0; i < nRows; ++i){uchar* ptr_1 = trans_1.ptr<uchar>(i + rows_1); //访问trans_1中的指定行像素值uchar* ptr = trans.ptr<uchar>(i + rows_1); //访问trans 中的指定行像素值for (int j = 0; j < nCols; ++j){int nj = j * image_1_temp.channels();//若两张影像对应列像素值不同(3通道),则是非重合区,该过程仅仅是为了使配准后的影像进行融合,而非配准if (ptr[nj + len] == 0 && ptr[nj + len + 1] == 0 && ptr[nj + len + 2] == 0 &&ptr_1[nj + len] != 0 && ptr_1[nj + len + 1] != 0 && ptr_1[nj + len + 2] != 0){flag_1 = true;if (flag_2) //表明从重合区域过度到了非重合区域{for (int p = -1; p <= 1; ++p) //保存边界3x3区域像素{for (int q = -1; q <= 1; ++q){vector<int> pos;pos.push_back(i + rows_1 + p);pos.push_back(j + cols_1 + q);positions.push_back(pos); //保存边缘位置坐标}}flag_2 = false;}ptr[nj + len] = ptr_1[nj + len];ptr[nj + len + 1] = ptr_1[nj + len + 1];ptr[nj + len + 2] = ptr_1[nj + len + 2];}else{ //对于重合区域flag_2 = true;if (flag_1) //表明从非重合区域过度到了重合区域{for (int p = -1; p <= 1; ++p) //保存边界3x3区域像素{for (int q = -1; q <= 1; ++q){vector<int> pos;pos.push_back(i + rows_1 + p);pos.push_back(j + cols_1 + q);positions.push_back(pos); //保存边缘位置坐标}}flag_1 = false;}ptr[nj + len] = saturate_cast<uchar>(((float)ptr[nj + len] + (float)ptr_1[nj + len]) / 2);ptr[nj + len + 1] = saturate_cast<uchar>(((float)ptr[nj + len + 1] + (float)ptr_1[nj + len + 1]) / 2);ptr[nj + len + 2] = saturate_cast<uchar>(((float)ptr[nj + len + 2] + (float)ptr_1[nj + len + 2]) / 2);}}}break;default:break;}//根据获取的边缘区域的坐标,对边缘像素进行中值滤波,消除边缘效应median_filter(trans, positions);//删除多余的区域Mat left_up = T_1 * (Mat_<float>(3, 1) << 0, 0, 1); //左上角Mat left_down = T_1 * (Mat_<float>(3, 1) << 0, rows_2 - 1, 1); //左下角Mat right_up = T_1 * (Mat_<float>(3, 1) << cols_2 - 1, 0, 1); //右上角Mat right_down = T_1 * (Mat_<float>(3, 1) << cols_2 - 1, rows_2 - 1, 1); //右下角//对于透视变换,需要除以一个因子left_up = left_up / left_up.at<float>(2, 0);left_down = left_down / left_down.at<float>(2, 0);right_up = right_up / right_up.at<float>(2, 0);right_down = right_down / right_down.at<float>(2, 0);//计算x,y坐标的范围float temp_1 = min(left_up.at<float>(0, 0), left_down.at<float>(0, 0));float temp_2 = min(right_up.at<float>(0, 0), right_down.at<float>(0, 0));float min_x = min(temp_1, temp_2);temp_1 = max(left_up.at<float>(0, 0), left_down.at<float>(0, 0));temp_2 = max(right_up.at<float>(0, 0), right_down.at<float>(0, 0));float max_x = max(temp_1, temp_2);temp_1 = min(left_up.at<float>(1, 0), left_down.at<float>(1, 0));temp_2 = min(right_up.at<float>(1, 0), right_down.at<float>(1, 0));float min_y = min(temp_1, temp_2);temp_1 = max(left_up.at<float>(1, 0), left_down.at<float>(1, 0));temp_2 = max(right_up.at<float>(1, 0), right_down.at<float>(1, 0));float max_y = max(temp_1, temp_2);int X_min = max(cvFloor(min_x), 0);int X_max = min(cvCeil(max_x), 3 * cols_1 - 1);int Y_min = max(cvFloor(min_y), 0);int Y_max = min(cvCeil(max_y), 3 * rows_1 - 1);if (X_min > cols_1)X_min = cols_1;if (X_max < 2 * cols_1 - 1)X_max = 2 * cols_1 - 1;if (Y_min > rows_1)Y_min = rows_1;if (Y_max < 2 * rows_1 - 1)Y_max = 2 * rows_1 - 1;//提取有价值区域Range Y_range(Y_min, Y_max + 1);Range X_range(X_min, X_max + 1);fusion_image = trans(Y_range, X_range);matched_image = trans_2(Y_range, X_range);Mat ref_matched = trans_1(Y_range, X_range);//生成棋盘网格图像/*Mat chessboard_1, chessboard_2;mosaic_map(trans_1(Y_range, X_range), trans_2(Y_range, X_range), chessboard_1, chessboard_2, mosaic_image, 100);*//*cv::imwrite(".\\image_save\\参考图像棋盘图像.jpg", chessboard_1);cv::imwrite(".\\image_save\\待配准图像棋盘图像.jpg", chessboard_2);*/cv::imwrite(".\\image_save\\配准后的参考图像.jpg", ref_matched);cv::imwrite(".\\image_save\\配准后的待配准图像.jpg", matched_image);
}/******该函数计算参考图像一个描述子和待配准图像所有描述子的欧式距离,并获得最近邻和次近邻距离,以及对应的索引*//*sub_des_1表示参考图像的一个描述子*des_2表示待配准图像描述子*num_des_2值待配准图像描述子个数*dims_des指的是描述子维度*dis保存最近邻和次近邻距离*idx保存最近邻和次近邻索引*/
inline void min_dis_idx(const float* ptr_1, const Mat& des_2, int num_des2, int dims_des, float dis[2], int idx[2])
{float min_dis1 = 1000, min_dis2 = 2000;int min_idx1, min_idx2;for (int j = 0; j < num_des2; ++j){const float* ptr_des_2 = des_2.ptr<float>(j);float cur_dis = 0;for (int k = 0; k < dims_des; ++k){float diff = ptr_1[k] - ptr_des_2[k];cur_dis += diff * diff;}if (cur_dis < min_dis1) {min_dis1 = cur_dis;min_idx1 = j;}else if (cur_dis >= min_dis1 && cur_dis < min_dis2) {min_dis2 = cur_dis;min_idx2 = j;}}dis[0] = sqrt(min_dis1); dis[1] = sqrt(min_dis2);idx[0] = min_idx1; idx[1] = min_idx2;
}/*加速版本的描述子匹配,返回匹配点候选集函数,该加速版本比前面版本速度提升了3倍*/
void myMatch::match_des(const Mat& des_1, const Mat& des_2, vector<vector<DMatch>>& dmatchs, DIS_CRIT dis_crite)
{int num_des_1 = des_1.rows;int num_des_2 = des_2.rows;int dims_des = des_1.cols;vector<DMatch> match(2);//对于参考图像上的每一点,和待配准图像进行匹配if (dis_crite == 0) //欧几里得距离{for (int i = 0; i < num_des_1; ++i) //对于参考图像中的每个描述子{const float* ptr_des_1 = des_1.ptr<float>(i);float dis[2];int idx[2];min_dis_idx(ptr_des_1, des_2, num_des_2, dims_des, dis, idx);match[0].queryIdx = i;match[0].trainIdx = idx[0];match[0].distance = dis[0];match[1].queryIdx = i;match[1].trainIdx = idx[1];match[1].distance = dis[1];dmatchs.push_back(match);}}else if (dis_crite == 1)//cos距离{Mat trans_des2;transpose(des_2, trans_des2);double aa = (double)getTickCount();Mat mul_des = des_1 * trans_des2;//gemm(des_1, des_2, 1, Mat(), 0, mul_des, GEMM_2_T);double time1 = ((double)getTickCount() - aa) / getTickFrequency();cout << "cos距离中矩阵乘法花费时间: " << time1 << "s" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < num_des_1; ++i){float max_cos1 = -1000, max_cos2 = -2000;int max_idx1, max_idx2;float* ptr_1 = mul_des.ptr<float>(i);for (int j = 0; j < num_des_2; ++j){float cur_cos = ptr_1[j];if (cur_cos > max_cos1) {max_cos1 = cur_cos;max_idx1 = j;}else if (cur_cos <= max_cos1 && cur_cos > max_cos2) {max_cos2 = cur_cos;max_idx2 = j;}}match[0].queryIdx = i;match[0].trainIdx = max_idx1;match[0].distance = acosf(max_cos1);match[1].queryIdx = i;match[1].trainIdx = max_idx2;match[1].distance = acosf(max_cos2);dmatchs.push_back(match);}}
}/*******************建立尺度直方图、ROM 直方图************************/
void myMatch::scale_ROM_Histogram(const vector<DMatch>& matches, float* scale_hist, float* ROM_hist, int n)
{int len = matches.size();//使用AutoBuffer分配一段内存,这里多出4个空间的目的是为了方便后面平滑直方图的需要AutoBuffer<float> buffer((4 * len) + n + 4);//X保存水平差分,Y保存数值差分,Mag保存梯度幅度,Ori保存梯度角度,W保存高斯权重float* X = buffer, * Y = buffer + len, * Mag = Y, * Ori = Y + len, * W = Ori + len;float* temp_hist = W + len + 2; //临时保存直方图数据for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)temp_hist[i] = 0.f; //数据清零
}/*******************该函数删除错误匹配点对,并完成匹配************************/
/*image_1表示参考图像,image_2表示待配准图像dmatchs表示最近邻和次近邻匹配点对keys_1表示参考图像特征点集合keys_2表示待配准图像特征点集合model表示变换模型right_matchs表示参考图像和待配准图像正确匹配点对matched_line表示在参考图像和待配准图像上绘制连接线该函数返回变换模型参数*/
Mat myMatch::match(const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, const vector<vector<DMatch>>& dmatchs, vector<KeyPoint> keys_1,vector<KeyPoint> keys_2, string model, vector<DMatch>& right_matchs, Mat& matched_line, vector<DMatch>& init_matchs)
{//获取初始匹配的关键点的位置vector<Point2f> point_1, point_2;for (size_t i = 0; i < dmatchs.size(); ++i) //增加一个一个0.8,正确匹配点数增加2{double dis_1 = dmatchs[i][0].distance; //distance对应的是特征点描述符的欧式距离double dis_2 = dmatchs[i][1].distance;//比率测试筛选误匹配点(初步筛选),如果满足则认为是有候选集中有正确匹配点if ((dis_1 / dis_2) < dis_ratio3) //最近邻和次近邻距离比阈值{//queryIdx、trainIdx和distance是DMatch类中的一些属性 //pt是KeyPoint类中的成员,对应关键点的坐标point_1.push_back(keys_1[dmatchs[i][0].queryIdx].pt); //queryIdx对应的是特征描述子的下标,也是对应特征点的下标point_2.push_back(keys_2[dmatchs[i][0].trainIdx].pt); //trainIdx对应的是特征描述子的下标,也是对应特征点的下标init_matchs.push_back(dmatchs[i][0]); //保存正确的dmatchs}}cout << "距离比之后初始匹配点对个数是: " << init_matchs.size() << endl;int min_pairs = (model == string("similarity") ? 2 : (model == string("affine") ? 3 : 4));if (point_1.size() < min_pairs)CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, "match模块距离比阶段匹配特征点个数不足!");//使用ransac算法再次对匹配点进行筛选,然后使用最后确定的匹配点计算变换矩阵的参数vector<bool> inliers; //存放的是 bool 类型的数据,对应特征点float rmse;//homography是一个(3,3)矩阵,是待配准影像到参考影像的变换矩阵,初始误差阈值是 1.5Mat homography = ransac(point_1, point_2, model, 1.5, inliers, rmse);//提取出处正确匹配点对int i = 0;vector<Point2f> point_11, point_22;vector<DMatch>::iterator itt = init_matchs.begin();for (vector<bool>::iterator it = inliers.begin(); it != inliers.end(); ++it, ++itt){if (*it) //如果是正确匹配点对{right_matchs.push_back(*itt);// init_matchs 中匹配点对的存储顺序和 point_1 中特征点的存储顺序是一一对应的point_11.push_back(point_1.at(i));point_22.push_back(point_2.at(i));}++i;}cout << "使用RANSAC删除错误点对,且返回正确匹配个数: " << right_matchs.size() << endl;cout << "误差rmse: " << rmse << endl;//绘制初始匹配点对连线图,此时初始匹配指的是经过 KnnMatch 筛选后的匹配Mat initial_matched; //输出矩阵,类似画布drawMatches(image_1, keys_1, image_2, keys_2, init_matchs, initial_matched,Scalar(255, 0, 255), Scalar(0, 255, 0), vector<char>()); //该函数用于绘制特征点并对匹配的特征点进行连线imwrite(".\\image_save\\初始匹配点对.jpg", initial_matched); //保存图片,第一个颜色控制连线,第二个颜色控制特征点//绘制正确匹配点对连线图drawMatches(image_1, keys_1, image_2, keys_2, right_matchs, matched_line,Scalar(255, 0, 255), Scalar(0, 255, 0), vector<char>());imwrite(".\\image_save\\正确匹配点对.jpg", matched_line);//保存和显示检测到的特征点Mat keys_image_1, keys_image_2; //输出矩阵,类似画布drawKeypoints(image_1, keys_1, keys_image_1, Scalar(0, 255, 0)); //该函数用于绘制图像中的特征点drawKeypoints(image_2, keys_2, keys_image_2, Scalar(0, 255, 0));imwrite(".\\image_save\\参考图像检测到的特征点.jpg", keys_image_1);imwrite(".\\image_save\\待配准图像检测到的.jpg", keys_image_2);return homography;
}myMatch::~myMatch()
{
}5、 myDisplay.h
#pragma#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include<opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp>
#include<vector>using namespace cv;
using namespace std;class myDisplay
{
public:myDisplay() {}void mosaic_pyramid(const vector<vector<Mat>>& pyramid, Mat& pyramid_image, int nOctaceLayers, string str);void write_mosaic_pyramid(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr_1, const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr_1,const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr_2, const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr_2, int nOctaveLayers);//没用到,后文没有对其进行定义void write_keys_image(vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,const Mat& image_1, const Mat& image_2, Mat& image_1_keys, Mat& image_2_keys, bool double_size);
};6、 myDisplay.cpp
#include "myDisplay.h"#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<vector>
#include<sstream>/***************************该函数把金字塔放在一副图像上(包络高斯金字塔和DOG金字塔)******************/
/*pyramid表示高斯金字塔或者DOG金字塔pyramid_image表示生成的金字塔图像nOctaveLayers表示每组中间层数,默认是3str表示是高斯金字塔还是DOG金字塔
*/
void myDisplay::mosaic_pyramid(const vector<vector<Mat>>& pyramid, Mat& pyramid_image, int nOctaceLayers, string str)
{//获得每组金字塔图像大小vector<vector<int>> temp_size;for (auto beg = pyramid.cbegin(); beg != pyramid.cend(); ++beg){vector<int> temp_vec;int rows = (*beg)[0].rows;int cols = (*beg)[0].cols;temp_vec.push_back(rows);temp_vec.push_back(cols);temp_size.push_back(temp_vec);}//计算最后生成的金字塔图像pyramid_image的大小int total_rows = 0, total_cols = 0;for (auto beg = temp_size.begin(); beg != temp_size.end(); ++beg){total_rows = total_rows + (*beg)[0];//获取行大小if (beg == temp_size.begin()) {if (str == string("高斯金字塔"))total_cols = (nOctaceLayers + 3) * ((*beg)[1]);//获取列大小else if (str == string("DOG金字塔"))total_cols = (nOctaceLayers + 2) * ((*beg)[1]);//获取列大小}}pyramid_image.create(total_rows, total_cols, CV_8UC1);int i = 0, accumulate_row = 0;for (auto beg = pyramid.cbegin(); beg != pyramid.cend(); ++beg, ++i){int accumulate_col = 0;accumulate_row = accumulate_row + temp_size[i][0];for (auto it = (*beg).cbegin(); it != (*beg).cend(); ++it){accumulate_col = accumulate_col + temp_size[i][1];Mat temp(pyramid_image, Rect(accumulate_col - temp_size[i][1], accumulate_row - temp_size[i][0], it->cols, it->rows));Mat temp_it;normalize(*it, temp_it, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_32FC1);convertScaleAbs(temp_it, temp_it, 1, 0);temp_it.copyTo(temp);}}
}/**************************该函数保存拼接后的高斯金字塔和DOG金字塔图像**************************/
/*gauss_pyr_1表示参考高斯金字塔dog_pyr_1表示参考DOG金字塔gauss_pyr_2表示待配准高斯金字塔dog_pyr_2表示待配准DOG金字塔nOctaveLayers表示金字塔每组中间层数*/
void myDisplay::write_mosaic_pyramid(const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr_1, const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr_1,const vector<vector<Mat>>& gauss_pyr_2, const vector<vector<Mat>>& dog_pyr_2, int nOctaveLayers)
{//显示参考和待配准高斯金字塔图像Mat gauss_image_1, gauss_image_2;mosaic_pyramid(gauss_pyr_1, gauss_image_1, nOctaveLayers, string("高斯金字塔"));mosaic_pyramid(gauss_pyr_2, gauss_image_2, nOctaveLayers, string("高斯金字塔"));imwrite(".\\image_save\\参考图像高斯金字塔.jpg", gauss_image_1);imwrite(".\\image_save\\待配准图像高斯金字塔.jpg", gauss_image_2);//显示参考和待配准DOG金字塔图像Mat dog_image_1, dog_image_2;mosaic_pyramid(dog_pyr_1, dog_image_1, nOctaveLayers, string("DOG金字塔"));mosaic_pyramid(dog_pyr_2, dog_image_2, nOctaveLayers, string("DOG金字塔"));imwrite(".\\image_save\\参考图像DOG金字塔.jpg", dog_image_1);imwrite(".\\image_save\\待配准图像DOG金字塔.jpg", dog_image_2);
}7、 main.cpp
#include"mySift.h"
#include"myDisplay.h"
#include"myMatch.h"
#include<direct.h>#include<opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2\calib3d\calib3d.hpp>
#include<opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>#include<fstream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<direct.h>int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{/********************** 1、读入数据 **********************/Mat image_1 = imread("..\\test_data\\perspective_graf_1.ppm", -1);Mat image_2 = imread("..\\test_data\\perspective_graf_2.ppm", -1);string change_model = "perspective"; //affine为仿射变换,初始为perspectivestring folderPath = ".\\image_save";_mkdir(folderPath.c_str());double total_count_beg = (double)getTickCount(); //算法运行总时间开始计时mySift sift_1(0, 3, 0.04, 10, 1.6, true); //类对象/********************** 1、参考图像特征点检测和描述 **********************/vector<vector<Mat>> gauss_pyr_1, dog_pyr_1; //高斯金字塔和高斯差分金字塔vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1; //特征点vector<vector<vector<float>>> all_cell_contrasts_1; //所有尺度层中所有单元格的对比度vector<vector<float>> average_contrast_1; //所有尺度层中多有单元格的平均对比度vector<vector<int>> n_cells_1; //所有尺度层,每一尺度层中所有单元格所需特征数vector<int> num_cell_1; //当前尺度层中所有单元格中的所需特征数vector<vector<int>> available_n_1; //所有尺度层,每一尺度层中所有单元格可得到特征数vector<int> available_num_1; //一个尺度层中所有单元格中可用特征数量vector<KeyPoint> final_keypoints1; //第一次筛选结果vector<KeyPoint> Final_keypoints1; //第二次筛选结果vector<KeyPoint> Final_Keypoints1; //第三次筛选结果Mat descriptors_1; //特征描述子double detect_1 = (double)getTickCount(); //特征点检测运行时间开始计时sift_1.detect(image_1, gauss_pyr_1, dog_pyr_1, keypoints_1, all_cell_contrasts_1,average_contrast_1, n_cells_1, num_cell_1, available_n_1, available_num_1, final_keypoints1, Final_keypoints1, Final_Keypoints1); //特征点检测cout << "参考图像检测出的总特征数 =" << keypoints_1.size() << endl;//getTickFrequency() 返回值为一秒的计时周期数,二者比值为特征点检测时间double detect_time_1 = ((double)getTickCount() - detect_1) / getTickFrequency();cout << "参考图像特征点检测时间是: " << detect_time_1 << "s" << endl;double comput_1 = (double)getTickCount();vector<Mat> sar_harris_fun_1;vector<Mat> amplit_1;vector<Mat> orient_1;sift_1.comput_des(gauss_pyr_1, keypoints_1, amplit_1, orient_1, descriptors_1);double comput_time_1 = ((double)getTickCount() - comput_1) / getTickFrequency();cout << "参考图像特征点描述时间是: " << comput_time_1 << "s" << endl;/********************** 1、待配准图像特征点检测和描述 **********************/vector<vector<Mat>> gauss_pyr_2, dog_pyr_2;vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_2;vector<vector<vector<float>>> all_cell_contrasts_2; //所有尺度层中所有单元格的对比度vector<vector<float>> average_contrast_2; //所有尺度层中多有单元格的平均对比度vector<vector<int>> n_cells_2; //所有尺度层,每一尺度层中所有单元格所需特征数vector<int> num_cell_2; //当前尺度层中所有单元格中的所需特征数vector<vector<int>> available_n_2; //所有尺度层,每一尺度层中的一个单元格可得到特征数vector<int> available_num_2; //一个尺度层中所有单元格中可用特征数量vector<KeyPoint> final_keypoints2; //第一次筛选结果vector<KeyPoint> Final_keypoints2; //第二次筛选结果vector<KeyPoint> Final_Keypoints2; //第三次筛选结果Mat descriptors_2;double detect_2 = (double)getTickCount();sift_1.detect(image_2, gauss_pyr_2, dog_pyr_2, keypoints_2, all_cell_contrasts_2,average_contrast_2, n_cells_2, num_cell_2, available_n_2, available_num_2, final_keypoints2, Final_keypoints2, Final_Keypoints2);cout << "待配准图像检测出的总特征数 =" << keypoints_2.size() << endl;double detect_time_2 = ((double)getTickCount() - detect_2) / getTickFrequency();cout << "待配准图像特征点检测时间是: " << detect_time_2 << "s" << endl;double comput_2 = (double)getTickCount();vector<Mat> sar_harris_fun_2;vector<Mat> amplit_2;vector<Mat> orient_2;sift_1.comput_des(gauss_pyr_2, keypoints_2, amplit_2, orient_2, descriptors_2);double comput_time_2 = ((double)getTickCount() - comput_2) / getTickFrequency();cout << "待配准特征点描述时间是: " << comput_time_2 << "s" << endl;/********************** 1、最近邻与次近邻距离比匹配,两幅影像进行配准 **********************/myMatch mymatch;double match_time = (double)getTickCount(); //影像配准计时开始//knnMatch函数是DescriptorMatcher类的成员函数,FlannBasedMatcher是DescriptorMatcher的子类Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher1 = new FlannBasedMatcher;Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher2 = new FlannBasedMatcher;vector<vector<DMatch>> dmatchs; //vector<DMatch>中存放的是一个描述子可能匹配的候选集vector<vector<DMatch>> dmatch1;vector<vector<DMatch>> dmatch2;matcher1->knnMatch(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, dmatchs, 2);cout << "距离比之前初始匹配点对个数是:" << dmatchs.size() << endl;Mat matched_lines; //同名点连线vector<DMatch> init_matchs, right_matchs; //用于存放正确匹配的点//该函数返回的是空间映射模型参数Mat homography = mymatch.match(image_1, image_2, dmatchs, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, change_model, right_matchs, matched_lines, init_matchs);double match_time_2 = ((double)getTickCount() - match_time) / getTickFrequency();cout << "特征点匹配花费时间是: " << match_time_2 << "s" << endl;cout << change_model << "变换矩阵是:" << endl;cout << homography << endl;/********************** 1、把正确匹配点坐标写入文件中 **********************/ofstream ofile;ofile.open(".\\position.txt"); //创建文件for (size_t i = 0; i < right_matchs.size(); ++i){ofile << keypoints_1[right_matchs[i].queryIdx].pt << " "<< keypoints_2[right_matchs[i].trainIdx].pt << endl;}/********************** 1、图像融合 **********************/double fusion_beg = (double)getTickCount();Mat fusion_image, mosaic_image, regist_image;mymatch.image_fusion(image_1, image_2, homography, fusion_image, regist_image);imwrite(".\\image_save\\融合后的图像.jpg", fusion_image);double fusion_time = ((double)getTickCount() - fusion_beg) / getTickFrequency();cout << "图像融合花费时间是: " << fusion_time << "s" << endl;double total_time = ((double)getTickCount() - total_count_beg) / getTickFrequency();cout << "总花费时间是: " << total_time << "s" << endl;/********************** 1、生成棋盘图,显示配准结果 **********************///生成棋盘网格图像Mat chessboard_1, chessboard_2, mosaic_images;Mat image1 = imread(".\\image_save\\配准后的参考图像.jpg", -1);Mat image2 = imread(".\\image_save\\配准后的待配准图像.jpg", -1);mymatch.mosaic_map(image1, image2, chessboard_1, chessboard_2, mosaic_images, 50);imwrite(".\\image_save\\参考图像棋盘图像.jpg", chessboard_1);imwrite(".\\image_save\\待配准图像棋盘图像.jpg", chessboard_2);imwrite(".\\image_save\\两幅棋盘图像叠加.jpg", mosaic_images);return 0;
}四、SIFT 算法实验结果
1、实验数据


说明:该数据是从网上下载的两个时相影像,左侧为旧时相影像,右侧为新时相影像;
2、实验结果
(1)特征点检测结果

(2)最终匹配结果

(3)配准效果

说明:把两张图像交叉重叠在一起,可以观察其配准效果;
五、配置说明
该结果是在 VS2019 + opencv4.4.0 + Debug x64 环境下跑出来的;
如果感觉复制麻烦,完整工程见:SIFT算法C++代码实现-C/C++文档类资源-CSDN下载