ResNet结构和pytorch实现

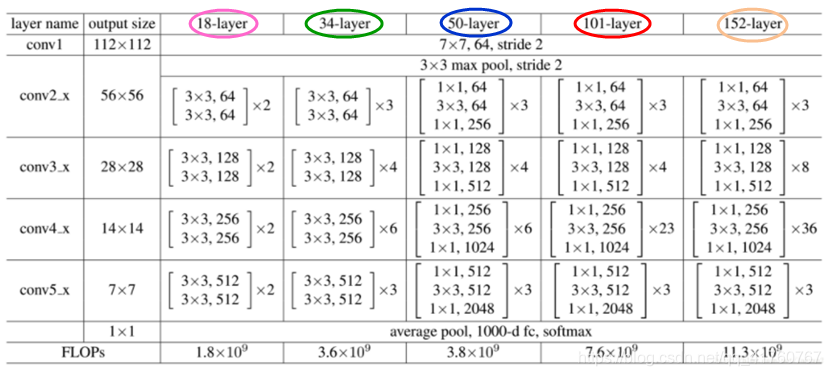
resnet的网络结构都是经过5个不同数量的残差块+最后一个全连接分类完成的。
在resnet50以后,由于层数的增加残差块发生了变化,从原来3x3卷积变为三层卷积,卷积核分别为1x1、3x3、1x1,减少了网络参数。主要通过两种方式:1.用zero-padding去增加维度 2.用1x1卷积来增加维度

这是我之前做的读书笔记,忘记看的什么书了,就不加引用了,抱歉
from torch import nn
import torch as t
from torch.nn import functional as F
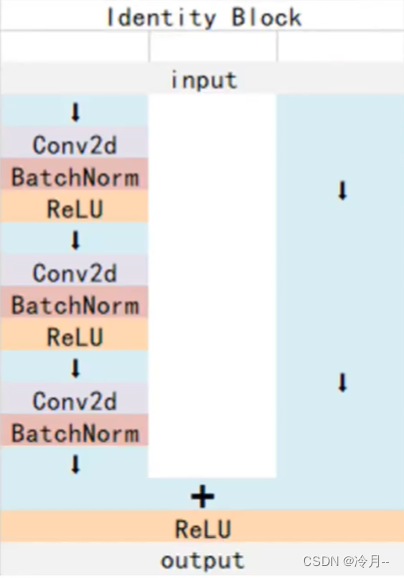
import cv2class ResdiualBlock(nn.Module):"""实现子module:Residual Block"""def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1, shortcut=None):super(ResdiualBlock, self).__init__()self.left = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel))self.right = shortcutdef forward(self, x):out = self.left(x)residual = x if self.right is None else self.right(x)out += residualreturn F.relu(out)class ResNet(nn.Module):"""实现主Module:ResNet34ResNet34包含多个layer, 每个layer又包含多个residual block用子module实现residual block, 用_make_layer函数实现layer"""def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):super(ResNet, self).__init__()# 图像转换self.pre = nn.Sequential(# in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, stride, paddingnn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, 3, bias=False, ),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1))# 重复的layer, 分别有3,4,6,3 个residual blockself.layer1 = self._make_layer(64, 128, 3)self.layer2 = self._make_layer(128, 256, 4, stride=2)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(256, 512, 6, stride=2)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(512, 512, 3, stride=2)# 全连接分类self.fc = nn.Linear(512, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, inchannel, outchannel, block_num, stride=1):"""构建residual block"""shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, 1, stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel))layers = []layers.append(ResdiualBlock(inchannel, outchannel, stride, shortcut))for i in range(1, block_num):layers.append(ResdiualBlock(outchannel, outchannel))return nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):x = self.pre(x)x = self.layer1(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = self.layer3(x)x = self.layer4(x)x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 7)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)return self.fc(x)model = ResNet()
# input = t.autograd.Variable(t.randn(1,2,244,244))
# out = model(input)print(model)
查看pytorch提供的resnet的网络结构
import torch
from torchvision import models
from torchsummary import summaryresnet = models.resnet101()
print(resnet)
summary(resnet, (3, 224, 224), device='cpu')
下面进行用pytorch实现resnet101网络,resnet50和152只是残差块数量不同,其他一致。
代码有点乱,望多多包含
import torch
from torchvision import models
from torchsummary import summary
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as Fresnet = models.resnet101()
print(resnet)
summary(resnet, (3, 224, 224), device='cpu')class ResNet101(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, num_class):super(ResNet101, self).__init__()self.in_channels = in_channelsself.out_channels = num_classself.pre = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=2, padding=3),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, padding=1))self.conv2 = self._make_layer(64, 64, 3, stride=1)self.conv3 = self._make_layer(256, 128, 4, stride=2)self.conv4 = self._make_layer(512, 256, 23, stride=2)self.conv5 = self._make_layer(1024, 512, 3, stride=2)self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)self.linear = nn.Linear(2048, num_class)def _make_layer(self, in_channels, out_channels, block_num, stride=1, expansion=4):layer = []layer.append(Bottleneck(in_channels, out_channels, stride=stride, sample=True))for i in range(1, block_num):layer.append((Bottleneck(out_channels * expansion, out_channels)))return nn.Sequential(*layer)def forward(self, x):x = self.pre(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = self.conv3(x)x = self.conv4(x)x = self.conv5(x)print(x.size())x = self.pool(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.linear(x)return xclass Bottleneck(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, sample=False, expansion=4):super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()self.in_channels = in_channelsself.out_channels = out_channelsself.expansion = expansionself.sample = sampleself.block = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1,stride=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * expansion),nn.ReLU())if self.sample:self.downsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels * expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * expansion))def forward(self, x):out = self.block(x)print(out.size())residual = self.downsample(x) if self.sample is not False else xout += residualreturn F.relu(out)if __name__ == "__main__":res = ResNet101(3, 10)print(res)input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)out = res(input)print(out.shape)# summary(res, (3, 512, 512), device='cpu') #太占用内存介绍我在实现过程中遇到的问题,期间参考的博客在下方提供链接。
问题1.在101_layer中conv2_x中最后一层256通道的1x1卷积在conv3_x怎么变成了128。
下图说明其卷积操作的过程

第二个问题是输出的feature map是通过设置卷积的stride来逐倍缩小的。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/86376627




![[NCTF2019]SQLi 1regexp注入](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4c262ff483944f478d13a83053002daf.png)
![buuctf-[NCTF2019]Keyboard](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0d2cd646c0514b2198e62508d8e3c204.jpg)

![[NCTF2019]Fake XML cookbook](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/98fc6bd960dd496585955723c35c48fb.png)
![[NCTF2019]True XML cookbook](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20210804132458265.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzUyOTA3ODM4,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
![[NCTF2019]Sore](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/33348eac02774c0a82a5420314156de5.png)
![[NCTF 2018]Easy_Audit](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2771ba9438c645f998e2ce26895cc89c.png)

![[NCTF 2018]签到题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/1d07b8d57d692fce62ab23139c24d11d.png)


![[NCTF2019]SQLi](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/773dbc3972184457a1249911fb29ef26.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA6ICBeW91bmflj6_niLE=,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
![BUUCTF:[NCTF2019]phar matches everything](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200728174242861.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L21vY2h1Nzc3Nzc3Nw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)