SIFT features
Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) is an approach for detecting and extracting local feature descriptors that are reasonably invariant to change in illumination, image noise, rotation, scaling, and small changes in viewpoint.
SIFT是一种可以检测并计算出对于在光照、图像噪点、旋转、缩放和视点变换时提取出不变的局部特征值的算法。
Detection stages for SIFT features:
· Scale-space extrema detection
· Keypoint localization
· Orientation assignment
· Generation of keypoint descriptors
SIFT特征值的计算步骤:
· 检测尺度空间的极值点
· 定位关键点
· 分配指向
· 关键点的描述符的生成
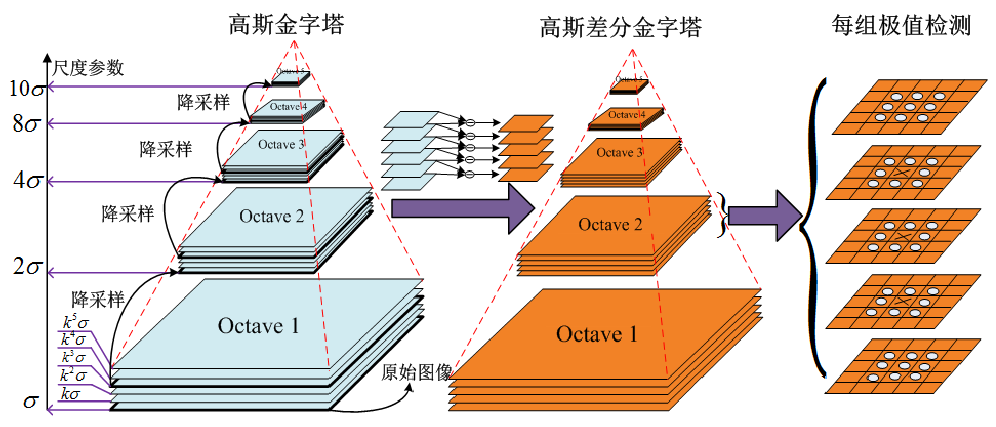
Scale-space extrema detection

可能理解有误,有待后期确定!!具体参照SIFT进阶

1. Local extrema detection, the pixel marked ‘x’ is compared against its 26 neighbours in a 3*3*3 neighbourhood that spans adjacent DoG images (from Lowe, 2004)
1. 局部极值的检测,被标记为‘x’的像素会与其周围的26个像素比较。(即同层的8个像素,以及上下相邻的两层的一共18个像素比较。)
2. If the pixel is a local maximum or minimum, it is selected as a candidate keypoint.
2. 如果像素是局部的最大值或者最小值,则会被作为备选的特征值。
For each candidate keypoint:
· Interpolation of nearby data is used to accurately determine its position.
· Keypoints with low contrast are removed
· Responses along edges are eliminated
· The keypoint is assigned an orientation
对于每一个备选特征值来说:
· 与附近的数据做插值运算是为了能保证其精确的定位
· 去掉对比较低的特征值
· 消除边缘回应
· 为特征值分配指向
To determine the keypoint orientation, a gradient orientation histogram is computed in the neighbourhood of the keypoint.
为了定位特征值的指向,会使用到一个计算出的周围特征值的变换指向直方图来表示。
Peaks in the histogram correspond to dominant orientations. A separate keypoint is created for the direction corresponding to the histogram maximum, and any other direction within 80% of the maximum value.
直方图中的峰值就是主方向,其他的达到最大值80%的方向可作为辅助方向。
All the properties of the keypoint are measured relative to the keypoint orientation, this provides invariance to rotation.
特征值的所有性质都与特征点的指向相关,这样对于旋转来说就是不变的了。
SIFT feature representation

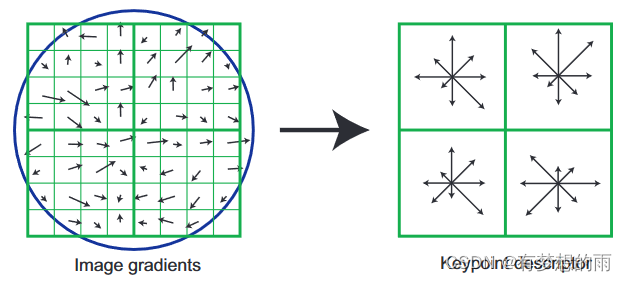
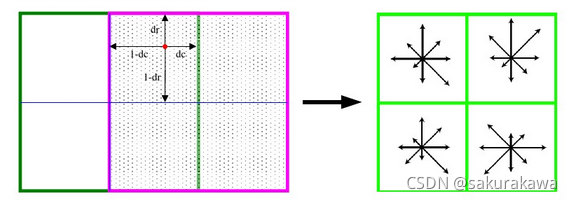
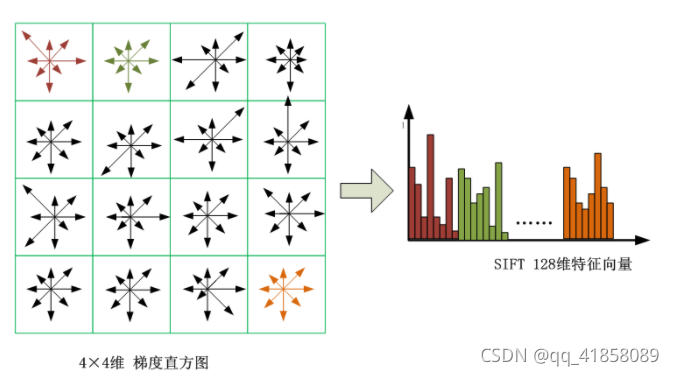
Once a keypoint orientation has been selected, the feature descriptor is computed as a set of orientation histograms on 4*4 pixel neighbourhoods. The orientation histograms are relative to the keypoint orientation, the orientation data comes from the Gaussian image closest in scale to the keypoint’s scale.
如果一个关键点的指向选定之后,特征描述符就会按照一个邻近4×4像素的指向直方图来计算。指向直方图与关键点的指向相关,指向数据来源于高斯图像最接近关键点的尺度的那些值。
Just like before, the contribution of each pixel is weighted by the gradient magnitude, and a Gaussian with σ 1.5 times the scale of the keypoint.
与之前类似,每一个像素的影响是按照它的梯度的加权来的。
Histograms contain 8 bins each, and each descriptor contains an array of 4 histograms around the keypoint. This leads to a SIFT feature vector with 4*4*8 = 128 elements. This vector is normalized to enhance invariance to changes in illumination.
每个直方图有8方向的梯度方向,每一个描述符包含一个位于关键点附近的四个直方图数组。这就导致了SIFT的特征向量有128维。(先是一个4×4的来计算出一个直方图,每个直方图有8个方向。所以是4×4×8=128维)将这个向量归一化之后,就进一步去除了光照的影响。
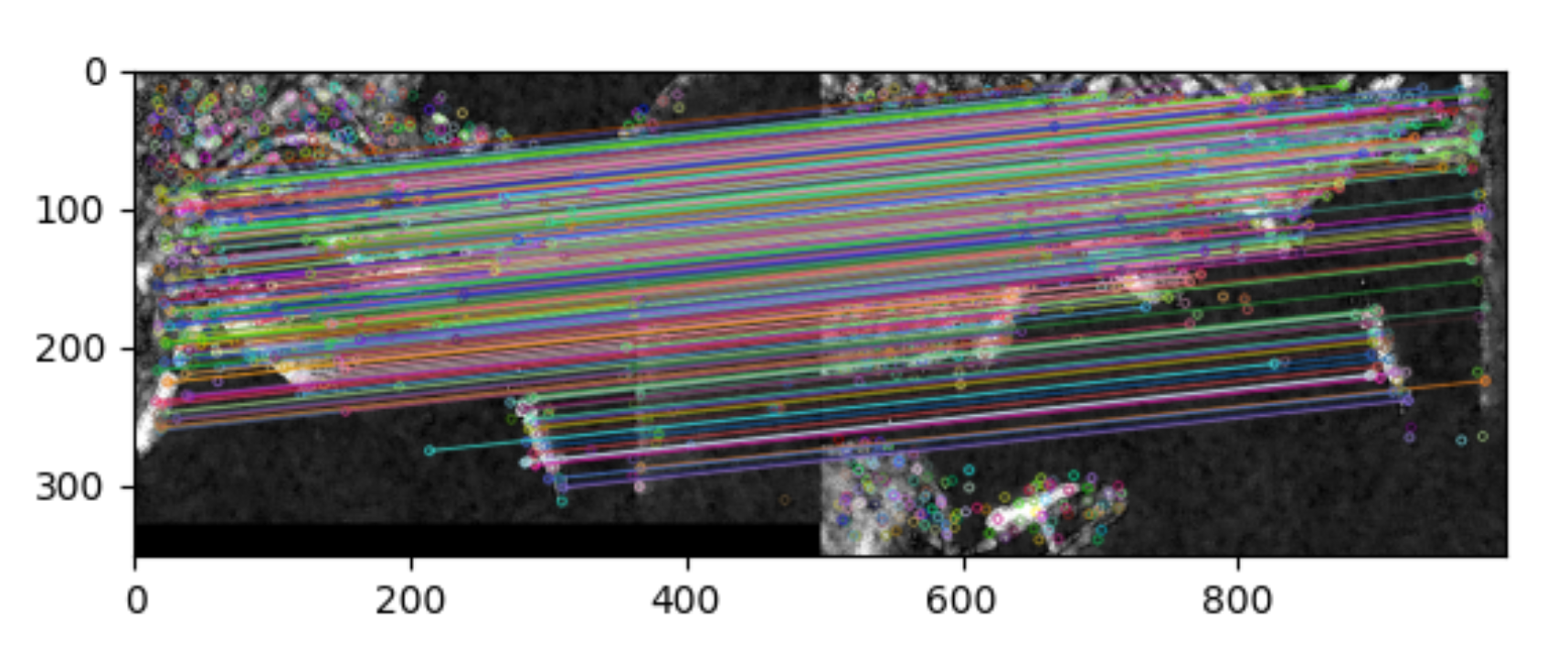
SIFT feature matching
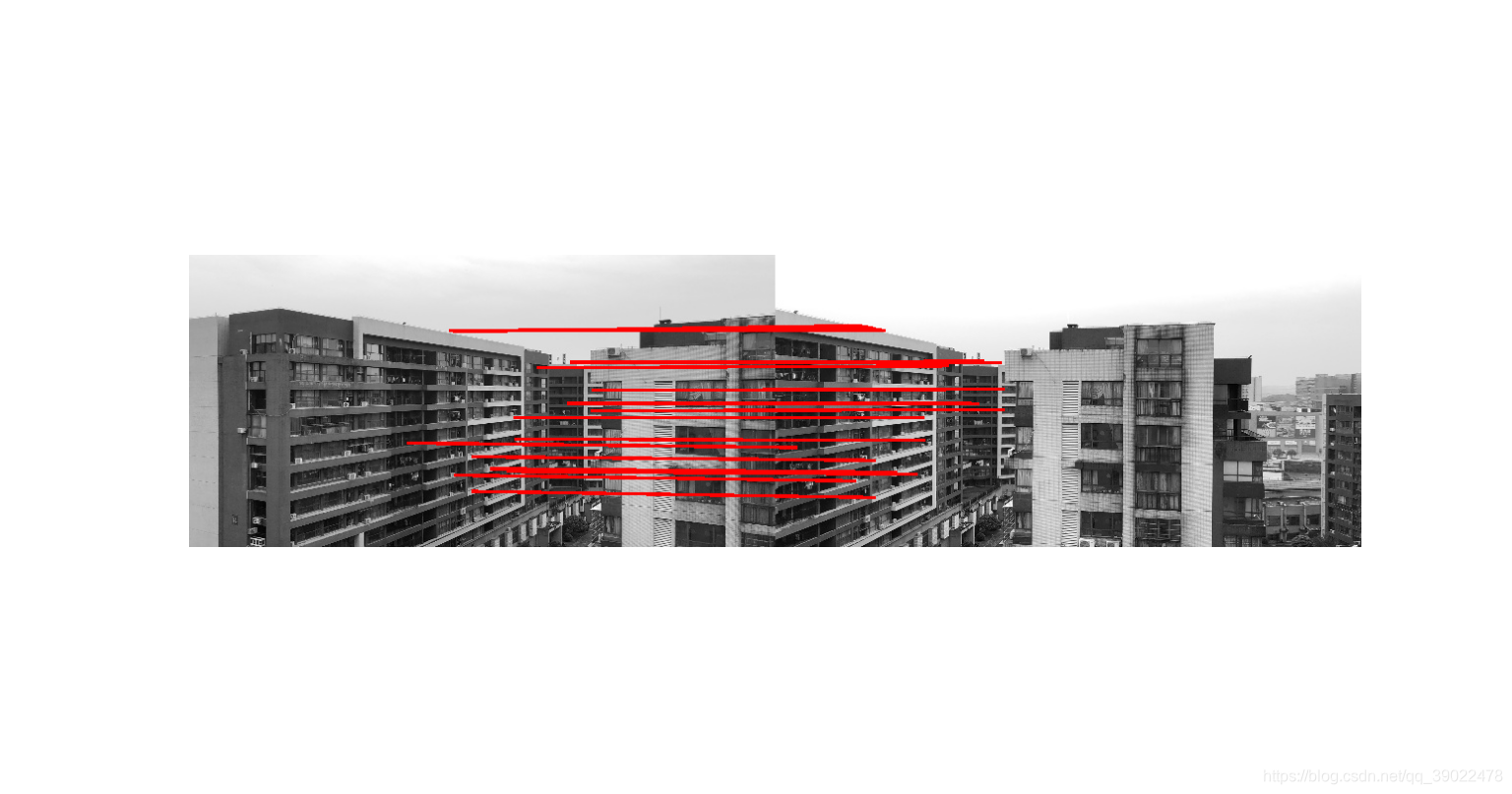
· Find nearest neighbour in a database of SIFT features from training images.
· For robustness, use ratio of nearest neighbour to ratio of second nearest neighbour
· Neighbour with minimum Euclidean distance -> expensive search
· Use an approximate, fast method to find nearest neighbour with high probability.
SIFT特征拟合
· 在图片的SIFT特征值数据库中找到最近的特征值
· 为了使的更为健全,使用最近一个点的比去闭上第二近的点
· 计算临近的点的最短欧式距离(很费时的查找)
· 使用一个大概、但是更快的且可能性更高的方法来查找最近的邻居。
Recognition using SIFT features
· Compute SIFT features on the input image
· Match these features to the SIFT feature database
· Each keypoint specifies 4 parameters: 2D location, scale, and orientation.
· To increase recognition robustness: Hough transform to identify clusters of matches that vote for the same object pose.
· Each keypoint votes for the set of object poses that are consistent with the keypoint’s location, scale, and orientation.
· Locations in the Hough accumulator that accumulate at least 3 votes are selected as candidate object/pose matches.
· A verification step matches the training image for the hypothesized object/pose to the image using a least-square fit to the hypothesized location, scale, and orientation of the object.
使用SIFT特征值进行识别
· 计算输入图像的SIFT特征值
· 把这些特征值与SIFT特征值数据库进行匹配拟合
· 每一个关键点详述了4个参数:二维的位置、尺度及指向
· 为了提高识别的健壮性:使用霍夫转换来识别一串匹配的点,这些点指示了相同的物体姿态
· 每一个关键点指示的物体姿态应该与关键点的位置、尺度和指向一致
· 霍夫叠加器叠加了至少3个提议的位置会被选为备选的物体/姿态拟合
· 核实阶段,使用实验图片去匹配输入图片的假定的物体/姿态,这时使用的是最小二平方来拟合假定的物体位置、尺度和指向。