一、Jdk底层实现
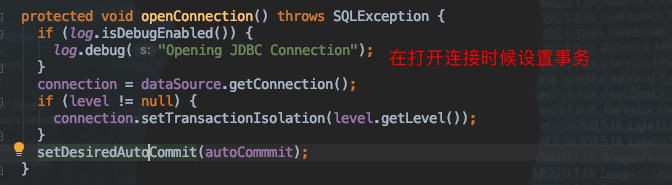
Java JDK中提供了标准接口Connection,不同的数据库驱动负责具体的实现。后面无论是Spring还是Mybatis对事务的处理,无论怎么的封装,最终究其到底都是由Connection来提供的能力。
public interface Connection extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {
Statement createStatement() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
}
例如 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl。具体负责跟mysql进行通信执行命令。
二、Mybatis实现
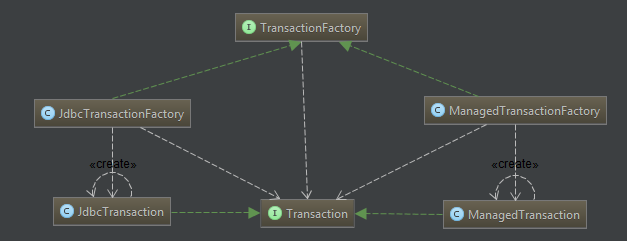
首先我们来看Mybatis是如何对Connection进行事务的封装。首先我们先来看一个图。
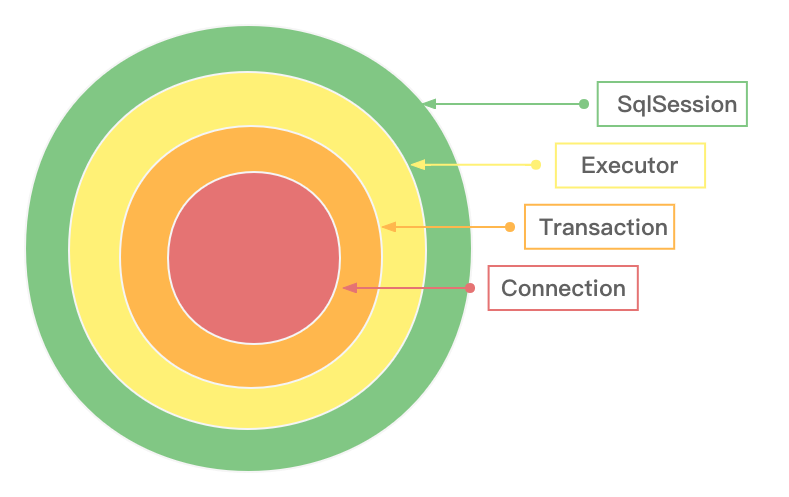
2.1 调用流程
根据上面的图我们看,都是一层一层的封装进行委派最终由Connection的具体数据库驱动来进行实现的。
-
SqlSession -
Executor -
Transaction
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
void commit();
void rollback();
}
public interface Executor {
void commit();
void rollback();
}
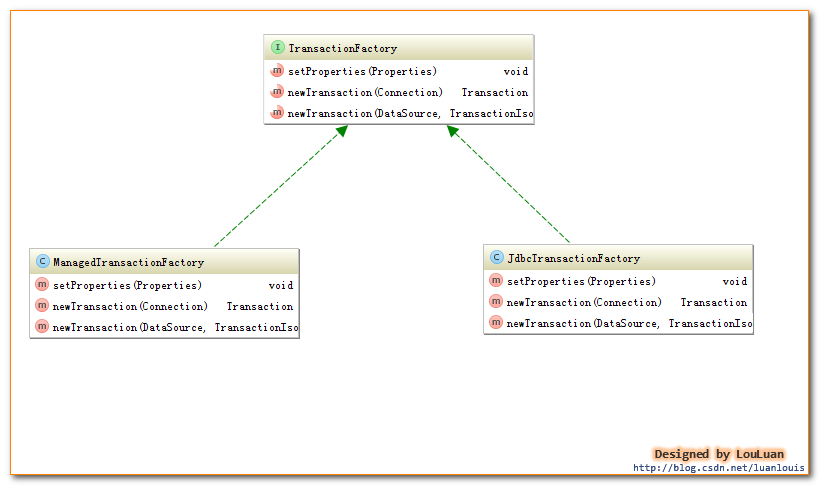
public interface Transaction {
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
}
2.2 实现原理
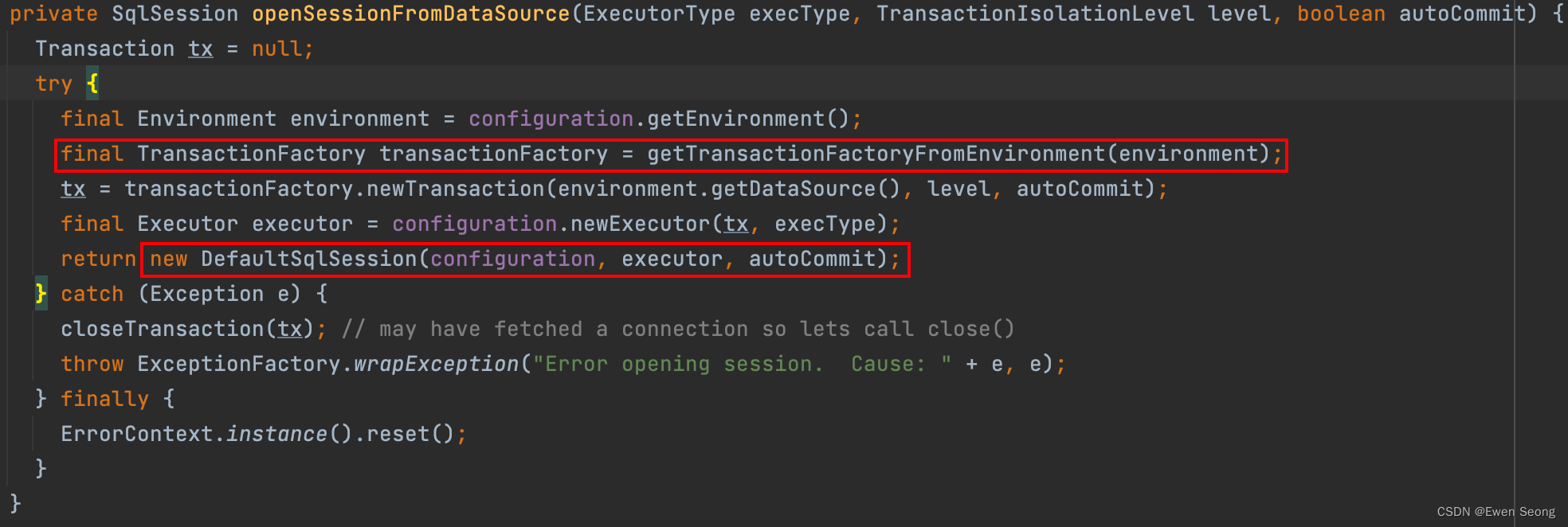
Mybatis中我们的接口是使用代理进行跟数据库进行交互的。所以他的事务提交逻辑是嵌套在代理方法中的。 通过前面的调用流程学习,第04篇:Mybatis代理对象生成我们知道最终都是在MapperMethod对SqlSession的调用执行数据库操作的。 而SqlSession是有两个包装类的。
-
SqlSession 通过底层的封装提供具体的调用指令 -
SqlSessionManager 对SqlSession进行代理,自动对事务进行处理 -
SqlSessionTemplate 事务的处理完全外包给Spring来处理
下面我们分别来看下每个类具体都做了什么吧。
SqlSessionManager
SqlSessionManager 是对SqlSession的一个包装,它会自己来管理SqlSession。他的具体实现是通过对SqlSession 生成代理,代理拦截每个方法进行增强。
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
SqlSessionInterceptor
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
public SqlSessionInterceptor() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get();
if (sqlSession != null) {
try {
return method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} else {
try (SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession()) {
try {
final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args);
autoSqlSession.commit();
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
autoSqlSession.rollback();
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
}
}
-
从ThreadLocal中获取SqlSession,如果有,说明是调用方要自己处理事务,那么就只进行执行数据库操作,不进行事务处理和连接的关闭。 -
如果没有,说明要自己来管理事务,那么就新生成SqlSession,帮我们调用SqlSession#commit来提交事务,失败进行回滚。
根据其中原理我们知道有两种使用办法,
-
首先第一种自己管理SqlSession的方式
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 实例化sqlSessionManager
SqlSessionManager sqlSessionManager = SqlSessionManager.newInstance(inputStream);
// 第一步: 开启管理SqlSession,创建一个SqlSession并存入到ThreadLocal中
sqlSessionManager.startManagedSession();
// 使用
UserMapper mapper = sqlSessionManager.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.save(new User("孙悟空"));
// 第二步: 因为事务是我们自己开启的,所以要自己来操作提交事务,或者回滚
sqlSessionManager.commit();
// 第三步: 关闭连接
sqlSessionManager.close();
-
第二种,自动管理SqlSession
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 实例化sqlSessionManager
SqlSessionManager sqlSessionManager = SqlSessionManager.newInstance(inputStream);
UserMapper mapper = sqlSessionManager.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.save(new User("孙悟空"));
// 只用关心关闭就好了,事务的信息,都帮我们完成了。
sqlSessionManager.close();
SqlSessionTemplate
线程安全、Spring 管理、与 Spring 事务管理一起使用的SqlSession ,以确保实际使用的 SqlSession 是与当前 Spring 事务关联的那个。此外,它还管理会话生命周期,包括根据 Spring 事务配置根据需要关闭、提交或回滚会话。 模板需要一个 SqlSessionFactory 来创建 SqlSession,作为构造函数参数传递。也可以构造指示要使用的执行器类型,如果没有,将使用会话工厂中定义的默认执行器类型。 此模板将 MyBatis PersistenceExceptions 转换为未经检查的 DataAccessExceptions,默认情况下使用MyBatisExceptionTranslator 。
==SqlSessionTemplate== 和 ==SqlSessionManager==
-
相同点:都是通过对SqlSession进行代理对方法进行增强的 -
不同点:前者是将SqlSession外包给Spring进行管理的,后者是自己通过ThreadLocal进行管理的。
下面我们来具体看下是如何拦截增强的。
-
第一个点获取SqlSession不同。 -
从Spring中的事务管理器中获取当前线程的事务信息
-
-
第二个点方法执行完成后都会自动关闭SqlSession或减少引用 -
为解决嵌套事务的情况,每次执行完后会减少一次引用。当引用都减少为0才会真正进行关闭。
-
-
第三个点是否提交事务,有判定规则。 -
只有Spring事务管理器中没有事务时候才会自己进行提交,否则都外包给Spring进行管理。
-
下面我们具体来看下代码的实现吧。
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator
.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
getSqlSession
-
从Spring提供的事务管理器(TransactionSynchronizationManager)中获取当前线程拥有的SqlSession -
如果没有就新建一个并注册到TransactionSynchronizationManager上。
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
// 从Spring提供的事务管理器(TransactionSynchronizationManager)中获取当前线程拥有的SqlSession
// 逻辑很简单key=SqlSessionFactory value=SqlSessionHolder
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
// 如果没有就新建一个并注册到TransactionSynchronizationManager上。
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
registerSessionHolder
-
为了保险先判断下当前线程中是否已经存在同步器,如果存在还注册就提示: "SqlSession [" + session + "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active"); -
如果当前线程没有,判断事务管理器是否是SpringManagedTransactionFactory,如果是就注册一个。 -
SqlSessionHolder#requested() 注意这一行,创建后给引用次数加1.
private static void registerSessionHolder(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator, SqlSession session) {
SqlSessionHolder holder;
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
Environment environment = sessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment();
if (environment.getTransactionFactory() instanceof SpringManagedTransactionFactory) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registering transaction synchronization for SqlSession [" + session + "]");
holder = new SqlSessionHolder(session, executorType, exceptionTranslator);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(sessionFactory, holder);
TransactionSynchronizationManager
.registerSynchronization(new SqlSessionSynchronization(holder, sessionFactory));
holder.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
holder.requested();
} else {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(environment.getDataSource()) == null) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "SqlSession [" + session
+ "] was not registered for synchronization because DataSource is not transactional");
} else {
throw new TransientDataAccessResourceException(
"SqlSessionFactory must be using a SpringManagedTransactionFactory in order to use Spring transaction synchronization");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "SqlSession [" + session
+ "] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active");
}
closeSqlSession
-
如果是Spring的事务管理,就减少引用 -
如果不是Spring的事务管理,就直接关闭
public static void closeSqlSession(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
if ((holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session)) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Releasing transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
holder.released();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Closing non transactional SqlSession [" + session + "]");
session.close();
}
}
isSqlSessionTransactional
事务的判定逻辑:
-
如果从事务管理器中获取,说明当前线程是有事务的 -
当前线程中的事务SqlSession和这个方法中的SqlSession是同一个,说明是嵌套事务。
如果是Spring来管理事务,这就不会自动来提交事务。外包给Spring的事务拦截器自己去处理。
public static boolean isSqlSessionTransactional(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
notNull(session, NO_SQL_SESSION_SPECIFIED);
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
return (holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session);
}
好了,到这里Mybatis中事务的处理逻辑我们就到了解了。
SqlSession对底层进行封装提供具体的指令 SqlSessionManager和SqlSessionTemplate都是对SqlSession进行增强来自动或者委派Spring进行事务的处理的。
下面我们去看看Spring是如何来处理事务的吧。Spring事务的处理方式
感谢您的阅读,本文由 西魏陶渊明 版权所有。如若转载,请注明出处:西魏陶渊明(https://blog.springlearn.cn/)
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布